bore JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1639 of 2199

INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Soak clutch discs in transmission fluid while
assembling other clutch parts.
(2) Install new seal rings on clutch retainer hub
and input shaft, if necessary, (Fig. 227) and (Fig.
228).
(a) Be sure clutch hub seal ring is fully seated in
groove and is not twisted.
(3) Lubricate splined end of input shaft and clutch
retainer with transmission fluid. Then press input
shaft into retainer (Fig. 229). Use a suitably sized
press tool to support retainer as close to input shaft
as possible.
(4) Install input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 226).
(5) Invert retainer and press input shaft in oppo-
site direction until snap-ring is seated.
(6) Install new seals on clutch piston. Be sure lip
of each seal faces interior of clutch retainer.
(7) Lubricate lip of piston seals with generous
quantity of MopartDoor Ease. Then lubricate
retainer hub and bore with light coat of transmission
fluid.
(8) Install clutch piston in retainer. Use twisting
motion to seat piston in bottom of retainer. A thin
strip of plastic (about 0.0209thick), can be used to
guide seals into place if necessary.
CAUTION: Never push the clutch piston straight in.
This will fold the seals over causing leakage and
clutch slip. In addition, never use any type of metal
tool to help ease the piston seals into place. Metal
tools will cut, shave, or score the seals.
(9) Install piston spring in retainer and on top of
piston (Fig. 230). Concave side of spring faces down-
ward (toward piston).
(10) Install wave spring in retainer (Fig. 230). Be
sure spring is completely seated in retainer groove.
(11) Install bottom pressure plate (Fig. 225).
Ridged side of plate faces downward (toward piston)
and flat side toward clutch pack.
(12) Install first clutch disc in retainer on top of
bottom pressure plate. Then install a clutch plate fol-
lowed by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is
installed (4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig.
225).
(13) Install top pressure plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
(15) Using a suitable gauge bar and dial indicator,
measure clutch pack clearance (Fig. 231).
(a) Position gauge bar across the clutch drum
with the dial indicator pointer on the pressure
plate (Fig. 231).
(b) Using two small screw drivers, lift the pres-
sure plate and release it.
Fig. 226 Removing Input Shaft Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING
3 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
21 - 120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1641 of 2199

The selective snap-ring thicknesses are:
²0.107-0.109 in.
²0.098-0.100 in.
²0.095-0.097 in.
²0.083-0.085 in.
²0.076-0.078 in.
²0.071-0.073 in.
²0.060-0.062 in.
(16) Coat rear clutch thrust washer with petro-
leum jelly and install washer over input shaft and
into clutch retainer (Fig. 232). Use enough petroleum
jelly to hold washer in place.REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION
The rear (low/reverse) servo consists of a single
stage or diameter piston and a spring loaded plug.
The spring is used to cushion the application of the
rear (low/reverse) band.
OPERATION
While in the de-energized state (no pressure
applied), the piston is held up in its bore by the pis-
ton spring. The plug is held down in its bore, in the
piston, by the plug spring. When pressure is applied
to the top of the piston, the plug is forced down in its
bore, taking up any clearance. As the piston moves, it
causes the plug spring to compress, and the piston
moves down over the plug. The piston continues to
move down until it hits the shoulder of the plug and
fully applies the band. The period of time from the
initial application, until the piston is against the
shoulder of the plug, represents a reduced shocking
of the band that cushions the shift.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove small snap-ring and remove plug and
spring from servo piston (Fig. 233).
(2) Remove and discard servo piston seal ring.
CLEANING
Remove and discard the servo piston seal ring (Fig.
234). Then clean the servo components with solvent
and dry with compressed air. Replace either spring if
collapsed, distorted or broken. Replace the plug and
piston if cracked, bent, or worn. Discard the servo
snap-rings and use new ones at assembly.
