service JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 742 of 1803

(3) Raise the pivot block latch release tab until it
is perpendicular to the rear wiper blade superstruc-
ture (Fig. 14).
(4) Insert the hook formation on the tip of the
wiper arm through the window in the wiper blade
pivot block/latch unit.
(5) Slide the wiper blade pivot block/latch up into
the hook formation on the tip of the wiper arm until
the hook is firmly seated against the pivot block.
(6) Press the pivot block latch release tab down-
ward until it snaps into its locked position over the
top of the wiper arm.
(7) Gently lower the wiper arm and place the arm
support in the tailgate park ramp.
REAR WIPER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The rear wiper motor is concealed within the tail-
gate, below the rear flip-up glass opening and behind
the tailgate inner trim panel. The end of the motor
output shaft that protrudes through the tailgate
outer panel to drive the rear wiper arm and blade is
the only visible component of the rear wiper motor
(Fig. 15). A rubber gasket, a bezel, and a nut secure
and seal the motor output shaft to the tailgate outer
panel. A molded plastic nut cover snaps onto the
bezel to conceal the nut and improve appearance. An
integral connector receptacle connects the rear wipermotor to the vehicle electrical system through a ded-
icated take out and connector of the tailgate wire
harness. The rear wiper motor consists of the follow-
ing major components:
²Bracket- The rear wiper motor bracket consists
of a stamped steel mounting plate for the wiper
motor that is secured with screws through two rub-
ber insulators to the tailgate inner panel.
²Rear Wiper Module- The rear wiper motor
electronic controls are concealed beneath a molded
plastic cover and includes the rear wiper system elec-
tronic logic and rear wiper motor electronic controls.
²Motor- The permanent magnet rear wiper
motor is secured with screws to the rear wiper motor
bracket. The wiper motor includes an integral trans-
mission, and the motor output shaft.
The rear wiper motor cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If any component of the motor is faulty or
damaged, the entire rear wiper motor unit must be
replaced. The motor output shaft gasket, bezel, nut,
and nut cover are available for service replacement.
OPERATION
The rear wiper motor receives non-switched bat-
tery current through a fuse in the Junction Block
(JB) on a fused B(+) circuit and is connected to
ground at all times. The rear wiper motor operation
is controlled by the vehicle operator through battery
current signal inputs received by the rear wiper
motor electronic control module from the rear wiper
switch circuitry that is integral to the right (wiper)
control stalk of the multi-function switch on the
steering column. The module also receives an exter-
nal control input from the flip-up glass ajar switch
sense circuit. If the rear wiper module senses that
the flip-up glass is ajar, it will not allow the rear
wiper motor to operate.
The rear wiper module electronic control logic uses
these inputs, its internal inputs, and its program-
ming to provide a continuous wipe mode, an inter-
mittent wipe mode, a wipe-after-wash mode, and off-
the-glass wiper blade parking. The wiper blade
cycling is controlled by the internal electronic con-
trols of the module. The module controls current flow
to the wiper motor brushes and provides an elec-
tronic speed control that speeds the wiper blade near
the center of the glass, but slows the wiper blade
during directional reversals at each end of the wipe
pattern and during wiper blade off-the-glass parking
for quieter operation. The wiper motor transmission
converts the rotary output of the wiper motor to the
back and forth wiping motion of the rear wiper arm
and blade on the rear flip-up glass.
Fig. 15 Rear Wiper Motor
1 - SCREW (2)
2 - INSULATOR (2)
3 - BRACKET
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT
5 - SEAL
6 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
7 - COVER
8 - MOTOR
KJREAR WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 41
REAR WIPER BLADE (Continued)
Page 753 of 1803

CIRCUIT FUNCTION
U OPEN
V SPEED CONTROL, WIPER/
WASHER
W OPEN
X AUDIO SYSTEMS
Y OPEN
Z GROUNDS
DESCRIPTION - SECTION IDENTIFICATION AND
INFORMATION
The wiring diagrams are grouped into individual
sections. If a component is most likely found in a par-
ticular group, it will be shown complete (all wires,
connectors, and pins) within that group. For exam-
ple, the Auto Shutdown Relay is most likely to be
found in Group 30, so it is shown there complete. It
can, however, be shown partially in another group if
it contains some associated wiring.
Splice diagrams in Section 8W-70 show the entire
splice and provide references to other sections the
splices serves. Section 8W-70 only contains splice dia-
grams that are not shown in their entirety some-
where else in the wiring diagrams.
