ignition cylinder switch remove JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 516 of 2199

²Ten-way power drivers and passenger seats
with Memory- This power seat option is standard
on Overland models and optional on Limited models.
This option includes a six-way adjustable seat cush-
ion track with power seat back recliners and power
lumbar supports. Heated Seats are standard with
this option.
Refer toHeated Seat Systemfor more informa-
tion on the heated seat option. Refer toMemory
Systemin the Memory System section of this group
for more information on the memory system.
The power seat system includes the following com-
ponents:
²Power lumbar adjuster (ten-way power seat
only)
²Power lumbar switch (ten-way power seat only)
²Power seat recliner (ten-way power seat only)
²Power seat switch
²Power seat track.
Refer toPower Seatin Wiring Diagrams for com-
plete circuit diagrams. Following are general descrip-
tions of the major components in the power seat/
memory seat system.
DESCRIPTION - MEMORY SYSTEM
An electronic memory system is standard equip-
ment on the Limited model. The memory system is
able to store and recall the driver side power seat
positions (including the power recliner position), and
both outside power mirror positions for two drivers.
For vehicles with a radio connected to the Program-
mable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work, the memory system is also able to store and
recall up to twenty - ten AM and ten FM - radio sta-
tion presets for two drivers. The memory system also
will store and recall the last station listened to for
each driver, even if it is not one of the twenty preset
stations.
The memory system will automatically return to
all of these settings when the corresponding num-
bered and color-coded button (Driver 1 - Black, or
Driver 2 - Gray) of the memory switch on the driver
side front door trim panel is depressed, or when the
doors are unlocked using the corresponding num-
bered and color-coded (Driver 1 - Black, or Driver 2 -
Gray) Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter. A
customer programmable feature of the memory sys-
tem allows the RKE recall of memory features to be
disabled in cases where there are more than two
drivers of the vehicle.
The memory system also has a customer program-
mable easy exit feature that will move the driver
seat rearward 55 millimeters (two inches) or to the
end of its travel, whichever occurs first, when the key
is removed from the ignition switch lock cylinder.A Memory Seat Module (MSM) or Memory Heated
Seat Module (MHSM) are used on this model to con-
trol and integrate the many electronic functions and
features included in the memory system. On vehicles
equipped with the heated seat system option, the
MHSM also controls the functions and features of
that system.
The memory system includes the following compo-
nents:
²Memory seat module (or memory heated seat
module)
²Memory switch
²Position potentiometers on both outside power
mirrors
²Position potentiometers on the driver side power
seat track and power seat recliner motors.
²Radio receiver (if PCI data bus capable).
Certain functions and features of the memory sys-
tem rely upon resources shared with other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sensor
information. This helps to reduce wire harness com-
plexity, internal controller hardware, and component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities. For diagnosis of these electronic modules or of
the PCI data bus network, the use of a DRBtscan
tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual
are recommended.
The other electronic modules that may affect mem-
ory system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)- Refer toBody
Control Modulein Electronic Control Modules for
more information.
²Driver Door Module (DDM)- Refer toDoor
Modulein Electronic Control Modules for more
information.
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC)- Refer toElectronic Vehicle Information
Centerin Overhead Console Systems for more infor-
mation.
²Passenger Door Module (PDM)- Refer to
Door Modulein Electronic Control Modules for
more information.
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)- Refer to
Powertrain Control Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for more information.
²Radio Receiver- Refer toRadio Receiverin
Audio Systems for more information.
Refer toHeated Seat Systemfor more informa-
tion on this system. Refer toRemote Keyless Entry
Systemin Power Lock Systems for more information
on the RKE system. Refer toPower Mirrorin
Power Mirror Systems for more information on the
WJPOWER SEAT SYSTEM 8N - 19
POWER SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 594 of 2199

switch, or when the ªLockº button on the Remote
Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter is depressed. The
powerlock switch will not initiate the pre-arming
sequence if the key is in the ignition switch. When
the VTA is pre-armed, the arming sequence is
delayed until all of the doors, the tailgate and the
flip-up glass are closed.
