air filter JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 1425 of 1803

WARNING: THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD, EXHAUST
PIPES AND CATALYTIC CONVERTER BECOME
VERY HOT DURING ENGINE OPERATION. ALLOW
ENGINE TO COOL BEFORE REMOVING OXYGEN
SENSOR.
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Disconnect wire connector from O2S sensor.
CAUTION: When disconnecting sensor electrical
connector, do not pull directly on wire going into
sensor.
(3) Remove O2S sensor with an oxygen sensor
removal and installation tool.
(4) Clean threads in exhaust pipe using appropri-
ate tap.
INSTALLATION
Threads of new oxygen sensors are factory coated
with anti-seize compound to aid in removal.DO
NOT add any additional anti-seize compound to
threads of a new oxygen sensor.
(1) Install O2S sensor. Tighten to 30 N´m (22 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect O2S sensor wire connector.
(3) Lower vehicle.
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The throttle body is located on the intake manifold.
Fuel does not enter the intake manifold through the
throttle body. Fuel is sprayed into the manifold by
the fuel injectors.
OPERATION
Filtered air from the air cleaner enters the intake
manifold through the throttle body. The throttle body
contains an air control passage controlled by an Idle
Air Control (IAC) motor. The air control passage is
used to supply air for idle conditions. A throttle valve
(plate) is used to supply air for above idle conditions.
Certain sensors are attached to the throttle body.
The accelerator pedal cable, speed control cable and
transmission control cable (when equipped) are con-
nected to the throttle body linkage arm.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the PCM.
REMOVAL
2.4L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
(1) Remove air cleaner tube at throttle body.
(2) Disconnect throttle body electrical connectors
at IAC motor and TPS.
(3) Remove all control cables from throttle body
(lever) arm. Refer to the Accelerator Pedal and Throt-
tle Cable section for removal/installation procedures.
(4) Disconnect necessary vacuum lines at throttle
body.
(5) Remove 3 throttle body mounting bolts (Fig.
23).
(6) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
(7) Check condition of old throttle body-to-intake
manifold o-ring.
3.7L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
(1) Remove air cleaner tube at throttle body.
(2) Disconnect throttle body electrical connectors
at IAC motor and TPS.
Fig. 23 THROTTLE BODY MOUNTING BOLTS - 2.4L
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - IGNITION COIL
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
KJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 43
OXYGEN SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1466 of 1803

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS . . . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS . 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIND NOISE . . . 3
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY
LUBRICATION.........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAT STAKING . . 3
SPECIFICATIONS........................4
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY...............................5BODY STRUCTURE.......................6
HOOD................................119
DOOR - FRONT........................121
DOORS - REAR........................128
SWING GATE..........................135
EXTERIOR............................140
INSTRUMENT PANEL....................147
INTERIOR.............................156
PAINT................................162
SEATS...............................164
STATIONARY GLASS....................172
SUNROOF.............................175
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................185
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: EYE PROTECTION SHOULD BE USED
WHEN SERVICING GLASS COMPONENTS. PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²USE A OSHA APPROVED BREATHING FILTER
WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN A CON-
FINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH
PETROLEUM OR ALCOHOL±BASED CLEANING
SOLVENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT STAND UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE
THAT IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched
in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the
outer body panel, electrical wiring, or other compo-
nents. Damage to vehicle can result.
²Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
²Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use
when welding.
²Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from
the battery when servicing electrical components
that are live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to
electrical system can result.²Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds
on painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
²Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning sol-
vents on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage
to finish or color can result.
²Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel
when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can
break.
