connectors JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 640 of 1803

NOTE: The integral flange on the left side of the
ACM cover is secured to the floor panel transmis-
sion tunnel with a short piece of double-faced tape
as an assembly aid during the manufacturing pro-
cess, but this tape does not require replacement
following service removal.
(7) Reinstall the center console onto the top of the
floor panel transmission tunnel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLATION).
(8) Do not reconnect the battery negative cable at
this time. The airbag system verification test proce-
dure should be performed following service of any
supplemental restraint system component. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - VERIFICATION TEST).
CHILD TETHER ANCHOR
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with three, fixed-position,
child seat tether anchors (Fig. 9). Two anchors are
integral to the back of the right rear seat back panel,
and one is integral to the left rear seat back panel.
The child seat tether anchors cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, they must be
replaced as a unit with the rear seat back panel.
OPERATION
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the proper use of the factory-in-
stalled child seat tether anchors.
CLOCKSPRING
DESCRIPTION
The clockspring assembly is secured with two inte-
gral plastic latches onto the upper steering column
housing near the top of the steering column behind
the steering wheel (Fig. 10). The clockspring consists
of a flat, round molded plastic case with a stubby tail
that hangs below the steering column and contains
two connector receptacles that face toward the
instrument panel (Fig. 11). Within the plastic hous-
ing is a spool-like molded plastic rotor with a large
exposed hub and several plastic rollers. The upper
surface of the rotor hub has a large center hole, a
release button, a clear plastic inspection window, two
short pigtail wires with connectors, and a connector
receptacle that faces toward the steering wheel. Two
versions of the clockspring are used on this model,
one is a seven circuit unit for vehicles not equipped
with optional remote radio switches on the steering
wheel and can be visually identified by the use of yel-
low heat-shrink tubing on the pigtail wires, while the
other is a nine circuit unit for vehicles with remote
radio switches and can be visually identified by the
use of black heat-shrink tubing on the pigtail wires.
A rubber bumper block is located on each side of
the tower formation that contains the connector
receptacle and pigtail wires on the upper surface of
the rotor hub. The lower surface of the rotor hub has
Fig. 9 Child Tether Anchors
1 - REAR SEAT BACK (LEFT)
2 - REAR SEAT BACK (RIGHT)
3 - CHILD TETHER ANCHOR (3)
Fig. 10 Clockspring
1 - PIGTAIL WIRE (2)
2 - UPPER CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
3 - BUMPER (2)
4 - BRACKET (2)
5 - LABEL
6 - SHIELD
7 - CASE
8 - WINDOW
9 - ROTOR
KJRESTRAINTS 8O - 13
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 641 of 1803

a molded plastic turn signal cancel cam with a single
lobe that is integral to the rotor. Within the plastic
case and wound around the rotor spool is a long rib-
bon-like tape that consists of several thin copper wire
leads sandwiched between two thin plastic mem-
branes. The outer end of the tape terminates at the
connector receptacles that face the instrument panel,
while the inner end of the tape terminates at the pig-
tail wires and connector receptacle on the hub of the
clockspring rotor that face the steering wheel.
Service replacement clocksprings are shipped pre-
centered and with a molded plastic shield that snaps
onto the rotor over the release button. The release
button secures the centered clockspring rotor to the
clockspring case and the shield prevents the release
button from being inadvertently depressed during
shipment and handling, but the shield must be
removed from the clockspring after it is installed on
the steering column. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - CLOCKSPRING CENTERING).
The clockspring cannot be repaired. If the clock-
spring is faulty, damaged, or if the driver airbag has
been deployed, the clockspring must be replaced.
OPERATION
The clockspring is a mechanical electrical circuit
component that is used to provide continuous electri-
cal continuity between the fixed instrument panel
wire harness and the electrical components mounted
on or in the rotating steering wheel. On this model
the rotating electrical components include the driver
airbag, the horn switch, the speed control switches,and the remote radio switches, if the vehicle is so
equipped. The clockspring case is positioned and
secured to the upper steering column housing near
the top of the steering column. The connector recep-
tacles on the tail of the fixed clockspring case connect
the clockspring to the vehicle electrical system
through two take outs with connectors from the
instrument panel wire harness. The clockspring rotor
is movable and is keyed by the tower formation that
is molded onto the upper surface of the rotor hub to
an opening that is cast into the steering wheel arma-
ture. Rubber bumper blocks on either side of the
clockspring tower formation eliminate contact noise
between the clockspring tower and the steering
wheel. The lobe of the turn signal cancel cam on the
lower surface of the clockspring rotor hub contacts a
turn signal cancel actuator of the multi-function
switch to provide automatic turn signal cancellation.
