set 1 2 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 18 of 2199
JUMP STARTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - JUMP STARTING
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS. DO NOT
JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT JUMP START WHEN
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY INDICATOR DOT IS
YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. DO NOT JUMP
START A VEHICLE WHEN THE BATTERY FLUID IS
BELOW THE TOP OF LEAD PLATES. DO NOT
ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO TOUCH
EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A BOOSTER
SOURCE. DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY. REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCING OF BATTERY CURRENT. WHEN
USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING DEVICE, DO
NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO EXCEED 16
VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED
WITH DEVICE BEING USED.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach.
Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, place
the automatic transmission in PARK or the manual
transmission in NEUTRAL and turn the ignition
OFF.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake. Turn off all accesso-
ries.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result.
Review all warnings in this procedure.
(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to positive (+) terminal. Connect BLACK
jumper cable clamp to engine ground as close to the
ground cable attaching point as possible (Fig. 8).
(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(7) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
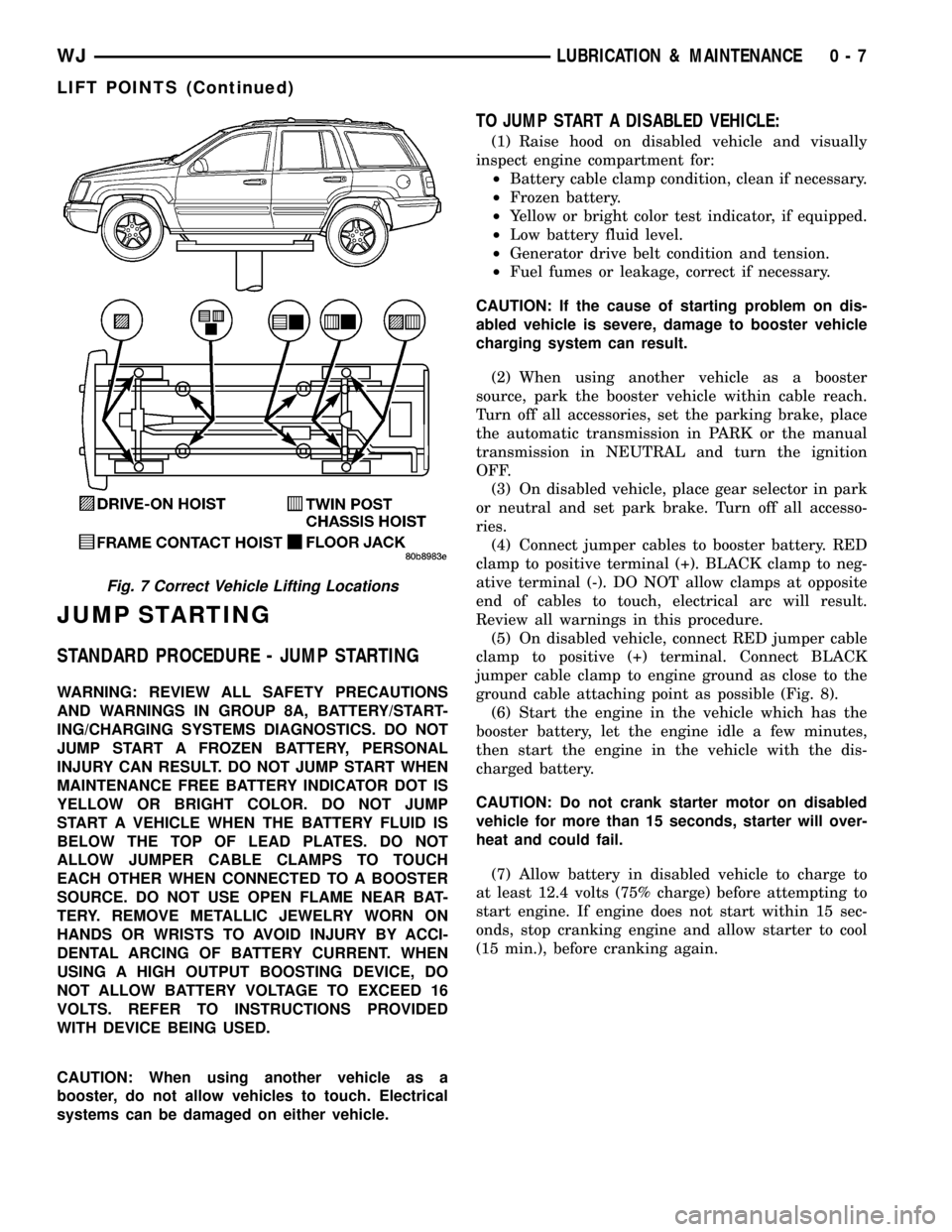
Fig. 7 Correct Vehicle Lifting Locations
WJLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
LIFT POINTS (Continued)
Page 24 of 2199

WHEEL ALIGNMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CAMBER.......3STANDARD PROCEDURE - CASTER.......4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TOE POSITION . . 4
SPECIFICATIONS
ALIGNMENT..........................5
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION
Wheel alignment involves the correct positioning of
the wheels in relation to the vehicle. The positioning
is accomplished through suspension and steering
linkage adjustments. An alignment is considered
essential for efficient steering, good directional stabil-
ity and to minimize tire wear. The most important
measurements of an alignment are caster, camber
and toe position (Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Never attempt to modify suspension or
steering components by heating or bending.
CAUTION: Components attached with a nut and cot-
ter pin must be torqued to specification. Then if the
slot in the nut does not line up with the cotter pin
