Connecting rod torque JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1260 of 2199
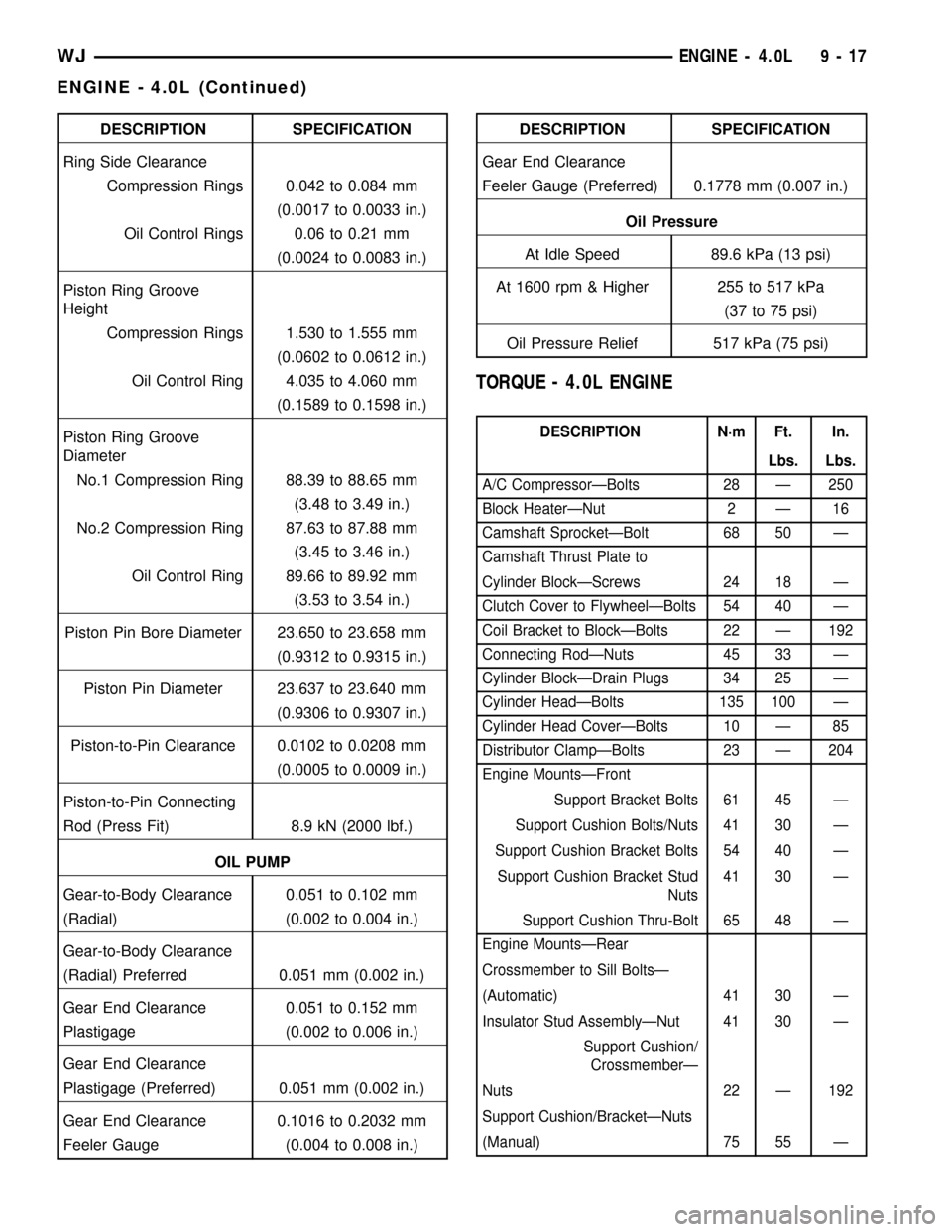
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Ring Side Clearance
Compression Rings 0.042 to 0.084 mm
(0.0017 to 0.0033 in.)
Oil Control Rings 0.06 to 0.21 mm
(0.0024 to 0.0083 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Height
Compression Rings 1.530 to 1.555 mm
(0.0602 to 0.0612 in.)
Oil Control Ring 4.035 to 4.060 mm
(0.1589 to 0.1598 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Diameter
No.1 Compression Ring 88.39 to 88.65 mm
(3.48 to 3.49 in.)
No.2 Compression Ring 87.63 to 87.88 mm
(3.45 to 3.46 in.)
Oil Control Ring 89.66 to 89.92 mm
(3.53 to 3.54 in.)
Piston Pin Bore Diameter 23.650 to 23.658 mm
(0.9312 to 0.9315 in.)
Piston Pin Diameter 23.637 to 23.640 mm
(0.9306 to 0.9307 in.)
Piston-to-Pin Clearance 0.0102 to 0.0208 mm
(0.0005 to 0.0009 in.)
