sensor JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 512 of 2199

POWER MIRROR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
Both the right and left power outside mirrors are
controlled by a single multi-function switch unit
located on the driver side front door trim panel. The
power mirror switch unit includes a three-position
rocker selector switch and four momentary direc-
tional push button switches.
The power mirror switch unit is integral to the
Driver Door Module (DDM). The power mirror switch
cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if faulty or dam-
aged, the entire DDM unit must be replaced. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/DRIVER DOOR MODULE - REMOVAL)
for the DDM service procedures.
OPERATION
The power mirror selector switch is moved right
(right mirror control), left (left mirror control), or
center to turn the power outside mirror system off.
When the selector switch is in the right mirror con-
trol or left mirror control position, one of the four
directional control buttons is depressed to control
movement of the selected mirror up, down, right, or
left. When the selector switch is in the Off position,
depressing any of the directional switches will not
change either mirror position.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the power mirror switches.
SIDEVIEW MIRROR
DESCRIPTION
Mechanically folding, power operated outside rear
view mirrors are standard equipment on this model.
Each power mirror housing contains two electric
motors, two drive mechanisms, an electric heating
grid, the mirror glass case and the mirror glass. One
motor and drive controls mirror up-and-down (verti-
cal) movement, and the other controls right-and-left
(horizontal) movement. If the vehicle is equipped
with the optional memory system, each mirror head
also contains two position potentiometers. One posi-
tion potentiometer monitors the vertical mirror
motor, and the other monitors the horizontal mirror
motor.
An optional driver side automatic dimming mirror
is able to automatically change its reflectance level.
This mirror is controlled by the circuitry of the auto-
matic day/night inside rear view mirror. A thin layer
of electrochromic material between two pieces of con-
ductive glass make up the face of the mirror. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER MIRRORS/AUTO-MATIC DAY / NIGHT MIRROR - DESCRIPTION) for
more information on this feature.
The power mirror unit cannot be repaired. Only
the mirror glass and glass case are serviced sepa-
rately. The replacement mirror glass is supplied with
an instruction sheet that details the recommended
replacement procedure. If any other component of the
power mirror unit is faulty or damaged, the entire
power mirror unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
Each of the two outside power mirrors includes two
reversible electric motors that are secured within the
power mirror housing. Each motor moves the mirror
case and glass through an integral drive unit. When
a power mirror motor is supplied with battery cur-
rent and ground, it moves the mirror case and glass
through its drive unit in one direction. When the bat-
tery current and ground feeds to the motor are
reversed, it moves the mirror case and glass in the
opposite direction.
The power mirrors are equipped with a standard
equipment electric heating grid that is applied to the
back of each outside rear view mirror glass. When an
electrical current is passed through the resistor wire
of the heating grid, it warms the mirror glass. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED MIRRORS -
DESCRIPTION) for more information on the opera-
tion of the heated mirrors and the rear window
defogger system.
If the driver side mirror is equipped with the auto-
matic dimming outside mirror option, two photocell
sensors on the inside rear view mirror are used to
monitor light levels and adjust the reflectance of both
the inside and driver side outside mirrors. This
change in reflectance helps to reduce the glare of
headlamps approaching the vehicle from the rear.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER MIRRORS/AU-
TOMATIC DAY / NIGHT MIRROR - OPERATION)
for more information on this feature.
If the vehicle is equipped with the optional mem-
ory system, the Driver Door Module (DDM) and the
Passenger Door Module (PDM) store the mirror posi-
tion information as monitored through the mirror
motor position potentiometers. When the memory
system requests a recall of the stored mirror position,
the DDM and the PDM are able to duplicate the
stored mirror positions by moving the mirror motors
until the potentiometer readings match the stored
values.
WJPOWER MIRRORS 8N - 15
Page 516 of 2199

²Ten-way power drivers and passenger seats
with Memory- This power seat option is standard
on Overland models and optional on Limited models.
This option includes a six-way adjustable seat cush-
ion track with power seat back recliners and power
lumbar supports. Heated Seats are standard with
this option.
Refer toHeated Seat Systemfor more informa-
tion on the heated seat option. Refer toMemory
Systemin the Memory System section of this group
for more information on the memory system.
The power seat system includes the following com-
ponents:
²Power lumbar adjuster (ten-way power seat
only)
²Power lumbar switch (ten-way power seat only)
²Power seat recliner (ten-way power seat only)
²Power seat switch
²Power seat track.