ARMING
Passive arming of the VTSS occurs when the vehi-
cle is exited with the key removed from the ignition
switch, the headlamps are turned off, and the doors
are locked while they are open using the power lock
switch. The power lock switch will not function if the
key is in the ignition switch or the headlamps are
turned on with the driver side front door open. The
VTSS will not arm if the driver side front door is
locked using the key in the lock cylinder or using the
mechanical lock button. Active arming of the VTSS
occurs when the ªLockº button on the Remote Key-
less Entry (RKE) transmitter is depressed to lock the
vehicle, even if the doors and/or the liftgate are open
when the RKE transmitter Lock button is depressed.
However, the VTSS arming will not be complete until
all of the doors, the liftgate and the liftgate flip-up
glass are closed. On vehicles equipped with the hood
ajar switch, VTSS arming will complete if the hood is
open, but the underhood area will not be protected
unless the hood is closed when the VTSS is armed.
Following successful passive or active VTSS arm-
ing, the VTSS indicator on the top of the instrument
panel will flash rapidly for about sixteen seconds
after the illuminated entry system times out. This
indicates that VTSS arming is in progress. Once the
sixteen second arming function is successfully com-
pleted, the indicator will flash at a slower rate, indi-
cating that the VTSS is armed.
DISARMING
Passive disarming of the VTSS occurs when the
vehicle is unlocked using the key to unlock the driver
side front door. Active disarming of the VTSS occurs
when the vehicle is unlocked by depressing the
ªUnlockº button of the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
transmitter. Once the alarm has been activated,
either disarming method will also deactivate the
alarm. Depressing the ªPanicº button on the RKE
transmitter will also disarm the VTSS, but the horn
will continue to pulse and the exterior lamps will
continue to flash for about three minutes as part of
the Panic feature function. The Panic feature is over-
ridden if the ªPanicº button is depressed a second
time, or if a vehicle speed of about 24 kilometers-per-
hour (15 miles-per-hour) is attained.POWER-UP MODE
When the armed VTSS senses that the battery has
been disconnected and reconnected, it enters its pow-
er-up mode. In the power-up mode the alarm system
remains armed following a battery failure or discon-
nect. If the VTSS was armed prior to a battery dis-
connect or failure, the technician or vehicle operator
will have to actively or passively disarm the alarm
system after the battery is reconnected. The pow-
er-up mode will also apply if the battery goes dead
while the system is armed, and battery jump-starting
is then attempted. The VTSS will be armed until it is
actively or passively disarmed. If the VTSS is in the
disarmed mode prior to a battery disconnect or fail-
ure, it will remain disarmed after the battery is
reconnected or replaced, or if jump-starting is
attempted.
ALARM
The VTA alarm output varies by the version of the
VTA with which the vehicle is equipped. In all cases,
the alarm provides both visual and audible outputs;
however, the time intervals of these outputs vary by
the requirements of the market for which the vehicle
is manufactured. In all cases, the visual output will
be a flashing of the exterior lamps. For vehicles
equipped with North American or the base version of
the VTA, the audible output will be the pulsing of the
horn. For vehicles with the premium version of the
VTA, the audible output will be the cycling of the
siren. The inputs that will trigger the alarm include
the door ajar switch, the flip-up glass ajar switch,
and in vehicles built for certain markets where they
are required, the hood ajar switch and the Intrusion
Transceiver Module (ITM).
TAMPER ALERT
The VTSS tamper alert feature will sound the horn
(or the alarm siren for the premium version) three
times upon VTA disarming, if the alarm was trig-
gered and has since timed-out (about eighteen min-
utes). This feature alerts the vehicle operator that
the VTA alarm was activated while the vehicle was
unattended.
INTRUSION ALARM
The Intrusion Alarm is an exclusive feature of the
premium version of the VTA, which is only available
in certain markets, where it is required. When the
VTA is armed, a motion sensor in the Intrusion
Transceiver Module (ITM) monitors the interior of
the vehicle for movement. If motion is detected, the
ITM sends a message to the BCM over the PCI bus
to invoke the visual alarm feature, and sends a mes-
sage to the alarm siren over a dedicated serial bus to
invoke the audible alarm feature. The motion detec-
WJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 3
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 603 of 2199

The ITM microprocessor continuously monitors
inputs from its on-board motion sensor as well as
inputs from the BCM and the alarm siren module.