Section 8W-80 shows each connector and the cir-
cuits involved with that connector. The connectors
are identified using the name/number on the dia-
gram pages.
WIRING SECTION CHART
GROUP TOPIC
8Wa-01 thru
8W-09General information and Diagram
Overview
8Wa-10 thru
8W-19Main Sources of Power and
Vehicle Grounding
8Wa-20 thru
8W-29Starting and Charging
8Wa-30 thru
8W-39Powertrain/Drivetrain Systems
8Wa-40 thru
8W-49Body Electrical items and A/C
8Wa-50 thru
8W-59Exterior Lighting, Wipers and
Trailer Tow
8Wa-60 thru
8W-69Power Accessories
8Wa-70 Splice Information
8Wa-80 Connector Pin Outs
8Wa-91 Connector, Ground and Splice
Locations
DESCRIPTION - CONNECTOR, GROUND AND
SPLICE INFORMATION
CAUTION: Not all connectors are serviced. Some
connectors are serviced only with a harness. A typ-
ical example might be the Supplemental Restraint
System connectors. Always check parts availability
before attempting a repair.
IDENTIFICATION
In-line connectors are identified by a number, as
follows:
²In-line connectors located in the engine compart-
ment are C100 series numbers
²In-line connectors located in the Instrument
Panel area are C200 series numbers.
²In-line connectors located in the body are C300
series numbers.
²Jumper harness connectors are C400 series
numbers.
²Grounds and ground connectors are identified
with a ªGº and follow the same series numbering as
the in-line connectors.
²Splices are identified with an ªSº and follow the
same series numbering as the in-line connectors.
²Component connectors are identified by the com-
ponent name instead of a number. Multiple connec-
tors on a component use a C1, C2, etc. identifier.
LOCATIONS
Section 8W-91 contains connector/ground/splice
location illustrations. The illustrations contain the
connector name (or number)/ground number/splice
number and component identification. Connector/
ground/splice location charts in section 8W-91 refer-
ence the figure numbers of the illustrations.
The abbreviation T/O is used in the component
location section to indicate a point in which the wir-
ing harness branches out to a component. The abbre-
viation N/S means Not Shown in the illustrations
WARNINGS - GENERAL
WARNINGSprovide information to prevent per-
sonal injury and vehicle damage. Below is a list of
general warnings that should be followed any time a
vehicle is being serviced.
WARNING:: ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES FOR
EYE PROTECTION.
WARNING: USE SAFETY STANDS ANYTIME A PRO-
CEDURE REQUIRES BEING UNDER A VEHICLE.
8Wa - 01 - 6 8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATIONKJ
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1217 of 1803

ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION.........................39
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING............................39
CLEANING............................39
INSPECTION..........................40
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING
ROD BEARING - FITTING...............40
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................42
REMOVAL.............................43
INSPECTION..........................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE
MAIN BEARING - FITTING...............45
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL.............................46
INSTALLATION.........................47
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL.............................48
INSTALLATION.........................48
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL.............................49
INSTALLATION.........................49
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION.........................49
STANDARD PROCEDURE
