Check transmission JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1636 of 2199
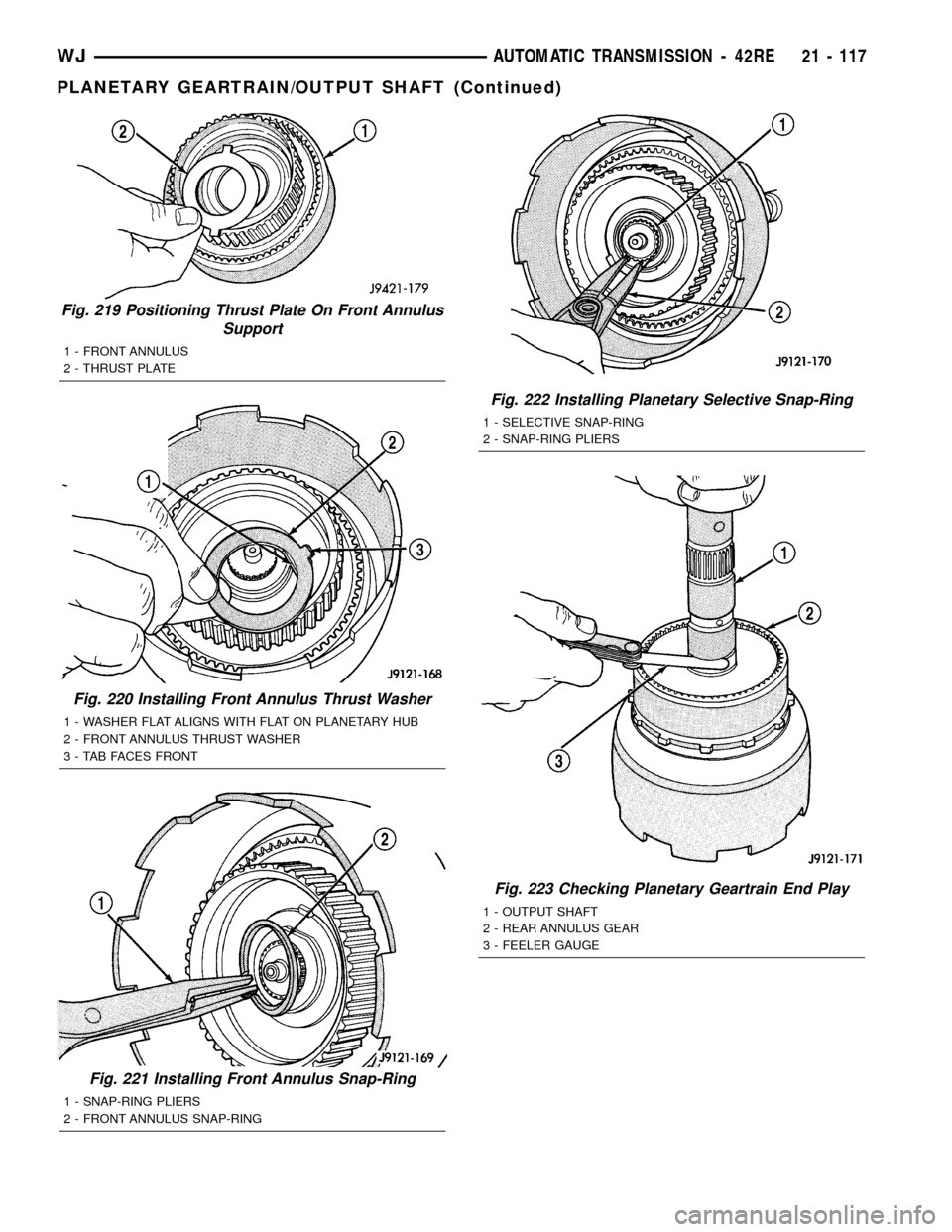

Fig. 219 Positioning Thrust Plate On Front Annulus
Support
1 - FRONT ANNULUS
2 - THRUST PLATE
Fig. 220 Installing Front Annulus Thrust Washer
1 - WASHER FLAT ALIGNS WITH FLAT ON PLANETARY HUB
2 - FRONT ANNULUS THRUST WASHER
3 - TAB FACES FRONT
Fig. 221 Installing Front Annulus Snap-Ring
1 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
2 - FRONT ANNULUS SNAP-RING
Fig. 222 Installing Planetary Selective Snap-Ring
1 - SELECTIVE SNAP-RING
2 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
Fig. 223 Checking Planetary Geartrain End Play
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - REAR ANNULUS GEAR