hole, tighten nut until it is aligned. Never loosen the
nut to align the cotter pin hole.
NOTE: Periodic lubrication of the front suspension/
steering system components may be required. Rub-
ber bushings must never be lubricated, Refer to
Lubrication And Maintenance for the recommended
maintenance schedule.
OPERATION
²CASTERis the forward or rearward tilt of the
steering knuckle from vertical. Tilting the top of the
knuckle rearward provides positive caster. Tilting the
top of the knuckle forward provides negative caster.
Caster is a directional stability angle. This angle
enables the front wheels to return to a straight
ahead position after turns (Fig. 1).
²CAMBERis the inward or outward tilt of the
wheel relative to the center of the vehicle. Tilting the
top of the wheel inward provides negative camber.
Tilting the top of the wheel outward provides positive
camber. Incorrect camber will cause wear on theinside or outside edge of the tire. The angle is not
adjustable, damaged component(s) must be replaced
to correct the camber angle (Fig. 1).
²WHEEL TOE POSITIONis the difference
between the leading inside edges and trailing inside
edges of the front tires. Incorrect wheel toe position
is the most common cause of unstable steering and
uneven tire wear. The wheel toe position is thefinal
front wheel alignment adjustment (Fig. 1).
²STEERING AXIS INCLINATION ANGLEis
measured in degrees and is the angle that the steer-
ing knuckles are tilted. The inclination angle has a
fixed relationship with the camber angle. It will not
change except when a spindle or ball stud is dam-
aged or bent. The angle is not adjustable, damaged
component(s) must be replaced to correct the steering
axis inclination angle.
²THRUST ANGLEis the angle of the rear axle
relative to the centerline of the vehicle. Incorrect
thrust angle can cause off-center steering and exces-
sive tire wear. This angle is not adjustable, damaged
component(s) must be replaced to correct the thrust
angle (Fig. 1).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CAMBER
Before each alignment reading the vehicle should
be jounced (rear first, then front). Grasp each
bumper at the center and jounce the vehicle up and
down three times. Always release the bumper in the
down position.
To obtain an accurate alignment, a 4 wheel align-
ment machine must be used and the equipment cali-
bration verified.
The wheel camber angle is preset. This angle is not
adjustable and cannot be altered.
WJWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 3
Page 25 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - CASTER
Before each alignment reading the vehicle should
be jounced (rear first, then front). Grasp each
bumper at the center and jounce the vehicle up and
down three times. Always release the bumper in the
down position.