The yellow-sleeved pigtail wires on the upper surface
of the clockspring rotor connect the clockspring to the
driver airbag, while a steering wheel wire harness
connects the connector receptacle on the upper sur-
face of the clockspring rotor to the horn switch and,
if the vehicle is so equipped, to the optional speed
control switches and remote radio switches on the
steering wheel.
Like the clockspring in a timepiece, the clockspring
tape has travel limits and can be damaged by being
wound too tightly during full stop-to-stop steering
wheel rotation. To prevent this from occurring, the
clockspring is centered when it is installed on the
steering column. Centering the clockspring indexes
the clockspring tape to the movable steering compo-
nents so that the tape can operate within its
designed travel limits. However, if the clockspring is
removed from the steering column or if the steering
shaft is disconnected from the steering gear, the
clockspring spool can change position relative to the
movable steering components and must be re-cen-
tered following completion of the service or the tape
may be damaged. Service replacement clocksprings
are shipped pre-centered and with a plastic shield
installed over the clockspring release button. This
shield should not be removed and the release button
should not be depressed until the clockspring has
been installed on the steering column. If the release
button is depressed before the clockspring is installed
on a steering column, the clockspring centering pro-
cedure must be performed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING CENTERING).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING
CENTERING
The clockspring is designed to wind and unwind
when the steering wheel is rotated, but is only
Fig. 11 Clockspring Latches
1 - CASE
2 - LATCH (2)
3 - ROTOR
4 - CANCEL CAM
5 - LOWER CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE (2)
8O - 14 RESTRAINTSKJ
CLOCKSPRING (Continued)
Page 643 of 1803

WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
NOTE: Before starting this procedure, be certain to
turn the steering wheel until the front wheels are in
the straight-ahead position.
(1) Place the front wheels in the straight ahead
position.
(2) Remove the driver airbag from the steering
wheel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
DRIVER AIRBAG - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the steering wheel wire harness
connector from the upper clockspring connector
receptacle.
(4) Remove the steering wheel from the steering
column. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/STEER-
ING WHEEL - REMOVAL).
(5) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional tilt
steering column, move the tilt steering column to the
fully lowered position and leave the tilt release lever
in the released (down) position.
(6) From below the steering column, remove the
two screws that secure the lower shroud to the upper
shroud (Fig. 13).
(7) Using hand pressure, push gently inward on
both sides of the upper shroud near the parting line
between the upper and lower shrouds to release the
snap features that secure the two halves to each
other.
(8) Remove both the upper and lower shrouds from
the steering column.
(9) Disconnect the two instrument panel wire har-
ness connectors for the clockspring from the two con-
nector receptacles below the steering column on the
back of the clockspring housing.
(10) Using a small thin-bladed screwdriver, release
the two integral plastic latches that secure the back
of the clockspring housing to the steering column
lock housing.(11) Remove the clockspring from the steering col-
umn lock housing. The clockspring cannot be
repaired. It must be replaced if faulty or damaged, or
if the driver airbag has been deployed.
(12) If the removed clockspring is to be reused, be
certain that the release button on the clockspring
rotor is raised and latched to secure the rotor to the
clockspring case to maintain clockspring centering
until it is reinstalled on the steering column. If clock-
spring centering is not maintained, the clockspring
must be centered again before it is reinstalled. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING CEN-
TERING).
INSTALLATION
The clockspring cannot be repaired. It must be
replaced if faulty or damaged, or if the driver airbag
has been deployed.
