Drive JEEP WRANGLER 1994 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: WRANGLER, Model: JEEP WRANGLER 1994Pages: 1770, PDF Size: 75.27 MB
Page 43 of 1770

Fig. 13 Differential Housing Cover Installed
Fig. 14 Front Drive Shaft (4WD)ÐTypical
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 27
Page 44 of 1770

Fig. 17 Front Axle Vent HoseÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 15 Rear Drive Shaft (4WD)ÐTypical
0 - 28 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 83 of 1770

FUEL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE CABLE... 16
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM................. 2
FUEL TANKS........................... 12
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)ÐCOMPO-
NENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATION . 17MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION . . . 54
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS.................. 32
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 62
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation or
by the particular vehicle nameplate. A chart showing
a breakdown of the alphabetical designations is in-
cluded in the Introduction section at the beginning of
this manual.
TheFuel Systemconsists of: the fuel tank, an
electric (fuel tank mounted) fuel pump and a fuel fil-
ter. It also consists of fuel tubes/lines/hoses, vacuum
hoses, throttle body and fuel injectors.
TheFuel Delivery Systemconsists of: the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel tubes/lines/hoses, fuel rail,
fuel injectors and fuel pressure regulator.
AFuel Return Systemis used on all vehicles.
The system consists of: the fuel tubes/lines/hoses that
route fuel back to the fuel tank.
TheFuel Tank Assemblyconsists of: the fuel
tank, filler tube, fuel gauge sending unit/electric fuel
pump module, a pressure relief/rollover valve and a
pressure-vacuum filler cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
Evaporation Control System.This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Group 25, Emission
Control Systems.
FUEL USAGE STATEMENT
Your vehicle was designed to meet all emission reg-
ulations and provide excellent fuel economy using
high quality unleaded gasoline. Only use unleaded
gasolines having a minimum posted octane of 87.
If your vehicle develops occasional light spark
knock (ping) at low engine speeds, this is not harm-
ful. However,continued heavy knock at high
speeds can cause damage and should be re-
ported to your dealer immediately.Engine dam-age as a result of heavy knock operation may not be
covered by the new vehicle warranty.
In addition to using unleaded gasoline with the
proper octane rating,those that contain deter-
gents, corrosion and stability additives are rec-
ommended.Using gasolines that have these
additives will help improve fuel economy, reduce
emissions and maintain vehicle performance. Gener-
ally, premium unleaded gasolines contain more addi-
tive than regular unleaded gasolines.
Poor quality gasolinecan cause problems such
as hard starting, stalling and stumble. If you experi-
ence these problems, use another brand of gasoline
before considering service for the vehicle.
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
materials that contain oxygen such as alcohol, MTBE
and ETBE. The type and amount of oxygenate used
in the blend is important. The following are generally
used in gasoline blends:
ETHANOL
Ethanol (Ethyl or Grain Alcohol) properly blended,
is used as a mixture of 10 percent ethanol and 90
percent gasoline.Gasoline with ethanol may be
used in your vehicle.
METHANOL
CAUTION: DO NOT USE GASOLINES CONTAINING
METHANOL.Use of methanol/gasoline blends may re-
sult in starting and driveability problems. In addition,
damage may be done to critical fuel system compo-
nents.
Methanol (Methyl or Wood Alcohol) is used in a va-
riety of concentrations blended with unleaded gaso-
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 84 of 1770

line. You may encounter fuels containing 3 percent
or more methanol along with other alcohols called co-
solvents.
Problems that are the result of using methanol/gas-
oline blends are not the responsibility of Chrysler
Corporation. They may not be covered by the vehicle
warranty.
MTBE/ETBE
Gasoline and MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether)
blends are a mixture of unleaded gasoline and up to
15 percent MTBE. Gasoline and ETBE (Ethyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether) are blends of gasoline and up to
17 percent ETBE. Gasoline blended with MTBE or
ETBE may be used in your vehicle.CLEAN AIR GASOLINE
Many gasolines are now being blended that con-
tribute to cleaner air, especially in those areas of the
country where air pollution levels are high. These
new blends provide a cleaner burning fuel and some
are referred to asReformulated Gasoline.