CONNECTING ROD BEARING - FITTING . . . 49
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON
FITTING.............................50
REMOVAL.............................50
CLEANING............................51
INSPECTION..........................51
INSTALLATION.........................51
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING.............................52
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL.............................54
INSTALLATION.........................55
STRUCTURAL COVER
DESCRIPTION.........................55
OPERATION...........................55
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................55
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................56
INSTALLATION.........................57
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................57
INSTALLATION.........................57
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION.........................57
OPERATION...........................58DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK...............................60
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE..........................60
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL
AREA LEAKS.........................61
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL.....61
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL.............................63
INSTALLATION.........................63
OIL PAN
DESCRIPTION.........................63
REMOVAL.............................63
CLEANING............................63
INSPECTION..........................63
INSTALLATION.........................64
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................65
OPERATION...........................65
REMOVAL.............................65
INSTALLATION.........................65
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL.............................65
DISASSEMBLY.........................65
INSPECTION..........................66
ASSEMBLY............................67
INSTALLATION.........................67
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................68
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS.....................68
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................69
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................69
REMOVAL.............................69
INSTALLATION.........................70
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION.........................71
OPERATION...........................71
STANDARD PROCEDURE
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR.......71
SERVICE PROCEDURES...............72
BALANCE SHAFT
REMOVAL.............................74
INSTALLATION.........................74
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................74
INSTALLATION.........................76
IDLER SHAFT
REMOVAL.............................77
INSTALLATION.........................77
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKET(S
REMOVAL.............................77
INSPECTION..........................79
INSTALLATION.........................80
9 - 2 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
Page 1219 of 1803
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING)ÐPERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
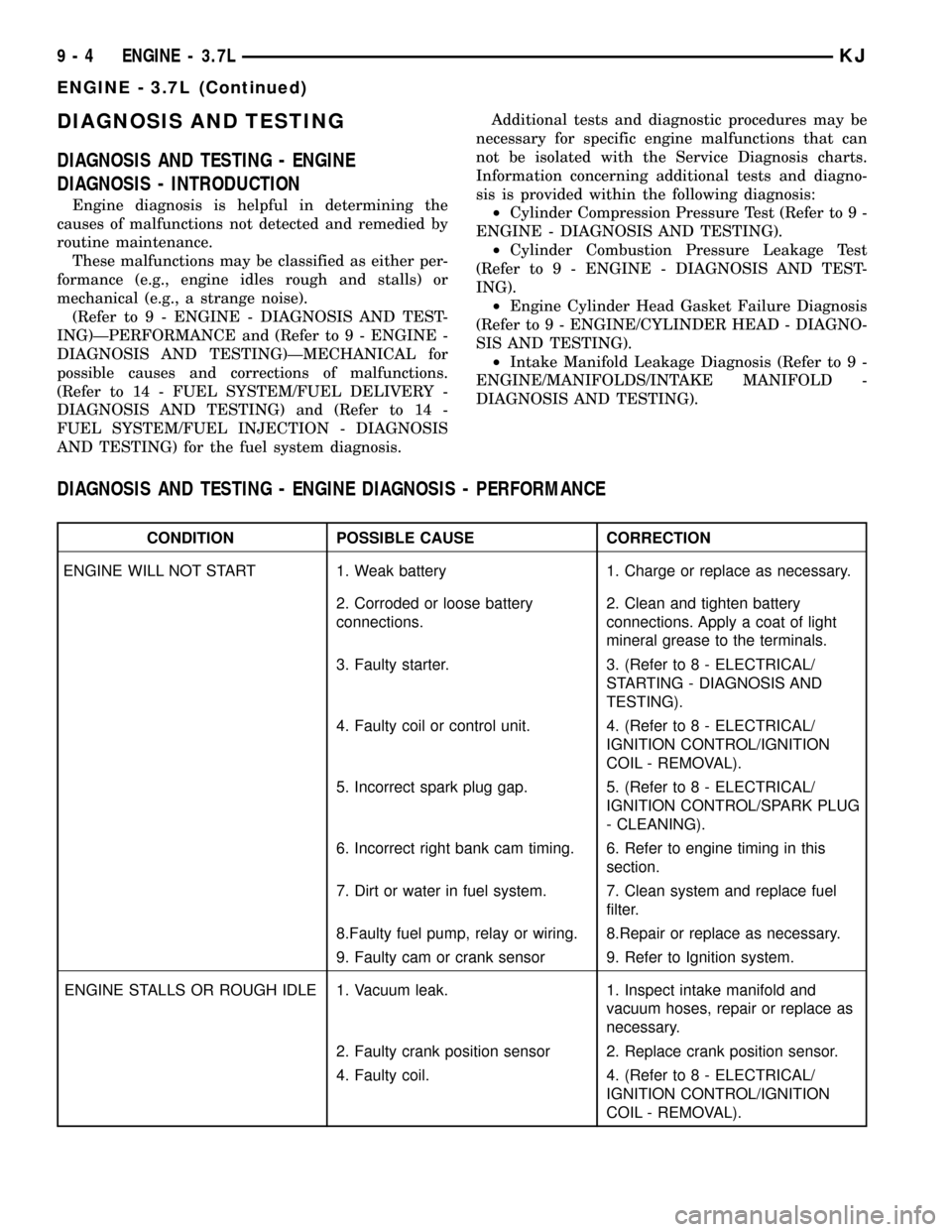
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Incorrect right bank cam timing. 6. Refer to engine timing in this
section.
7. Dirt or water in fuel system. 7. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
8.Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 8.Repair or replace as necessary.