3 - FEELER GAUGE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 117
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1638 of 2199
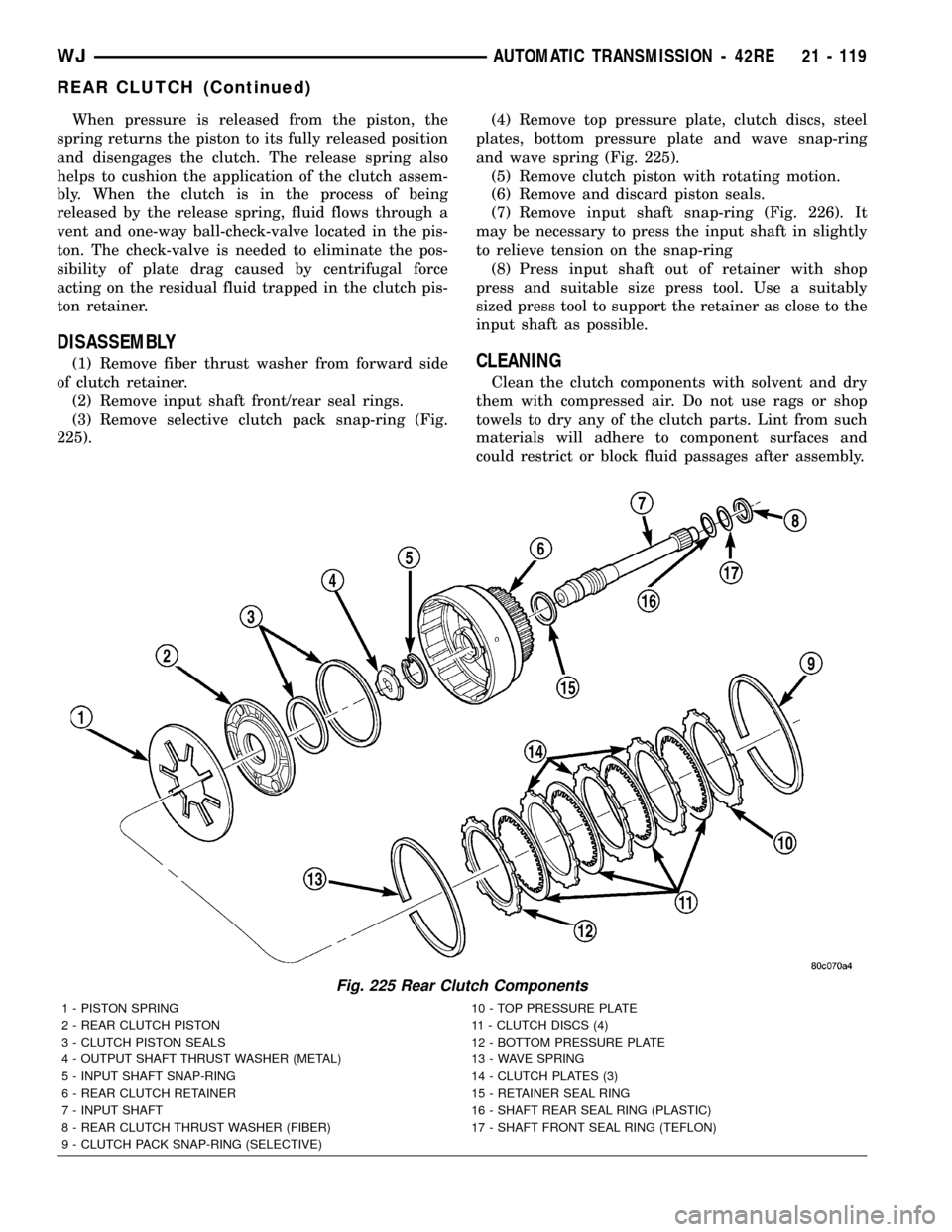
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the pis-
ton. The check-valve is needed to eliminate the pos-
sibility of plate drag caused by centrifugal force
acting on the residual fluid trapped in the clutch pis-
ton retainer.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove fiber thrust washer from forward side
of clutch retainer.
(2) Remove input shaft front/rear seal rings.
(3) Remove selective clutch pack snap-ring (Fig.
225).(4) Remove top pressure plate, clutch discs, steel
plates, bottom pressure plate and wave snap-ring
and wave spring (Fig. 225).
(5) Remove clutch piston with rotating motion.