DaimlerChrysler Corporation uses many different
types of push-in fasteners to secure the interior and
exterior trim to the body. Most of these fasteners can
be reused to assemble the trim during various repair
procedures. At times, a push-in fastener cannot be
removed without damaging the fastener or the com-
ponent it is holding. If it is not possible to remove a
fastener without damaging a component or body, cut
or break the fastener and use a new one when
installing the component. Never pry or pound on a
plastic or pressed-board trim component. Using a
suitable fork-type prying device, pry the fastener
from the retaining hole behind the component being
removed. When installing, verify fastener alignment
with the retaining hole by hand. Push directly on or
over the fastener until it seats. Apply a low-force pull
to the panel to verify that it is secure.
When it is necessary to remove components to ser-
vice another, it should not be necessary to apply
excessive force or bend a component to remove it.
Before damaging a trim component, verify hidden
fasteners or captured edges holding the component in
place.
KJBODY 23 - 1
Page 1702 of 1803

(1) Install the evaporator coil unit into of the lower
half of the HVAC housing. Be certain that the evap-
orator foam insulator wrap and rubber tube seal are
reinstalled.
(2) Reassemble and install the HVAC housing.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - ASSEMBLY)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLA-
TION)
NOTE: If the evaporator was replaced, add 60 milli-
liters (2 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the refrig-
erant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
A/C ORIFICE TUBE
DESCRIPTION
The fixed orifice tube is installed in the liquid line
(left-hand drive) or liquid line jumper (right-hand
drive) between the outlet of the condenser and the
inlet of the evaporator. The fixed orifice tube islocated in the end of the liquid line or liquid line
jumper that is closest to the condenser outlet tube.
The inlet end of the fixed orifice tube has a nylon
mesh filter screen, which filters the refrigerant and
helps to reduce the potential for blockage of the
metering orifice by refrigerant system contaminants
(Fig. 11). The outlet end of the tube has a nylon
mesh diffuser screen. The O-rings on the plastic body
of the fixed orifice tube seal the tube to the inside of
the liquid line and prevent the refrigerant from
bypassing the fixed metering orifice.
OPERATION
The fixed orifice tube is used to meter the flow of
liquid refrigerant into the evaporator coil. The high-
pressure liquid refrigerant from the condenser
expands into a low-pressure liquid as it passes
through the metering orifice and diffuser screen of
the fixed orifice tube.
The fixed orifice tube cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or plugged, the liquid line and fixed orifice
tube unit or liquid line jumper and fixed orifice tube
unit must be replaced.
REMOVAL
The fixed orifice tube is located in the liquid line
(Left-Hand Drive) or the liquid line jumper (Right-
Hand Drive) near the condenser. The orifice has filter
screens on the inlet and outlet ends of the tube body.
If the fixed orifice tube is faulty or plugged, the liq-
uid line unit or liquid line jumper unit must be
replaced. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/LIQUID LINE - REMOVAL)
INSTALLATION
The fixed orifice tube is located in the liquid line
(Left-Hand Drive) or the liquid line jumper (Right-
Hand Drive) near the condenser. The orifice has filter
screens on the inlet and outlet ends of the tube body.
If the fixed orifice tube is faulty or plugged, the liq-
uid line unit or liquid line jumper unit must be
Fig. 10 Blend Door
1 - DEFROSTER DOOR
2- HEATER CORE
3- BLEND DOORS
4- BLOWER MOTOR HOUSING
5- EVAPORATOR (A/C ONLY)
6- LOWER HVAC CASE ASSEMBLY
Fig. 11 FIXED ORIFICE TUBE - TYPICAL
1 - DIFFUSER SCREEN
2-9O9RINGS
3 - INLET FILTER SCREENS
4 - ORIFICE
24 - 50 PLUMBINGKJ
A/C EVAPORATOR (Continued)
Page 1703 of 1803

replaced. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/LIQUID LINE - REMOVAL)
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The accumulator is mounted in the engine com-
partment between the evaporator coil outlet tube and
the compressor inlet.
OPERATION
Refrigerant enters the accumulator canister as a
low pressure vapor through the inlet tube. Any liq-
uid, oil-laden refrigerant falls to the bottom of the
canister, which acts as a separator. A desiccant bag is
mounted inside the accumulator canister to absorb
any moisture which may have entered and become
trapped within the refrigerant system (Fig. 12).
