evap JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 1406 of 1803

(14) If fuel injectors are to be removed, refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
INSTALLATION
2.4L Engine
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Clean out fuel injector machined bores in
intake manifold.
(3) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(4) Position fuel rail/fuel injector assembly to
machined injector openings in intake manifold.
(5) Guide each injector into cylinder head. Be care-
ful not to tear injector o-rings.
(6) Push fuel rail down until fuel injectors have
bottomed on shoulders.
(7) Install 2 fuel rail mounting bolts and tighten.
Refer to torque specifications.
(8) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 37). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
(9) Snap 2 injection wiring harness clips (Fig. 35)
into brackets.
(10) Connect 2 main engine harness connectors at
rear of intake manifold (Fig. 34).
(11) Tighten 5 intake manifold mounting bolts.
Refer to Engine Torque Specifications.
(12) Install PCV valve and hose.
(13) Install thermostat and radiator hose. Fill with
coolant. Refer to Cooling.
(14) Connect necessary vacuum lines to throttle
body.
(15) Connect fuel line latch clip and fuel line to
fuel rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(16) Install air duct to throttle body.
(17) Connect battery cable to battery.
(18) Start engine and check for leaks.
3.7L Engine
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Clean out fuel injector machined bores in
intake manifold.
(3) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(4) Position fuel rail/fuel injector assembly to
machined injector openings in cylinder head.
(5) Guide each injector into cylinder head. Be care-
ful not to tear injector o-rings.
(6) Pushrightside of fuel rail down until fuel
injectors have bottomed on cylinder head shoulder.Pushleftfuel rail down until injectors have bot-
tomed on cylinder head shoulder.
(7) Install 4 fuel rail mounting bolts and tighten.
Refer to torque specifications.
(8) Install 6 ignition coils. Refer to Ignition Coil
Removal/Installation.
(9) Connect electrical connectors to throttle body.
(10) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 37). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
(11) Connect necessary vacuum lines to throttle
body.
(12) Connect fuel line latch clip and fuel line to
fuel rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Install air box to throttle body.
(14) Install air duct to air box.
(15) Connect battery cable to battery.
(16) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module, and certain ORVR
components.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
A check (control) valve is mounted into the top sec-
tion of the 2±piece fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel
Tank Check Valve for additional information.
An evaporation control system is connected to the
fuel tank to reduce emissions of fuel vapors into the
atmosphere. When fuel evaporates from the fuel
tank, vapors pass through vent hoses or tubes to a
charcoal canister where they are temporarily held.
When the engine is running, the vapors are drawn
into the intake manifold. Certain models are also
equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) and/or an ORVR system.
Refer to Emission Control System for additional
information.
14 - 24 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1408 of 1803

(11) Remove module lockring (Fig. 40) using a
brass drift and hammer (counter-clockwise).
(12) Carefully lift upper section of pump module
from fuel tank a few inches(lift upper section
from tank very slowly until rubber gasket can
be retained. If not, gasket will fall into fuel
tank).
(13) Using an approved gas holding tank, drain
fuel tank through fuel pump module opening.
Tank Removal
(1) After draining tank, temporarily place upper
section of fuel pump module back into fuel tank.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) If equipped, remove fuel tank skid plate and
tow hooks. Certain equipment packages will also
require removal of the trailer hitch. Refer to Tow
Hooks, Trailer Hitch or Skid Plate in 23, Body for
removal/installation procedures.
(4) Disconnect fuel filter ground strap.
(5) Disconnect fuel filter outlet line from body
retention clip located on frame near front/center of
tank (Fig. 41). Place a small screwdriver into side of
clip and twist for removal. Also disconnect Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) line (Fig. 41) from this clip.(6) Remove both 3/4º hoses at sides of Leak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP) (Fig. 41).
(7) Disconnect 3/4º flow management valve hose
(Fig. 41) at EVAP canister.
(8) Remove fuel fill hose clamp (Fig. 42) at fuel
tank, and disconnect hose from fuel tank.
(9) A third fuel line is attached to bottom of fuel
filter. The disconnection point (quick-connect fitting)
for this 3rd line is approximately 1 foot from front of
tank towards front of vehicle (Fig. 41). Clean connec-
tion point before disconnection. Disconnect by press-
ing on tabs at side of quick-connect fitting. Also
disconnect LDP vent line near this same point.
(10) Disconnect 2 vacuum/vent hoses from plastic
retention clip at left/front of fuel tank line (Fig. 41).