If the clockspring is not properly centered in rela-
tion to the steering wheel, steering shaft and steer-
ing gear, it may be damaged. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING CEN-
Fig. 13 Clockspring Remove/Install
1 - UPPER SHROUD
2 - CLOCKSPRING
3 - LATCH (2)
4 - SCREW (2)
5 - LOWER SHROUD
6 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR (2)
7 - MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH
8 - STEERING COLUMN
8O - 16 RESTRAINTSKJ
CLOCKSPRING (Continued)
Page 644 of 1803

TERING). Service replacement clocksprings are
shipped pre-centered, with the release button
engaged (raised) and a molded plastic shield installed
over the release button. This release button should
not be disengaged and the shield should not be
removed until the clockspring has been installed on
the steering column. If the release button is disen-
gaged before the clockspring is installed on a steering
column, the clockspring centering procedure must be
performed.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
NOTE: Before starting this procedure, be certain to
turn the steering wheel until the front wheels are in
the straight-ahead position.
(1) Carefully slide the centered clockspring down
over the steering column upper shaft until the two
integral plastic latches on the back of the clockspring
housing are fully engaged through their openings in
the steering column lock housing (Fig. 13).
(2) Reconnect the two instrument panel wire har-
ness connectors for the clockspring to the two connec-
tor receptacles below the steering column on the back
of the clockspring housing.
(3) Position the upper and lower shrouds onto the
steering column.
(4) Align the snap features on the lower shroud
with the receptacles on the upper shroud and apply
hand pressure to snap them together.
(5) From below the steering column, install and
tighten the two screws that secure the lower shroud
to the upper shroud. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (18
in. lbs.).
(6) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional tilt
steering column, move the tilt steering column back
to the fully raised position and move the tilt release
lever back to the locked (up) position.(7) Reinstall the steering wheel onto the steering
column. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/STEER-
ING WHEEL - INSTALLATION).
NOTE: Be certain that the steering wheel mounting
screw is tightened to the proper torque specifica-
tion to ensure proper clockspring operation.
(8) Reconnect the steering wheel wire harness con-
nector to the upper clockspring connector receptacle.
(9) Reinstall the driver airbag onto the steering
wheel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
DRIVER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION
The black, injection molded, thermoplastic driver
airbag protective trim cover is the most visible part
of the driver airbag (Fig. 14). The driver airbag is
located in the center of the steering wheel, where it
is secured with two screws to the two horizontal
spokes of the four-spoke steering wheel armature.
Base models have a Jeeptlogo embossed in the cen-
ter of the trim cover, while premium models feature a
stamped, satin polished emblem with the Jeeptlogo
applied to the center of the trim cover. Concealed
beneath the driver airbag trim cover are the horn
switch, the folded airbag cushion, the airbag retainer
or housing, the airbag inflator, and the retainers that
secure the inflator to the airbag housing. The airbag
cushion, housing, and inflator are secured within an
integral receptacle molded into the back of the trim
cover.
Fig. 14 Driver Airbag Trim Cover
1 - STEERING WHEEL
2 - TRIM COVER
KJRESTRAINTS 8O - 17
CLOCKSPRING (Continued)
Page 647 of 1803

(4) Disconnect the steering wheel wire harness
connector for the horn switch from the horn switch
feed pigtail wire connector, which is located on the
back of the driver airbag housing.
CAUTION: Do not pull on the clockspring pigtail
wires or pry on the connector insulator to disen-
gage the connector from the driver airbag inflator
connector receptacle. Improper removal of these
pigtail wires and their connector insulators can
result in damage to the airbag circuits or connector
insulators.
(5) The clockspring driver airbag pigtail wire con-
nectors are secured by integral latches to the airbag
inflator connector receptacles, which are located on
the back of the driver airbag housing. Depress the
latches on each side of each connector insulator and
pull the insulators straight out from the airbag infla-
tor to disconnect them from the connector recepta-
cles.
(6) Remove the driver airbag from the steering
wheel.
(7) If the driver airbag has been deployed, the
clockspring must be replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
The following procedure is for replacement of a
faulty or damaged driver airbag. If the driver airbag
has been deployed, the clockspring must also be
replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLATION).
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.WARNING: USE EXTREME CARE TO PREVENT ANY
FOREIGN MATERIAL FROM ENTERING THE DRIVER
AIRBAG, OR BECOMING ENTRAPPED BETWEEN
THE DRIVER AIRBAG CUSHION AND THE DRIVER
AIRBAG TRIM COVER. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS
WARNING COULD RESULT IN OCCUPANT INJURIES
UPON AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.
WARNING: THE DRIVER AIRBAG TRIM COVER
MUST NEVER BE PAINTED. REPLACEMENT AIR-
BAGS ARE SERVICED IN THE ORIGINAL COLORS.