Piston-to-Pin Connecting
Rod (Press Fit) 8.9 kN (2000 lbf.)
OIL PUMP
Gear-to-Body Clearance 0.051 to 0.102 mm
(Radial) (0.002 to 0.004 in.)
Gear-to-Body Clearance
(Radial) Preferred 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Gear End Clearance 0.051 to 0.152 mm
Plastigage (0.002 to 0.006 in.)
Gear End Clearance
Plastigage (Preferred) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Gear End Clearance 0.1016 to 0.2032 mm
Feeler Gauge (0.004 to 0.008 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Gear End Clearance
Feeler Gauge (Preferred) 0.1778 mm (0.007 in.)
Oil Pressure
At Idle Speed 89.6 kPa (13 psi)
At 1600 rpm & Higher 255 to 517 kPa
(37 to 75 psi)
Oil Pressure Relief 517 kPa (75 psi)
TORQUE - 4.0L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
A/C CompressorÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Block HeaterÐNut 2 Ð 16
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 68 50 Ð
Camshaft Thrust Plate to
Cylinder BlockÐScrews 24 18 Ð
Clutch Cover to FlywheelÐBolts 54 40 Ð
Coil Bracket to BlockÐBolts 22 Ð 192
Connecting RodÐNuts 45 33 Ð
Cylinder BlockÐDrain Plugs 34 25 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts 135 100 Ð
Cylinder Head CoverÐBolts 10 Ð 85
Distributor ClampÐBolts 23 Ð 204
Engine MountsÐFront
Support Bracket Bolts 61 45 Ð
Support Cushion Bolts/Nuts 41 30 Ð
Support Cushion Bracket Bolts 54 40 Ð
Support Cushion Bracket Stud
Nuts41 30 Ð
Support Cushion Thru-Bolt 65 48 Ð
Engine MountsÐRear
Crossmember to Sill BoltsÐ
(Automatic) 41 30 Ð
Insulator Stud AssemblyÐNut 41 30 Ð
Support Cushion/
CrossmemberÐ
Nuts 22 Ð 192
Support Cushion/BracketÐNuts
(Manual) 75 55 Ð
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 17
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1277 of 2199

BEARING-TO-JOURNAL CLEARANCE
(1) Wipe the oil from the connecting rod journal.
(2) Use short rubber hose sections over rod bolts
during installation.
(3) Lubricate the upper bearing insert and install
in connecting rod.
(4) Use piston ring compressor to install the rod
and piston assemblies. The oil squirt holes in the
rods must face the camshaft. The arrow on the piston
crown should point to the front of the engine (Fig.
38). Verify that the oil squirt holes in the rods face
the camshaft and that the arrows on the pistons face
the front of the engine.
(5) Install the lower bearing insert in the bearing
cap. The lower insert must be dry. Place strip of Plas-
tigage across full width of the lower insert at the cen-
ter of bearing cap. Plastigage must not crumble in
use. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
(6) Install bearing cap and connecting rod on the
journal and tighten nuts to 45 N´m (33 ft. lbs.)
torque. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
(7) Remove the bearing cap and determine amount
of bearing-to- journal clearance by measuring the
width of compressed Plastigage (Fig. 39).Plastigageshould indicate the same clearance across the
entire width of the insert. If the clearance var-
ies, it may be caused by either a tapered jour-
nal, bent connecting rod or foreign material
trapped between the insert and cap or rod.
(8) If the correct clearance is indicated, replace-
ment of the bearing inserts is not necessary. Remove
the Plastigage from crankshaft journal and bearing
insert. Proceed with installation.
(9) If bearing-to-journal clearance exceeds the
specification, install a pair of 0.0254 mm (0.001 inch)
undersize bearing inserts. All the odd size inserts
must be on the bottom. The sizes of the service
replacement bearing inserts are stamped on the
backs of the inserts. Measure the clearance as
described in the previous steps.