In areas of the country where carbon monoxide lev-
els are high, gasolines are being treated with oxy-
genated materials such as MTBE, ETBE and
ethanol.
Chrysler Corporation supports these efforts toward
cleaner air and recommends that you use these gas-
olines as they become available.
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
Fuel Filter............................... 8
Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test............... 7
Fuel Pressure Release Procedure............. 5
Fuel Pump Capacity Test................... 7
Fuel Pump Electrical Control................. 5Fuel Pump Module........................ 2
Fuel System Pressure Test.................. 5
Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps........... 9
Quick-Connect Fittings..................... 9
FUEL PUMP MODULE
The fuel pump module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank. The fuel pump module contains the follow-
ing components:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²In-tank fuel filter
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply and return tube connections
The fuel pump used on all vehicles is a gear/rotor
type pump. It is driven by a permanent magnet 12
volt electric motor that is immersed in the fuel tank.
The electrical pump is integral with the fuel sender
unit. The pump/sender assembly is installed inside
the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a check valve at the outlet end
that consists of a ball held against a seat by force ap-
plied from a spring. When the pump is operating,
fuel pressure overcomes spring pressure and forces
the ball off its seat, allowing fuel to flow. When the
pump is not operating, spring pressure forces the ball
back against the seat preventing fuel backflow
through the pump.
Fuel system pressure is maintained at approxi-
mately 214 kPa (31 psi). This is when the pump is
operating and vacuum is supplied to the fuel pres-
sure regulator. If vacuum is not supplied to the pres-
sure regulator, fuel pressure will be approximately
55-69 kPa (8-10 psi) higher. This may be due to a
broken or clogged vacuum line. When the fuel pumpis not operating, system fuel pressure of 131-269 kPa
(19-39 psi) is maintained. This is done by the fuel
pump outlet check valve and the vacuum assisted
fuel pressure regulator.
REMOVALÐXJ MODELS
The fuel pump/gauge sender unit assembly can be
removed from the fuel tank without removing the
tank from the vehicle.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RE-
LEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RE-
LEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
WARNING: EXTINGUISH ALL TOBACCO SMOKING
PRODUCTS BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM. KEEP OPEN FLAME AWAY FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap. Perform the Fuel Pres-
