spec JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 140 of 2199
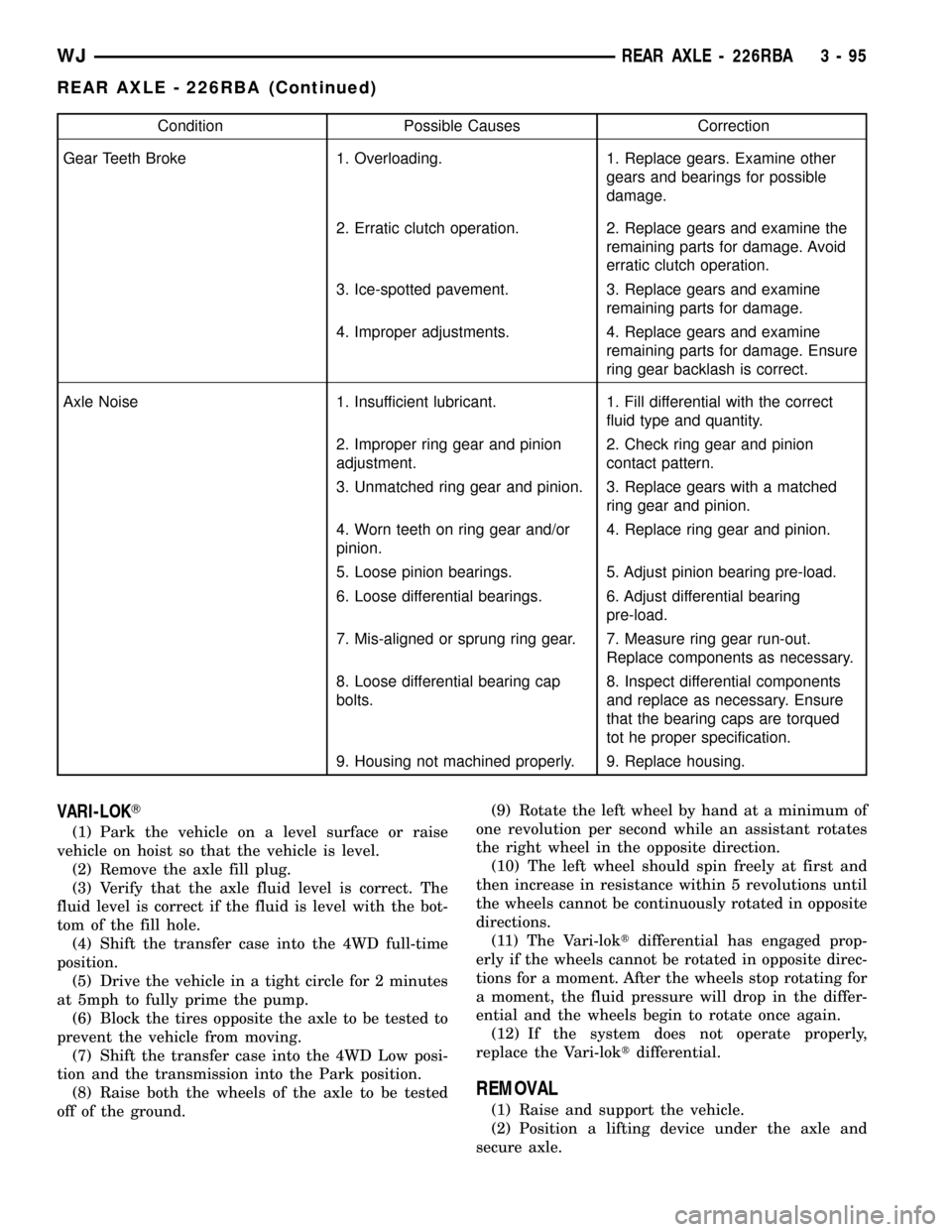
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
VARI-LOKT
(1) Park the vehicle on a level surface or raise
vehicle on hoist so that the vehicle is level.
(2) Remove the axle fill plug.
(3) Verify that the axle fluid level is correct. The
fluid level is correct if the fluid is level with the bot-
tom of the fill hole.
(4) Shift the transfer case into the 4WD full-time
position.
(5) Drive the vehicle in a tight circle for 2 minutes
at 5mph to fully prime the pump.