(10) The clearance is measured with a pair of
0.0254 mm (0.001 inch) undersize bearing inserts
installed. This will determine if two 0.0254 mm
(0.001 inch) undersize inserts or another combination
Fig. 36 Locking Tab Inspection
1 - ABNORMAL CONTACT AREA CAUSED BY LOCKING TABS
NOT FULLY SEATED OR BEING BENT
Fig. 37 Scoring Caused by Insufficient Lubrication
or Damaged Crankshaft Journal
Fig. 38 Rod and Piston Assembly Installation
Fig. 39 Measuring Bearing Clearance with
Plastigage
1 - PLASTIGAGE SCALE
2 - COMPRESSED PLASTIGAGE
9 - 34 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1278 of 2199
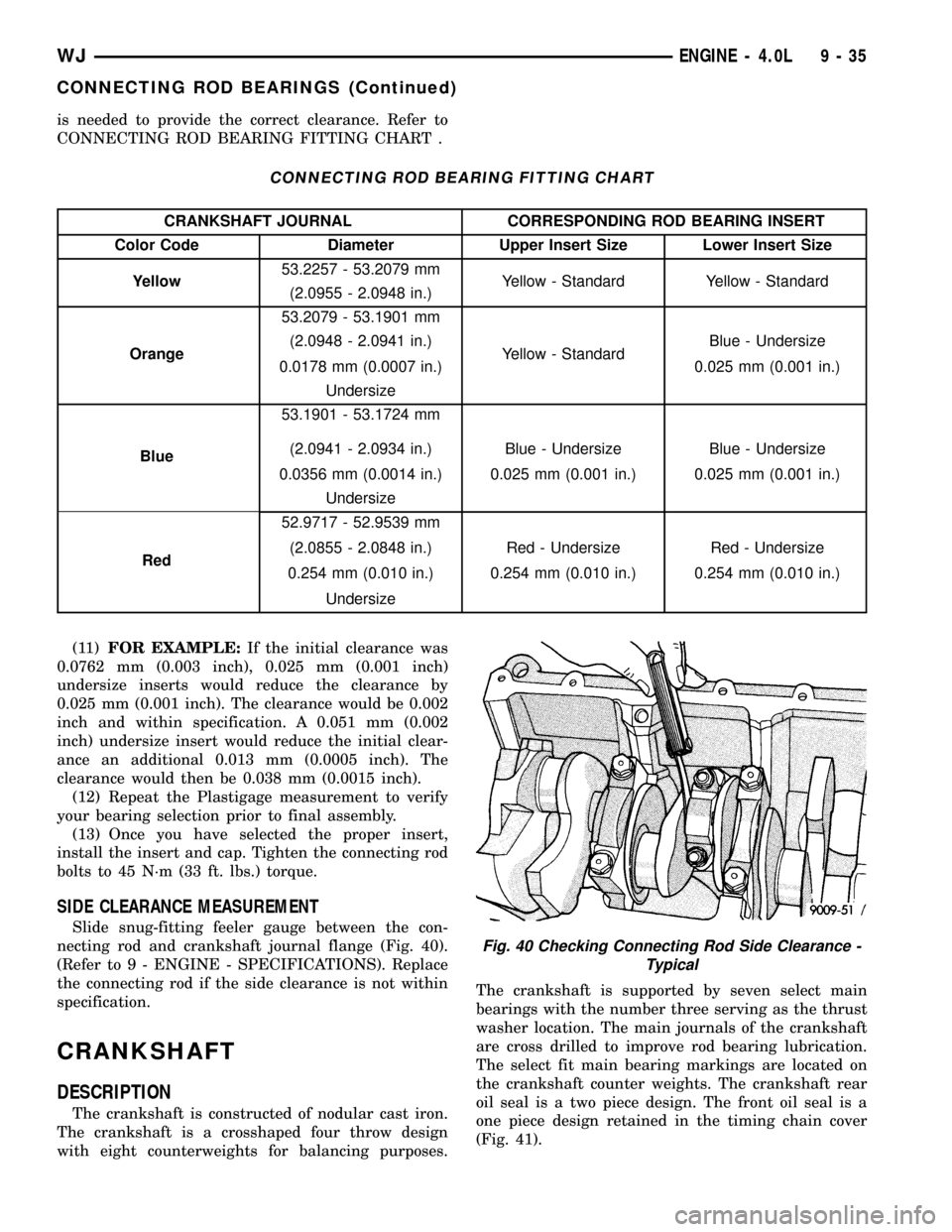
is needed to provide the correct clearance. Refer to
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING CHART .
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING CHART
CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL CORRESPONDING ROD BEARING INSERT
Color Code Diameter Upper Insert Size Lower Insert Size
Yellow53.2257 - 53.2079 mm
Yellow - Standard Yellow - Standard
(2.0955 - 2.0948 in.)
Orange53.2079 - 53.1901 mm
Yellow - StandardBlue - Undersize (2.0948 - 2.0941 in.)
0.0178 mm (0.0007 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Blue53.1901 - 53.1724 mm
Blue - Undersize Blue - Undersize (2.0941 - 2.0934 in.)
0.0356 mm (0.0014 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Red52.9717 - 52.9539 mm
Red - Undersize Red - Undersize (2.0855 - 2.0848 in.)
0.254 mm (0.010 in.) 0.254 mm (0.010 in.) 0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
Undersize
(11)FOR EXAMPLE:If the initial clearance was
0.0762 mm (0.003 inch), 0.025 mm (0.001 inch)
undersize inserts would reduce the clearance by
0.025 mm (0.001 inch). The clearance would be 0.002
inch and within specification. A 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) undersize insert would reduce the initial clear-
ance an additional 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch). The
clearance would then be 0.038 mm (0.0015 inch).