Fig. 231 Checking Rear Clutch Pack Clearance
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - PRESSURE PLATE
3 - SNAP-RING
4-STAND
5 - REAR CLUTCH
6 - GAUGE BAR
Fig. 232 Installing Rear Clutch Thrust Washer
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - REAR CLUTCH THRUST WASHER
Fig. 233 Rear Servo Components
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - PISTON SEAL
3 - PISTON PLUG
4 - SPRING RETAINER
5 - SNAP-RING
6 - PISTON SPRING
7 - CUSHION SPRING
8 - PISTON
21 - 122 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1662 of 2199
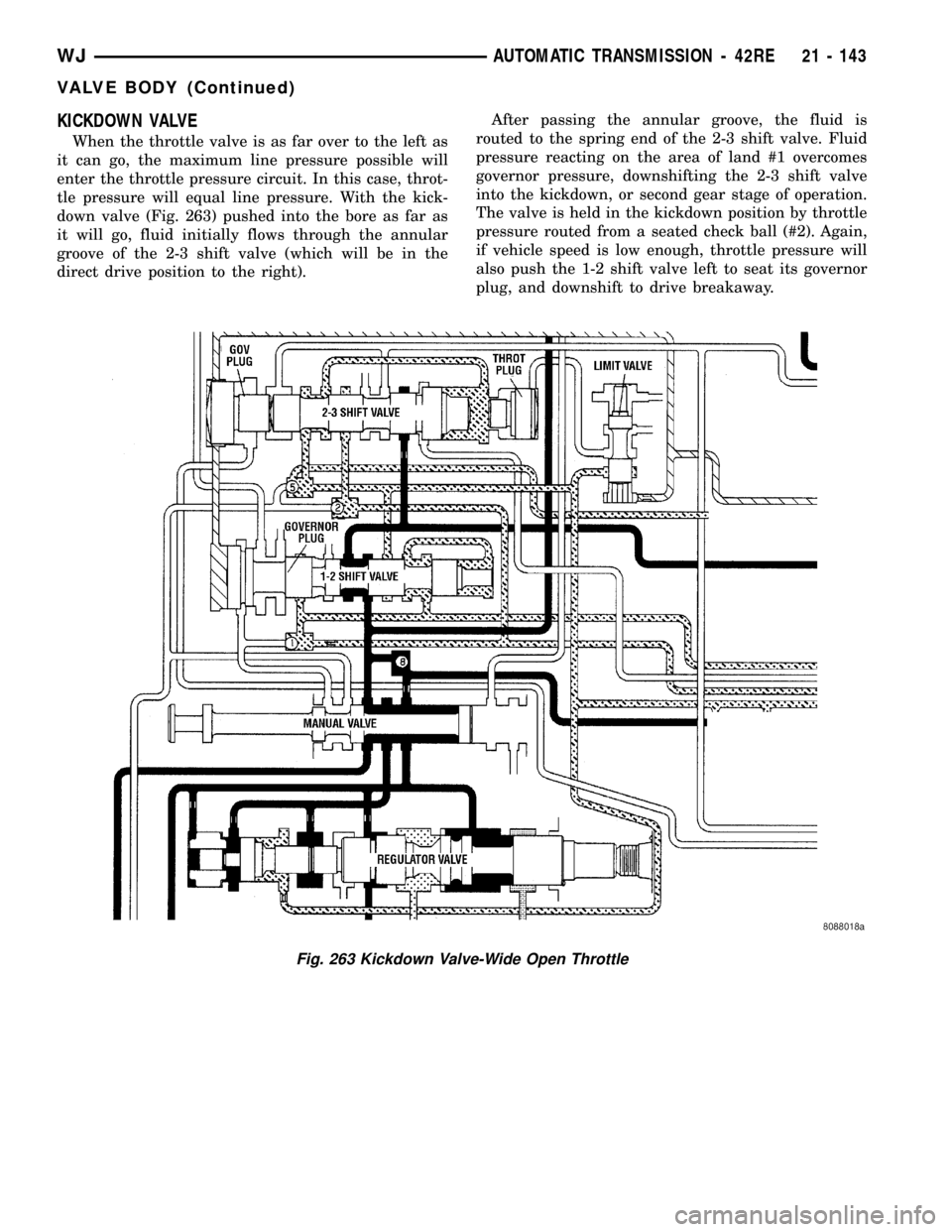
KICKDOWN VALVE
When the throttle valve is as far over to the left as
it can go, the maximum line pressure possible will
enter the throttle pressure circuit. In this case, throt-
tle pressure will equal line pressure. With the kick-
down valve (Fig. 263) pushed into the bore as far as
it will go, fluid initially flows through the annular
groove of the 2-3 shift valve (which will be in the
direct drive position to the right).After passing the annular groove, the fluid is
routed to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve. Fluid
pressure reacting on the area of land #1 overcomes
governor pressure, downshifting the 2-3 shift valve
into the kickdown, or second gear stage of operation.