9. Faulty cam or crank sensor 9. Refer to Ignition system.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Vacuum leak. 1. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
2. Faulty crank position sensor 2. Replace crank position sensor.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
9 - 4 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1221 of 1803
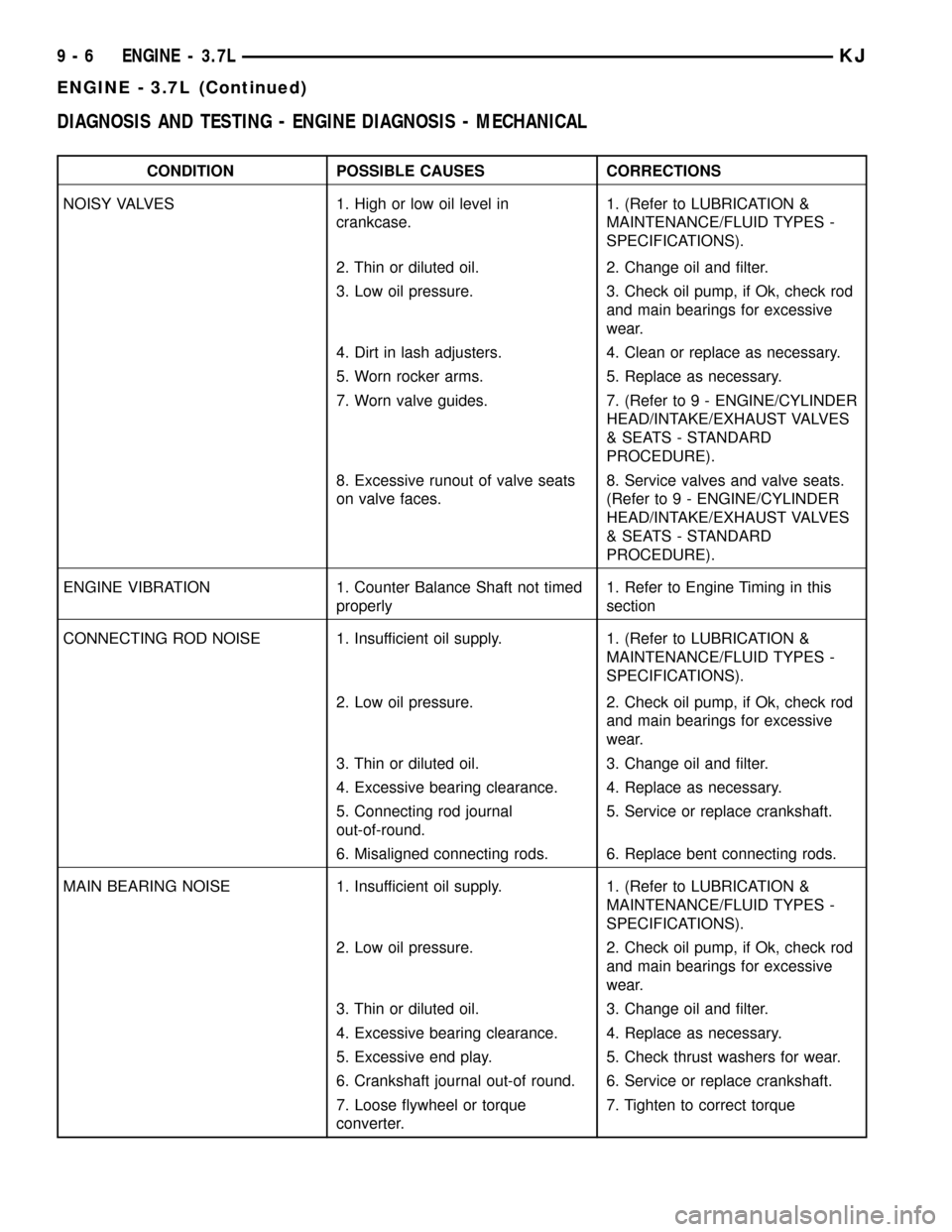
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Clean or replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. Service valves and valve seats.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
ENGINE VIBRATION 1. Counter Balance Shaft not timed
properly1. Refer to Engine Timing in this
section
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
9 - 6 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1225 of 1803

²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Remove hood. Mark hood hinge location for
reinstallation.
(3) Remove air cleaner assembly.(4) Remove radiator core support bracket.
(5) Remove fan shroud with electric fan assembly.