Refer toPower Seatin Wiring Diagrams for com-
plete circuit diagrams. Following are general descrip-
tions of the major components in the power seat/
memory seat system.
DESCRIPTION - MEMORY SYSTEM
An electronic memory system is standard equip-
ment on the Limited model. The memory system is
able to store and recall the driver side power seat
positions (including the power recliner position), and
both outside power mirror positions for two drivers.
For vehicles with a radio connected to the Program-
mable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work, the memory system is also able to store and
recall up to twenty - ten AM and ten FM - radio sta-
tion presets for two drivers. The memory system also
will store and recall the last station listened to for
each driver, even if it is not one of the twenty preset
stations.
The memory system will automatically return to
all of these settings when the corresponding num-
bered and color-coded button (Driver 1 - Black, or
Driver 2 - Gray) of the memory switch on the driver
side front door trim panel is depressed, or when the
doors are unlocked using the corresponding num-
bered and color-coded (Driver 1 - Black, or Driver 2 -
Gray) Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter. A
customer programmable feature of the memory sys-
tem allows the RKE recall of memory features to be
disabled in cases where there are more than two
drivers of the vehicle.
The memory system also has a customer program-
mable easy exit feature that will move the driver
seat rearward 55 millimeters (two inches) or to the
end of its travel, whichever occurs first, when the key
is removed from the ignition switch lock cylinder.A Memory Seat Module (MSM) or Memory Heated
Seat Module (MHSM) are used on this model to con-
trol and integrate the many electronic functions and
features included in the memory system. On vehicles
equipped with the heated seat system option, the
MHSM also controls the functions and features of
that system.
The memory system includes the following compo-
nents:
²Memory seat module (or memory heated seat
module)
²Memory switch
²Position potentiometers on both outside power
mirrors
²Position potentiometers on the driver side power
seat track and power seat recliner motors.
²Radio receiver (if PCI data bus capable).
Certain functions and features of the memory sys-
tem rely upon resources shared with other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sensor
information. This helps to reduce wire harness com-
plexity, internal controller hardware, and component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities. For diagnosis of these electronic modules or of
the PCI data bus network, the use of a DRBtscan
tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual
are recommended.
The other electronic modules that may affect mem-
ory system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)- Refer toBody
Control Modulein Electronic Control Modules for
more information.
²Driver Door Module (DDM)- Refer toDoor
Modulein Electronic Control Modules for more
information.
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC)- Refer toElectronic Vehicle Information
Centerin Overhead Console Systems for more infor-
mation.
²Passenger Door Module (PDM)- Refer to
Door Modulein Electronic Control Modules for
more information.
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)- Refer to
Powertrain Control Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for more information.
²Radio Receiver- Refer toRadio Receiverin
Audio Systems for more information.
Refer toHeated Seat Systemfor more informa-
tion on this system. Refer toRemote Keyless Entry
Systemin Power Lock Systems for more information
on the RKE system. Refer toPower Mirrorin
Power Mirror Systems for more information on the
WJPOWER SEAT SYSTEM 8N - 19
POWER SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 530 of 2199
POWER WINDOWS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER WINDOWS
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................34
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
WINDOWS...........................34
POWER WINDOW SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
WINDOW SWITCH.....................37REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................38
WINDOW MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................38
OPERATION...........................38
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WINDOW
MOTOR .............................38
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................39
POWER WINDOWS
DESCRIPTION
Power operated driver side and passenger side
front and rear door windows are standard factory-in-
stalled equipment on this model. The power window
system allows each of the door windows to be raised
or lowered electrically by operating a switch on the
trim panel for that door. Additionally, the master
switches on the driver side front door trim panel
allow all of the windows to be operated from the
driver seat position. A power window lockout switch
on the driver side front door trim panel will allow the
driver to disable all of the passenger door window
switches.
The power window system functionally operates
when the ignition switch is in the On position. How-
ever, a unique feature of this system will allow the
power windows to be operated for up to forty-five sec-
onds after the ignition switch is turned to the Off
position, or until a front door is opened, whichever
occurs first.
An auto-down feature allows the driver side front
door window to be lowered all the way, even if the
window switch is released. The driver side front door
window switch must be depressed in the down direc-
tion to a second detent to begin an auto-down event.
Depressing the switch again in any direction cancel
the auto-down event and begin movement in the
direction specified.