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)
(3) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
low pressure cycling clutch switch.
(4) Loosen the screw that secures the accumulator
retaining band to the support bracket on the dash
panel (Fig. 13).
(5) Disconnect the suction line from the accumula-
tor outlet tube refrigerant line fitting. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COUPLERS)
Install plugs in, or tape over all of the opened refrig-
erant line fittings.
(6) Disconnect the accumulator inlet tube refriger-
ant line fitting from the evaporator outlet tube.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE
COUPLERS) Install plugs in, or tape over all of the
opened refrigerant line fittings.
(7) Pull the accumulator and retaining band unit
forward until the screw in the band is clear of the
slotted hole in the support bracket on the dash panel.
(8) Remove the accumulator from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
(1) Install the accumulator and retaining band as
a unit by sliding the screw in the band into the slot-
ted hole in the support bracket on the dash panel.
(2) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the accumulator inlet tube and the
Fig. 12 ACCUMULATOR - TYPICAL
1 - A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
2 - PRESSURE SWITCH FITTING
3 - OUTLET TO COMPRESSOR
4 - ANTI-SIPHON HOLE
5 - DESICCANT BAG
6 - OIL RETURN ORIFICE FILTER
7 - VAPOR RETURN TUBE
8 - ACCUMULATOR DOME
9 - O-RING SEAL
10 - INLET FROM EVAPORATOR
KJPLUMBING 24 - 51
A/C ORIFICE TUBE (Continued)
Page 1726 of 1803

an associated limp in will take two trips to illumi-
nate the MIL.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components. For example, a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injectoris installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIRFLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PCM CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT
The PCM may not be able to determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, it might store
diagnostic trouble codes as a result of spread connec-
tor pins.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE
ENGINE IDLE/NEUTRAL 2500 RPM/NEUTRAL
All Engines 2% to 8% of Maximum Load 9% to 17% of Maximum Load
25 - 20 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1731 of 1803

Fig. 1 FUEL DELIVERY COMPONENTS
1 - FUEL TANK 10 - EVAP CANISTER
2 - FUEL TANK STRAPS 11 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
3 - FUEL PUMP MODULE LOCK RING 12 - FRESH AIR TUBE
4 - CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE 13 - HOSE SLEEVE
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE FLANGE 14 - FUEL FILTER
6 - FUEL FILL HOSE 15 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
7 - FRESH AIR FILTER 16 - HEAT SHIELD
8 - FUEL FILL CAP/BEZEL 17 - SKID PLATE
9 - FUEL FILL TUBE
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 25
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 1734 of 1803

The pump contains a 3 port solenoid, a pump that
contains a switch, a spring loaded canister vent valve
seal, 2 check valves and a spring/diaphragm.
OPERATION
Immediately after a cold start, engine temperature
between 40ÉF and 86ÉF, the 3 port solenoid is briefly
energized. This initializes the pump by drawing air
into the pump cavity and also closes the vent seal.
During non-test test conditions, the vent seal is held
open by the pump diaphragm assembly which pushes
it open at the full travel position. The vent seal will
remain closed while the pump is cycling. This is due
to the operation of the 3 port solenoid which prevents
the diaphragm assembly from reaching full travel.
After the brief initialization period, the solenoid is
de-energized, allowing atmospheric pressure to enter
the pump cavity. This permits the spring to drive the
diaphragm which forces air out of the pump cavity
and into the vent system. When the solenoid is ener-
gized and de-energized, the cycle is repeated creating
flow in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump
is controlled in 2 modes:
PUMP MODE:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate
to achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten
the overall test time.
TEST MODE:The solenoid is energized with a
fixed duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur
when the diaphragm reaches the switch closure
point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5 inches
of water.