To obtain an accurate alignment, a 4 wheel align-
ment machine must be used and the equipment cali-
bration verified.
The wheel caster angle is preset. This angle is not
adjustable and cannot be altered.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TOE POSITION
Before each alignment reading the vehicle should
be jounced (rear first, then front). Grasp each
bumper at the center and jounce the vehicle up and
down three times. Always release the bumper in the
down position.To obtain an accurate alignment, a 4 wheel align-
ment machine must be used and the equipment cali-
bration verified.
NOTE: For an accurate wheel toe position adjust-
ment the engine must be engine running.
(1) Apply parking brakes.
(2) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the steering wheel. Center and
secure the steering wheel.
(3) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts (Fig. 2).
(4) Turn the sleeve to obtain the preferred positive
TOE-IN specification. Position the clamp bolts as
shown (Fig. 2) for proper clearance.
(5) Tighten the clamp bolts to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 1 Wheel Alignment Measurements
1 - WHEEL CENTERLINE
2 - NEGATIVE CAMBER ANGLE
3 - PIVOT CENTERLINE
4 - SCRUB RADIUS
5 - TRUE VERTICAL6 - KING PIN
7 - VERTICAL
8 - POSITIVE CASTER
2 - 4 WHEEL ALIGNMENTWJ
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 26 of 2199
NOTE: Make sure the toe setting does not change
during clamp tightening.
(6) Verify alignment specifications, then turn the
engine off.
STEERING WHEEL CENTERING
NOTE: The steering wheel can be centered without
affecting the toe position.
(1) Loosen the drag link adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts.
(2) Turn the adjustment sleeve to center the
wheel.
(3) Position the clamp bolts as shown (Fig. 2)for
proper clearance.
(4) Tighten the clamp bolts to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(5) Road test the vehicle to verify the wheel is cen-
tered.
SPECIFICATIONS
ALIGNMENT
NOTE: Specifications are in degrees.
FRONT WHEELS - STANDARD SUSPENSION
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PREFERRED CASTER
+ 6.75ÉCAMBER
20.37ÉTOTAL
TOE-IN
+ 0.20É
RANGE + 6.0É to
+ 7.5É20.75É
to + 0.5É+ .14É to
+ .26É
MAX RT/LT
DIFFERENCE0.5É 0.5É 0.5É
FRONT WHEELS - UP-COUNTRY SUSPENSION
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PREFERRED CASTER
+ 6.5ÉCAMBER
20.37ÉTOTAL
TOE-IN
+ 0.20É
RANGE + 5.7É to
+ 7.2É20.75É
to+0É+ 0.0É to
+ .36É
MAX RT/LT
DIFFERENCE0.5É 0.5É 0.06É
REAR AXLE
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PREFERRED CAMBER
±.37ÉTHRUST
ANGLE
0ÉTOTAL
TOE-IN
+.37É
RANGE 0É to
±.75É 0.25É 0É to
+.70É
Fig. 2 Steering Linkage
1 - DRAG LINK ADJUSTMENT SLEEVE
2 - TIE ROD ADJUSTMENT SLEEVE
WJWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 5
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 53 of 2199

SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: Individual components of cardan universal
joints are not serviceable. If worn or leaking, they
must be replaced as an assembly.
(1) Remove the propeller shaft.
(2) Tap the outside of the bearing cap assembly
with a drift to loosen snap ring.
(3) Remove snap rings from both sides of yoke
(Fig. 12).
(4) Set the yoke in an arbor press or vise with a
socket whose inside diameter is large enough to
receive the bearing cap positioned beneath the yoke.
(5) Position the yoke with the grease fitting, if
equipped, pointing up.
(6) Place a socket with an outside diameter
smaller than the upper bearing cap on the upper
bearing cap and press the cap through the yoke to
release the lower bearing cap (Fig. 13).
(7) If the bearing cap will not pull out of the yoke
by hand after pressing, tap the yoke ear near the
bearing cap to dislodge the cap.