The ITM motion sensor transmits ultrasonic signals
into the vehicle cabin through a transmit transducer,
then listens to the returning signals as the bounce off
of objects in the vehicle interior. If an object is mov-
ing in the interior, a detection circuit in the ITM
senses this movement through the modulation of the
returning ultrasonic signals that occurs due to the
Doppler effect. The motion detect function of the ITM
can be disabled by depressing the ªLockº button on
the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter three
times within fifteen seconds, while the security indi-
cator is still flashing rapidly or by cycling the key in
the driver door cylinder from the center to the lock
position. The ITM will signal the alarm siren module
to provide a single siren ªchirpº as an audible confir-
mation that the motion sensor function has been dis-
abled.
If movement is detected, the ITM sends an mes-
sage to the BCM over the PCI data bus to flash the
exterior lighting and send a message to the alarm
siren module over a dedicated serial bus line to
sound the siren. When the BCM detects a breach in
the perimeter protection through a door, tailgate,
flip-up glass, or hood ajar switch input, it sends an
message to the ITM and the ITM sends an message
to the BCM over the PCI data bus to flash the exte-
rior lighting and send a message to the alarm siren
module over a dedicated serial bus line to sound the
siren. The ITM also monitors inputs from the alarm
siren module for siren battery or siren input/output
circuit tamper alerts, and siren battery condition
alerts, then sets active and stored Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTC) for any monitored system faults it
detects. An active fault only remains for the current
ignition switch cycle, while a stored fault causes a
DTC to be stored in memory by the ITM. If a fault
does not reoccur for fifty ignition cycles, the ITM will
automatically erase the stored DTC.
The ITM is connected to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through the overhead wire harness. The ITM
receives battery voltage on a B(+) circuit through a
fuse in the Junction Block (JB), and is grounded to
the chassis at G303. These connections allow the
ITM to remain operational, regardless of the ignition
switch position. The hard wired inputs and outputs
for the ITM may be diagnosed and tested using con-
ventional diagnostic tools and procedures. However,
conventional diagnostic methods will not prove con-
clusive in the diagnosis of the ITM, the PCI data bus
network, or the electronic message inputs to and out-
puts from the ITM. The most reliable, efficient, and
accurate means to diagnose the ITM, the PCI data
bus network, and the message inputs to and outputsfrom the ITM requires the use of a DRBIIItscan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) While pulling downward lightly on the rear cor-
ner of the Intrusion Transceiver Module (ITM) trim
cover, insert a small thin-bladed screwdriver through
each of the service holes on the rear edge of the trim
cover to release the two integral rear latch features
of the module from the mounting bracket above the
headliner (Fig. 7).
(3) Pull the ITM trim cover rearward far enough
to disengage the two front latch features of the mod-
ule from the mounting bracket above the headliner.
(4) Pull the ITM and trim cover down from the
headliner far enough to access and disconnect the
overhead wire harness connector for the ITM from
the module connector.
(5) Remove the ITM from the headliner.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the Intrusion Transceiver Module
(ITM) to the headliner.
(2) Reconnect the overhead wire harness connector
for the ITM to the module connector.
(3) Align the two front latch features of the ITM
with the two front latch receptacles of the mounting
bracket above the headliner (Fig. 8).
(4) Push the ITM trim cover forward far enough to
insert the two rear latch features of the module into
Fig. 7 INTRUSION TRANSCEIVER MODULE
REMOVE
1 - SMALL SCREWDRIVER
2 - HEADLINER
3 - SERVICE HOLES
4 - ITM
8Q - 12 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYWJ
INTRUSION TRANSCEIVER MODULE (Continued)
Page 606 of 2199

cluster circuitry that controls the lamp, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING). If the instrument cluster turns
on the SKIS indicator lamp after the bulb test, either
solid or flashing, it indicates that a SKIS malfunction
has occurred or that the SKIS is inoperative. For
proper diagnosis of the SKIS, the PCI data bus, or
the message inputs to the instrument cluster that
control the SKIS indicator lamp, a DRBIIItscan tool
and the appropriate diagnostic information are
required.