(6) Remove mechanical cooling fan.
(7) Remove drive belt.
NOTE: It is NOT necessary to discharge the A/C
system to remove the engine.
(8) Remove A/C compressor and secure away from
engine with lines attached.
(9) Remove generator and secure away from
engine.
NOTE: Do NOT remove the phenolic pulley from the
P/S pump. It is not required for P/S pump removal.
(10) Remove power steering pump with lines
attached and secure away from engine.
(11) Drain cooling system.
(12) Remove coolant bottle.
(13) Disconnect the heater hoses from the engine.
(14) Disconnect heater hoses from heater core and
remove hose assembly.
(15) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(16) Remove upper radiator hose from engine.
(17) Remove lower radiator hose from engine.
(18) Disconnect the engine to body ground straps
at the left side of cowl.
(19) Disconnect the engine wiring harness at the
following points:
²Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
²Fuel Injectors
²Throttle Position (TPS) Switch
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Engine Oil Pressure Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure MAP) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
(20) Remove coil over plugs.
(21) Release fuel rail pressure.
(22) Remove fuel rail and secure away from
engine.
NOTE: It is not necessary to release the quick con-
nect fitting from the fuel supply line for engine
removal.
(23) Remove the PCV hose.
(24) Remove the breather hoses.
(25) Remove the vacuum hose for the power brake
booster.
(26) Disconnect knock sensors.
(27) Remove engine oil dipstick tube.
(28) Remove intake manifold.
(29) Install engine lift plate.
Fig. 2 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
9 - 10 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1234 of 1803

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 3.7L
Housing removal is not necessary for element (fil-
ter) replacement.
(1) Pry up 2 spring clips (Fig. 3) from front of
housing cover (spring clips retain cover to housing).
(2) Release housing cover from 4 locating tabs
located on rear of housing, and remove cover.
(3) Remove air cleaner element (filter) from hous-
ing.
(4) Clean inside of housing before replacing ele-
ment.
INSTALLATION - 3.7L
(1) Install element into housing.
(2) Position housing cover into housing locating
tabs.
(3) Pry up spring clips and lock cover to housing.
If any air filter, air resonator, air intake tubes or
air filter housing clamps had been loosened or
removed, tighten them to 5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and
are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are
not replaceable or serviceable, and valve guide ream-
ing is not recommended. If the guides are worn
beyond acceptable limits, replace the cylinder heads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
²Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
²Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
²Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Fig. 3 AIR CLEANER ELEMENT - 3.7L
1 - AIR INTAKE HOSE
2 - HOSE CLAMP
3 - COVER
4 - CLIPS (2)
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 19
Page 1245 of 1803

(9) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, install the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(10) Install the cylinder head cover. Refer to Cylin-
der Head Cover in this Section.
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder heads are made of an aluminum alloy.
The cylinder head features two valves per cylinder
with pressed in powdered metal valve guides. The
cylinder heads also provide enclosures for the timing
chain drain, necessitating unique left and right cylin-
der heads.
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and
are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are
not replaceable or serviceable, and valve guide ream-
ing is not recommended. If the guides are worn
beyond acceptable limits, replace the cylinder heads.
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Each
valve is actuated by a roller rocker arm which pivots
on a stationary lash adjuster. All valves use three
bead lock keepers to retain the springs and promote
valve rotation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
²Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
²Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
²Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
9 - 30 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1246 of 1803

VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the right side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant. Refer to COOLING
SYSTEM.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold. Refer to proce-
dure.
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover. Refer to proce-
dure.
(8) Remove the fan shroud. Refer to COOLING
SYSTEM.
(9) Remove oil fill housing from cylinder head.
(10) Remove accessory drive belt. Refer to COOL-
ING SYSTEM.
(11) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper timing
mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark.
(12) Verify the V6 mark on the camshaft sprocket
is at the 12 o'clock position. Rotate the crankshaft
one turn if necessary.
(13) Remove the crankshaft damper. Refer to pro-
cedure.
(14) Remove the timing chain cover. Refer to pro-
cedure.
(15) Lock the secondary timing chains to the idler
sprocket using Special Tool 8429 Timing Chain Hold-
ing Fixture.NOTE: Mark the secondary timing chain prior to
removal to aid in installation.
(16) Mark the secondary timing chain, one link on
each side of the V6 mark on the camshaft drive gear.
(17) Remove the right side secondary chain ten-
sioner. Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets in this
section.