The valve is held in the kickdown position by throttle
pressure routed from a seated check ball (#2). Again,
if vehicle speed is low enough, throttle pressure will
also push the 1-2 shift valve left to seat its governor
plug, and downshift to drive breakaway.
Fig. 263 Kickdown Valve-Wide Open Throttle
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 143
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1663 of 2199
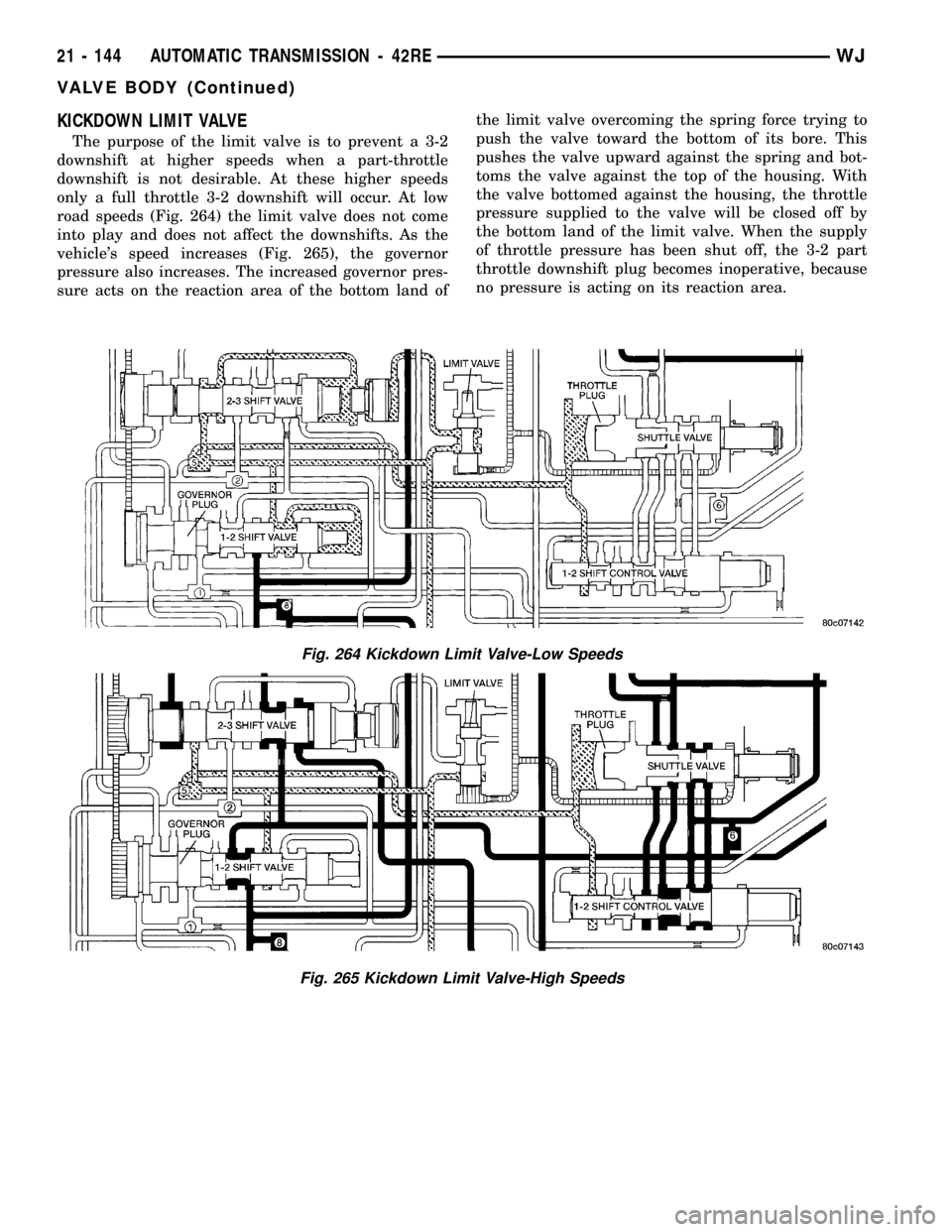
KICKDOWN LIMIT VALVE
The purpose of the limit valve is to prevent a 3-2
downshift at higher speeds when a part-throttle
downshift is not desirable. At these higher speeds
only a full throttle 3-2 downshift will occur. At low
road speeds (Fig. 264) the limit valve does not come
into play and does not affect the downshifts. As the
vehicle's speed increases (Fig. 265), the governor
pressure also increases. The increased governor pres-
sure acts on the reaction area of the bottom land ofthe limit valve overcoming the spring force trying to
push the valve toward the bottom of its bore. This