(6) Block the tires opposite the axle to be tested to
prevent the vehicle from moving.
(7) Shift the transfer case into the 4WD Low posi-
tion and the transmission into the Park position.
(8) Raise both the wheels of the axle to be tested
off of the ground.(9) Rotate the left wheel by hand at a minimum of
one revolution per second while an assistant rotates
the right wheel in the opposite direction.
(10) The left wheel should spin freely at first and
then increase in resistance within 5 revolutions until
the wheels cannot be continuously rotated in opposite
directions.
(11) The Vari-loktdifferential has engaged prop-
erly if the wheels cannot be rotated in opposite direc-
tions for a moment. After the wheels stop rotating for
a moment, the fluid pressure will drop in the differ-
ential and the wheels begin to rotate once again.
(12) If the system does not operate properly,
replace the Vari-loktdifferential.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle and
secure axle.
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 95
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 144 of 2199

NOTE: Arbor Discs 6927A has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
(5) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(6) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in axle housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 8). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator face to the pointer. Tighten
dial indicator face lock screw.
(7) With scooter block still in position against the
pinion height block, slowly slide the dial indicator
probe over the edge of the pinion height block.
(8) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 11). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Bring dial
pointer back to zero against the arbor bar, do not
turn dial face. Continue moving the dial probe to the
crest of the arbor bar and record the highest reading.
If the dial indicator can not achieve the zero reading,
the rear bearing cup or the pinion depth gauge set is
not installed correctly.
(9) Select a depth shim equal to the dial indicator
reading plus the pinion depth variance number
etched in the face of the pinion (Fig. 6). For example,
if the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD & GEAR
BACKLASH
Differential side bearing preload and gear backlash
is achieved by selective shims positioned behind the
differential side bearing cones. The proper shim
thickness can be determined using slip-fit Dummy
Bearings 6929-A in place of the differential side bear-
ings and a Dial Indicator C-3339. Before proceeding
with the differential bearing preload and gear back-
lash measurements, measure the pinion gear depth
and prepare the pinion for installation. Establishing
proper pinion gear depth is essential to establishing
gear backlash and tooth contact patterns. After the
overall shim thickness to take up differential side
play is measured, the pinion is installed, and the
gear backlash shim thickness is measured. The over-
all shim thickness is the total of the dial indicator
reading and the preload specification added together.
The gear backlash measurement determines the
thickness of the shim used on the ring gear side of
the differential case. Subtract the gear backlash shim
thickness from the total overall shim thickness and
select that amount for the pinion gear side of the dif-
ferential (Fig. 12). Differential shim measurements
are performed with the spreader W-129-B removed.
SHIM SELECTION
NOTE: It is difficult to salvage the differential side
bearings during the removal procedure. Install
replacement bearings if necessary.
(1) Remove differential side bearings from differ-
ential case.
Fig. 10 GAUGE TOOLS IN HOUSING
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 11 PINION GEAR DEPTH MEASUREMENT
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 99
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 145 of 2199

(2) Install ring gear on differential case and
tighten bolts to specification.
(3)
Install Dummy Bearings 6929-A on differential case.
(4) Install differential case in the housing.
(5) Record the thickness of Dummy Shims 8107,
then insert the shims between the dummy bearings
and the differential housing (Fig. 13).(6) Install the bearing caps in their original posi-
tions and snug the bolts (Fig. 14).
(7) With a dead-blow hammer, seat the differential
dummy bearings to each side of the housing (Fig. 15)
and (Fig. 16).
Fig. 12 ADJUSTMENT SHIM LOCATIONS
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
3 - RING GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
5 - COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
Fig. 13 DUMMY SHIM POINT
1 - DUMMY SHIMS
2 - HOUSING
3 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
4 - DUMMY BEARINGS
Fig. 14 TIGHTEN BEARING CAP BOLTS
1 - BEARING CAPS
2 - HOUSING
3 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 15 SEAT DUMMY BEARING
1 - HAMMER
2 - HOUSING
3 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
3 - 100 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 148 of 2199

(32) Position the indicator plunger against a ring
gear tooth (Fig. 22).
(33) Push and hold ring gear upward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate.
(34) Zero dial indicator face to pointer.