TRANSPONDER KEY
DESCRIPTION
Each ignition key used in the Sentry Key Immobi-
lizer System (SKIS) has an integral transponder chip
(Fig. 10). Ignition keys with this feature can be
readily identified by a gray rubber cap molded onto
the head of the key, while conventional ignition keys
have a black molded rubber cap. The transponder
chip is concealed beneath the molded rubber cap,
where it is molded into the head of the metal key.
Each new Sentry Key has a unique transponder iden-
tification code permanently programmed into it by
the manufacturer. The Sentry Key transponder if
faulty or damaged, must be replaced.
OPERATION
When the ignition switch is turned to the On posi-
tion, the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM)communicates through its antenna with the Sentry
Key transponder using a Radio Frequency (RF) sig-
nal. The SKIM then waits for a RF response from the
transponder through the same antenna. The Sentry
Key transponder chip is within the range of the
SKIM transceiver antenna ring when it is inserted
into the ignition lock cylinder. The SKIM determines
whether a valid key is present in the ignition lock
cylinder based upon the response from the transpon-
der. If a valid key is detected, that fact is communi-
cated by the SKIM to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) over the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus, and the PCM allows the
engine to continue running. If the PCM receives an
invalid key message, or receives no message from the
SKIM over the PCI data bus, the engine will be dis-
abled after about two seconds of operation. The Elec-
troMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) will also
respond to the invalid key message on the PCI data
bus by flashing the SKIS indicator on and off.
Each Sentry Key has a unique transponder identi-
fication code permanently programmed into it by the
manufacturer. Likewise, the SKIM has a unique
Secret Key code programmed into it by the manufac-
turer. When a Sentry Key is programmed into the
memory of the SKIM, the SKIM stores the transpon-
der identification code from the Sentry Key, and the