(12) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
(13) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 45 N´m (33 ft. lbs.) torque.
SIDE CLEARANCE MEASUREMENT
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the con-
necting rod and crankshaft journal flange (Fig. 40).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Replace
the connecting rod if the side clearance is not within
specification.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is constructed of nodular cast iron.
The crankshaft is a crosshaped four throw design
with eight counterweights for balancing purposes.The crankshaft is supported by seven select main
bearings with the number three serving as the thrust
washer location. The main journals of the crankshaft
are cross drilled to improve rod bearing lubrication.
The select fit main bearing markings are located on
the crankshaft counter weights. The crankshaft rear
oil seal is a two piece design. The front oil seal is a
one piece design retained in the timing chain cover
(Fig. 41).
Fig. 40 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance -
Typical
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 35
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1287 of 2199
It is not necessary to charge the tappets with
engine oil. They will charge themselves within a very
short period of engine operation.
(1) Dip each tappet in MopartEngine Oil Supple-
ment, or equivalent.
(2) Use Hydraulic Valve Tappet Removal/Installa-
tion Tool to install each tappet in the same bore from
where it was originally removed.
(3) Install the cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the push rods in their original locations.
(5) Install the rocker arms and bridge and pivot
assemblies at their original locations. Loosely install
the capscrews at each bridge.
(6) Tighten the capscrews alternately, one turn at
a time, to avoid damaging the bridges. Tighten the
capscrews to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7)
Pour the remaining MopartEngine Oil Supple-
ment, or equivalent over the entire valve actuating
assembly. The MopartEngine Oil Supplement, or equiv-
alent must remain with the engine oil for at least 1 609
km (1,000 miles). The oil supplement need not be
drained until the next scheduled oil change.
(8) Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons (Fig. 55) are made of a high strength
aluminum alloy, the piston skirts are coated with a
solid lubricant (Molykote) to reduce friction and pro-
vide scuff resistance. The connecting rods are made
of cast iron.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING
(1) To correctly select the proper size piston, a cyl-
inder bore gauge, capable of reading in 0.003 mm
(.0001 in.) INCREMENTS is required. If a bore
gauge is not available, do not use an inside microme-
ter.
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at a point 49.5 mm (1-15/16 inches) below top of
bore. Start perpendicular (across or at 90 degrees) to
the axis of the crankshaft at point A and then take
an additional bore reading 90 degrees to that at point
B (Fig. 57).
(3) The coated pistons will be serviced with the
piston pin and connecting rod pre-assembled.The
coated piston connecting rod assembly can be
used to service previous built engines and
MUST be replaced as complete sets.Tin coated
pistons should not be used as replacements for coated
pistons.
(4) The coating material is applied to the piston
after the final piston machining process. Measuring
the outside diameter of a coated piston will not pro-
vide accurate results (Fig. 56). Therefore measuring
the inside diameter of the cylinder bore with a dial
Bore Gauge isMANDATORY. To correctly select the
proper size piston, a cylinder bore gauge capable of
reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.) increments is
required.
(5) Piston installation into the cylinder bore
requires slightly more pressure than that required
for non-coated pistons. The bonded coating on the
piston will give the appearance of a line-to-line fit
with the cylinder bore.
Fig. 55 Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
Fig. 56 Moly Coated Piston
1 - MOLY COATED
2 - MOLY COATED
9 - 44 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (Continued)
Page 1294 of 2199

crankshaft is drilled internally to pass oil from the
main bearing journals (except number 4 main bear-
ing journal) to the connecting rod journals. Each con-
necting rod bearing cap has a small squirt hole, oil
passes through the squirt hole and is thrown off as
the rod rotates. This oil throwoff lubricates the cam-
shaft lobes, distributor drive gear, cylinder walls, and
piston pins.
The hydraulic valve tappets receive oil directly
from the main oil gallery. Oil is provided to the cam-
shaft bearing through galleries. The front camshaft
bearing journal passes oil through the camshaft
sprocket to the timing chain. Oil drains back to the
oil pan under the number one main bearing cap.
The oil supply for the rocker arms and bridged
pivot assemblies is provided by the hydraulic valve
tappets which pass oil through hollow push rods to a
hole in the corresponding rocker arm. Oil from the
rocker arm lubricates the valve train components,
then passes down through the push rod guide holes
in the cylinder head past the valve tappet area, and
returns to the oil pan (Fig. 73).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Disconnect connector and remove oil pressure
sending unit.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292 or equivalent. Start engine and record pres-
sure. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.If the oil leak source is not pos-itively identified at this time, proceed with the air
leak detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the CCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the CCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service informa-
tion procedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS .
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the CCV valve and breather cap hose.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 51
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1320 of 2199

DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Outer Rotor Clearance
(MAX).235 mm (.0093 in.)