PAINT MAY CHANGE THE WAY IN WHICH THE
MATERIAL OF THE TRIM COVER RESPONDS TO AN
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT. FAILURE TO OBSERVE
THIS WARNING COULD RESULT IN OCCUPANT
INJURIES UPON AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.
(1) Position the driver airbag close enough to the
steering wheel to reconnect all three electrical con-
nections on the back of the airbag housing.
(2) When installing the driver airbag, reconnect
the two clockspring driver airbag pigtail wire connec-
tors to the airbag inflator connector receptacles by
pressing straight in on the connectors (Fig. 16). Be
certain to engage each keyed and color-coded connec-
tor to the matching connector receptacle. You can be
certain that each connector is fully engaged in its
receptacle by listening carefully for a distinct, audi-
ble click as the connector latches snap into place.
(3) Reconnect the steering wheel wire harness con-
nector for the horn switch to the horn switch feed
pigtail wire connector, which is located at the back of
the driver airbag housing.
(4) Carefully position the driver airbag in the
steering wheel. Be certain that the clockspring pig-
tail wires and steering wheel wire harness in the
steering wheel hub area are not pinched between the
driver airbag and the steering wheel armature.
(5) From the underside of the steering wheel,
install and tighten the two screws that secure the
driver airbag to the steering wheel armature.
Tighten the screws to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(6) Do not reconnect the battery negative cable at
this time. The airbag system verification test proce-
dure should be performed following service of any
supplemental restraint system component. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - VERIFICATION TEST).
8O - 20 RESTRAINTSKJ
DRIVER AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 675 of 1803

A ªtap downº feature is used to decelerate without
disengaging the speed control system. To decelerate
from an existing recorded target speed, momentarily
depress the COAST switch. For each switch activa-
tion, speed will be lowered approximately 1 mph.
OVERSHOOT/UNDERSHOOT
If the vehicle operator repeatedly presses and
releases the SET button with their foot off of the
accelerator (referred to as a ªlift foot setº), the vehicle
may accelerate and exceed the desired set speed by
up to 5 mph (8 km/h). It may also decelerate to less
than the desired set speed, before finally achieving
the desired set speed.
The Speed Control System has an adaptive strat-
egy that compensates for vehicle-to-vehicle variations
in speed control cable lengths. When the speed con-
trol is set with the vehicle operators foot off of the
accelerator pedal, the speed control thinks there is
excessive speed control cable slack and adapts
accordingly. If the ªlift foot setsº are continually used,
a speed control overshoot/undershoot condition will
develop.
To ªunlearnº the overshoot/undershoot condition,
the vehicle operator has to press and release the set
button while maintaining the desired set speed using
the accelerator pedal (not decelerating or accelerat-
ing), and then turning the cruise control switch to
the OFF position (or press the CANCEL button if
equipped) after waiting 10 seconds. This procedure
must be performed approximately 10±15 times to
completely unlearn the overshoot/undershoot condi-
tion.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Perform a vehicle road test to verify reports of
speed control system malfunction. The road testshould include attention to the speedometer. Speed-
ometer operation should be smooth and without flut-
ter at all speeds.
Flutter in the speedometer indicates a problem
which might cause surging in the speed control sys-
tem. The cause of any speedometer problems should
be corrected before proceeding. Refer to Group 8J,
Instrument Cluster for speedometer diagnosis.
If a road test verifies a system problem and the
speedometer operates properly, check for:
²A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). If a DTC
exists, conduct tests per the Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures service manual.
²A misadjusted brake (stop) lamp switch. This
could also cause an intermittent problem.
²Loose, damaged or corroded electrical connec-
tions at the servo. Corrosion should be removed from
electrical terminals and a light coating of Mopar
MultiPurpose Grease, or equivalent, applied.
²Leaking vacuum reservoir.
²Loose or leaking vacuum hoses or connections.
²Defective one-way vacuum check valve.
²Secure attachment of both ends of the speed con-
trol servo cable.
²Smooth operation of throttle linkage and throttle
body air valve.
²Failed speed control servo. Do the servo vacuum
test.