When the pump starts, the cycle rate is quite high.
As the system becomes pressurized pump rate drops.
If there is no leak the pump will quit. If there is a
leak, the test is terminated at the end of the test
mode.
If there is no leak, the purge monitor is run. If the
cycle rate increases due to the flow through the
purge system, the test is passed and the diagnostic is
complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank (Fig. 3). The LDP
fresh air filter is located on the end of a hose. This
hose is attached to the fuel fill tube assembly below
and near the fuel fill opening (Fig. 1). The LDP and
LDP filter are typically replaced (serviced) as one
unit.
(1) Raise vehicle.(2) Carefully remove two 3/4º vent hoses at sides
of LDP.
(3) Carefully remove other vapor/vacuum hoses
from LDP.
(4) Place a hydraulic jack under fuel tank.
(5) Loosen 2 fuel tank strap mounting bolts at
front of tank about 10 turns.
(6) Lower front of fuel tank about 1/2º.
(7) Remove 2 LDP mounting nuts (Fig. 3) and
lower LDP slightly to gain access to electrical connec-
tor (Fig. 4).
(8) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP. To dis-
connect: Slide red colored tab upward. Push on black
colored tab while removing connector.
(9) Remove LDP from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank. The LDP filter is
located on the end of a hose. This hose is attached to
the fuel fill tube assembly below and near the fuel
fill opening. The LDP and LDP filter are replaced
(serviced) as one unit.
(1) Install electrical connector to LDP. Push red
colored tab downward to lock connector to LDP.
(2) Position LDP and LDP bracket to fuel tank
mounting studs and install 2 nuts. Tighten nuts to 1
N´m (11 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Raise fuel tank to body and tighten 2 strap
bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 3 LDP LOCATION / MOUNTING
1 - LDP
2 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
3 - MOUNTING NUTS
4 - FRONT OF FUEL TANK
25 - 28 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1735 of 1803

(4) Carefully install vapor/vacuum lines to LDP,
and install hose to LDP filter.The vapor/vacuum
lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister duty cycle purge sole-
noid for damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled. Cer-
tain ORVR components can be found in (Fig. 1).
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DESCRIPTION
2.4L
The 2.4L 4-cylinder engine is equipped with a
closed crankcase ventilation system and a Positive
Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
²a PCV valve attached to the left/front side of the
valve cover (Fig. 5). It is secured with 1 bolt. An
o-ring is used to seal valve to valve cover (Fig. 6).
²the air cleaner housing
²tubes and hoses to connect the system compo-
nents.
3.7L
The 3.7L V-6 engine is equipped with a closed
crankcase ventilation system and a Positive Crank-
case Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 7). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 8).
²tubes and hoses to connect the system compo-
nents.
Fig. 4 LDP ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP (LDP)
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - FUEL FILTER
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1737 of 1803
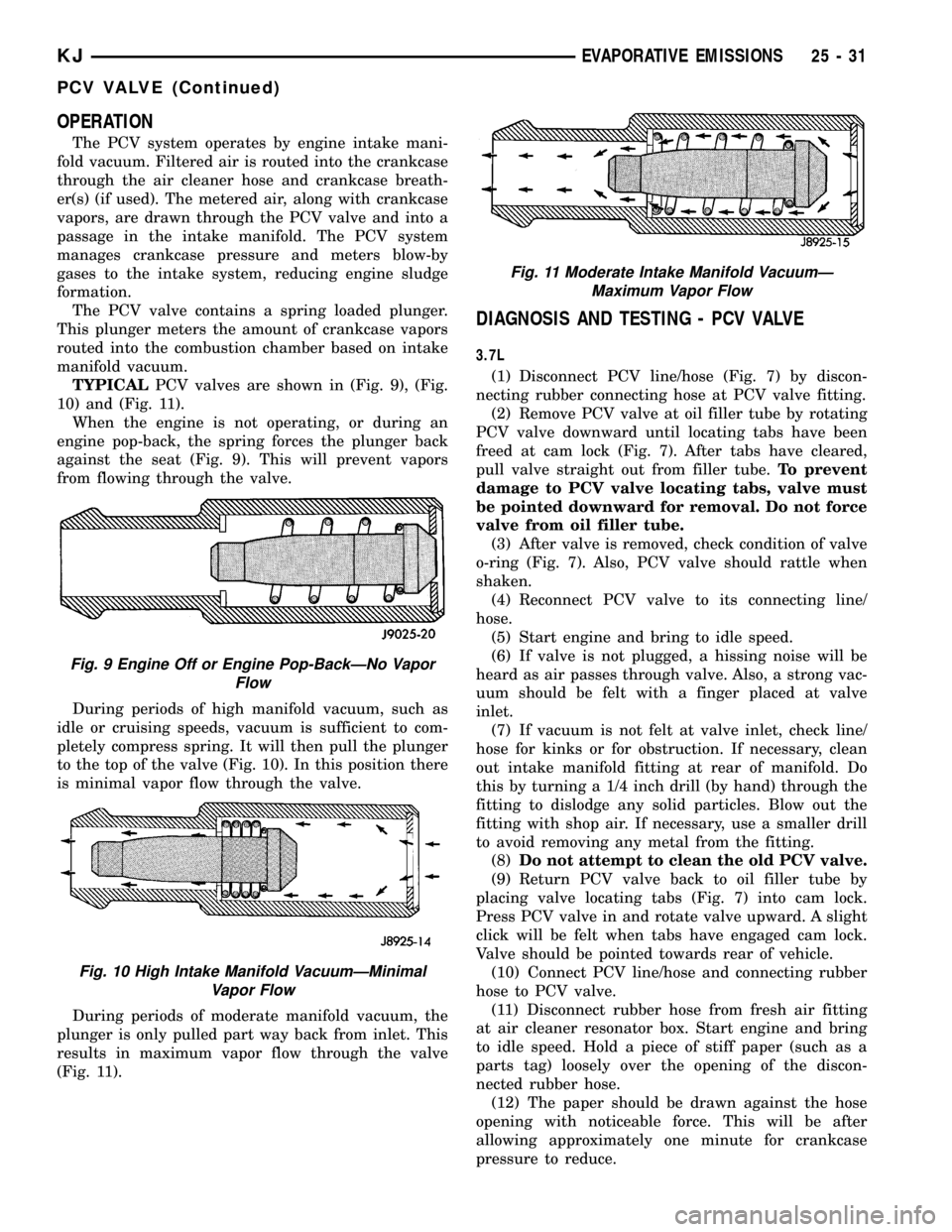
OPERATION
The PCV system operates by engine intake mani-
fold vacuum. Filtered air is routed into the crankcase
through the air cleaner hose and crankcase breath-
er(s) (if used). The metered air, along with crankcase
vapors, are drawn through the PCV valve and into a
passage in the intake manifold. The PCV system
manages crankcase pressure and meters blow-by
gases to the intake system, reducing engine sludge
formation.
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
This plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
TYPICALPCV valves are shown in (Fig. 9), (Fig.
10) and (Fig. 11).
When the engine is not operating, or during an
engine pop-back, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat (Fig. 9). This will prevent vapors
from flowing through the valve.
During periods of high manifold vacuum, such as
idle or cruising speeds, vacuum is sufficient to com-
pletely compress spring. It will then pull the plunger
to the top of the valve (Fig. 10). In this position there
is minimal vapor flow through the valve.
During periods of moderate manifold vacuum, the
plunger is only pulled part way back from inlet. This
results in maximum vapor flow through the valve
(Fig. 11).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE
3.7L
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 7) by discon-
necting rubber connecting hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward until locating tabs have been
freed at cam lock (Fig. 7). After tabs have cleared,
pull valve straight out from filler tube.To prevent
damage to PCV valve locating tabs, valve must
be pointed downward for removal. Do not force
valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 7). Also, PCV valve should rattle when
shaken.