Outer Rotor Diameter
(MIN)85.925 mm (0.400 in.)
Tip Clearance Between
Rotors
(MAX) .150 mm (0.006 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
At Curb Idle Speed
(MIN)*25 kPa (4 psi)
@ 3000 rpm 170 - 758 kPa (25 - 110
psi)
* CAUTION: If pressure is zero at curb idle, DO
NOT run
engine at 3000 rpm.
SPECIFICATIONS - 4.7L H.O. ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Engine Type 90É SOHC V-8 16-Valve
Displacement 4.7 Liters / 4701cc
(287 Cubic Inches)
Bore 93.0 mm (3.66 in.)
Stroke 86.5 mm (3.40 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.7:1
Horsepower 270 BHP @ 5100 RPM
Torque 330 LB-FT @ 3600 RPM
Lead Cylinder #1 Left Bank
Firing Order 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Block Cast Iron
Bore Diameter 93.010 .0075 mm
(3.6619 0.0003 in.)
Out of Round (MAX) 0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Taper (MAX) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
PISTONS
Material Aluminum Alloy
Diameter 92.975 mm (3.6605 in.)
Weight 383.5 grams (13.52 oz)
Ring Groove Diameter
No. 1 83.37 - 83.13 mm
(3.296 - 3.269 in.)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
No. 2 82.833 - 83.033 mm
(3.261 - 3.310 in.)
No. 3 83.88 - 84.08 mm
(3.302 - 3.310 in.)
PISTON PINS
Type Full Floating
Clearance In Piston 0.010 - 0.019 mm
(0.0004 - 0.0008 in.)
Clearance in Rod 0.006 - 0.015 mm
(0.0002 - 0.0005 in.)
Diameter 24.017 - 24.020 mm
(0.9455 - 0.9456 in.)
PISTON RINGS
Ring Gap
Top Compression Ring 0.37 - 0.63 mm
(0.0146 - 0.0249 in.)
Second Compression
Ring0.37 - 0.63 mm
(0.0146 - 0.0249 in.)
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.25 - 0.76 mm
(0.0099 - 0.30 in.)
Side Clearance
Top Compression Ring .051 - .094 mm
(0.0020 - 0.0037 in.)
Second Compression
Ring0.040 - 0.080 mm
(0.0016 - 0.0031 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Ring) .019 - .229 mm
(.0007 - .0091 in.)
Ring Width
Top Compression Ring 1.472 - 1.490 mm
(0.057 - 0.058 in.)
Second Compression
Ring1.472 - 1.490 mm
(0.057 - 0.058 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 0.445 - 0.470 mm
(0.017 - 0.018 in.)
CONNECTING RODS
Bearing Clearance 0.010 - 0.048 mm
(0.0004 - 0.0019 in.)
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 77
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1322 of 2199
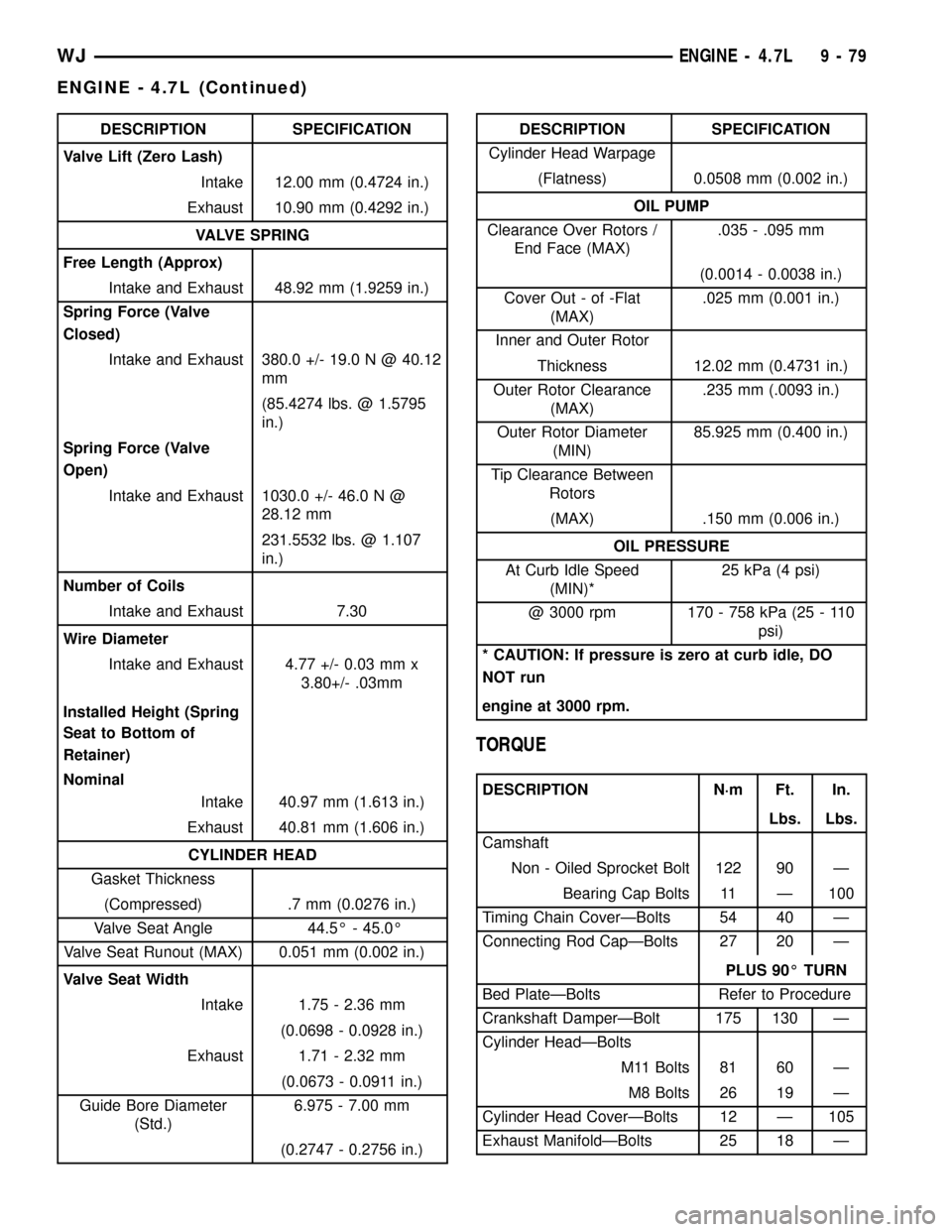
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Valve Lift (Zero Lash)
Intake 12.00 mm (0.4724 in.)