(35) Push and hold ring gear downward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate. Dial indicator
reading should be between 0.076 mm (0.003 in.) and
0.15 mm (0.006 in.). If backlash is not within specifi-
cations transfer the necessary amount of shim thick-
ness from one side of the housing to the other (Fig.
23).
(36) Verify differential case and ring gear runout
by measuring ring to pinion gear backlash at eight
locations around the ring gear. Readings should not
vary more than 0.05 mm (0.002 in.). If readings vary
more than specified, the ring gear or the differential
case is defective.
After the proper backlash is achieved, perform
Gear Contact Pattern procedure.
GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring gear and pinion teeth contact patterns
will show if the pinion depth is correct in the axle
housing. It will also show if the ring gear backlashhas been adjusted correctly. The backlash can be
adjusted within specifications to achieve desired
tooth contact patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on a ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution in
both directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
24) and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as
necessary.
Fig. 22 RING GEAR BACKLASH
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 23 BACKLASH SHIM
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 103
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 150 of 2199

DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD CHECK
The final check on the differential assembly before
installing the axles is torque to rotate pinion and dif-
ferential combined. This will verify the correct differ-
ential bearing preload.Torque to rotate the differential and pinion should
be the torque to rotate the pinion plus 0.79-1.24 N´m
(7-11 in. lbs.).
SPECIFICATIONS
AXLE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Axle Ratio 3.31, 3.55, 3.73, 3.91
Differential Bearing Preload 0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
Ring Gear Diameter 226 mm (8.9 in.)
Ring Gear Backlash 0.076.-0.15 mm (0.003-0.006 in.)
Pinion Gear Std. Depth 109.52 mm (4.312 in.)
Pinion Bearing Preload - Original Bearings 1-2 N´m (10-20 in. lbs.)
Pinion Bearing Preload - New Bearings 2.8-4 N´m (25-35 in. lbs.)
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Differential Cover Bolts 41 30 -
Bearing Cap Bolts 85 63 -
Ring Gear Bolts 136 100 -
Pinion Nut 298-380 220-280 -
Pinion Mate Shaft Screw 17.6 13 -
Axle Bearing Retainer Plate
Nuts61 45 -
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 105
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 151 of 2199
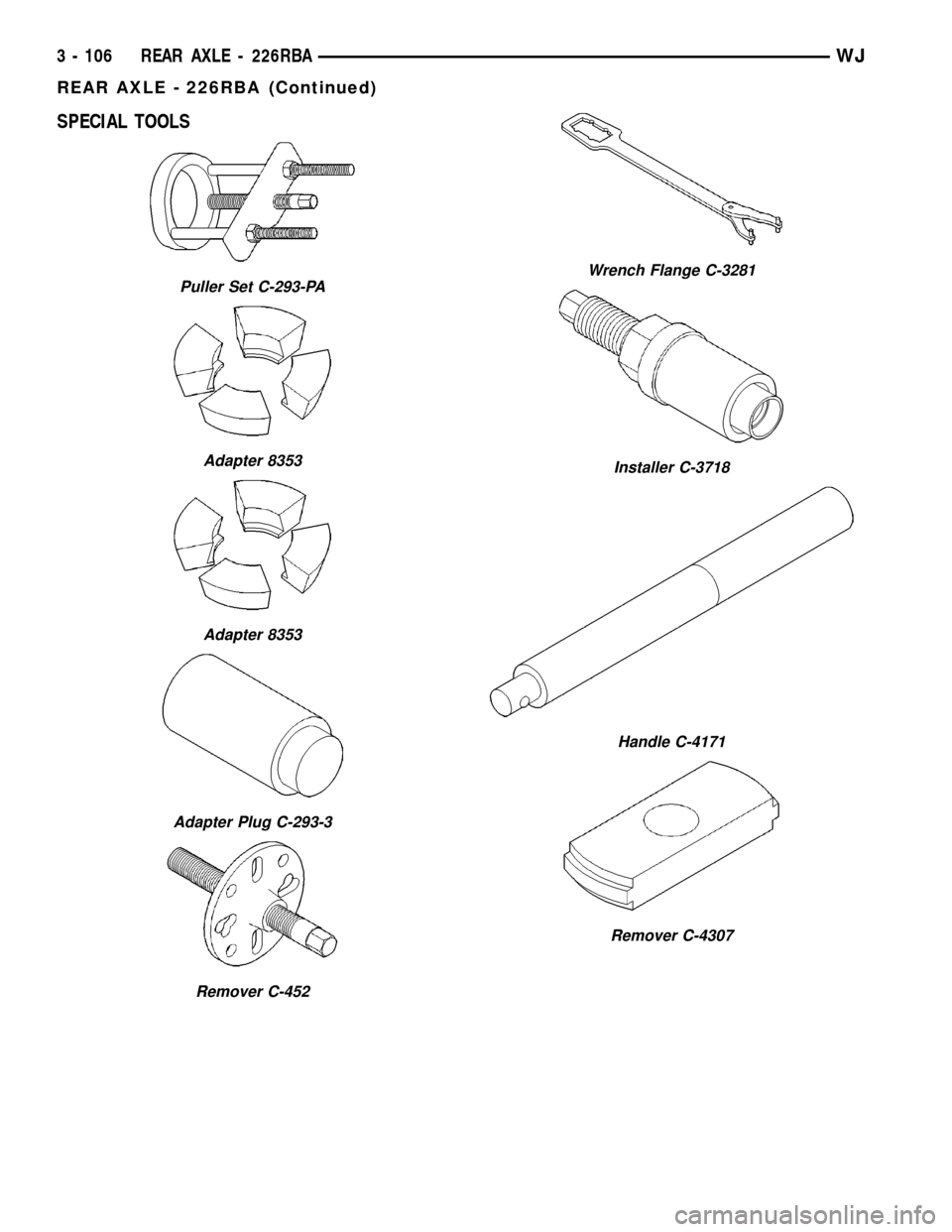
SPECIAL TOOLS
Puller Set C-293-PA
Adapter 8353
Adapter 8353
Adapter Plug C-293-3
Remover C-452
Wrench Flange C-3281
Installer C-3718