(8) To remove the opposite bearing cap, turn the
yoke over and straighten the cross in the open hole.
Then, carefully press the end of the cross until the
remaining bearing cap can be removed (Fig. 14).
CAUTION: If the cross or bearing cap are not
straight during installation, the bearing cap willscore the walls of the yoke bore and damage can
occur.
Fig. 12 REMOVE SNAP RING
1 - SNAP RING
Fig. 13 PRESS OUT BEARING
1 - PRESS
2 - SOCKET
Fig. 14 PRESS OUT REMAINING BEARING
1 - CROSS
2 - BEARING CAP
3 - 8 PROPELLER SHAFTWJ
Page 60 of 2199

FRONT AXLE - 186FBI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................16
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
ADJUSTMENTS........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................30
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................31
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
AXLE - C/V JOINT
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
AXLE - U-JOINT
REMOVAL.............................36INSTALLATION.........................37
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................39
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL.............................40
DISASSEMBLY.........................42
ASSEMBLY............................42
INSTALLATION.........................43
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI
DESCRIPTION
The Front Beam-design Iron (FBI) axle consists of
a cast iron differential housing with axle shaft tubes
extending from either side. The tubes are pressed
into the differential housing and welded. The axles
are semi-floating axle shafts, meaning the loads are
supported by the hub bearings. The axle shafts are
retained by nuts at the hub bearings.
The differential case is a one-piece design. Differ-
ential bearing preload and ring gear backlash is
adjusted by the use of shims located between the dif-
ferential bearing cups and housing. Pinion bearing
preload is set and maintained by the use of a collaps-
ible spacer. A differential cover provides a means for
inspection and servicing.
An optional Vari-Loktdifferential has a one-piece
differential case which contains the gerotor pump
assembly and the clutch mechinism. This unit is ser-
viced as an assembly.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transfer case
through the front propeller shaft. The front propeller
shaft is connected to the pinion gear which rotatesthe differential through the gear mesh with the ring
gear bolted to the differential case. The engine power
is transmitted to the axle shafts through the pinion
mate and side gears. The side gears are splined to
the axle shafts.
STANDARD DIFFERENTIAL
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pinion
gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the pin-
ion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig. 1).
When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. The difference must be compensated
for to prevent the tires from scuffing and skidding
through turns. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
2). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 15
Page 61 of 2199

VARI-LOKTDIFFERENTIAL
In a standard differential if one wheel spins, the
opposite wheel will generate only as much torque as
the spinning wheel.
A gerotor pump and clutch pack are used to pro-
vide the torque transfer capability. One axle shaft is
splined to the gerotor pump and one of the differen-
tial side gears, which provides the input to the pump.
As a wheel begins to lose traction, the speed differ-
ential is transmitted from one side of the differential
to the other through the side gears. The motion of
one side gear relative to the other turns the inner
rotor of the pump. Since the outer rotor of the pump
is grounded to the differential case, the inner and
outer rotors are now moving relative to each other
and therefore creates pressure in the pump. The tun-ing of the front and rear axle orifices and valves
inside the gerotor pump is unique and each system
includes a torque-limiting pressure relief valve to
protect the clutch pack, which also facilitates vehicle
control under extreme side-to-side traction varia-
tions. The resulting pressure is applied to the clutch
pack and the transfer of torque is completed.