Exhaust 10.90 mm (0.4292 in.)
VALVE SPRING
Free Length (Approx)
Intake and Exhaust 48.92 mm (1.9259 in.)
Spring Force (Valve
Closed)
Intake and Exhaust 380.0 +/- 19.0 N @ 40.12
mm
(85.4274 lbs. @ 1.5795
in.)
Spring Force (Valve
Open)
Intake and Exhaust 1030.0 +/- 46.0 N @
28.12 mm
231.5532 lbs. @ 1.107
in.)
Number of Coils
Intake and Exhaust 7.30
Wire Diameter
Intake and Exhaust 4.77 +/- 0.03 mm x
3.80+/- .03mm
Installed Height (Spring
Seat to Bottom of
Retainer)
Nominal
Intake 40.97 mm (1.613 in.)
Exhaust 40.81 mm (1.606 in.)
CYLINDER HEAD
Gasket Thickness
(Compressed) .7 mm (0.0276 in.)
Valve Seat Angle 44.5É - 45.0É
Valve Seat Runout (MAX) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Valve Seat Width
Intake 1.75 - 2.36 mm
(0.0698 - 0.0928 in.)
Exhaust 1.71 - 2.32 mm
(0.0673 - 0.0911 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter
(Std.)6.975 - 7.00 mm
(0.2747 - 0.2756 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Cylinder Head Warpage
(Flatness) 0.0508 mm (0.002 in.)
OIL PUMP
Clearance Over Rotors /
End Face (MAX).035 - .095 mm
(0.0014 - 0.0038 in.)
Cover Out - of -Flat
(MAX).025 mm (0.001 in.)
Inner and Outer Rotor
Thickness 12.02 mm (0.4731 in.)
Outer Rotor Clearance
(MAX).235 mm (.0093 in.)
Outer Rotor Diameter
(MIN)85.925 mm (0.400 in.)
Tip Clearance Between
Rotors
(MAX) .150 mm (0.006 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
At Curb Idle Speed
(MIN)*25 kPa (4 psi)
@ 3000 rpm 170 - 758 kPa (25 - 110
psi)
* CAUTION: If pressure is zero at curb idle, DO
NOT run
engine at 3000 rpm.
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Camshaft
Non - Oiled Sprocket Bolt 122 90 Ð
Bearing Cap Bolts 11 Ð 100
Timing Chain CoverÐBolts 54 40 Ð
Connecting Rod CapÐBolts 27 20 Ð
PLUS 90É TURN
Bed PlateÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Crankshaft DamperÐBolt 175 130 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts
M11 Bolts 81 60 Ð
M8 Bolts 26 19 Ð
Cylinder Head CoverÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Exhaust ManifoldÐBolts 25 18 Ð
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 79
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1352 of 2199

free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
CLEANING
Thoroughly clean the oil pan and engine block gas-
ket surfaces.
Use compressed air to clean out:
²The galley at the oil filter adaptor hole.
²The front and rear oil galley holes.
²The feed holes for the crankshaft main bearings.