Handle C-4171
Remover C-4307
3 - 106 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 159 of 2199

(9) Remove pinion shaft seal with Remover 7794-A
and slide hammer (Fig. 40).
(10)
Remove front pinion bearing using a pair of pick
tools to pull the bearing off the pinion gear shaft.
NOTE: If the pinion bearing becomes bound on the
pinion shaft, lightly tap the end of the shaft with a
rawhide/rubber mallet.
(11) Remove the collapsible spacer.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install anewcollapsible spacer on pinion
shaft.
(2) Install pinion front bearing on the pinion shaft.
(3) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal and install seal with an appropriate
installer (Fig. 41).
(4) Install yoke with Installer C-3718 and Spanner
Wrench 6958 (Fig. 42).(5) Install yoke washer andnewnut on the pinion
gear. Tighten the nut to 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion rotating torque and never exceed specified pre-
load torque. If preload torque or rotating torque is
exceeded a new collapsible spacer must be installed.
(6) Using yoke with Spanner Wrench 6958 and a
torque wrench set at 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.), (Fig. 43)
slowly tighten the nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) incre-
ments until the rotating torque is achieved. Measure
the rotating torque frequently to avoid over crushing
the collapsible spacer (Fig. 44).
Fig. 43 PINION NUT
1 - SPANNER WRENCH
2 - PIPE
3 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 40 PINION SEAL REMOVER
1 - REMOVER
2 - SLIDE HAMMER
3 - PINION SEAL
Fig. 41 PINION SEAL INSTALLER
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
Fig. 42 Pinion Yoke Installer
1 - INSTALLER
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
4 - SPANNER WRENCH
3 - 114 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER (Continued)
Page 164 of 2199

(12) Install cover and tighten bolts in a criss-cross
pattern to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(13) Refill the differential with Mopar Hypoid
Gear Lubricant or equivalent to bottom of the fill
plug hole.
(14) Install fill hole plug.
(15) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Before removing the unit for repair,
drain, flush and refill the axle with the specified
lubricant. A container of Mopar Trac-loktLubricant
(friction modifier) should be added after repair ser-
vice or during a lubricant change.
After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu-
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches. This
will correct the condition in most instances. If the
chatter persists, clutch damage could have occurred.
DIFFERENTIAL TEST
The differential can be tested without removing the
differential case by measuring rotating torque. Make
sure brakes are not dragging during this measure-
ment.