(6) Remove and discard piston seals.
(7) Remove input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 226). It
may be necessary to press the input shaft in slightly
to relieve tension on the snap-ring
(8) Press input shaft out of retainer with shop
press and suitable size press tool. Use a suitably
sized press tool to support the retainer as close to the
input shaft as possible.CLEANING
Clean the clutch components with solvent and dry
them with compressed air. Do not use rags or shop
towels to dry any of the clutch parts. Lint from such
materials will adhere to component surfaces and
could restrict or block fluid passages after assembly.
Fig. 225 Rear Clutch Components
1 - PISTON SPRING 10 - TOP PRESSURE PLATE
2 - REAR CLUTCH PISTON 11 - CLUTCH DISCS (4)
3 - CLUTCH PISTON SEALS 12 - BOTTOM PRESSURE PLATE
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT THRUST WASHER (METAL) 13 - WAVE SPRING
5 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING 14 - CLUTCH PLATES (3)
6 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER 15 - RETAINER SEAL RING
7 - INPUT SHAFT 16 - SHAFT REAR SEAL RING (PLASTIC)
8 - REAR CLUTCH THRUST WASHER (FIBER) 17 - SHAFT FRONT SEAL RING (TEFLON)
9 - CLUTCH PACK SNAP-RING (SELECTIVE)
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 119
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1639 of 2199

INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Soak clutch discs in transmission fluid while
assembling other clutch parts.
(2) Install new seal rings on clutch retainer hub
and input shaft, if necessary, (Fig. 227) and (Fig.
228).
(a) Be sure clutch hub seal ring is fully seated in
groove and is not twisted.
(3) Lubricate splined end of input shaft and clutch
retainer with transmission fluid. Then press input
shaft into retainer (Fig. 229). Use a suitably sized
press tool to support retainer as close to input shaft
as possible.
(4) Install input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 226).
(5) Invert retainer and press input shaft in oppo-
site direction until snap-ring is seated.
(6) Install new seals on clutch piston. Be sure lip
of each seal faces interior of clutch retainer.
(7) Lubricate lip of piston seals with generous
quantity of MopartDoor Ease. Then lubricate
retainer hub and bore with light coat of transmission
fluid.
(8) Install clutch piston in retainer. Use twisting
motion to seat piston in bottom of retainer. A thin
strip of plastic (about 0.0209thick), can be used to
guide seals into place if necessary.
CAUTION: Never push the clutch piston straight in.
This will fold the seals over causing leakage and
clutch slip. In addition, never use any type of metal
tool to help ease the piston seals into place. Metal
tools will cut, shave, or score the seals.
(9) Install piston spring in retainer and on top of
piston (Fig. 230). Concave side of spring faces down-
ward (toward piston).
(10) Install wave spring in retainer (Fig. 230). Be
sure spring is completely seated in retainer groove.
(11) Install bottom pressure plate (Fig. 225).
Ridged side of plate faces downward (toward piston)
and flat side toward clutch pack.
(12) Install first clutch disc in retainer on top of
bottom pressure plate. Then install a clutch plate fol-
lowed by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is
installed (4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig.
225).
(13) Install top pressure plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
(15) Using a suitable gauge bar and dial indicator,
measure clutch pack clearance (Fig. 231).
(a) Position gauge bar across the clutch drum
with the dial indicator pointer on the pressure
plate (Fig. 231).
(b) Using two small screw drivers, lift the pres-
sure plate and release it.
Fig. 226 Removing Input Shaft Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING
3 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
21 - 120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1641 of 2199

The selective snap-ring thicknesses are:
²0.107-0.109 in.
²0.098-0.100 in.
²0.095-0.097 in.
²0.083-0.085 in.
²0.076-0.078 in.
²0.071-0.073 in.
²0.060-0.062 in.
(16) Coat rear clutch thrust washer with petro-
leum jelly and install washer over input shaft and
into clutch retainer (Fig. 232). Use enough petroleum
jelly to hold washer in place.REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION
The rear (low/reverse) servo consists of a single
stage or diameter piston and a spring loaded plug.
The spring is used to cushion the application of the
rear (low/reverse) band.
OPERATION
While in the de-energized state (no pressure
applied), the piston is held up in its bore by the pis-
ton spring. The plug is held down in its bore, in the
piston, by the plug spring. When pressure is applied
to the top of the piston, the plug is forced down in its
bore, taking up any clearance. As the piston moves, it
causes the plug spring to compress, and the piston
moves down over the plug. The piston continues to
move down until it hits the shoulder of the plug and
fully applies the band. The period of time from the
initial application, until the piston is against the
shoulder of the plug, represents a reduced shocking
of the band that cushions the shift.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove small snap-ring and remove plug and
spring from servo piston (Fig. 233).