Sentry Key learns the Secret Key code from the
SKIM. Once the Sentry Key learns the Secret Key
code of the SKIM, it is permanently stored in the
memory of the transponder. Therefore, once a Sentry
Key has been programmed to a particular vehicle, it
cannot be used on any other vehicle. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSPONDER PRO-
GRAMMING).
VTSS INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) indica-
tor consists of a red Light-Emitting Diode that is
mounted and integral to the automatic headlamp
light sensor photo diode unit, which is located on the
top of the instrument panel. The remainder of the
housing including the mount and the electrical con-
nection are concealed beneath the instrument panel
top cover.
The VTSS indicator cannot be adjusted or repaired
the entire automatic headlamp light sensor/VTSS
indicator must be replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/AUTO HEAD-
LAMP SENSOR - REMOVAL).
Fig. 10 Sentry Key Immobilizer Transponder
1 - MOLDED CAP
2 - TRANSPONDER CHIP
3 - MOLDED CAP REMOVED
4 - TRANSPONDER KEY
WJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 15
SKIS INDICATOR LAMP (Continued)
Page 1311 of 2199
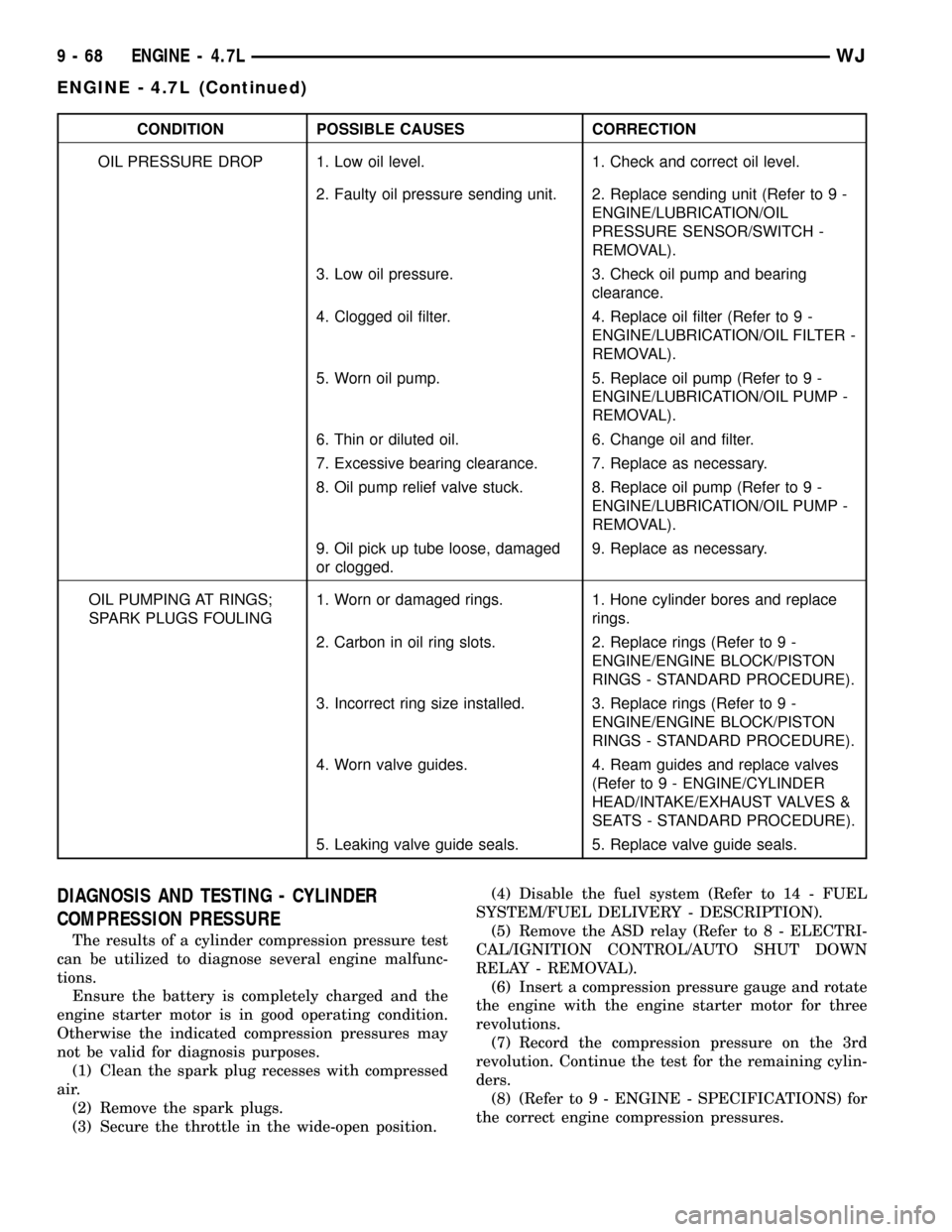
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER -
REMOVAL).
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP -
REMOVAL).
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP -
REMOVAL).
9. Oil pick up tube loose, damaged
or clogged.9. Replace as necessary.
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS;
SPARK PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
5. Leaking valve guide seals. 5. Replace valve guide seals.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.(4) Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
(5) Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUT DOWN
RELAY - REMOVAL).
(6) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(7) Record the compression pressure on the 3rd
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(8) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct engine compression pressures.