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - SPEED CONTROL
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Servo Mounting Bracket-to-Servo Nuts 9 - 75
Servo Mounting Bracket-to-Body Bolts 12 - 105
Speed Control Switch Mounting Screws 1.5 - 14
Vacuum Reservoir Mounting Screws 3 - 20
8P - 2 SPEED CONTROLKJ
SPEED CONTROL (Continued)
Page 682 of 1803
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VEHICLE THEFT
SECURITY SYSTEM....................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SKIS
INITIALIZATION........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SENTRY KEY
TRANSPONDER PROGRAMMING..........8
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DOOR
CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH..............10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
HOOD AJAR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HOOD AJAR
SWITCH............................12REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
HOOD AJAR SWITCH BRACKET
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
HOOD AJAR SWITCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................14
INTRUSION TRANSCEIVER MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................15
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................16
SIREN
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................17
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
TRANSPONDER KEY
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
DESCRIPTION
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) is an
available factory-installed option on this model (Fig.
1). The VTSS is comprised of two primary sub-
systems: Vehicle Theft Alarm (VTA) and Sentry Key
Immobilizer System (SKIS). The VTA is an active
system that provides visual and audible responses as
deterrents to and warnings of unauthorized vehicle
tampering. The SKIS is a passive system that effec-
tively immobilizes the vehicle against unauthorized
operation. Following are paragraphs which describe
the various components that are included in each of
these subsystems of the VTSS.
Hard wired circuitry connects many of the VTSS
components to each other through the electrical sys-
tem of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
VTSS components through the use of a combination
of soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectorsand insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
VEHICLE THEFT ALARM The VTA is available in
two different configurations for this vehicle: One con-
figuration is designed for vehicles manufactured for
sale in North America; while, the other configuration
is designed for vehicles manufactured for sale in
markets outside of North America, also referred to as
Rest-Of-World or ROW. In addition, the VTA for
ROW is available in two versions: base and premium.
All vehicles equipped with VTA are also equipped
with the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system and
the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS), regard-
less of their market destination. The North American
and ROW base version of the VTA provides perimeter
vehicle protection by monitoring the vehicle doors,
the tailgate, the rear flip-up glass and, for vehicles
built for certain markets where it is required equip-
ment, the hood. If unauthorized vehicle use or tam-
pering is detected, these systems respond by pulsing
the horn and flashing certain exterior lamps. The
ROW premium version of the VTA is only available
KJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 1
Page 687 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VEHICLE THEFT
SECURITY SYSTEM
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) is
divided into two basic subsystems: Vehicle Theft
Alarm (VTA) and Sentry Key Immobilizer System
(SKIS). Following are the recommended procedures
for diagnosis and testing of each of these two sub-
systems.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
VEHICLE THEFT ALARM
Models equipped with the Rest-Of-World (ROW)
premium version of the Vehicle Theft Alarm (VTA)
provide some preliminary diagnostic feedback by illu-minating the security indicator located in the Elec-
troMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC). If the
security indicator illuminates with the ignition
switch in the On position, it indicates that there is a
communication problem between the Intrusion
Transceiver Module (ITM) and the Body Control
Module (BCM), or between the ITM and the siren
module. The BCM will also turn on the security indi-
cator if it receives a message from the ITM indicating
that the ITM has stored a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) for a siren module fault.
The hard wired circuits and components of the
VTA may be diagnosed and tested using conventional
diagnostic tools and procedures. However, conven-
tional diagnostic methods may not prove conclusive
in the diagnosis of the Body Control Module (BCM),
the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC),
the Intrusion Transceiver Module (ITM), or the Pro-
grammable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus
network. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the BCM, the EMIC, the ITM,
and the PCI data bus network inputs and outputs
related to the VTA requires the use of a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
8Q - 6 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYKJ
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 688 of 1803

SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SKIS INDICATOR FAILS TO
LIGHT DURING BULB TEST1. SKIS indicator faulty. 1. Test and replace the instrument cluster as
required.
2. Fuse faulty. 2. Test and replace the SKIM fused B(+) and
fused ignition switch output (run-start) fuses in the
Junction Block (JB) as required.
3. Ground circuit faulty. 3. Test and repair the SKIM ground circuit as
required.
4. Fused B(+) circuit faulty. 4. Test and repair the SKIM fused B(+) circuit as
required.