This group covers the following components of the
power window system:
²Power window switches
²Power window motors.
Certain functions and features of the power win-
dow system rely upon resources shared with other
electronic modules in the vehicle over the Program-mable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work. The PCI data bus network allows the sharing
of sensor information. This helps to reduce wire har-
ness complexity, internal controller hardware, and
component sensor current loads. At the same time,
this system provides increased reliability, enhanced
diagnostics, and allows the addition of many new fea-
ture capabilities. For diagnosis of these electronic
modules or of the PCI data bus network, the use of a
DRB scan tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures
manual are recommended.
The other electronic modules that may affect power
window system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)- (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODUL
- DESCRIPTION) for more information.
²Driver Door Module (DDM)-(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/DRIVER DOOR MODULE - DESCRIPTION)
for more information.
²Passenger Door Module (PDM)- (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/DRIVER DOOR MODULE - DESCRIPTION)
for more information.
This group covers diagnosis and service of only the
electrical components in the power window system.
For service of mechanical components, such as the
regulator, lift plate, window tracks, or glass refer to
Body. Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
The wiring information includes wiring diagrams,
proper wire and connector repair procedures, details
of wire harness routing and retention, connector pin-
out information and location views for the various
wire harness connectors, splices and grounds. Follow-
ing are general descriptions of the major components
in the power window system.
WJPOWER WINDOWS 8N - 33
Page 538 of 2199

RESTRAINTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
RESTRAINTS
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................4
WARNING - RESTRAINT SYSTEM...........5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM...................5
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HANDLING
NON-DEPLOYED SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINTS.........................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SERVICE
AFTER A SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
DEPLOYMENT.........................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VERIFICATION
TEST................................8
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................12
CHILD TETHER ANCHOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................14
CLOCKSPRING
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................15
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING
CENTERING.........................15
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................17
DRIVER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................19
REMOVAL.............................19
DISASSEMBLY.........................20
ASSEMBLY............................21
INSTALLATION.........................22
FRONT IMPACT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................24REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................25
FRONT IMPACT SENSOR & BRACKET
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................26
FRONT SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................28
FRONT SEAT BELT BUCKLE
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................29
PASSENGER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................30
REMOVAL.............................31
INSTALLATION.........................32
REAR CENTER SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR
REMOVAL.............................32
INSTALLATION.........................34
REAR OUTBOARD SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................35
REAR SEAT BELT BUCKLE
REMOVAL.............................36
INSTALLATION.........................36
SEAT BELT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................37
SEAT BELT TURNING LOOP ADJUSTER
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................38
SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................42
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................42
OPERATION...........................43
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................44
RESTRAINTS
DESCRIPTION
An occupant restraint system is standard factory-
installed safety equipment on this model. Availableoccupant restraints for this model include both active
and passive types. Active restraints are those which
require the vehicle occupants to take some action to
employ, such as fastening a seat belt; while passive
restraints require no action by the vehicle occupants
to be employed (Fig. 1).
WJRESTRAINTS 8O - 1
Page 539 of 2199

Fig. 1 Supplemental Restraints
1 - FRONT IMPACT SENSOR (2)
2 - PASSENGER AIRBAG
3 - DRIVER AIRBAG4 - AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
5 - SIDE IMPACT SENSOR (2)
6 - SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG (2)
8O - 2 RESTRAINTSWJ
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 540 of 2199

ACTIVE RESTRAINTS
The active restraints for this model include:
²Front Seat Belts- Both front seating positions
are equipped with three-point seat belt systems
employing a lower B-pillar mounted inertia latch-
type retractor, height-adjustable upper B-pillar
mounted turning loops, a fixed lower seat belt anchor
secured to the lower B-pillar, and a fixed end-release
seat belt buckle secured to the side of the floor panel
transmission tunnel. Both front seat belt buckles
include an integral Hall-effect seat belt switch that
detects whether its respective seat belt has been fas-
tened.