(4) Reconnect PCV valve to its connecting line/
hose.
(5) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(6) If valve is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through valve. Also, a strong vac-
uum should be felt with a finger placed at valve
inlet.
(7) If vacuum is not felt at valve inlet, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at rear of manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out the
fitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
(8)Do not attempt to clean the old PCV valve.
(9) Return PCV valve back to oil filler tube by
placing valve locating tabs (Fig. 7) into cam lock.
Press PCV valve in and rotate valve upward. A slight
click will be felt when tabs have engaged cam lock.
Valve should be pointed towards rear of vehicle.
(10) Connect PCV line/hose and connecting rubber
hose to PCV valve.
(11) Disconnect rubber hose from fresh air fitting
at air cleaner resonator box. Start engine and bring
to idle speed. Hold a piece of stiff paper (such as a
parts tag) loosely over the opening of the discon-
nected rubber hose.
(12) The paper should be drawn against the hose
opening with noticeable force. This will be after
allowing approximately one minute for crankcase
pressure to reduce.
Fig. 9 Engine Off or Engine Pop-BackÐNo Vapor
Flow
Fig. 10 High Intake Manifold VacuumÐMinimal
Vapor Flow
Fig. 11 Moderate Intake Manifold VacuumÐ
Maximum Vapor Flow
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 31
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 1752 of 1803

HVAC CONTROL ASSEMBLY WINDOW
DEFOGGER FUNCTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, REAR..................8G-9
HVAC HOUSING - ASSEMBLY...........24-34
HVAC HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY........24-34
HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLATION........24-34
HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL............24-33
HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..........9-19,9-30
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.............21-79
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS, SCHEMATICS
AND DIAGRAMS....................21-100
HYDROMETER TEST - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................8F-11
IDENTIFICATION - DESCRIPTION,
FASTENER.........................Intro.-1
IDENTIFICATION AND INFORMATION -
DESCRIPTION, SECTION.............8W-01-6
IDENTIFICATION NUMBER -
DESCRIPTION, VEHICLE..............Intro.-8
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................14-35
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR -
INSTALLATION.......................14-36
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR -
OPERATION.........................14-35
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR - REMOVAL . . 14-36
IDLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION...........9-77
IDLER SHAFT - REMOVAL...............9-77
IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE -
DESCRIPTION.........................8E-13
IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE - OPERATION . . 8E-15
IGNITION COIL - DESCRIPTION...........8I-9
IGNITION COIL - INSTALLATION.........8I-10
IGNITION COIL - OPERATION.............8I-9
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL.............8I-10
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR -
DESCRIPTION........................8I-16
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR -
INSTALLATION.......................8I-16
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR - OPERATION . . 8I-16
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR - REMOVAL . . . 8I-16
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE, 2.4L.........8I-2
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE, 3.7L V-6.....8I-3
IGNITION CONTROL - DESCRIPTION.......8I-1
IGNITION CONTROL - OPERATION.........8I-1
IGNITION SWITCH - DESCRIPTION........19-8
IGNITION SWITCH - DESCRIPTION,
KEY-IN.............................19-10
IGNITION SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................19-8
IGNITION SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, KEY-IN.....................19-10
IGNITION SWITCH INSTALLATION,
INSTALLATION........................19-9
IGNITION SWITCH REMOVAL, REMOVAL . . . 19-9
IGNITION SYSTEM - TORQUE............8I-3
IGNITION TIMING - SPECIFICATIONS......8I-2
IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................8F-14
ILLUMINATION BULB - INSTALLATION,
COMPASS MINI-TRIP
.................8L-75
ILLUMINATION BULB - INSTALLATION,
HEATER-A/C CONTROL
................8L-78