pushes the valve upward against the spring and bot-
toms the valve against the top of the housing. With
the valve bottomed against the housing, the throttle
pressure supplied to the valve will be closed off by
the bottom land of the limit valve. When the supply
of throttle pressure has been shut off, the 3-2 part
throttle downshift plug becomes inoperative, because
no pressure is acting on its reaction area.
Fig. 264 Kickdown Limit Valve-Low Speeds
Fig. 265 Kickdown Limit Valve-High Speeds
21 - 144 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1667 of 2199
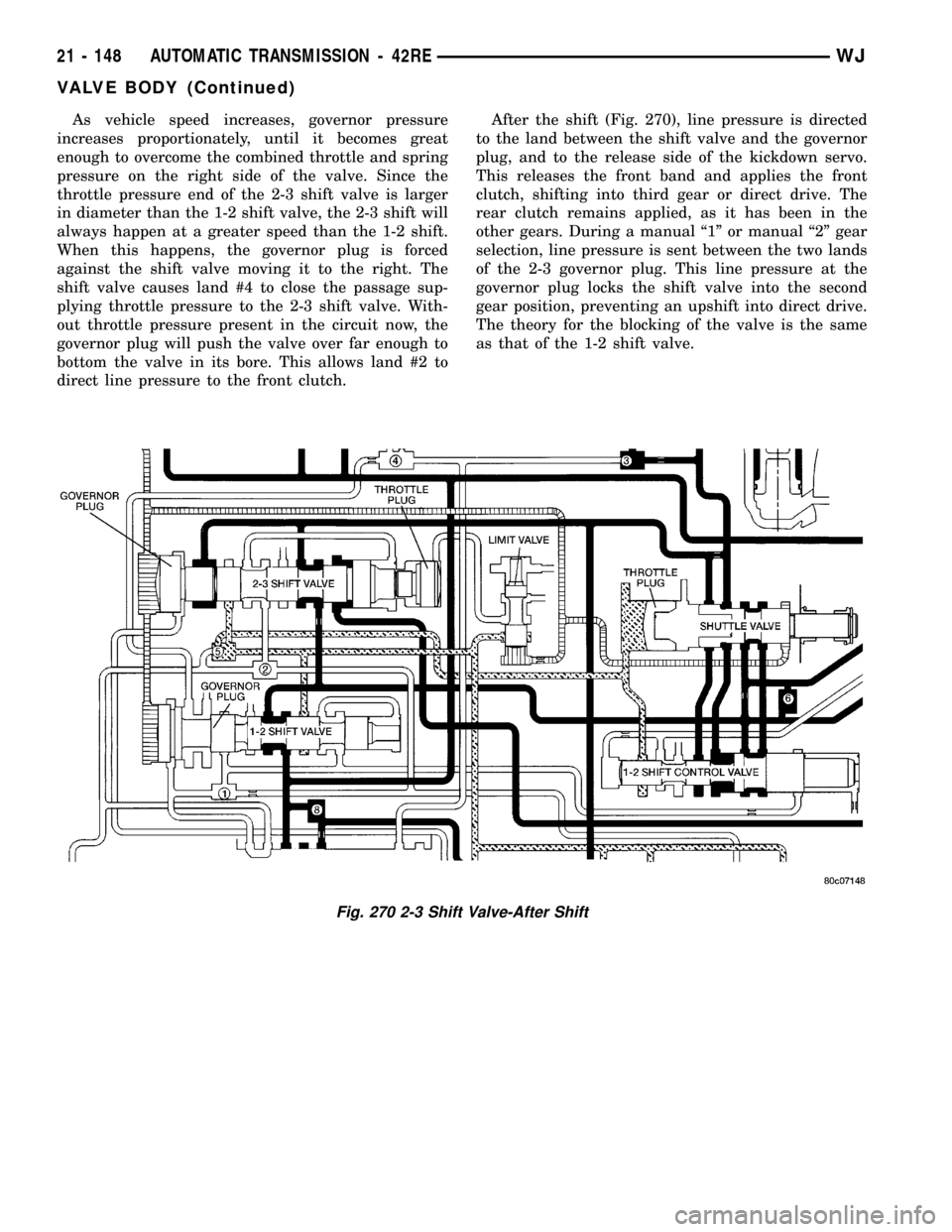
As vehicle speed increases, governor pressure
increases proportionately, until it becomes great
enough to overcome the combined throttle and spring
pressure on the right side of the valve. Since the
throttle pressure end of the 2-3 shift valve is larger
in diameter than the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift will
always happen at a greater speed than the 1-2 shift.
When this happens, the governor plug is forced
against the shift valve moving it to the right. The
shift valve causes land #4 to close the passage sup-
plying throttle pressure to the 2-3 shift valve. With-
out throttle pressure present in the circuit now, the
governor plug will push the valve over far enough to
bottom the valve in its bore. This allows land #2 to
direct line pressure to the front clutch.After the shift (Fig. 270), line pressure is directed
to the land between the shift valve and the governor
plug, and to the release side of the kickdown servo.
This releases the front band and applies the front
clutch, shifting into third gear or direct drive. The
rear clutch remains applied, as it has been in the
other gears. During a manual ª1º or manual ª2º gear
selection, line pressure is sent between the two lands
of the 2-3 governor plug. This line pressure at the
governor plug locks the shift valve into the second
gear position, preventing an upshift into direct drive.
The theory for the blocking of the valve is the same
as that of the 1-2 shift valve.