²Rear Seat Belts- Both outboard rear seating
positions are equipped with three-point seat belt sys-
tems. The outboard seating position belts employ a
lower C-pillar mounted inertia latch-type retractor,
height-adjustable upper C-pillar mounted turning
loops, and a fixed lower seat belt anchor secured to
the floor panel. The center rear seating position of
vehicles manufactured for sale in North America has
a lap belt that is anchored to the rear floor panel
with the right outboard seat belt buckle. Vehicles
manufactured for sale outside of North America are
equipped with a three-point seat belt in the rear seat
center seating position. This seat belt has an inertia
latch-type retractor that is integral to the rear seat
back panel, and the lower belt anchor is secured to
the rear floor panel with the right outboard seat belt
buckle. A cable from the seat back latch locks the
center belt retractor spool unless the seat back is
fully latched. All three rear seat belts have fixed end-
release seat belt buckles secured to the rear floor
panel, a single buckle unit on the right side and a
double buckle unit on the left side.
²Child Seat Tether Anchors- All vehicles are
equipped with three, fixed-position, child seat upper
tether anchors and two lower anchors. Two upper
anchors are integral to the back of the right rear seat
back panel, and one is integral to the left rear seat
back panel. The two lower anchors are integral to the
outboard rear seat back brackets.
PASSIVE RESTRAINTS
The passive restraints available for this model
include the following:
²Dual Front Airbags- Multistage driver and
front passenger airbags are available for this model.
This airbag system is a passive, inflatable, Supple-
mental Restraint System (SRS) and vehicles with
this equipment can be readily identified by the ªSRS
- AIRBAGº logo molded into the driver airbag trim
cover in the center of the steering wheel and also
into the passenger airbag door area of the instru-
ment panel top pad above the glove box (Fig. 2).
Vehicles with the airbag system can also be identifiedby the airbag indicator, which will illuminate in the
instrument cluster for about seven seconds as a bulb
test each time the ignition switch is turned to the On
position.
²Side Curtain Airbags- Optional side curtain
airbags are available for this model when it is also
equipped with dual front airbags. This airbag system
is a passive, inflatable, Supplemental Restraint Sys-
tem (SRS) and vehicles with this equipment can be
readily identified by a molded identification trim but-
ton with the ªSRS - AIRBAGº logo located on the
headliner above each B-pillar (Fig. 2).
The supplemental restraint system includes the
following major components, which are described in
further detail elsewhere in this service information:
²Airbag Control Module- The Airbag Control
Module (ACM) is also sometimes referred to as the
Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC). The ACM is
located on a mount on the floor panel transmission
tunnel near the park brake release mechanism,
under the center floor console.
²Airbag Indicator- The airbag indicator is inte-
gral to the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster
(EMIC), which is located on the instrument panel in
front of the driver.
²Clockspring- The clockspring is located near
the top of the steering column, directly beneath the
steering wheel.
²Driver Airbag- The driver airbag is located in
the center of the steering wheel, beneath the driver
airbag trim cover.
²Driver Knee Blocker- The driver knee blocker
is a structural unit secured to the back side of and
integral to the instrument panel steering column
opening cover.
²Front Impact Sensor- Two front impact sen-
sors are used on vehicles equipped with dual front
airbags, one left side and one right side. One sensor
is located on a bracket on the lower inboard side of
each vertical member of the radiator support.
Fig. 2 SRS Logo
WJRESTRAINTS 8O - 3
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 541 of 2199

²Passenger Airbag- The passenger airbag is
located on the instrument panel, beneath the instru-
ment panel top pad and above the glove box on the
passenger side of the vehicle.
²Passenger Knee Blocker- The passenger knee
blocker is a structural reinforcement that is integral
to and concealed within the glove box door.
²Side Impact Sensor- Two side impact sensors
are used on vehicles with the optional side curtain
airbags, one left side and one right side. One sensor
is located behind the B-pillar trim near the base of
each B-pillar.
²Side Curtain Airbag- In vehicles equipped
with this option, a side curtain airbag is located on
each inside roof side rail above the headliner, and
extends from the A-pillar to just beyond the C-pillar.
The ACM and the EMIC each contain a central
processing unit and programming that allow them to
communicate with each other using the Programma-
ble Communication Interface (PCI) data bus network.
This method of communication is used by the ACM
for control of the airbag indicator on all models
equipped with dual front airbags. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/
COMMUNICATION - DESCRIPTION).