(11) Support tank with a hydraulic jack.
(12) Remove 4 fuel tank strap bolts (Fig. 41) (2 at
front of tank; 2 at rear of tank), and remove both
tank support straps (Fig. 41).
(13) Carefully lower tank a few inches and discon-
nect electrical connector at top of LDP (Fig. 43). To
disconnect electrical connector: Push upward on red
colored tab to unlock. Push on black colored tab
while removing connector.
Fig. 40 TOP OF FUEL PUMP MODULE
1 - LOCK RING
2 - ALIGNMENT NOTCH
3 - FUEL FILTER FITTINGS (2)
4 - ORVR SYSTEM HOSE AND CLAMP
5 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
7 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
8 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
9 - FUEL PUMP MODULE (UPPER SECTION)Fig. 41 FRONT OF FUEL TANK
1 - TANK MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - TANK MOUNTING STRAPS (2)
3 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP (LDP)
4 - BODY RETENTION CLIP (CENTER)
5 - LDP HOSES
6 - HOSE TO FUEL MANAGEMENT VALVE
7 - BODY RETENTION CLIP (LEFT/FRONT)
8 - QUICK-CONECT FITTING
9 - LDP LINE
14 - 26 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1409 of 1803

(14) Continue lowering tank while guiding remain-
ing hoses and lines.
(15) If fuel tank is to be replaced, remove LDP,
fuel filter and fuel pump module from tank. Refer to
Leak Detection Pump, Fuel Filter and Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation procedures.
INSTALLATION
(1) If fuel tank is to be replaced, install LDP, fuel
filter and fuel pump module to tank. Refer to Leak
Detection Pump, Fuel Filter and Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation procedures.
(2) Position fuel tank to hydraulic jack.
(3) Raise tank while carefully guiding vent tubes/
hoses through frame rail and crossmember. Before
tank reaches body, connect electrical connector to
Leak Detection Pump (LDP).
(4) Continue raising tank until positioned to body.
(5) Attach two fuel tank mounting straps and 4
mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(6) Connect 2 hoses to body retention clip at left/
front of tank.
(7) Connect fuel filter fuel line to main fuel line
(snaps together). After connecting, snap this line into
body retention clip. Also connect LDP vacuum hose
near this point.(8) Install fuel fill hose and hose clamp to fuel
tank fitting. Rotate hose until white painted index
mark on hose (Fig. 42) is located between alignment
notches on fuel tank fitting. Tighten clamp to 3.4
N´m (30 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Connect fresh air and recirculation lines to fuel
fill tube.
(10) Connect 3/4º lines to Leak Detection Pump
(LDP).
(11) Connect 3/4º flow management valve hose to
EVAP canister.
(12) Snap remaining lines into body retention clip
at front/center of fuel tank.
(13) If equipped, install fuel tank skid plate,
trailer hitch and tow hooks. Refer to Tow Hooks,
Trailer Hitch or Skid Plate in 23, Body for removal/
installation procedures.
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Attach (snap on) 2 fuel filter fuel lines to top
of fuel pump module.
(16) Install electrical connector to top of fuel pump
module.
(17) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(18) Fill fuel tank with fuel.
(19) Start engine and check for fuel leaks near top
of module.
(20) Apply silicone sealant to bottom of fuel pump
module metal access plate.
Fig. 42 FUEL FILL HOSE AT TANK
1 - FUEL FILL HOSE AT TANK
2 - HOSE CLAMP
3 - WHITE PAINTED INDEX MARK
4 - ALIGNMENT NOTCHES
5 - LEFT SIDE OF FUEL TANK
6 - FUEL FILL FITTINGFig. 43 LDP ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP (LDP)
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - FUEL FILTER
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 27
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1410 of 1803

(21) Install fuel pump module metal access plate
and 4 nuts. Tighten nuts to 3 N´m (26 in. lbs.)
torque.
(22) Position carpet and install 2 new cargo clamp
rivets into each cargo holdown clamp.
FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is equipped with a check valve. The
valve (also referred to as a control valve) is located in
the top section of the fuel pump module assembly
(Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The fuel tank check valve (also referred to as
either a control valve, one-way check valve or float
valve) will prevent fuel flow through the fuel tank
vent in the event of an accidental vehicle rollover. It
is also used as a part of the ORVR system. The
EVAP canister and ORVR system draw fuel vapors
from the fuel tank through this valve. Refer to ORVR
in Emissions for additional information.