Fig. 270 2-3 Shift Valve-After Shift
21 - 148 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1672 of 2199
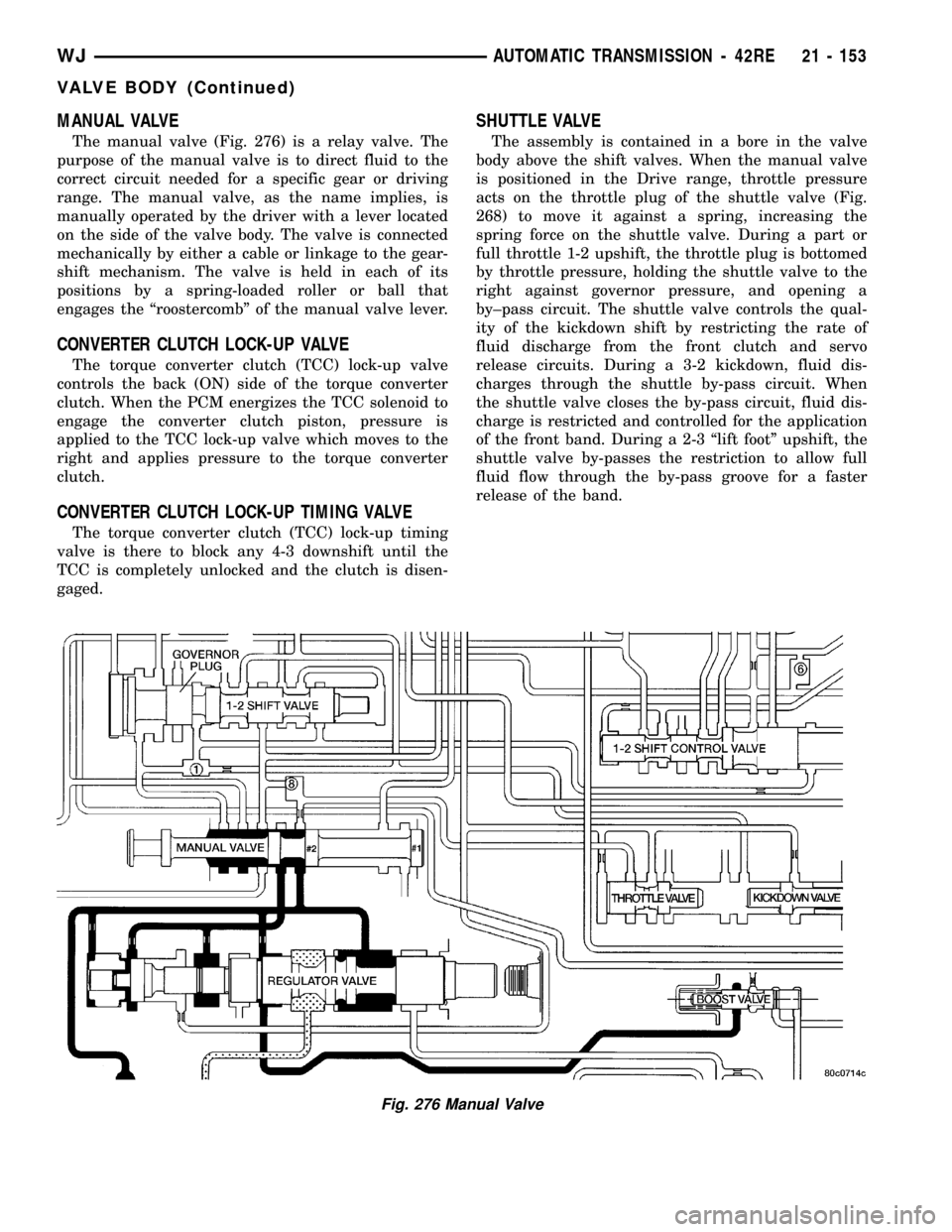
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 276) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
268) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 276 Manual Valve
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 153
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1674 of 2199

DISASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Do not clamp any valve body component
in a vise. This practice can damage the component
resulting in unsatisfactory operation after assembly
and installation. Do not use pliers to remove any of
the valves, plugs or springs and do not force any of
the components out or into place. The valves and
valve body housings will be damaged if force is
used. Tag or mark the valve body springs for refer-
ence as they are removed. Do not allow them to
become intermixed.
(1) Disconnect wires from governor pressure sen-
sor and solenoid.
(2) Remove screws attaching governor body and
retainer plate to transfer plate.
(3) Remove retainer plate, governor body and gas-
ket from transfer plate.