sure Release Procedure as outlined in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(3) Using an approved portable gasoline siphon/
storage tank, drain fuel tank until fuel level is below
one quarter (1/4) full.
(4) Raise and support vehicle.
14 - 2 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 92 of 1770
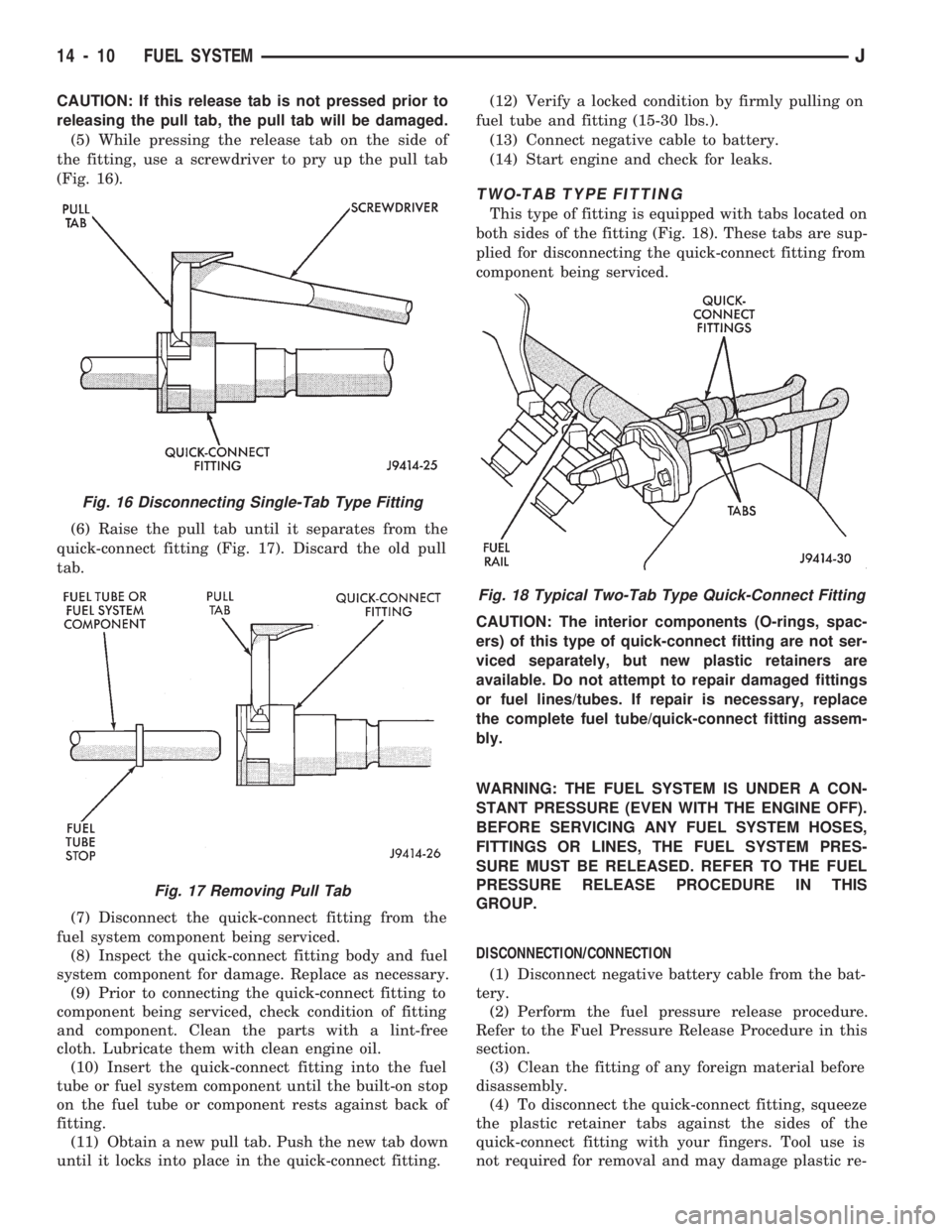
CAUTION: If this release tab is not pressed prior to
releasing the pull tab, the pull tab will be damaged.
(5) While pressing the release tab on the side of
the fitting, use a screwdriver to pry up the pull tab
(Fig. 16).
(6) Raise the pull tab until it separates from the
quick-connect fitting (Fig. 17). Discard the old pull
tab.
(7) Disconnect the quick-connect fitting from the
fuel system component being serviced.
(8) Inspect the quick-connect fitting body and fuel
system component for damage. Replace as necessary.
(9) Prior to connecting the quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean the parts with a lint-free
cloth. Lubricate them with clean engine oil.
(10) Insert the quick-connect fitting into the fuel
tube or fuel system component until the built-on stop
on the fuel tube or component rests against back of
fitting.
(11) Obtain a new pull tab. Push the new tab down
until it locks into place in the quick-connect fitting.(12) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(13) Connect negative cable to battery.
(14) Start engine and check for leaks.
TWO-TAB TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting is equipped with tabs located on
both sides of the fitting (Fig. 18). These tabs are sup-
plied for disconnecting the quick-connect fitting from
component being serviced.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new plastic retainers are
available. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings
or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace
the complete fuel tube/quick-connect fitting assem-
bly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from the bat-
tery.
(2) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Clean the fitting of any foreign material before
disassembly.
(4) To disconnect the quick-connect fitting, squeeze
the plastic retainer tabs against the sides of the
quick-connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is
not required for removal and may damage plastic re-
Fig. 16 Disconnecting Single-Tab Type Fitting
Fig. 17 Removing Pull Tab
Fig. 18 Typical Two-Tab Type Quick-Connect Fitting
14 - 10 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 93 of 1770

tainer. Pull the fitting from the fuel system compo-
nent being serviced. The plastic retainer will remain
on the component being serviced after fitting is dis-
connected. The O-rings and spacer will remain in the
quick-connect fitting connector body.
(5) Inspect the quick-connect fitting body and com-
ponent for damage. Replace as necessary.