Hard wired circuitry connects the supplemental
restraint system components to each other through
the electrical system of the vehicle. These hard wired
circuits are integral to several wire harnesses, which
are routed throughout the vehicle and retained by
many different methods. These circuits may be con-
nected to each other, to the vehicle electrical system,
and to the supplemental restraint system compo-
nents through the use of a combination of soldered
splices, splice block connectors, and many different
types of wire harness terminal connectors and insu-
lators. Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
The wiring information includes wiring diagrams,
proper wire and connector repair procedures, further
details on wire harness routing and retention, as well
as pin-out and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
OPERATION
ACTIVE RESTRAINTS
The primary passenger restraints in this or any
other vehicle are the standard equipment factory-in-
stalled seat belts. Seat belts are referred to as an
active restraint because the vehicle occupants are
required to physically fasten and properly adjust
these restraints in order to benefit from them. See
the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features, use and operation of all
of the factory-installed active restraints.PASSIVE RESTRAINTS
The passive restraints system is referred to as a
supplemental restraint system because they were
designed and are intended to enhance the protection
for the vehicle occupants of the vehicleonlywhen
used in conjunction with the seat belts. They are
referred to as passive systems because the vehicle
occupants are not required to do anything to make
them operate; however, the vehicle occupants must
be wearing their seat belts in order to obtain the
maximum safety benefit from the factory-installed
supplemental restraint systems.
The supplemental restraint system electrical cir-
cuits are continuously monitored and controlled by a
microprocessor and software contained within the
Airbag Control Module (ACM). An airbag indicator in
the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC)
illuminates for about seven seconds as a bulb test
each time the ignition switch is turned to the On or
Start positions. Following the bulb test, the airbag
indicator is turned on or off by the ACM to indicate
the status of the supplemental restraint system. If
the airbag indicator comes on at any time other than
during the bulb test, it indicates that there is a prob-
lem in the supplemental restraint system electrical
circuits. Such a problem may cause airbags not to
deploy when required, or to deploy when not
required.
Deployment of the supplemental restraints
depends upon the angle and severity of an impact.
Deployment is not based upon vehicle speed; rather,
deployment is based upon the rate of deceleration as
measured by the forces of gravity (G force) upon the
impact sensors. When an impact is severe enough,
the microprocessor in the ACM signals the inflator
unit of the airbag module to deploy the airbag. Dur-
ing a frontal vehicle impact, the knee blockers work
in concert with properly fastened and adjusted seat
belts to restrain both the driver and the front seat
passenger in the proper position for an airbag deploy-
ment. The knee blockers also absorb and distribute
the crash energy from the driver and the front seat
passenger to the structure of the instrument panel.
Typically, the vehicle occupants recall more about
the events preceding and following a collision than
they have of an airbag deployment itself. This is
because the airbag deployment and deflation occur so
rapidly. In a typical 48 kilometer-per-hour (30 mile-
per-hour) barrier impact, from the moment of impact
until the airbags are fully inflated takes about 40
milliseconds. Within one to two seconds from the
moment of impact, the airbags are almost entirely
deflated. The times cited for these events are approx-
imations, which apply only to a barrier impact at the
given speed. Actual times will vary somewhat,
8O - 4 RESTRAINTSWJ
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 542 of 2199

depending upon the vehicle speed, impact angle,
severity of the impact, and the type of collision.
When the ACM monitors a problem in any of the
airbag system circuits or components, it stores a
fault code or Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in its
memory circuit and sends an electronic message to
the EMIC to turn on the airbag indicator. Proper
testing of the airbag system components, the Pro-
grammable Communication Interface (PCI) data bus,
the data bus message inputs to and outputs from the
EMIC or the ACM, as well as the retrieval or erasure
of a DTC from the ACM or EMIC requires the use of
a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of all of the factory-installed passive restraints.
WARNING - RESTRAINT SYSTEM
WARNING: DURING AND FOLLOWING ANY SEAT
BELT SERVICE, CAREFULLY INSPECT ALL SEAT
BELTS, BUCKLES, MOUNTING HARDWARE, AND
RETRACTORS FOR PROPER INSTALLATION,
OPERATION, OR DAMAGE. REPLACE ANY BELT
THAT IS CUT, FRAYED, OR TORN. STRAIGHTEN
ANY BELT THAT IS TWISTED. TIGHTEN ANY
LOOSE FASTENERS. REPLACE ANY BELT THAT
HAS A DAMAGED OR INOPERATIVE BUCKLE OR
RETRACTOR. REPLACE ANY BELT THAT HAS A
BENT OR DAMAGED LATCH PLATE OR ANCHOR
PLATE. NEVER ATTEMPT TO REPAIR A SEAT BELT
COMPONENT. ALWAYS REPLACE DAMAGED OR
FAULTY SEAT BELT COMPONENTS WITH THE COR-
RECT, NEW AND UNUSED REPLACEMENT PARTS
LISTED IN THE DAIMLERCHRYSLER MOPAR PARTS
CATALOG.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, FRONT IMPACT SENSOR,
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT
TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO
DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.WARNING: AN AIRBAG INFLATOR UNIT MAY CON-
TAIN SODIUM AZIDE AND POTASSIUM NITRATE.