5. Fused ignition switch
output circuit faulty.5. Test and repair the SKIM fused ignition switch
output (run-start) circuit as required.
SKIS INDICATOR FLASHES
WHEN IGNITION SWITCH IS
TURNED TO9ON9
POSITION1. Invalid key in ignition
switch lock cylinder.1. Replace the key with a known valid key.
2. Key-related fault. 2. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to diagnose the
key-related fault. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
SKIS INDICATOR LIGHTS
SOLID FOLLOWING BULB
TEST1. SKIS system malfunction/
fault detected.1. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to diagnose the SKIS.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
2. SKIS system inoperative. 2. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to diagnose the SKIS.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
SKIS INDICATOR FAILS TO LIGHT DURING BULB TEST
If the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) indi-
cator in the instrument cluster fails to illuminate for
about three seconds after the ignition switch is
turned to the On position (bulb test), perform the
instrument cluster actuator test. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). If the SKIS indicator still fails to
light during the bulb test, a wiring problem resulting
in the loss of battery current or ground to the Sentry
Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) should be sus-
pected, and the following procedure should be used
for diagnosis. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
details of wire harness routing and retention, connec-
tor pin-out information and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
NOTE: The following tests may not prove conclu-
sive in the diagnosis of this system. The most reli-
able, efficient, and accurate means to diagnose the
Sentry Key Immobilizer System requires the use of
a DRBIIITscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information.(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse (Fuse 33 - 10
ampere) in the Junction Block (JB). If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
(Fuse 33 - 10 ampere) in the JB. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the open B(+) circuit between the
JB and the battery as required.
(3) Check the fused ignition switch output (run-
start) fuse (Fuse 15 - 10 ampere) in the JB. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or
component as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (run-start) fuse (Fuse 15 - 10 ampere) in the
JB. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open
fused ignition switch output (run-start) circuit
between the JB and the ignition switch as required.
(5) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector for the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module
(SKIM) from the SKIM connector receptacle. Check
for continuity between each of the two ground circuit
cavities of the instrument panel wire harness connec-
tor for the SKIM and a good ground. There should be
KJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 7
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 691 of 1803
Theft Security System (VTSS) have a door cylinder
lock switch secured to the back of the key lock cylin-
der inside each front door (Fig. 2). The door cylinder
lock switch is a resistor multiplexed momentary
switch that is hard wired in series between the door
lock switch ground and right or left cylinder lock
switch mux circuits of the Body Control Module
(BCM) through the front door wire harness. The door
cylinder lock switches are driven by the key lock cyl-
inders and contain two internal resistors. One resis-
tor value is used for the Lock position, and one for
the Unlock position.
The door cylinder lock switches cannot be adjusted
or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, they must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The door cylinder lock switches are actuated by the
key lock cylinder when the key is inserted in the lock
cylinder and turned to the lock or unlock positions.
The door cylinder lock switch close a circuit between
the door lock switch ground circuit and the left or
right cylinder lock switch mux circuits through one of
two internal resistors for the Body Control Module
(BCM) when either front door key lock cylinder is in
the Lock, or Unlock positions. The BCM reads the
switch status through an internal pull-up, then uses
this information as an input for the Vehicle Theft
Security System (VTSS) operation.
The door cylinder lock switches and circuits can be
diagnosed using conventional diagnostic tools and
methods.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DOOR CYLINDER
LOCK SWITCH
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect the door cylinder lock switch pigtail
wire connector from the door wire harness connector.
(2) Using a ohmmeter, check the switch resistance
checks between the two terminals in the door cylin-
der lock switch pigtail wire connector. Actuate the
switch by rotating the key in the door lock cylinder
to test for the proper resistance values in each of the
two switch positions, as shown in the Door Cylinder
Lock Switch Test table.
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH TEST
Switch Position Resistance
( 10%)
Left Side Right Side
Lock (Clockwise) Unlock
(Counterclockwise)473 Ohms
Unlock
(Counterclockwise)Lock (Clockwise) 1.994 Kilohms
(3) If a door cylinder lock switch fails either of the
resistance tests, replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the outside door handle unit from the
outer door panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOOR -
FRONT/EXTERIOR HANDLE - REMOVAL).