Under conditions in which opposite wheels are on
surfaces with widely different friction characteristics,
Vari-loktdelivers far more torque to the wheel on
the higher traction surface than do conventional
Trac-loktsystems. Because conventional Trac-lokt
differentials are initially pre-loaded to assure torque
transfer, normal driving (where inner and outer
wheel speeds differ during cornering, etc.) produces
torque transfer during even slight side-to-side speed
variations. Since these devices rely on friction from
this preload to transfer torque, normal use tends to
cause wear that reduces the ability of the differential
to transfer torque over time. By design, the Vari-lokt
system is less subject to wear, remaining more con-
sistent over time in its ability to transfer torque. The
coupling assembly is serviced as a unit. From a ser-
vice standpoint the coupling also benefits from using
the same lubricant supply as the ring and pinion
gears.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
Fig. 1 DIFFERENTIAL-STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
Fig. 2 DIFFERENTIAL-ON TURNS
1 - PINION GEARS ROTATE ON PINION SHAFT
3 - 16 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 63 of 2199
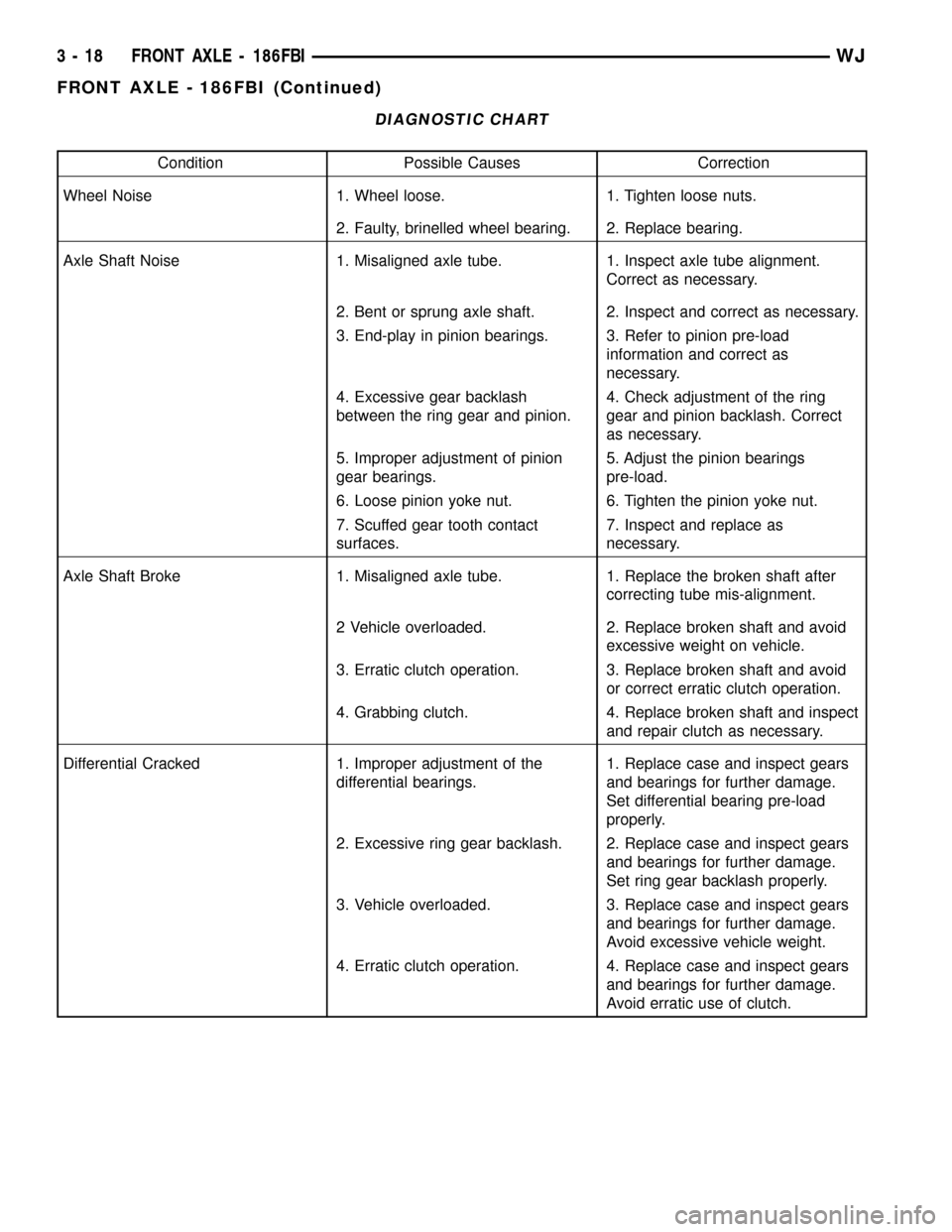
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load
information and correct as
necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash
between the ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring
gear and pinion backlash. Correct
as necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion
gear bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings
pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact
surfaces.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
3 - 18 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 66 of 2199

INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The weight of the vehicle must be sup-
ported by the springs before suspension arms and
track bar fasteners can be tightened. If springs are
not at their normal ride position, ride height and
handling could be affected.