The valve may be serviced by replacing the upper
section of the fuel pump module assembly.
REMOVAL
The fuel tank check (control) valve is attached into
the top section of the fuel pump module (Fig. 44). If
replacement is necessary, the top section of the fuel
pump module must be replaced. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
INSTALLATION
The fuel tank check (control) valve is attached to
the top section of the fuel pump module. If replace-
ment is necessary, the top section of the fuel pump
module must be replaced. Refer to Fuel Pump Mod-
ule Removal/Installation.
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL
The fuel pump inlet filter is located on the bottom/
side of the lower fuel pump module section (Fig. 45).
The fuel pump module assembly is located in the fuel
tank.
(1) Remove lower section of fuel pump module.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
(2) Remove filter by prying from pump module
with 2 small screwdrivers. Filter is snapped to mod-
ule with 2 release tabs (Fig. 45).
(3) Clean filter entrance into pump module open-
ing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Snap new filter to bottom of fuel pump module.
(2) Install lower section of fuel pump module.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
Fig. 44 UPPER SECTION - FUEL PUMP MODULE
1 - UPPER SECTION - FUEL PUMP MODULE
2 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
Fig. 45 INLET FILTER
1 - INLET FILTER
2 - RELEASE TABS (2)
3 - BOTTOM OF FUEL PUMP MODULE
14 - 28 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1653 of 1803

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS.......................1
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................2
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................2
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE.......................2DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE.......................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM
SYSTEM.............................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT.......................9
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE................9
SPECIFICATIONS.....................10
CONTROLS.............................11
DISTRIBUTION..........................29
PLUMBING.............................38
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER
All vehicles are equipped with a common HVAC
housing assembly (Fig. 1). The system combines air
conditioning, heating, and ventilating capabilities in
a single unit housing mounted under the instrument
panel. On heater-only systems, the evaporator coil is
omitted from the housing.
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the HVAC
system, the engine cooling system must be properly
maintained. The use of a bug screen is not recom-
mended. Any obstructions in front of the radiator or
condenser will reduce the performance of the air con-
ditioning and engine cooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the heater core
and the heater hoses. Refer to Engine Cooling for
more information before the opening of, or attempt-
ing any service to the engine cooling system.
Fig. 1 Blend Door
1 - DEFROSTER DOOR
2- HEATER CORE
3- BLEND DOORS
4- BLOWER MOTOR HOUSING
5- EVAPORATOR (A/C ONLY)
6- LOWER HVAC CASE ASSEMBLY
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 1654 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT
The two refrigerant system service ports are used
to charge, recover/recycle, evacuate, and test the air
conditioning refrigerant system. Unique service port
coupler sizes are used on the R-134a system, to
ensure that the refrigerant system is not accidentally
contaminated by the use of the wrong refrigerant
(R-12), or refrigerant system service equipment.
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
The heater and optional air conditioner are blend-
air type systems. In a blend-air system, a blend door
controls the amount of unconditioned air (or cooled
air from the evaporator on models with air condition-
ing) that is allowed to flow through, or around, the
heater core. A temperature control knob on the A/C
Heater control panel determines the discharge air
temperature by controlling an electric actuator,
which moves the blend door. This allows an almost
immediate control of the output air temperature of
the system.
The mode control knob on the heater-only or A/C
Heater control panel is used to direct the conditioned
air to the selected system outlets. Both mode control
switches use engine vacuum to control the mode
doors, which are operated by vacuum actuators.
On all vehicles, the outside air intake can be shut
off by selecting the Recirculation Mode with the
mode control knob. This will operate a vacuum actu-
ated recirculation door that closes off the outside
fresh air intake and recirculates the air that is
already inside the vehicle.
The optional air conditioner for all models is
designed for the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant.
The air conditioning system has an evaporator to cool
and dehumidify the incoming air prior to blending it
with the heated air. This air conditioning system
uses a fixed orifice tube in the liquid line near the
condenser outlet tube to meter refrigerant flow to the
evaporator coil. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, the
A/C low pressure switch on the accumulator cycles
the compressor clutch.
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the
refrigerant line, near the discharge port of the com-
pressor. The low pressure service port is located on
the liquid line at the side of the engine compartment,
near the condensor.Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low humidity air. The evaporator, located in the
HVAC housing on the dash panel below the instru-
ment panel, is cooled to temperatures near the freez-
ing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator and the moisture in the
air condenses on the evaporator fins. During periods
of high heat and humidity, an air conditioning sys-
tem will be more effective in the Recirculation Mode.