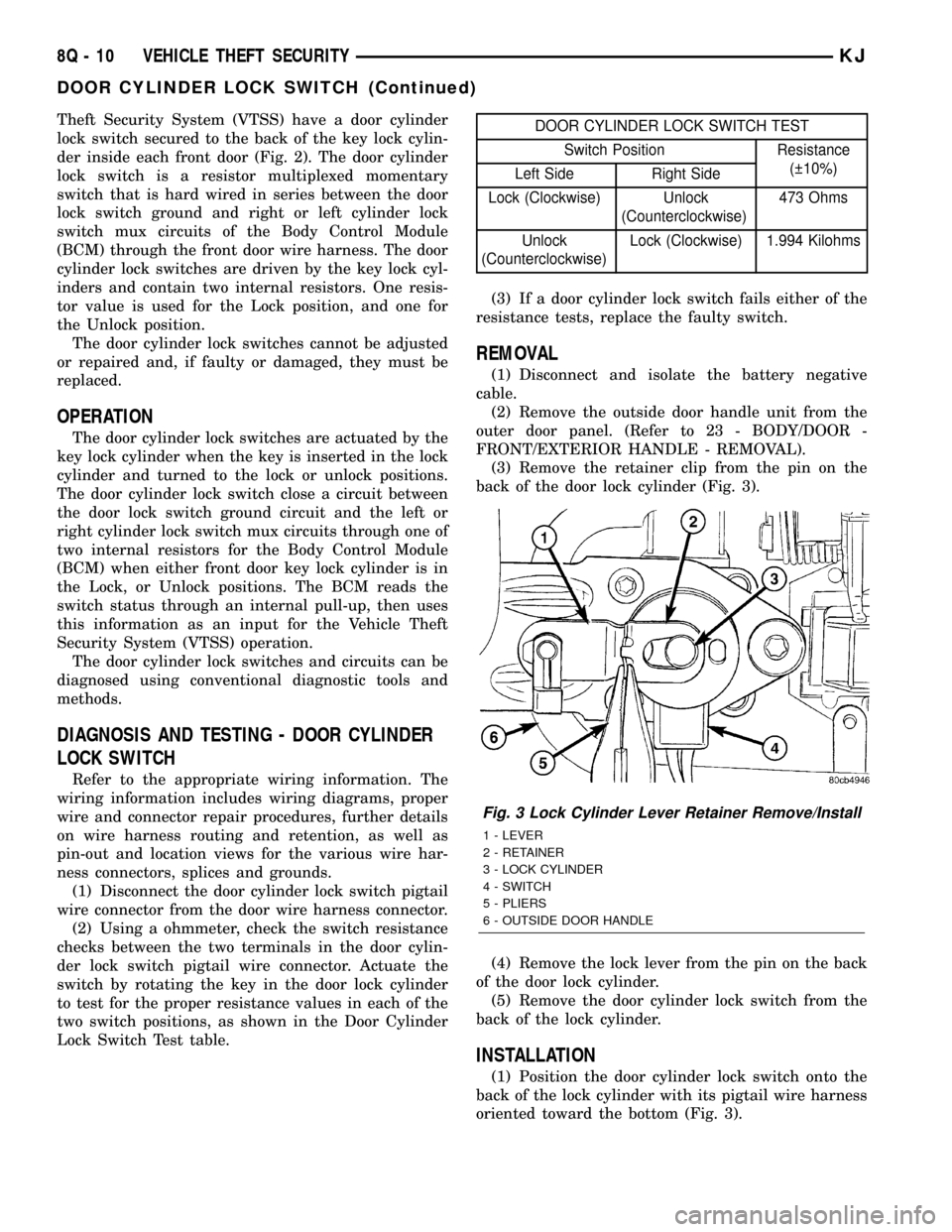
(3) Remove the retainer clip from the pin on the
back of the door lock cylinder (Fig. 3).
(4) Remove the lock lever from the pin on the back
of the door lock cylinder.
(5) Remove the door cylinder lock switch from the
back of the lock cylinder.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the door cylinder lock switch onto the
back of the lock cylinder with its pigtail wire harness
oriented toward the bottom (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 Lock Cylinder Lever Retainer Remove/Install
1 - LEVER
2 - RETAINER
3 - LOCK CYLINDER
4 - SWITCH
5 - PLIERS
6 - OUTSIDE DOOR HANDLE
8Q - 10 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYKJ
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH (Continued)