(2) Remove and discard servo piston seal ring.
CLEANING
Remove and discard the servo piston seal ring (Fig.
234). Then clean the servo components with solvent
and dry with compressed air. Replace either spring if
collapsed, distorted or broken. Replace the plug and
piston if cracked, bent, or worn. Discard the servo
snap-rings and use new ones at assembly.
Fig. 231 Checking Rear Clutch Pack Clearance
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - PRESSURE PLATE
3 - SNAP-RING
4-STAND
5 - REAR CLUTCH
6 - GAUGE BAR
Fig. 232 Installing Rear Clutch Thrust Washer
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - REAR CLUTCH THRUST WASHER
Fig. 233 Rear Servo Components
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - PISTON SEAL
3 - PISTON PLUG
4 - SPRING RETAINER
5 - SNAP-RING
6 - PISTON SPRING
7 - CUSHION SPRING
8 - PISTON
21 - 122 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1647 of 2199

NOTE: Be sure that as the cable is pulled forward
and centered on the throttle lever stud, the cable
housing moves smoothly with the cable. Due to the
angle at which the cable housing enters the spring
housing, the cable housing may bind slightly and
create an incorrect adjustment.
(8) Reconnect the T.V. cable (B) to the throttle
bellcrank lever (C).
(9) Check cable adjustment. Verify transmission
throttle lever and lever on throttle body move simul-
taneously.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 245) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the all transmission fluid
cooler(s) and lines.
Fig. 244 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 245 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - FRONT COVER
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
7 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 128 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 1652 of 2199

TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied and is released when fluid is vented from the
hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in fourth gear, and in third gear under various con-
ditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, when
the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after the
vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter clutch
will disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when the
vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 253). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
Fig. 252 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
Fig. 253 Checking Torque Converter Seating -
Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 133
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1653 of 2199

TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicle
is shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-
ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
The valve must be removed whenever the cooler
and lines are reverse flushed. The valve can be flow
tested when necessary. The procedure is exactly the
same as for flow testing a cooler.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 254). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The overdrive OFF lamp in the instrument panel
illuminates when the shift back to third occurs. The
transmission will not allow fourth gear operation
until fluid temperature decreases to approximately
110ÉC (230ÉF).
Fig. 254 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
Page 1654 of 2199

VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 255), (Fig. 256), (Fig.
257), and (Fig. 258):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure plug and sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²10 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 255 Upper Housing Control Valve Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - REGULATOR VALVE 9 - 1-2 GOVERNOR PLUG
3 - SWITCH VALVE 10 - GOVERNOR PLUG COVER
4 - REGULATOR VALVE SPRING 11 - THROTTLE PLUG
5 - KICKDOWN VALVE 12 - 2-3 GOVERNOR PLUG
6 - KICKDOWN DETENT 13 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
7 - THROTTLE VALVE AND SPRING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 135
Page 1658 of 2199
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
CHECK BALLS
CHECK BALL NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug.
2 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug.
3 Allows either the Reverse circuit or the 3rd gear circuit to pressurize the front
clutch.
4 Allows either the Manual Low circuit from the Manual Valve or the Reverse
from the Manual Valve circuit to pressurize the rear servo.
5 Directs line pressure to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve in either Manual
Low or Manual 2nd, forcing the downshift to 2nd gear regardless of governor
pressure.
6 Provides a by-pass around the front servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
7 Provides a by-pass around the rear clutch orifice so that the clutch can release
quickly.
8 Directs reverse line pressure through an orifice to the throttle valve eliminating
the extra leakage and insuring that Reverse line pressure pressure will be
sufficient.