CAUTION: When the quick-connect fitting was dis-
connected, the plastic retainer will remain on the
component being serviced. If this retainer must be
removed, very carefully release the retainer from
the component with two small screwdrivers. After
removal, inspect the retainer for cracks or any dam-
age.
(6) Prior to connecting the quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean the parts with a lint-free
cloth. Lubricate them with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert the quick-connect fitting to the compo-
nent being serviced and into the plastic retainer.
When a connection is made, a click will be heard.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery.
(10) Start engine and check for leaks.
PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 19) usually
black in color.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to re-
pair damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is
necessary, replace the complete fuel tube/quick-
connect fitting assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from the bat-
tery.
(2) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Clean the fitting of any foreign material before
disassembly.
(4) To release the fuel system component from the
quick-connect fitting, firmly push the fitting towards
the component being serviced while firmly pushing
the plastic retainer ring into the fitting (Fig. 19).
With the plastic ring depressed, pull the fitting from
the component.The plastic retainer ring must be
pressed squarely into the fitting body. If this re-
tainer is cocked during removal, it may be dif-
ficult to disconnect fitting. Use an open-end
wrench on the shoulder of the plastic retainer
ring to aid in disconnection.
After disconnection, the plastic retainer ring will
remain with the quick-connect fitting connector body.
(5) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(6) Prior to connecting the quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean the parts with a lint-free
cloth. Lubricate them with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert the quick-connect fitting into the compo-
nent being serviced until a click is felt.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(10) Start engine and check for leaks.
Fig. 19 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 11
Page 94 of 1770

FUEL TANKS
INDEX
page page
Fuel Gauge Sending Unit.................. 15
Fuel Tank.............................. 12
Fuel Tank Filler Tube Cap................. 12
Fuel Tank Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve...... 15General Information....................... 12
Heat Shields............................ 12
No-Lead Fuel Tank Filler Tube.............. 12
GENERAL INFORMATION
All vehicles pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with a pressure relief/roll-
over valve mounted in the top of the fuel pump mod-
ule. The return line from the fuel pump to the fuel
tank contains a one-way check valve.
An evaporative control system prevents raw fuel
vapor from escaping into the atmosphere. Fuel va-
pors from the fuel tank are collected in the EVAP
canister. When the engine is operating, the vapors
are drawn into the intake manifold to be used in
combustion. Refer to Group 25, Emission Control
System for more information.
Inspect all hose/tube connections for completeness.
Be sure that leaks are not present. Replace any hose
that is cracked, scuffed, swelled, has rubbed against
other vehicle components or shows any other sign of
wear that could lead to failure. If it is necessary to
replace a hose, only hose marked EFM/EFI may be
used.
When installing hoses, be sure that they are routed
away from contact with other vehicle components.
The hose clamps used on fuel injected vehicles are
of a special rolled edge construction to prevent the
edge of the clamp from cutting into the hose. Only
these rolled edge type clamps may be used on this
system. Other types of clamps may cut into the hoses
and cause high pressure fuel leaks.
NO-LEAD FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE
All vehicles are designed to operate using Un-
leaded fuels. The diameter of the opening in the fuel
tank filler neck is sized to only accept unleaded fuel
nozzles. Gasoline station pumps for unleaded and
leaded fuels have different size nozzles. Leaded fuel
nozzles are larger in diameter than unleaded nozzles.
The fuel tank filler neck opening is also equipped
with a deflector, which the smaller unleaded nozzle
pushes back upon entering the filler neck. The de-
flector will prevent the larger diameter leaded fuel
nozzles from entering the filler neck and will deflect
fuel away from the filler neck. This happens if filling
of the tank with leaded fuel is attempted.
A label is attached to the instrument panel under
the fuel gauge that reads UNLEADED FUEL ONLY
as a reminder to the driver. A similar label is located
near the fuel tank filler.
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE CAP
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of the filler neck
is prevented by the use of a safety filler cap. This
will release only under pressure of 10.9 to 13.45 kPa
(1.58 to 1.95 psi). The vacuum release is between .97
and 2.0 kPa (.14 and .29 psi). This cap must be re-
placed by a similar unit if replacement is necessary.
CAUTION: Remove the fuel tank filler tube cap prior
to removing or repairing fuel lines to relieve fuel
tank pressure.