THESE MATERIALS ARE POISONOUS AND
EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE. CONTACT WITH ACID,
WATER, OR HEAVY METALS MAY PRODUCE HARM-
FUL AND IRRITATING GASES (SODIUM HYDROXIDE
IS FORMED IN THE PRESENCE OF MOISTURE) OR
COMBUSTIBLE COMPOUNDS. AN AIRBAG INFLA-
TOR UNIT MAY ALSO CONTAIN A GAS CANISTER
PRESSURIZED TO OVER 2500 PSI. DO NOT
ATTEMPT TO DISMANTLE AN AIRBAG UNIT OR
TAMPER WITH ITS INFLATOR. DO NOT PUNCTURE,
INCINERATE, OR BRING INTO CONTACT WITH
ELECTRICITY. DO NOT STORE AT TEMPERATURES
EXCEEDING 93É C (200É F).
WARNING: REPLACE ALL RESTRAINT SYSTEM
COMPONENTS ONLY WITH PARTS SPECIFIED IN
THE DAIMLERCHRYSLER MOPAR PARTS CATA-
LOG. SUBSTITUTE PARTS MAY APPEAR INTER-
CHANGEABLE, BUT INTERNAL DIFFERENCES MAY
RESULT IN INFERIOR OCCUPANT PROTECTION.
WARNING: THE FASTENERS, SCREWS, AND
BOLTS ORIGINALLY USED FOR THE RESTRAINT
SYSTEM COMPONENTS HAVE SPECIAL COATINGS
AND ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. THEY MUST NEVER BE
REPLACED WITH ANY SUBSTITUTES. ANY TIME A
NEW FASTENER IS NEEDED, REPLACE IT WITH
THE CORRECT FASTENERS PROVIDED IN THE
SERVICE PACKAGE OR SPECIFIED IN THE
DAIMLERCHRYSLER MOPAR PARTS CATALOG.
WARNING: WHEN A STEERING COLUMN HAS AN
AIRBAG UNIT ATTACHED, NEVER PLACE THE COL-
UMN ON THE FLOOR OR ANY OTHER SURFACE
WITH THE STEERING WHEEL OR AIRBAG UNIT
FACE DOWN.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM
Proper diagnosis and testing of the supplemental
restraint system components, the PCI data bus, the
data bus message inputs to and outputs from the
ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) or the
Airbag Control Module (ACM), as well as the
retrieval or erasure of a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) from the ACM requires the use of a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
WJRESTRAINTS 8O - 5
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 543 of 2199

WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, FRONT IMPACT SENSOR,
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT
TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO
DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HANDLING
NON-DEPLOYED SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINTS
At no time should any source of electricity be per-
mitted near the inflator on the back of a non-de-
ployed airbag. When carrying a non-deployed airbag,
the trim cover or airbag cushion side of the unit
should be pointed away from the body to minimize
injury in the event of an accidental deployment. If
the airbag unit is placed on a bench or any other sur-
face, the trim cover or airbag cushion side of the unit
should be face up to minimize movement in the event
of an accidental deployment. In addition, the supple-
mental restraint system should be disarmed when-
ever any steering wheel, steering column, driver
airbag, passenger airbag, front impact sensor, side
impact sensor, side curtain airbag, or instrument
panel components require diagnosis or service. Fail-
ure to observe this warning could result in accidental
airbag deployment and possible personal injury.
All damaged, faulty or non-deployed airbags which
are replaced on vehicles are to be handled and dis-
posed of properly. If an airbag unit is faulty or dam-
aged and non-deployed, refer to the Hazardous
Substance Control System for proper disposal. Dis-
pose of all non-deployed and deployed airbags in a
manner consistent with state, provincial, local and
federal regulations.