With the system in the Recirculation Mode, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, the air conditioning system performance
levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the temper-
ature of the air delivered to the interior of the vehi-
cle. It is important to understand the effect that
humidity has on the performance of the air condition-
ing system. When humidity is high, the evaporator
has to perform a double duty. It must lower the air
temperature, and it must lower the temperature of
the moisture in the air that condenses on the evapo-
rator fins. Condensing the moisture in the air trans-
fers heat energy into the evaporator fins and tubing.
This reduces the amount of heat the evaporator can
absorb from the air. High humidity greatly reduces
the ability of the evaporator to lower the temperature
of the air.
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Remov-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from the
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
Before proceeding, (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION). The air temperature in
the test room and in the vehicle must be a minimum
of 21É C (70É F) for this test.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1656 of 1803
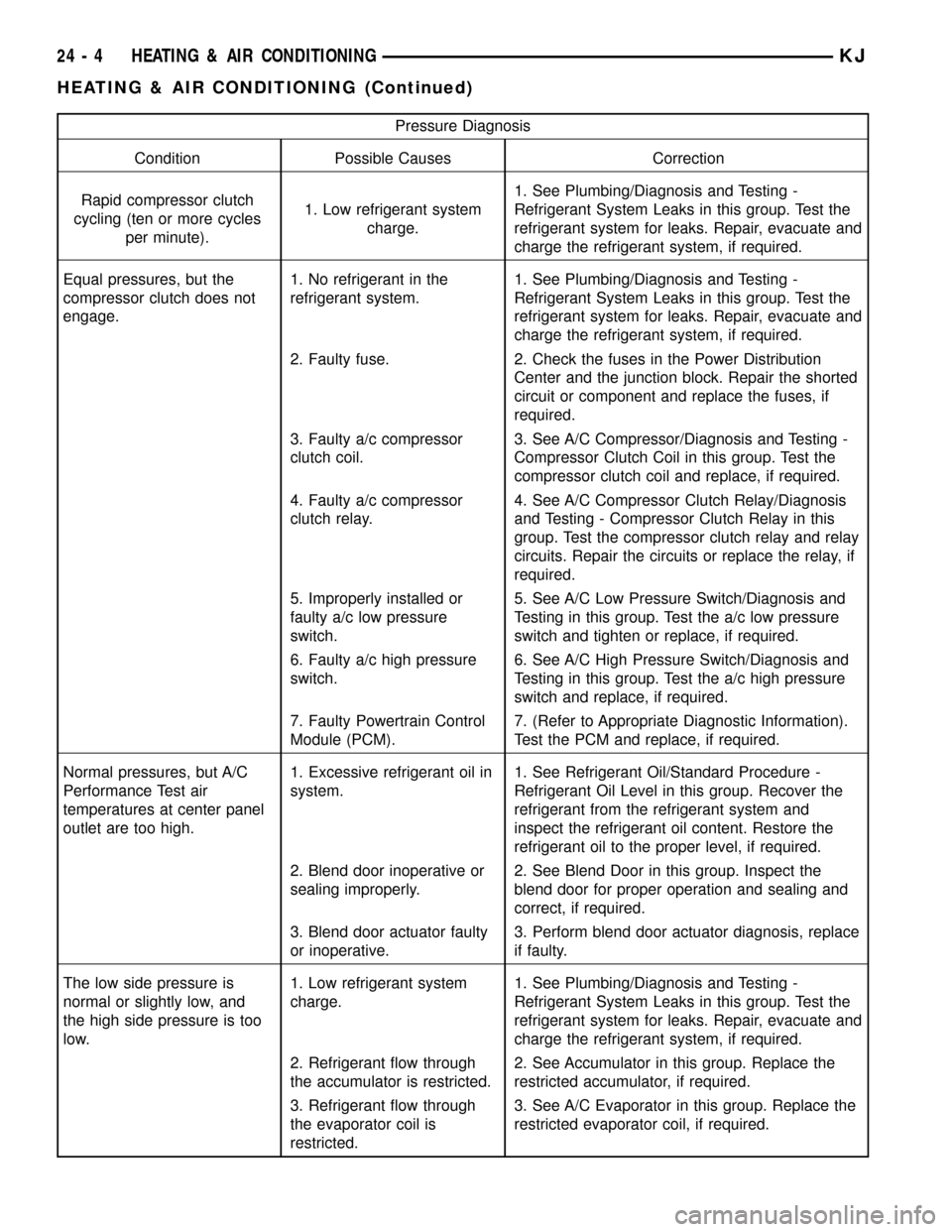
Pressure Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Rapid compressor clutch
cycling (ten or more cycles
per minute).1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
Equal pressures, but the
compressor clutch does not
engage.1. No refrigerant in the
refrigerant system.1. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
2. Faulty fuse. 2. Check the fuses in the Power Distribution
Center and the junction block. Repair the shorted
circuit or component and replace the fuses, if
required.
3. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch coil.3. See A/C Compressor/Diagnosis and Testing -
Compressor Clutch Coil in this group. Test the
compressor clutch coil and replace, if required.
4. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch relay.4. See A/C Compressor Clutch Relay/Diagnosis
and Testing - Compressor Clutch Relay in this
group. Test the compressor clutch relay and relay
circuits. Repair the circuits or replace the relay, if
required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty a/c low pressure
switch.5. See A/C Low Pressure Switch/Diagnosis and
Testing in this group. Test the a/c low pressure
switch and tighten or replace, if required.
6. Faulty a/c high pressure
switch.6. See A/C High Pressure Switch/Diagnosis and
Testing in this group. Test the a/c high pressure
switch and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).7. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information).
Test the PCM and replace, if required.
Normal pressures, but A/C
Performance Test air
temperatures at center panel
outlet are too high.1. Excessive refrigerant oil in
system.1. See Refrigerant Oil/Standard Procedure -
Refrigerant Oil Level in this group. Recover the
refrigerant from the refrigerant system and
inspect the refrigerant oil content. Restore the
refrigerant oil to the proper level, if required.
2. Blend door inoperative or
sealing improperly.2. See Blend Door in this group. Inspect the
blend door for proper operation and sealing and
correct, if required.
3. Blend door actuator faulty
or inoperative.3. Perform blend door actuator diagnosis, replace
if faulty.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly low, and
the high side pressure is too
low.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
2. Refrigerant flow through
the accumulator is restricted.2. See Accumulator in this group. Replace the
restricted accumulator, if required.
3. Refrigerant flow through
the evaporator coil is
restricted.3. See A/C Evaporator in this group. Replace the
restricted evaporator coil, if required.
24 - 4 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1670 of 1803

electric cooling fan operations. The switch is located
on the discharge line near the compressor. The
switch is screwed onto a fitting that contains a
Schrader-type valve, which allows the switch to be
serviced without discharging the refrigerant system.
The discharge line fitting is equipped with an O-ring
to seal the switch connection.
OPERATION
The A/C high pressure switch is connected in series
electrically with the A/C low pressure switch between
ground and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The switch contacts open and close causing the PCM
to turn the compressor clutch on and off. This pre-
vents compressor operation when the discharge line
pressure approaches high levels, and also reduces
electrical surging from compressor clutch engage-
ment.
The A/C high pressure switch controls the electric
cooling fan operation by monitoring refrigerant line
pressures. When the discharge line pressure rises
above 1900 to 2200 kPa (280 to 320 psi) the fan will
turn on. The cooling fan will turn off when the dis-
charge line pressure drops to 1600 kPa (235 psi).
The A/C high pressure switch controls the A/C
clutch operation by disengaging the clutch when the
discharge line pressure rises above 3100 to 3375 kPa
(450 to 490 psi). The switch contacts will close and
allow A/C clutch engagement when the discharge line
pressure drops to 1860 to 2275 kPa (270 to 330 psi).
The A/C high pressure switch is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The switch cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C HIGH
PRESSURE SWITCH
Before performing diagnosis of the A/C high pres-
sure switch, verify that the refrigerant system has
the correct refrigerant charge. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE)
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the A/C high pressure switch wire har-
ness connector from the switch on the refrigerant
system fitting.
(3) On the four terminal A/C high pressure switch,
check for continuity between terminals C and D. On
the two terminal A/C high pressure switch, check for
continuity between both terminals of the switch.
There should be continuity. If OK, test and repair theA/C switch sense circuit as required. If not OK,
replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
A/C high pressure switch, which is mounted to a fit-
ting on the non-flexible section of the discharge line
nearest the compressor.
(3) Unscrew the A/C high pressure switch from the
discharge line fitting.
(4) Remove the A/C high pressure switch from the
vehicle.
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the discharge line
fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the discharge line fitting.