ILLUMINATION BULB - INSTALLATION,
TRANSMISSION RANGE INDICATOR
......8L-83
ILLUMINATION BULB - REMOVAL,
COMPASS MINI-TRIP
.................8L-74
ILLUMINATION BULB - REMOVAL,
HEATER-A/C CONTROL
................8L-78
ILLUMINATION BULB - REMOVAL,
TRANSMISSION RANGE INDICATOR
......8L-82
IMMOBILIZER MODULE - DESCRIPTION,
SENTRY KEY
........................8E-15
IMMOBILIZER MODULE - INSTALLATION,
SENTRY KEY
........................8E-18
IMMOBILIZER MODULE - OPERATION,
SENTRY KEY
........................8E-16
IMMOBILIZER MODULE - REMOVAL,
SENTRY KEY
........................8E-17
IMPACT AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION, SIDE
..................8O-43
IMPACT AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE -
INSTALLATION, SIDE
.................8O-45
IMPACT AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION, SIDE
....................8O-43IMPACT AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE -
REMOVAL, SIDE.....................8O-44
IMPACT SENSOR - DESCRIPTION,
FRONT.............................8O-21
IMPACT SENSOR - INSTALLATION,
FRONT.............................8O-22
IMPACT SENSOR - OPERATION, FRONT . . . 8O-21
IMPACT SENSOR - REMOVAL, FRONT....8O-22
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, EFFECTS OF............21-125
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, ABS........8J-11
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, AIRBAG.....8J-12
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, BRAKE/
PARK BRAKE........................8J-13
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, CHARGING . . . 8J-15
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, COOLANT
LOW...............................8J-15
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, CRUISE.....8J-16
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, DOOR AJAR . . 8J-17
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, FOUR LOW
MODE.............................8J-29
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, FRONT FOG
LAMP..............................8J-19
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, FULL TIME . . . 8J-29
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, GATE AJAR . . 8J-20
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, GLASS
AJAR..............................8J-21
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, HIGH BEAM . . 8J-22
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, LOW FUEL . . . 8J-22
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, LOW OIL
PRESSURE..........................8J-23
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, OVERDRIVE
OFF ...............................8J-26
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, PART TIME . . 8J-29
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, REAR FOG
LAMP..............................8J-27
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, SEATBELT . . . 8J-27
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, SECURITY . . . 8J-28
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, SKIS........8J-31
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, TRANS
TEMP..............................8J-33
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, TURN
SIGNAL............................8J-34
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, WAIT-TO-
START .............................8J-35
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, WASHER
FLUID..............................8J-35
INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION, WATER-IN-
FUEL..............................8J-37
INDICATOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BRAKE.............................8J-14
INDICATOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
WASHER FLUID......................8J-36
INDICATOR - OPERATION, ABS..........8J-11
INDICATOR - OPERATION, AIRBAG.......8J-12
INDICATOR - OPERATION, BRAKE/PARK
BRAKE.............................8J-13
INDICATOR - OPERATION, CHARGING....8J-15
INDICATOR - OPERATION, COOLANT
LOW...............................8J-16
INDICATOR - OPERATION, CRUISE.......8J-17
INDICATOR - OPERATION, DOOR AJAR . . . 8J-17
INDICATOR - OPERATION, FOUR LOW
MODE.............................8J-30
INDICATOR - OPERATION, FRONT FOG
LAMP..............................8J-19
INDICATOR - OPERATION, FULL TIME....8J-30
INDICATOR - OPERATION, GATE AJAR....8J-20
INDICATOR - OPERATION, GLASS AJAR . . . 8J-21
INDICATOR - OPERATION, HIGH BEAM
....8J-22
INDICATOR - OPERATION, LOW FUEL
.....8J-22
INDICATOR - OPERATION, LOW OIL
PRESSURE
..........................8J-23
INDICATOR - OPERATION, OVERDRIVE
OFF
...............................8J-26