(4) Remove governor pressure sensor from gover-
nor body.
(5) Remove governor pressure solenoid by pulling
it straight out of bore in governor body. Remove and
discard solenoid O-rings if worn, cut, or torn.
(6) Remove small shoulder bolt that secures sole-
noid harness case connector to 3-4 accumulator hous-
ing (Fig. 281). Retain shoulder bolt. Either tape it toharness or thread it back into accumulator housing
after connector removal.
(7) Unhook overdrive/converter solenoid harness
from 3-4 accumulator cover plate (Fig. 282).
(8) Turn valve body over and remove screws that
attach overdrive/converter solenoid assembly to valve
body (Fig. 283).
(9) Remove solenoid and harness assembly from
valve body (Fig. 284).
(10) Remove boost valve cover (Fig. 285).
(11) Remove boost valve retainer, valve spring and
boost valve (Fig. 286).
Fig. 280 Valve Body
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - WIRE HARNESS
3 - PARK ROD
4 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
5 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
Fig. 281 Solenoid Harness Case Connector
Shoulder Bolt
1 - SOLENOID HARNESS CASE CONNECTOR
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
Fig. 282 Unhooking Solenoid Harness From
Accumulator Cover Plate
1 - OVERDRIVE/CONVERTER SOLENOID WIRE HARNESS
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR COVER PLATE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 155
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1685 of 2199

Wipe the governor pressure sensor and solenoid
valve with dry, lint free shop towels only. The O-rings
on the sensor and solenoid valve are the only service-
able components. Be sure the vent ports in the sole-
noid valve are open and not blocked by dirt or debris.
Replace the valve and/or sensor only when DRB scan
tool diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Or, if either
part has sustained physical damage (dented,
deformed, broken, etc.).
CAUTION: Do not turn the small screw at the end of
the solenoid valve for any reason. Turning the
screw in either direction will ruin solenoid calibra-
tion and result in solenoid failure. In addition, the
filter on the solenoid valve is NOT serviceable. Do
not try to remove the filter as this will damage the
valve housing.
INSPECTION
Inspect the throttle and manual valve levers and
shafts. Do not attempt to straighten a bent shaft or
correct a loose lever. Replace these components if
worn, bent, loose or damaged in any way.
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-
edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
CAUTION: Many of the valves and plugs, such as
the throttle valve, shuttle valve plug, 1-2 shift valve
and 1-2 governor plug, are made of coated alumi-
num. Aluminum components are identified by the
dark color of the special coating applied to the sur-
face (or by testing with a magnet). Do not sand alu-
minum valves or plugs under any circumstances.
This practice could damage the special coating
causing the valves/plugs to stick and bind.
Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Minor surface scratches on steel
valves and plugs can be removed with crocus cloth
butdo not round off the edges of the valve or
plug lands.Maintaining sharpness of these edges is
vitally important. The edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves and plugs and the
bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Check the two separator plates for distortion or
damage of any kind. Inspect the upper housing,
lower housing, 3-4 accumulator housing, and transfer
plate carefully. Be sure all fluid passages are clean
and clear. Check condition of the upper housing and
transfer plate check balls as well. The check balls
and ball seats must not be worn or damaged.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
Valve body bores do not change dimensionally with
use. If the valve body functioned correctly when new,
it will continue to operate properly after cleaning and
inspection. It should not be necessary to replace a
valve body assembly unless it is damaged in han-
dling.
The only serviceable valve body components are
listed below. The remaining valve body components
are serviced only as part of a complete valve body
assembly. Serviceable parts are:
²dual solenoid and harness assembly
²solenoid gasket
²solenoid case connector O-rings and shoulder
bolt
²switch valve and spring
Fig. 310 Accumulator Housing Components
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
3 - TEFLON SEALS
4 - PISTON SPRING
5 - COVER PLATE AND SCREWS
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1686 of 2199

²pressure adjusting screw and bracket assembly
²throttle lever
²manual lever and shaft seal
²throttle lever shaft seal, washer, and E-clip
²fluid filter and screws
²detent ball and spring
²valve body screws
²governor pressure solenoid
²governor pressure sensor and retaining clip
²park lock rod and E-clip
ASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Do not force valves or plugs into place
during reassembly. If the valve body bores, valves
and plugs are free of distortion or burrs, the valve
body components should all slide into place easily.