Once the block has been completely cleaned, apply
Loctite PST pipe sealant with Teflon 592 to the
threads of the front and rear oil galley plugs. Tighten
the plugs to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
INSPECTION
(1) It is mandatory to use a dial bore gauge to
measure each cylinder bore diameter. To correctly
select the proper size piston, a cylinder bore gauge,
capable of reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.) INCRE-
MENTS is required. If a bore gauge is not available,
do not use an inside micrometer (Fig. 46).
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at three levels below top of bore. Start perpen-
dicular (across or at 90 degrees) to the axis of the
crankshaft and then take two additional reading.(3) Measure the cylinder bore diameter crosswise
to the cylinder block near the top of the bore. Repeat
the measurement near the middle of the bore, then
repeat the measurement near the bottom of the bore.
(4) Determine taper by subtracting the smaller
diameter from the larger diameter.
(5) Rotate measuring device 90É and repeat steps
above.
(6) Determine out-of-roundness by comparing the
difference between each measurement.
(7) If cylinder bore taper does not exceed 0.025
mm (0.001 inch) and out-of-roundness does not
exceed 0.025 mm (0.001 inch), the cylinder bore can
be honed. If the cylinder bore taper or out- of-round
condition exceeds these maximum limits, the cylinder
block must be replaced. A slight amount of taper
always exists in the cylinder bore after the engine
has been in use for a period of time.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING ROD
BEARING FITTING
Inspect the connecting rod bearings for scoring and
bent alignment tabs (Fig. 47) (Fig. 48). Check the
bearings for normal wear patterns, scoring, grooving,
fatigue and pitting (Fig. 49). Replace any bearing
that shows abnormal wear.
Inspect the connecting rod journals for signs of
scoring, nicks and burrs.
Misaligned or bent connecting rods can cause
abnormal wear on pistons, piston rings, cylinder
walls, connecting rod bearings and crankshaft con-
necting rod journals. If wear patterns or damage to
any of these components indicate the probability of a
misaligned connecting rod, inspect it for correct rod
alignment. Replace misaligned, bent or twisted con-
necting rods.
(1) Wipe the oil from the connecting rod journal.
(2) Lubricate the upper bearing insert and install
in connecting rod.
(3) Use piston ring compressor and Guide Pins
Special Tool 8507 (Fig. 50) to install the rod and pis-
ton assemblies. The oil slinger slots in the rods must
face front of the engine. The ªFº's near the piston
wrist pin bore should point to the front of the engine.
(4) Install the lower bearing insert in the bearing
cap. The lower insert must be dry. Place strip of Plas-
tigage across full width of the lower insert at the cen-
ter of bearing cap. Plastigage must not crumble in
use. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
(5) Install bearing cap and connecting rod on the
journal and tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a
90É turn. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
Fig. 46 Bore GaugeÐTypical
1 - FRONT
2 - BORE GAUGE
3 - CYLINDER BORE
4-38MM
(1.5 in)
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 109
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1357 of 2199
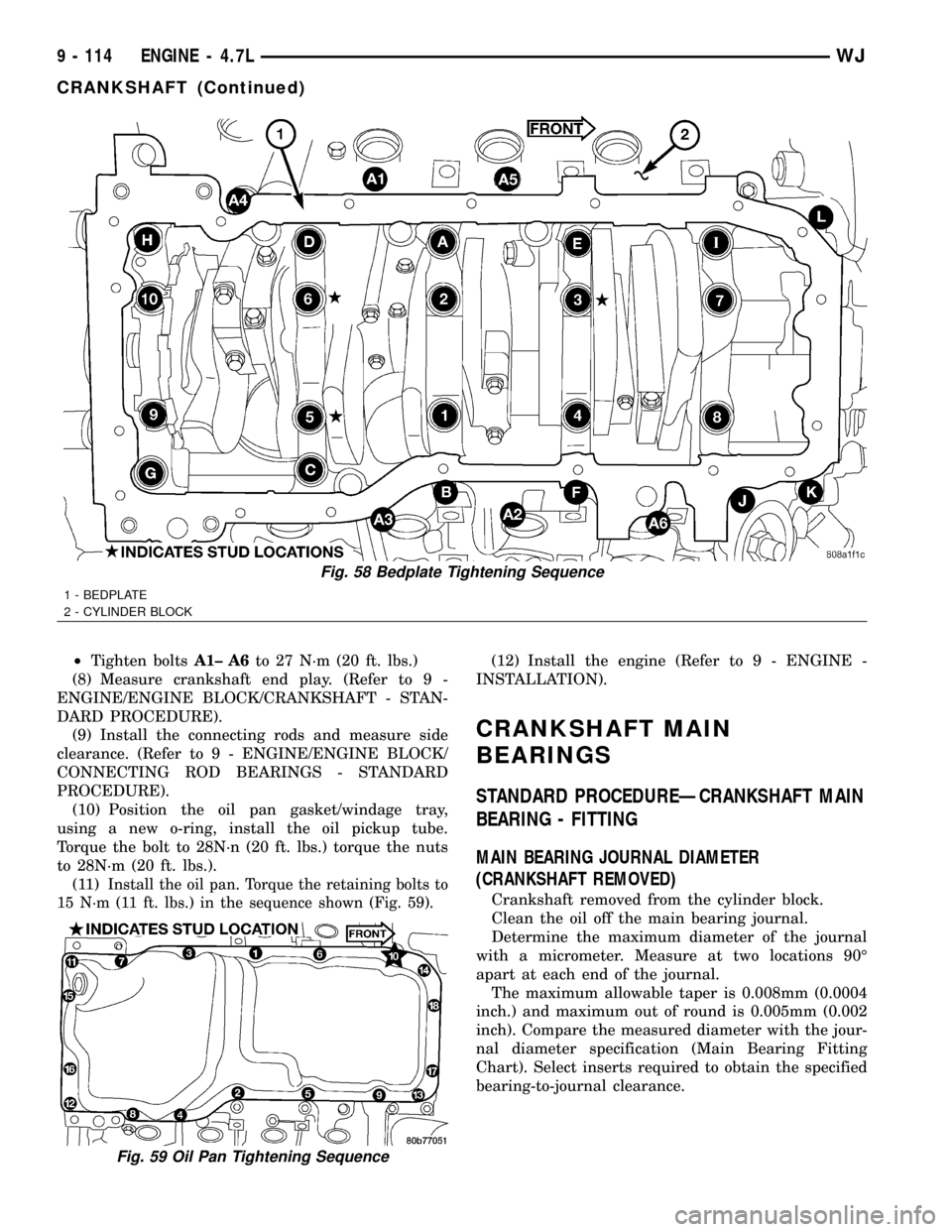

²Tighten boltsA1± A6to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