HEAT SHIELDS
The sheet metal heat shields may have to be re-
moved when servicing the fuel tank, fuel lines or va-
por vent line. The heat shields must be installed to
protect the lines and tank from the heat of the ex-
haust system. Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System
and Intake Manifold for proper installation.
FUEL TANK
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF) OF APPROXIMATELY 131-269 KPA (19-39
PSI). THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BE-
FORE SERVICING FUEL TANK.
FUEL TANK CAPACITIES
14 - 12 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 96 of 1770
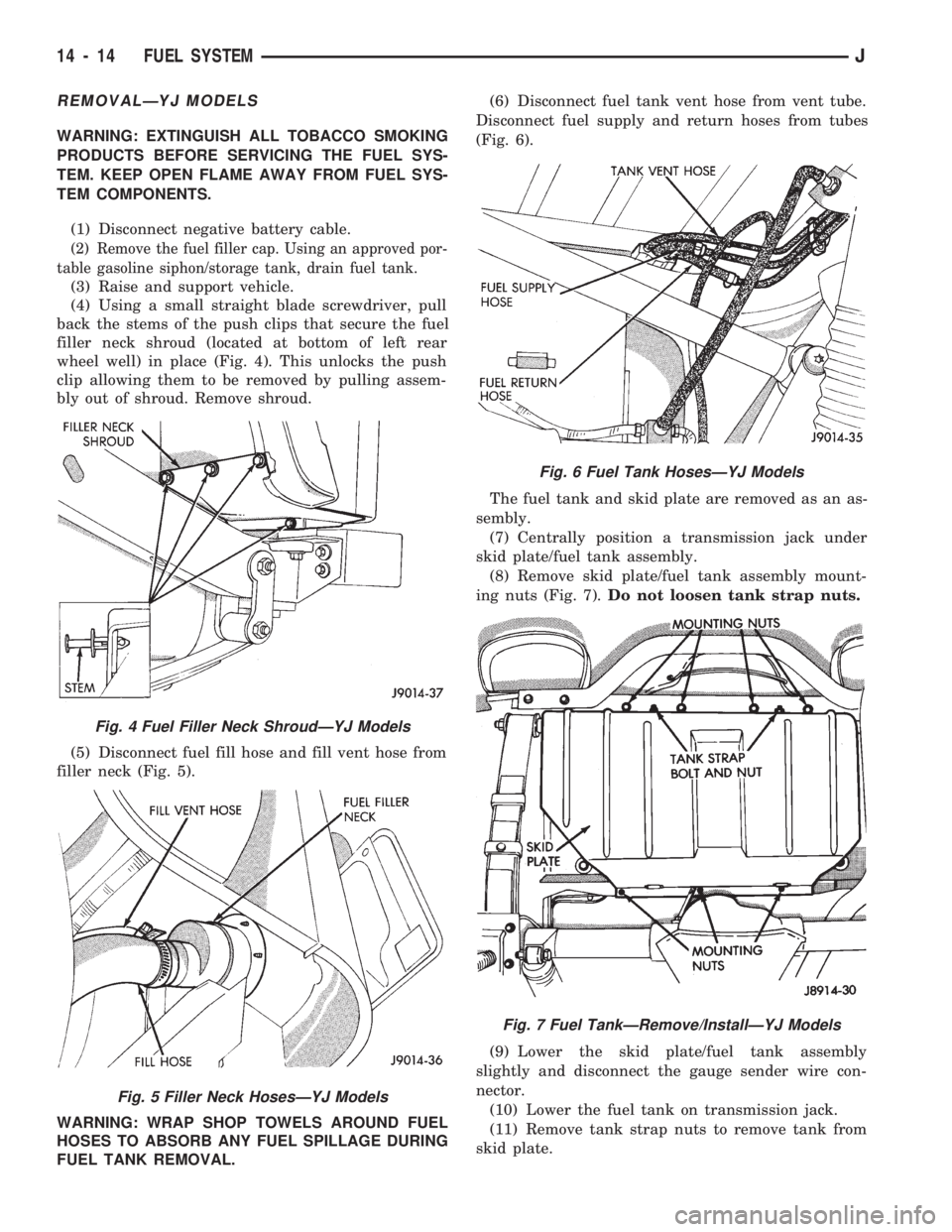
REMOVALÐYJ MODELS
WARNING: EXTINGUISH ALL TOBACCO SMOKING
PRODUCTS BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM. KEEP OPEN FLAME AWAY FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the fuel filler cap. Using an approved por-
table gasoline siphon/storage tank, drain fuel tank.