INDICATOR - OPERATION, PART TIME
....8J-29
INDICATOR - OPERATION, REAR FOG
LAMP
..............................8J-27
INDICATOR - OPERATION, SEATBELT
.....8J-28
INDICATOR - OPERATION, SECURITY
.....8J-28
INDICATOR - OPERATION, SKIS
.........8J-31
INDICATOR - OPERATION, TRANS TEMP
. . 8J-34
INDICATOR - OPERATION, TURN SIGNAL
. . 8J-34
INDICATOR - OPERATION, WAIT-TO-
START
.............................8J-35
INDICATOR - OPERATION, WASHER
FLUID
..............................8J-36INDICATOR - OPERATION, WATER-IN-
FUEL..............................8J-37
INDICATOR ILLUMINATION BULB -
INSTALLATION, TRANSMISSION
RANGE.............................8L-83
INDICATOR ILLUMINATION BULB -
REMOVAL, TRANSMISSION RANGE......8L-82
INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) - DESCRIPTION,
MALFUNCTION.......................8J-24
INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) - OPERATION,
MALFUNCTION.......................8J-24
INDICATOR TEST - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, BUILT-IN................8F-10
INDICATORS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TREAD WEAR................22-8
INFLATION - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
TIRE................................22-7
INITIAL OPERATION - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, POWER STEERING
PUMP.............................19-18
INITIALIZATION - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, SKIS....................8Q-8
INJECTION - DESCRIPTION, FUEL........14-29
INJECTOR - DESCRIPTION, FUEL........14-33
INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
FUEL..............................14-33
INJECTOR - OPERATION, FUEL..........14-33
INLET FILTER - INSTALLATION..........14-28
INLET FILTER - REMOVAL..............14-28
INPUT - OPERATION, ASD SENSE - PCM . . . 8I-4
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - ASSEMBLY . 21-138
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY -
DESCRIPTION......................21-133
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY -
DISASSEMBLY......................21-135
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - OPERATION . 21-135
INPUT SPEED SENSOR - DESCRIPTION . . 21-143
INPUT SPEED SENSOR - INSTALLATION . 21-143
INPUT SPEED SENSOR - OPERATION....21-143
INPUT SPEED SENSOR - REMOVAL.....21-143
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - ASSEMBLY.....8J-10
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DESCRIPTION . . . 8J-2
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................8J-7
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DISASSEMBLY . . . 8J-9
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - INSTALLATION . . 8J-11
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - OPERATION.....8J-4
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - REMOVAL......8J-9
INSTRUMENT PANEL ANTENNA CABLE -
INSTALLATION.......................8A-8
INSTRUMENT PANEL ANTENNA CABLE -
REMOVAL...........................8A-7
INSTRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY -
INSTALLATION......................23-151
INSTRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY -
REMOVAL.........................23-149
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL -
INSTALLATION......................23-154
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL -
REMOVAL.........................23-154
INSTRUMENT PANEL DRIVER SIDE
BEZELS - INSTALLATION..............23-154
INSTRUMENT PANEL DRIVER SIDE
BEZELS - REMOVAL.................23-153
INSTRUMENT PANEL END CAP -
INSTALLATION
......................23-153
INSTRUMENT PANEL END CAP -
REMOVAL
.........................23-153
INSTRUMENT PANEL PASSENGER SIDE
BEZEL - INSTALLATION
...............23-154
INSTRUMENT PANEL PASSENGER SIDE
BEZEL - REMOVAL
..................23-154
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER -
INSTALLATION
......................23-153
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER -
REMOVAL
.........................23-152
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION
.......................14-36
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
INSTALLATION
.......................14-38
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
OPERATION
.........................14-36
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
REMOVAL
..........................14-37
INTAKE MANIFOLD - DESCRIPTION
.......9-68
INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION
.......9-69
INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL
..........9-68
KJINDEX 13
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page