(8) Measure crankshaft end play. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(9) Install the connecting rods and measure side
clearance. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(10) Position the oil pan gasket/windage tray,
using a new o-ring, install the oil pickup tube.
Torque the bolt to 28N´n (20 ft. lbs.) torque the nuts
to 28N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(11)
Install the oil pan. Torque the retaining bolts to
15 N´m (11 ft. lbs.) in the sequence shown (Fig. 59).
(12) Install the engine (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
INSTALLATION).
CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARING - FITTING
MAIN BEARING JOURNAL DIAMETER
(CRANKSHAFT REMOVED)
Crankshaft removed from the cylinder block.
Clean the oil off the main bearing journal.
Determine the maximum diameter of the journal
with a micrometer. Measure at two locations 90É
apart at each end of the journal.
The maximum allowable taper is 0.008mm (0.0004
inch.) and maximum out of round is 0.005mm (0.002
inch). Compare the measured diameter with the jour-
nal diameter specification (Main Bearing Fitting
Chart). Select inserts required to obtain the specified
bearing-to-journal clearance.
Fig. 58 Bedplate Tightening Sequence
1 - BEDPLATE
2 - CYLINDER BLOCK
Fig. 59 Oil Pan Tightening Sequence
9 - 114 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1363 of 2199

Check the connecting rod for signs of twist or bend-
ing.
Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the piston for scoring, or scraping marks in
the piston skirts. Check the ring lands for cracks
and/or deterioration.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing piston and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, install the piston rings.
(2)
Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings. Tighten ring compressor.Ensure position
of rings do not change during this operation.
(3)Position bearing onto connecting rod. Ensure that
hole in bearing shell aligns with hole in connecting rod.
Lubricate bearing surface with clean engine oil.
(4) Install Special Tool 8507 Connecting Rod
Guides into connecting rod bolt threads (Fig. 72).(5) The pistons are marked on the piston pin bore
surface with an raised ªFº indicating installation
position. This mark must be pointing toward the
front of engine on both cylinder banks. The connect-
ing rod oil slinger slot faces the front of the engine
(Fig. 73).
(6) Wipe cylinder bore clean and lubricate with
engine oil.
(7) Rotate crankshaft until connecting rod journal
is on the center of cylinder bore. Insert rod and pis-
ton into cylinder bore and carefully position connect-
ing rod guides over crankshaft journal.
(8) Tap piston down in cylinder bore using a ham-
mer handle. While at the same time, guide connect-
ing rod into position on rod journal.
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Lubricate rod bolts and bearing surfaces with
engine oil. Install connecting rod cap and bearing.
Tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus 90É.
(10) Install the following components:
²Cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
²Timing chain and cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- INSTALLATION).
Fig. 72 Piston and Connecting RodÐInstallation
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 73 Piston and Connecting Rod Orientation
1 - MAJOR THRUST SIDE OF PISTON
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
9 - 120 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)