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT STORAGE
Airbags must be stored in their original, special
container until they are used for service. Also, they
must be stored in a clean, dry environment; away
from sources of extreme heat, sparks, and high elec-
trical energy. Always place or store any airbag on a
surface with its trim cover or airbag cushion side fac-ing up, to minimize movement in case of an acciden-
tal deployment.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SERVICE AFTER A
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT DEPLOYMENT
Any vehicle which is to be returned to use follow-
ing a supplemental restraint deployment, must have
the deployed restraints replaced. In addition, if the
driver airbag has been deployed, the clockspring
must be replaced. If the passenger airbag is
deployed, the instrument panel top pad must be
replaced. If a side curtain airbag has been deployed,
the complete airbag unit, the headliner, as well as
the upper A, B, C and D-pillar trim must be replaced.
These components are not intended for reuse and
will be damaged or weakened as a result of a supple-
mental restraint deployment, which may or may not
be obvious during a visual inspection.
The passenger airbag mounting points on the
instrument panel structural duct must be closely
inspected for damage, and the instrument panel
assembly replaced if structural duct damage is evi-
dent. On vehicles with an optional sunroof, the sun-
roof drain tubes and hoses must be closely inspected
following a side curtain airbag deployment. It is also
critical that the mounting surfaces and/or mounting
brackets for the front and side impact sensors be
closely inspected and restored to their original condi-
tions following any vehicle impact damage. Because
the ACM and each impact sensor are used by the
supplemental restraint system to monitor or confirm
the direction and severity of a vehicle impact,
improper orientation or insecure fastening of these
components may cause airbags not to deploy when
required, or to deploy when not required.
All other vehicle components should be closely
inspected following any supplemental restraint
deployment, but are to be replaced only as required
by the extent of the visible damage incurred.
AIRBAG SQUIB STATUS
Multistage airbags with multiple initiators (squibs)
must be checked to determine that all squibs were
used during the deployment event. The driver and
passenger airbags in this model are deployed by elec-
trical signals generated by the Airbag Control Mod-
ule (ACM) through the driver or passenger squib 1
and squib 2 circuits to the two initiators in the air-
bag inflators. Typically, both initiators are used and
all potentially hazardous chemicals are burned dur-
ing an airbag deployment event. However, it is possi-
ble for only one initiator to be used due to an airbag
system fault; therefore, it is always necessary to con-
firm that both initiators have been used in order to
avoid the improper handling or disposal of poten-
tially live pyrotechnic or hazardous materials. The
8O - 6 RESTRAINTSWJ
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 545 of 2199
WARNING: IF YOU EXPERIENCE SKIN IRRITATION
DURING CLEANUP, RUN COOL WATER OVER THE
AFFECTED AREA. ALSO, IF YOU EXPERIENCE IRRITA-
TION OF THE NOSE OR THROAT, EXIT THE VEHICLE
FOR FRESH AIR UNTIL THE IRRITATION CEASES. IF
IRRITATION CONTINUES, SEE A PHYSICIAN.
(1) Begin the cleanup by using a vacuum cleaner
to remove any residual powder from the vehicle inte-
rior. Clean from outside the vehicle and work your
way inside, so that you avoid kneeling or sitting on a
non-cleaned area.
(2) Be certain to vacuum the heater and air condi-
tioning outlets as well (Fig. 4). Run the heater and
air conditioner blower on the lowest speed setting
and vacuum any powder expelled from the outlets.
CAUTION: Deployed front airbags having two initia-
tors (squibs) in the airbag inflator may or may not
have live pyrotechnic material within the inflator. Do
not dispose of these airbags unless you are sure of
complete deployment. Refer to AIRBAG SQUIB STA-
TUS . Refer to the Hazardous Substance Control
System for proper disposal procedures. Dispose of
all non-deployed and deployed airbags in a manner
consistent with state, provincial, local, and federal
regulations.
(3) Next, remove the deployed supplemental
restraints from the vehicle. Refer to the appropriate
service removal procedures.
(4) You may need to vacuum the interior of the
vehicle a second time to recover all of the powder.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VERIFICATION TEST
The following procedure should be performed using
a DRBIIItscan tool to verify proper supplemental
restraint system operation following the service or
replacement of any supplemental restraint system
component.WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, FRONT IMPACT SENSOR,
SIDE IMPACT SENSOR, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT
TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO
DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) During the following test, the battery negative
cable remains disconnected and isolated, as it was
during the airbag component removal and installa-
tion procedures.
(2) Be certain that the DRBIIItscan tool contains
the latest version of the proper DRBIIItsoftware.