(3) Raise and support vehicle.
(4) Using a small straight blade screwdriver, pull
back the stems of the push clips that secure the fuel
filler neck shroud (located at bottom of left rear
wheel well) in place (Fig. 4). This unlocks the push
clip allowing them to be removed by pulling assem-
bly out of shroud. Remove shroud.
(5) Disconnect fuel fill hose and fill vent hose from
filler neck (Fig. 5).
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND FUEL
HOSES TO ABSORB ANY FUEL SPILLAGE DURING
FUEL TANK REMOVAL.(6) Disconnect fuel tank vent hose from vent tube.
Disconnect fuel supply and return hoses from tubes
(Fig. 6).
The fuel tank and skid plate are removed as an as-
sembly.
(7) Centrally position a transmission jack under
skid plate/fuel tank assembly.
(8) Remove skid plate/fuel tank assembly mount-
ing nuts (Fig. 7).Do not loosen tank strap nuts.
(9) Lower the skid plate/fuel tank assembly
slightly and disconnect the gauge sender wire con-
nector.
(10) Lower the fuel tank on transmission jack.
(11) Remove tank strap nuts to remove tank from
skid plate.
Fig. 4 Fuel Filler Neck ShroudÐYJ Models
Fig. 5 Filler Neck HosesÐYJ Models
Fig. 6 Fuel Tank HosesÐYJ Models
Fig. 7 Fuel TankÐRemove/InstallÐYJ Models
14 - 14 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 98 of 1770

ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE CABLE
GENERAL INFORMATION
The accelerator pedal is connected to the throttle body
linkage by the throttle cable. The cable is protected by a
plastic sheathing and is connected to the throttle body
linkage by a ball socket. It is connected to the upper part
of the accelerator pedal arm by a plastic retainer (clip)
(Fig. 10). This retainer (clip) snaps into the top of the ac-
celerator pedal arm. Retainer tabs (built into the cable
sheathing) (Fig. 10) fasten the cable to the dash panel.
Dual throttle return springs (attached to the throt-
tle shaft) are used to close the throttle.
CAUTION: Never attempt to remove or alter these springs.
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the ca-
ble core wire (within the cable sheathing) while ser-
vicing the accelerator pedal or throttle cable.
REMOVAL
(1) From inside the vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Remove plastic cable retainer (clip) and throttle cable
core wire from upper end of accelerator pedal arm (Fig.
10). Plastic cable retainer (clip) snaps into pedal arm.
(2) Remove accelerator pedal mounting bracket
nuts. Remove accelerator pedal assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place accelerator pedal assembly over studs
protruding from floor pan. Tighten mounting nuts to
5Nzm (36 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Slide throttle cable into opening in top of pedalarm. Push plastic cable retainer (clip) into accelera-
tor pedal arm opening until it snaps into place.
(3) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
THROTTLE CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) From inside the vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Remove plastic cable retainer (clip) and throttle cable
core wire from upper end of accelerator pedal arm (Fig.
10). Plastic cable retainer (clip) snaps into pedal arm.
(2) Remove the cable core wire at pedal arm.
(3) From inside the vehicle, pinch both sides of the
cable housing retainer tabs (Fig. 10) at the dash
panel. Remove cable housing from dash panel and
pull into the engine compartment.
(4) Remove cable from clip on the engine cylinder
head (valve) cover.
(5) Remove the throttle cable ball end socket at
throttle body linkage (snaps off) (Fig. 11).
(6) Remove throttle cable from throttle body mount-
ing bracket by compressing retainer tabs and pushing
cable through hole in bracket. Remove throttle cable
from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide throttle cable through hole in throttle body
bracket until retainer tabs lock into bracket. Connect
cable ball end to throttle body linkage ball (snaps on).
(2) Snap cable into clip on the engine cylinder
head (valve) cover.