In addition, do not overtighten the transfer plate
and valve body screws during reassembly. Over-
tightening can distort the housings resulting in
valve sticking, cross leakage and unsatisfactory
operation. Tighten valve body screws to recom-
mended torque only.
LOWER HOUSING
(1) Lubricate valves, springs, and the housing
valve and plug bores with clean transmission fluid
(Fig. 309).
(2) Install 3-4 timing valve spring and valve in
lower housing.
(3) Install 3-4 quick fill valve in lower housing.
(4) Install 3-4 quick fill valve spring and plug in
housing.
(5) Install timing valve end plate. Tighten end
plate screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
3-4 ACCUMULATOR
(1) Lubricate accumulator piston, seals and hous-
ing piston bore with clean transmission fluid (Fig.
310).
(2) Install new seal rings on accumulator piston.
(3) Install piston and spring in housing.
(4) Install end plate on housing.
TRANSFER PLATE
(1) Install rear clutch and rear servo check balls in
transfer plate (Fig. 311).
(2) Install filter screen in upper housing separator
plate (Fig. 312).
(3) Align and position upper housing separator
plate on transfer plate (Fig. 313).
(4) Install brace plate (Fig. 313). Tighten brace
attaching screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install remaining separator plate attaching
screws. Tighten screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
UPPER AND LOWER HOUSING
(1) Position upper housing so internal passages
and check ball seats are facing upward. Then install
check balls in housing (Fig. 314). Eight check balls
are used. The single large check ball is approxi-
mately 8.7 mm (11/32 in.) diameter. The single small
check ball is approximately 4.8 mm (3/16 in.) in
diameter. The remaining 6 check balls are approxi-
mately 6.3 mm (1/4 in.) in diameter.
(2) Position assembled transfer plate and upper
housing separator plate on upper housing (Fig. 315).
Be sure filter screen is seated in proper housing
recess.
Fig. 311 Rear Clutch And Rear Servo Check Ball
Locations
1 - REAR CLUTCH CHECK BALL
2 - REAR SERVO CHECK BALL
3 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 312 Separator Plate Filter Screen Installation
1 - UPPER HOUSING SEPARATOR PLATE
2 - FILTER SCREEN
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 167
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1687 of 2199

(3) Install the ECE check ball into the transfer
plate (Fig. 301). The ECE check ball is approximately
4.8 mm (3/16 in.) in diameter.
(4) Position lower housing separator plate on
transfer plate (Fig. 316).
(5) Install lower housing on assembled transfer
plate and upper housing (Fig. 317).
(6) Install and start all valve body screws by hand
except for the screws to hold the boost valve tube
brace. Save those screws for later installation. Then
tighten screws evenly to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
Start at center and work out to sides when tighten-
ing screws (Fig. 317).
Fig. 313 Brace Plate
1 - BRACE
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
3 - SEPARATOR PLATE
Fig. 314 Check Ball Locations In Upper Housing
1 - SMALL DIAMETER CHECK BALLS (6)
2 - LARGE DIAMETER CHECK BALL (1)
Fig. 315 Installing Transfer Plate On Upper Housing
1 - FILTER SCREEN
2 - TRANSFER PLATE/SEPARATOR PLATE ASSEMBLY
3 - UPPER HOUSING
Fig. 316 Lower Housing Separator Plate
1 - BE SURE TO ALIGN BORES
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
3 - LOWER HOUSING (OVERDRIVE) SEPARATOR PLATE
21 - 168 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)