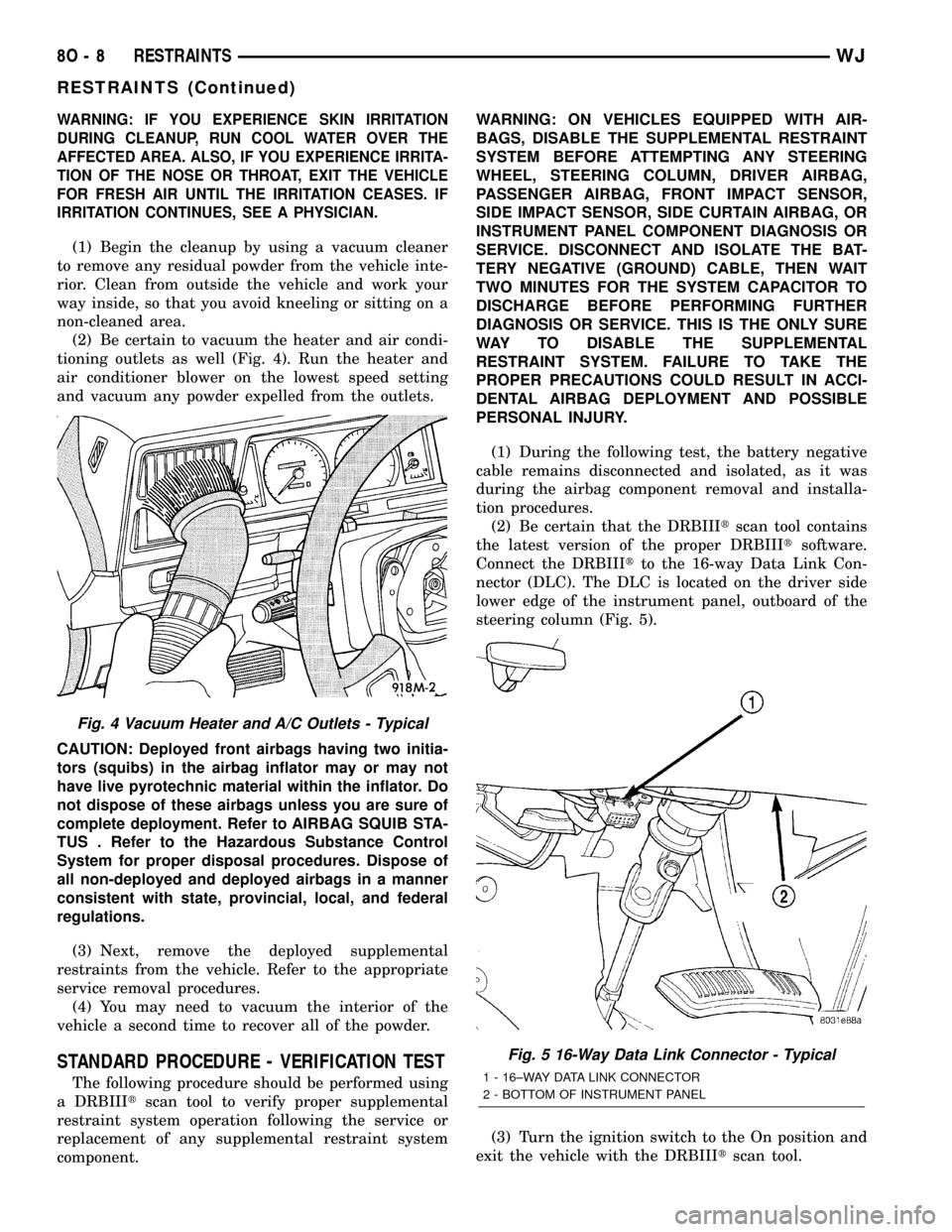
Connect the DRBIIItto the 16-way Data Link Con-
nector (DLC). The DLC is located on the driver side
lower edge of the instrument panel, outboard of the
steering column (Fig. 5).
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the On position and
exit the vehicle with the DRBIIItscan tool.
Fig. 4 Vacuum Heater and A/C Outlets - Typical
Fig. 5 16-Way Data Link Connector - Typical
1 - 16±WAY DATA LINK CONNECTOR
2 - BOTTOM OF INSTRUMENT PANEL
8O - 8 RESTRAINTSWJ
RESTRAINTS (Continued)