9 - 68 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1484 of 2199
COLUMN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS......7
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION.........................11
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................12
SPECIAL TOOLS
STEERING COLUMN...................12
IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - IGNITION
SWITCH............................12
REMOVAL
IGNITION SWITCH REMOVAL............13INSTALLATION
IGNITION SWITCH INSTALLATION........13
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH..............14
LOCK CYLINDER
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................15
STEERING WHEEL
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
DESCRIPTION
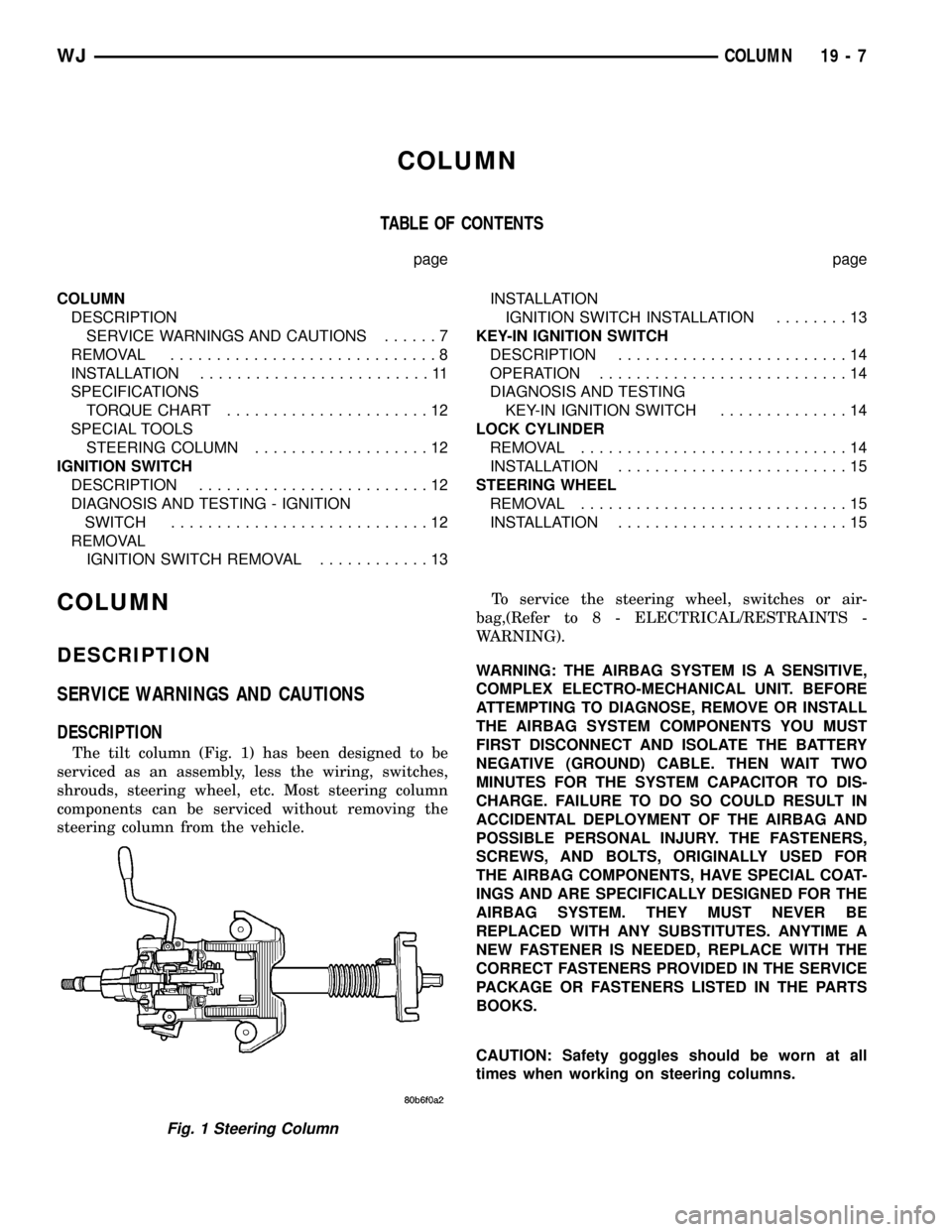
The tilt column (Fig. 1) has been designed to be
serviced as an assembly, less the wiring, switches,
shrouds, steering wheel, etc. Most steering column
components can be serviced without removing the
steering column from the vehicle.To service the steering wheel, switches or air-
bag,(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
WARNING).