Use only the specified O-rings as they are made of a
special material for the R-134a system. Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the com-
pressor in the vehicle(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - SPECIFICATIONS). (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/RE-
FRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
(2) Install and tighten the a/c high pressure switch
on the discharge line fitting. The switch should be
hand-tightened onto the discharge line fitting.
(3) Plug the wire harness connector into the a/c
high pressure switch.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The a/c low pressure switch is located on the top of
the accumulator. The switch is screwed onto an accu-
mulator fitting that contains a Schrader-type valve,
which allows the switch to be serviced without dis-
charging the refrigerant system. The accumulator fit-
ting is equipped with an O-ring to seal the switch
connection.
OPERATION
The a/c low pressure switch is connected in series
electrically with the a/c high pressure switch,
between ground and the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The switch contacts open and close causing
the PCM to turn the a/c compressor clutch on and
off. This regulates the refrigerant system pressure
and controls evaporator temperature. Controlling the
evaporator temperature prevents condensate water
24 - 18 CONTROLSKJ
A/C HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1671 of 1803

on the evaporator fins from freezing and obstructing
air conditioning system air flow.
The a/c low pressure switch contacts are open
when the suction pressure is approximately 141 kPa
(20.5 psi) or lower. The switch contacts will close
when the suction pressure rises to approximately 234
to 262 kPa (34 to 38 psi) or above. Lower ambient
temperatures, below approximately -1É C (30É F), will
also cause the switch contacts to open. This is due to
the pressure/temperature relationship of the refriger-
ant in the system.
The a/c low pressure switch is a factory-calibrated
unit. It cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if faulty
or damaged, it must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C LOW
PRESSURE SWITCH
Before performing diagnosis of the a/c low pressure
switch, be certain that the switch is properly
installed on the accumulator fitting. If the switch is
too loose it may not open the Schrader-type valve in
the accumulator fitting, which will prevent the
switch from correctly monitoring the refrigerant sys-
tem pressure. Remember that lower ambient temper-
atures, below about -1É C (30É F), during cold
weather will open the switch contacts and prevent
compressor operation due to the pressure/tempera-
ture relationship of the refrigerant.
Also verify that the refrigerant system has the cor-
rect refrigerant charge. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- A/C PERFORMANCE) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the a/c low pressure switch wire har-
ness connector from the switch on the accumulator
fitting.
(3) Install a jumper wire between the two cavities
of the a/c low pressure switch wire harness connector.
(4) Connect a manifold gauge set to the refrigerant
system service ports. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
EQUIPMENT) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE PORT)
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
(6) Place the A/C Heater mode control switch knob
in any A/C position and start the engine.
(7) Check for continuity between the two terminals
of the a/c low pressure switch. There should be con-
tinuity with a suction pressure reading of 262 kPa(38 psi) or above, and no continuity with a suction
pressure reading of 141 kPa (20.5 psi) or below. If
OK, test and repair the A/C switch sense circuit as
required. If not OK, replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the wire harness connector from the a/c
low pressure switch on the top of the accumulator
(Fig. 13).
(3) Unscrew the a/c low pressure switch from the
fitting on the top of the accumulator.
(4) Remove the O-ring seal from the accumulator
fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the accumulator fitting.
Use only the specified O-rings as they are made of a
special material for the R-134a system. Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the com-
pressor in the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT
OIL - DESCRIPTION)
Fig. 13 A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
1 - WIRING HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
3 - A/C LINE TO EVAPORATOR
4 - ACCUMULATOR MOUNTING BRACKET
5 - ACCUMULATOR
6 - A/C LOW PRESSURE LINE
KJCONTROLS 24 - 19
A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1679 of 1803

Fig. 21 HVAC CASE ASSEMBLY
1 - BLOWER MOTOR AND CAGE
2 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR LINKAGE
3 - RECIRCULATION DOOR VACUUM ACTUATOR
4 - CASE RETAINER SCREW
5 - BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR MOUNTING SCREWS
6 - ELECTRIC BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
7 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR FOR BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - HEATER CORE RETAINER TABS (4) AND SCREWS (2)9 - HEATER CORE
10 - HVAC CASE RETAINER CLIP
11 - HEATER CORE INPUT AND OUTPUT CONNECTIONS
12 - EVAPORATOR CONNECTION FLANGE
13 - HVAC CASE RETAINER SCREWS
14 - HVAC HOUSING
KJCONTROLS 24 - 27
RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)