(3) Push other end of cable through opening in
dash panel until retaining tabs lock into panel.
(4) From inside drivers compartment, slide throttle
cable core wire into opening in top of accelerator
pedal arm. Push cable retainer (clip) into pedal arm
opening until it snaps in place.
(5) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
Fig. 10 Accelerator Pedal MountingÐTypicalFig. 11 Throttle (Accelerator) CableÐTypical
14 - 16 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 99 of 1770

MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)ÐCOMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM
OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output.24
Air Conditioning (A/C) ControlsÐPCM Input.... 19
Auto Shut Down (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output.... 24
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) SenseÐPCM Input . 19
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input................ 19
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input.................. 20
Camshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input........ 20
Crankshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input....... 20
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Input............ 20
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output........... 24
EMR LampÐPCM Output.................. 24
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input . 21
Extended Idle SwitchÐPCM Input............ 21
Fuel InjectorsÐPCM Output................ 25
Fuel Pressure Regulator................... 30
Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output............. 25
Fuel Rail............................... 30
General Information....................... 17
Generator FieldÐPCM Output............... 25
Generator LampÐPCM Output.............. 25
Idle Air Control (IAC) MotorÐPCM Output...... 25
Ignition Circuit SenseÐPCM Input............ 21
Ignition CoilÐPCM Output.................. 26Intake Air Temperature SensorÐPCM Input.... 20
Malfunction Indicator LampÐPCM Output...... 26
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐ
PCM Input............................ 21
Open Loop/Closed Loop Modes of Operation . . . 27
Overdrive/Override Switch.................. 22
Oxygen (O2S) SensorÐPCM Input........... 22
Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input............. 22
Power Ground........................... 22
Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐPCM Input . . . 22
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............ 18
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output............ 26
SCI ReceiveÐPCM Input.................. 22
SCI TransmitÐPCM Output................. 26
Sensor ReturnÐPCM Input................. 23
Shift IndicatorÐPCM Output................ 26
Speed ControlÐPCM Input................. 23
Speed ControlÐPCM Output................ 27
TachometerÐPCM Output.................. 27
Throttle Body............................ 29
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input..... 23
Torque Converter Clutch RelayÐPCM Output . . . 27
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input........... 23
GENERAL INFORMATION
All 2.5L 4 cylinder and 4.0L 6 cylinder engines are
equipped with sequential Multi-Port Fuel Injection
(MFI). The MFI system provides precise air/fuel ra-
tios for all driving conditions.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the fuel system. The PCM was formerly referred to
as the SBEC or engine controller. The PCM is a pre-
programmed, dual microprocessor digital computer.
It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, emission
control devices, charging system, speed control, air
conditioning compressor clutch engagement and idle
speed. The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Inputsrep-
resent the instantaneous engine operating conditions.
Air-fuel mixture and ignition timing calibrations for
various driving and atmospheric conditions are pre-
programmed into the PCM. The PCM monitors and
analyzes various inputs. It then computes engine fuel
and ignition timing requirements based on these in-
puts. Fuel delivery control and ignition timing will
then be adjusted accordingly.
Other inputs to the PCM are provided by the brake
light switch, air conditioning select switch and the
speed control switches. All inputs to the PCM are
converted into signals.
Electrically operated fuel injectors spray fuel in
precise metered amounts into the intake port directlyabove the intake valve. The injectors are fired in a
specific sequence by the PCM. The PCM maintains
an air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1 by constantly adjusting
injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time that the injector opens and sprays fuel
into the chamber. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width by opening and closing the ground path to the
injector.
Manifold absolute pressure (air density) and engine
rpm (speed) are the primary inputs that determine
fuel injector pulse width. The PCM also monitors
other inputs when adjusting air-fuel ratio.
Inputs That Effect Fuel Injector Pulse Width
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
²Engine speed
²Throttle position
²Battery voltage
²Air conditioning selection
²Transmission gear selection (automatic transmis-
sions only)
²Speed control
The powertrain control module (PCM) adjusts igni-
tion timing by controlling ignition coil operation. The
ignition coil receives battery voltage when the igni-
tion key is in the run or starter position. The PCM
provides a ground for the ignition coil. The coil dis-
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 17