WARNING: THE AIRBAG SYSTEM IS A SENSITIVE,
COMPLEX ELECTRO-MECHANICAL UNIT. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE, REMOVE OR INSTALL
THE AIRBAG SYSTEM COMPONENTS YOU MUST
FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY
NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO
MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF THE AIRBAG AND
POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY. THE FASTENERS,
SCREWS, AND BOLTS, ORIGINALLY USED FOR
THE AIRBAG COMPONENTS, HAVE SPECIAL COAT-
INGS AND ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE
AIRBAG SYSTEM. THEY MUST NEVER BE
REPLACED WITH ANY SUBSTITUTES. ANYTIME A
NEW FASTENER IS NEEDED, REPLACE WITH THE
CORRECT FASTENERS PROVIDED IN THE SERVICE
PACKAGE OR FASTENERS LISTED IN THE PARTS
BOOKS.
CAUTION: Safety goggles should be worn at all
times when working on steering columns.
Fig. 1 Steering Column
WJCOLUMN 19 - 7
Page 1487 of 2199

(10) Disconnect the multifuction switch (Fig. 9)
and ignition switch harness.
(11) Remove the multifuction switch screw from
underneath the switch (Fig. 10). Slide the multifuc-
tion switch and clock spring off the column as an
assembly (Fig. 11).(12) Turn the ignition key to the on position then
release and remove the shifter interlock cable (Fig.
12) from the ignition lock cylinder housing.
Fig. 9 Multifuction Switch Harness
1 - MULTIFUNCTION SWITCH
2 - MULTIFUNCTION SWITCH HARNESS
Fig. 10 Multifuction
1 - CLOCK SPRING
2 - SCREW
3 - MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH MOUNTING HOUSING
Fig. 11 Multifuction Switch And Clock Spring
1 - MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - CLOCKSPRING
Fig. 12 Shifter Interlock Cable
1 - LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
2 - INTERLOCK CABLE
19 - 10 COLUMNWJ
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1488 of 2199

(13) Remove the column coupler bolt (Fig. 13) and
slide the coupler off the column shaft.
(14) Remove the column mounting nuts (Fig. 13)
and lower column off mounting studs. Remove the
column from the vehicle.
(15) Remove the ignition switch, cylinder and
SKIM, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOCK
CYLINDER HOUSING - REMOVAL). (Fig. 14).INSTALLATION
WARNING: BEFORE SERVICING THE STEERING COL-
UMN THE AIRBAG SYSTEM MUST BE DISARMED.
FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL
DEPLOYMENT OF THE AIRBAG AND POSSIBLE PER-
SONAL INJURY. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(1) Install the ignition switch, cylinder and SKIM-
,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/IGNITION
SWITCH - INSTALLATION).
(2) Install the column into the vehicle and lift the
column up onto the mounting studs. Install the
mounting nuts and tighten to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Slid the coupler onto the column shaft and
install the coupler bolt. Tighten the coupler bolt to 49
N´m (36 ft. lbs.).
(4) Turn the ignition key to the on position then
release and install the shifter interlock cable (Fig.
12) into ignition lock cylinder housing.
(5) Verify ignition switch and shifter interlock
operation.,(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 42RE/GEAR SHIFT CABLE -
ADJUSTMENTS).
(6) Slide the multifuction switch and clock spring
onto the column as an assembly (Fig. 11).
(7) Install the multifuction switch mounting screw
(Fig. 10).
(8) Connect the multifuction switch (Fig. 9) and
ignition switch harness.
(9) Install the upper fixed shroud and mounting
screws (Fig. 8).
(10) Install the lower steering column shroud to
the steering column. Install and tighten the mount-
ing screw.
(11) Install the upper column shroud. Align the
upper shroud to the lower shroud and snap the two
shroud halves together.
(12) Install the knee blocker cover (Fig. 5),(Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL - INSTALLA-
TION).
(13) Install the cluster bezel by inserting it into
the instrument panel (Fig. 4).
(14) Align the steering wheel with the column
index spline and install the wheel on the column
shaft. Pull the clockspring wire harness through the
steering wheel armature spokes.
(15) Install and tighten the steering wheel mount-
ing nut to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(16) Connect the steering wheel wire harness con-
nector to the clock spring connector.
(17) Install the airbag,(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(18) Connect the negative (ground) cable to the
battery.