(1) Install the springs and retainer clips. Tighten
the retainer bolts to 21 N´m (16 ft. lbs.).
(2) Support the axle on a lifting device and posi-
tion axle under the vehicle.
(3) Raise the axle and align it with the spring
pads.
(4) Position the upper and lower suspension arms
in the axle brackets. Loosely install bolts and nuts to
hold suspension arms to the axle brackets.
(5) Install vent hose to the axle shaft tube.
(6) Install track bar in the axle bracket and install
the bolt loosely.
(7) Install shock absorbers and tighten the bolts to
23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install stabilizer bar links to the axle brackets
and tighten the nuts to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install drag link and tie rod to the steering
knuckles.
(10) Install steering damper to the axle bracket
and tighten the nut to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install the brake rotors (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS - INSTALLA-
TION) and calipers.
(12) Connect the wheel speed sensor wiring har-
ness to the vehicle wiring harness.
(13) Align the previously made marks on the pro-
peller shaft and the yoke/pinion flange.
(14) Install propeller shaft to pinion flange bolts ,
if equipped.
(15) Install propeller shaft to yoke straps and
bolts, if equipped.
(16) Check and fill axle lubricant.
(17) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(18) Remove the lifting device from the axle and
lower the vehicle.
(19) Tighten the upper suspension arm nuts to 75
N´m (55 ft. lbs.). Tighten the lower suspension arm
nuts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(20) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 100 N´m (74 ft. lbs.).
(21) Check the front wheel alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched onto each gear (Fig. 3). A plus
(+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is etched
into the face of the pinion gear. This number is theamount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth varies
from the standard depth setting of a pinion etched
with a (0). The standard setting from the center line
of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion is 92.1
mm (3.625 in.). The standard depth provides the best
gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Backlash and
Contact Pattern Analysis paragraph in this section
for additional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/oil slinger. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 4).
Fig. 3 PINION GEAR ID NUMBERS
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - DRIVE PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
Fig. 4 ADJUSTMENT SHIM LOCATIONS
1 - PINION DEPTH SHIM/OIL SLINGER
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
3 - RING GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
5 - COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 21
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 67 of 2199

If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance etched into both the original and replace-
ment pinion. Add or subtract this number from the
thickness of the original depth shim/oil slinger to
compensate for the difference in the depth variances.
Refer to the Pinion Gear Depth Variance chart.
Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus the amount needed.Note the etched number on the face of the pinion
gear head (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers rep-
resent thousands of an inch deviation from the stan-
dard. If the number is negative, add that value to the
required thickness of the depth shims. If the number
is positive, subtract that value from the thickness of
the depth shim. If the number is 0 no change is nec-
essary.
PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
24232221 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.004
21+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.005
22+0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.006
23+0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.007
24020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.00720.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 5).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8804 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 5).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 6).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 5).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion, in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 7).
Install differential bearing caps on Arbor Discs and
tighten cap bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.(5) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(6) Posttion Scooter Block/Dial Indicator so dial
probe and scooter block are flush on the surface of
the pinion height block (Fig. 5). Hold scooter block
and zero the dial indicator.
(7) Hold scooter block against the pinion height
block and slowly slide across the pinion height block
to the arbor (Fig. 8). Move the scooter block till the
dial probe crests the arbors and record the highest
reading.
(8) Select a shim/oil slinger equal to the dial indi-
cator reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 3). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
3 - 22 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)