(18) Remove the cylinder head access plug.
(19) Remove the right side secondary chain guide.
Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets in this section.
CAUTION: The nut on the right side camshaft
sprocket should not be removed for any reason, as
the sprocket and camshaft sensor target wheel is
serviced as an assembly. If the nut was removed
retorque nut to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.).
(20) Remove the retaining bolt and the camshaft
drive gear.
CAUTION: Do not allow the engine to rotate. severe
damage to the valve train can occur.
CAUTION: Do not overlook the four smaller bolts at
the front of the cylinder head. Do not attempt to
remove the cylinder head without removing these
four bolts.
CAUTION: Do not hold or pry on the camshaft tar-
get wheel for any reason. A damaged target wheel
can result in a vehicle no start condition.
NOTE: The cylinder head is attached to the cylinder
block with twelve bolts.
(21) Remove the cylinder head retaining bolts.
(22) Remove the cylinder head and gasket. Discard
the gasket.
CAUTION: Do not lay the cylinder head on its gas-
ket sealing surface, do to the design of the cylinder
head gasket any distortion to the cylinder head
sealing surface may prevent the gasket from prop-
erly sealing resulting in leaks.
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components (Fig. 22). (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 31
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT (Continued)
Page 1247 of 1803

INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the cylinder head for out-of-flatness,
using a straightedge and a feeler gauge. If measure-
ments exceed 0.0508 mm (0.002 in.) replace the cyl-
inder head.
(2) Inspect the valve seats for damage. Service the
valve seats as necessary.
(3) Inspect the valve guides for wear, cracks or
looseness. If either condition exist, replace the cylin-
der head.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The cylinder head bolts are tightened using
a torque plus angle procedure. The bolts must be
examined BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked
down the bolts should be replaced.
Necking can be checked by holding a straight edge
against the threads. If all the threads do not contact
the scale, the bolt should be replaced.
CAUTION: When cleaning cylinder head and cylin-
der block surfaces, DO NOT use a metal scraper
because the surfaces could be cut or ground. Use
only a wooden or plastic scraper.
(1) Clean the cylinder head and cylinder block
mating surfaces.
(2) Position the new cylinder head gasket on the
locating dowels.CAUTION: When installing cylinder head, use care
not damage the tensioner arm or the guide arm.
(3) Position the cylinder head onto the cylinder
block. Make sure the cylinder head seats fully over
the locating dowels.
NOTE: The four M8 cylinder head mounting bolts
require sealant to be added to them before install-
ing. Failure to do so may cause leaks. Do not reuse
the old M8 bolts, use new M8 bolts.
(4) Lubricate the cylinder head bolt threads with
clean engine oil and install the eight M10 bolts.
(5) Coat the four M8 cylinder head bolts with
Mopar Lock and Seal Adhesivethen install the
bolts.
The cylinder head bolts are tightened using an
angle torque procedure, however, the bolts are not a
torque-to-yield design.
(6) Tighten the bolts in sequence using the follow-
ing steps and torque values:
²Step 1: Tighten bolts 1±10, 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.).
²Step 2: Tighten bolts 1±10, 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
Tighten bolts 11±14, 25 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
²Step 3: Tighten bolts 1±10, 90 degrees. Tighten
bolts 11±14, 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: The nut on the right side camshaft
sprocket should not be removed for any reason, as
the sprocket and camshaft sensor target wheel is
serviced as an assembly. If the nut was removed
retorque nut to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.).
(7) Position the secondary chain onto the camshaft
drive gear, making sure one marked chain link is on
either side of the V6 mark on the gear then using
Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench, position the
gear onto the camshaft.
CAUTION: Remove excess oil from camshaft
sprocket retaining bolt before reinstalling bolt. Fail-
ure to do so may cause over-torquing of bolt result-
ing in bolt failure.
(8) Install the camshaft drive gear retaining bolt.
(9) Install the right side secondary chain guide.
(10) Install the cylinder head access plug.
(11) Re-set and install the right side secondary
chain tensioner.
(12) Remove Special Tool 8429.
(13) Install the timing chain cover.
(14) Install the crankshaft damper.Tighten damper
bolt 175 N´m (130 Ft. Lbs.).
(15) Install accessory drive belt.
(16) Install the fan shroud.
(17) Install the cylinder head cover.
(18) Install the intake manifold.
Fig. 22 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
9 - 32 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT (Continued)