(1) Place blocks in front and rear of both front
wheels.
(2) Raise one rear wheel until it is completely off
the ground.
(3) Engine off, transmission in neutral, and park-
ing brake off.
(4) Remove wheel and bolt Special Tool 6790 or
equivalent tool to studs.
(5) Use torque wrench on special tool to rotate
wheel and read rotating torque (Fig. 56).
(6) If rotating torque is less than 41 N´m (56 ft.
lbs.) or more than 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.) on either
wheel the unit should be serviced.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Clamp side gear Holding Fixture 6965 in a vise
and position the differential case on the Holding Fix-
ture (Fig. 57).
(2) Remove ring gear if the ring gear is to be
replaced. The Trac-loktdifferential can be serviced
with the ring gear installed.
Fig. 56 ROTATING TORQUE TEST
1 - SPECIAL TOOL WITH BOLT IN CENTER HOLE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 57 DIFFERENTIAL CASE FIXTURE
1 - HOLDING FIXTURE
2 - VISE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 119
DIFFERENTIAL (Continued)
Page 166 of 2199

(8) Install Forcing Screw C-6960-4 and tighten
screw to 122 N´m (90 ft. lbs.) maximum to compress
Belleville springs in clutch packs (Fig. 62).
(9) With a feeler gauge remove thrust washers
from behind the pinion gears (Fig. 63).(10) Insert Turning Bar C-6960-2 into the pinion
mate shaft hole in the case (Fig. 64).
(11) Loosen the Forcing Screw in small increments
until the clutch pack tension is relieved and the dif-
ferential case can be turned using Turning Bar.
(12) Rotate differential case until the pinion gears
can be removed.
(13) Remove pinion gears from differential case.
(14) Remove Forcing Screw, Step Plate and
Threaded Adapter.
(15) Remove top side gear, clutch pack retainer
and clutch pack. Keep plates in correct order during
removal (Fig. 65).
(16) Remove differential case from the Holding
Fixture. Remove side gear, clutch pack retainer and
clutch pack. Keep plates in correct order during
removal.
CLEANING
Clean all components in cleaning solvent and dry
components with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Inspect clutch pack plates for wear, scoring or dam-
age. Replace both clutch packs if any one component
in either pack is damaged. Inspect side and pinion
gears for cracks chips or damage and replace as nec-
essary. Inspect differential case and pinion shaft and
replace if worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
Clean all components in cleaning solvent and dry
components with compressed air. Inspect clutch pack
plates for wear, scoring or damage. Replace both
clutch packs if any one component in either pack is
Fig. 62 COMPRESS BELLEVILLE SPRING
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - TOOL ASSEMBLED
3 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 63 PINION GEAR THRUST WASHER
1 - THRUST WASHER
2 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 64 PINION GEARS
1 - PINION GEARS
2 - TURNING BAR
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 121
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK (Continued)
Page 167 of 2199

damaged. Inspect side gears and pinions. Replace
any gear that is worn, cracked, chipped or damaged.
Inspect differential case and pinion shaft. Replace if
worn or damaged.
NOTE: New Plates and discs with fiber coating (no
grooves or lines) must be presoaked in Friction
Modifier before assembly. Soak plates and discs for
a minimum of 20 minutes.
(1) Lubricate each component with gear lubricant
before assembly.
(2) Assemble the clutch discs into packs and
secure disc packs with retaining clips (Fig. 66).
NOTE: Dished plate is position with the convex side
against the side gear.
(3) Position assembled clutch disc packs on the
side gear hubs.
(4) Install clutch pack and side gear in the ring
gear side of the differential case (Fig. 67).Be sure
clutch pack retaining clips remain in position
and are seated in the case pockets.
(5) Position the differential case on the Holding
Fixture 6965.
Fig. 65 SIDE GEARS AND CLUTCH DISCS
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - RETAINER
3 - SIDE GEAR AND CLUTCH DISC PACK
Fig. 66 CLUTCH PACK
1 - DISCS
2 - DISHED PLATE
3 - RETAINER
4 - SIDE GEAR
5 - RETAINER
6 - PLATES
Fig. 67 CLUTCH PACK AND LOWER SIDE GEAR
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - LOWER SIDE GEAR AND CLUTCH DISC PACK
3 - 122 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK (Continued)