9 Provides a by-pass around the rear servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
ECE (10) Allows the lockup clutch to used at WOT in 3rd gear by putting line pressure
from the 3-4 Timing Valve on the interlock area of the 2-3 shift valve, thereby
preventing a 3rd gear Lock-up to 2nd gear kickdown.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 139
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1662 of 2199
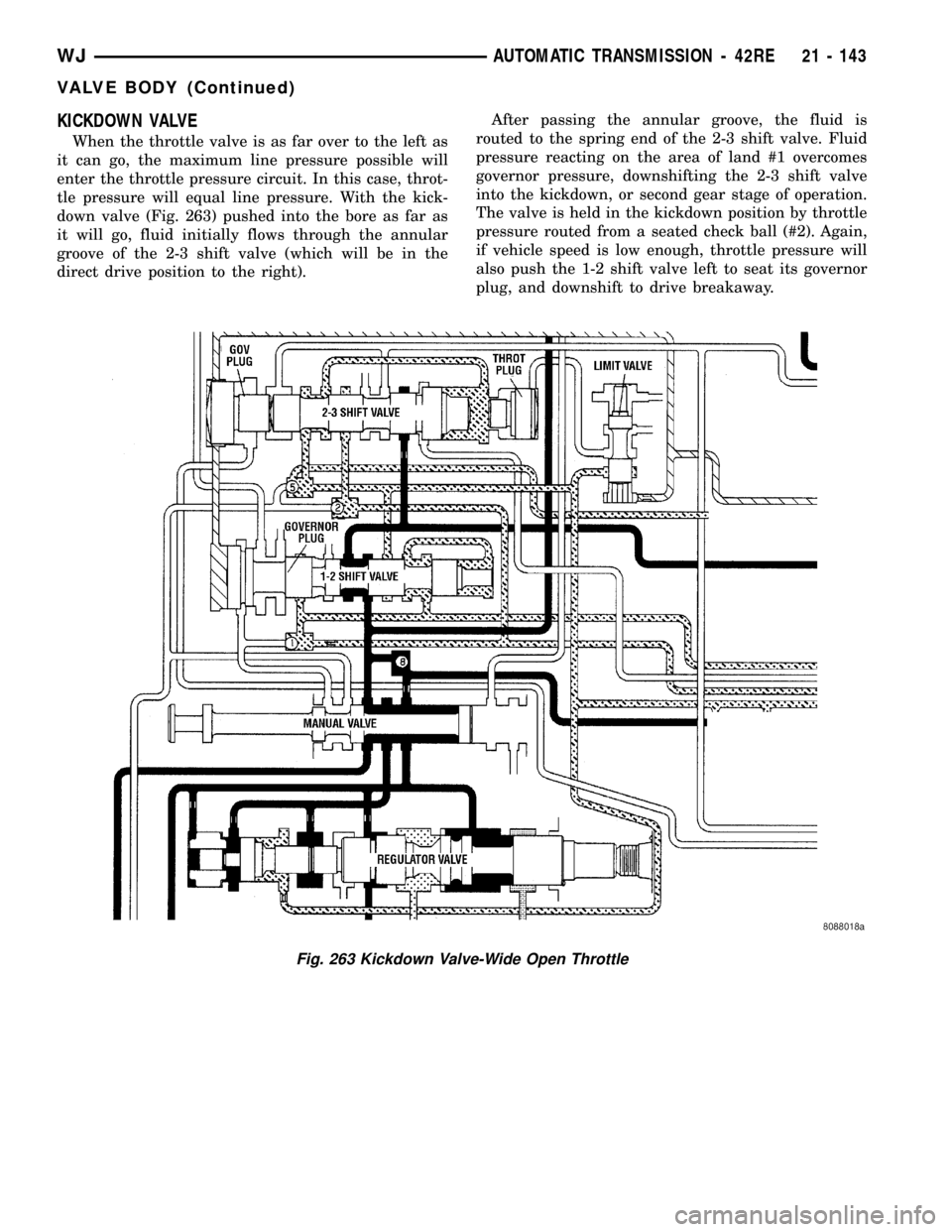
KICKDOWN VALVE
When the throttle valve is as far over to the left as
it can go, the maximum line pressure possible will
enter the throttle pressure circuit. In this case, throt-
tle pressure will equal line pressure. With the kick-
down valve (Fig. 263) pushed into the bore as far as
it will go, fluid initially flows through the annular
groove of the 2-3 shift valve (which will be in the
direct drive position to the right).After passing the annular groove, the fluid is
routed to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve. Fluid
pressure reacting on the area of land #1 overcomes
governor pressure, downshifting the 2-3 shift valve
into the kickdown, or second gear stage of operation.
The valve is held in the kickdown position by throttle
pressure routed from a seated check ball (#2). Again,
if vehicle speed is low enough, throttle pressure will
also push the 1-2 shift valve left to seat its governor
plug, and downshift to drive breakaway.
Fig. 263 Kickdown Valve-Wide Open Throttle
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 143
VALVE BODY (Continued)