Fig. 13 Column Coupler Bolt And Mounting Nuts
1 - COLUMN MOUNTING NUTS
2 - COUPLER BOLT
Fig. 14 Ignition Switch And SKIM
1 - SKIM
2 - IGNITION SWITCH
WJCOLUMN 19 - 11
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1490 of 2199

necessary, the steering column assembly must be
replaced,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN -
REMOVAL).
REMOVAL
IGNITION SWITCH REMOVAL
The ignition key must be in the key cylinder for
cylinder removal. The key cylinder must be removed
first before removing ignition switch.
(1) Remove key cylinder. Refer to previous steps.
(2) Remove lower steering column cover screws
and remove cover (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove ignition switch mounting screw (Fig.
17). Use tamper proof torx bit to remove the screw.
(4) Using a small screwdriver, push on locking tab
(Fig. 15) and remove switch from steering column.
(5) Disconnect two electrical connectors at rear of
ignition switch (Fig. 17).
INSTALLATION
IGNITION SWITCH INSTALLATION
The ignition key must be in the key cylinder for
cylinder removal. The key cylinder must be removed
first before removing ignition switch.(1) Before installing ignition switch, rotate the slot
in the switch to the ON position (Fig. 16).
(2) Connect two electrical connectors to rear of
ignition switch. Make sure that locking tabs are fully
seated into wiring connectors.
(3) Position switch to column and install tamper
proof screw. Tighten screw to 3 N´m (26 in. lbs.).
(4) Install steering column lower cover.
Fig. 15 Ignition Switch Lock Tab
1 - LOCK TAB
2 - IGNITION SWITCH
3 - SCREWDRIVER
Fig. 16 Switch In ON Position
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - ROTATE TO ON POSITION
Fig. 17 Ignition Switch Removal/Installation
1 - TAMPER PROOF SCREW
2 - IGNITION SWITCH
3 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
WJCOLUMN 19 - 13
IGNITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1491 of 2199

KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The key-in ignition switch is concealed within and
integral to the ignition switch, which is mounted on
the steering column. The key-in ignition switch is
actuated by the ignition lock cylinder mechanism,
and is hard wired between a body ground and the
Body Control Module (BCM) through the instrument
panel wire harness.
The key-in ignition switch cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the entire igni-
tion switch unit must be replaced,(Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
- REMOVAL). For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
Body Control Modulein the Contents of Wiring
Diagrams.
OPERATION
The key-in ignition switch closes a path to ground
for the BCM when the ignition key is inserted in the
ignition lock cylinder, and opens the ground path
when the key is removed from the ignition lock cyl-
inder. The BCM monitors the key-in ignition switch
status through an internal pull-up, then sends the
proper switch status messages to other electronic
modules over the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network. The key-in ignition
switch status is also used by the BCM as an input
for chime warning system operation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toBody Con-
trol Modulein the Contents of Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO GROUP 8M - PASSIVE
RESTRAINT SYSTEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the key-in ignition switch connector
receptacle on the ignition switch. Check for continu-
ity between the key-in ignition switch sense and
ground terminals of the key-in ignition switch con-
nector receptacle. There should be continuity with
the key inserted in the ignition lock cylinder, and no
continuity with the key removed from the ignition
lock cylinder. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace
the faulty ignition switch unit.
(2) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity of the instrument panel wire harness con-
nector for the key-in ignition switch and a good
ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(3) Disconnect the gray 26-way instrument panel
wire harness connector from the Body Control Mod-
ule (BCM) connector receptacle. Check for continuity
between the key-in ignition switch sense circuit cav-
ity of the instrument panel wire harness connector
for the key-in ignition switch and a good ground.
There should be no continuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair the shorted key-in ignition switch
sense circuit as required.
(4) Check for continuity between the key-in igni-
tion switch sense circuit cavities of the instrument
panel wire harness connector for the key-in ignition
switch and the gray 26-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the BCM. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, use a DRB scan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual to test the BCM. If
not OK, repair the open key-in ignition switch sense
circuit as required.
LOCK CYLINDER
REMOVAL
The ignition key must be in the key cylinder for
cylinder removal. The key cylinder must be removed
first before removing ignition switch.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
place shifter in PARK position.
(3) Rotate key to ON position.
19 - 14 COLUMNWJ