steering wheel adjustment JEEP XJ 1995 Service And User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: XJ, Model: JEEP XJ 1995Pages: 2158, PDF Size: 81.9 MB
Page 203 of 2158
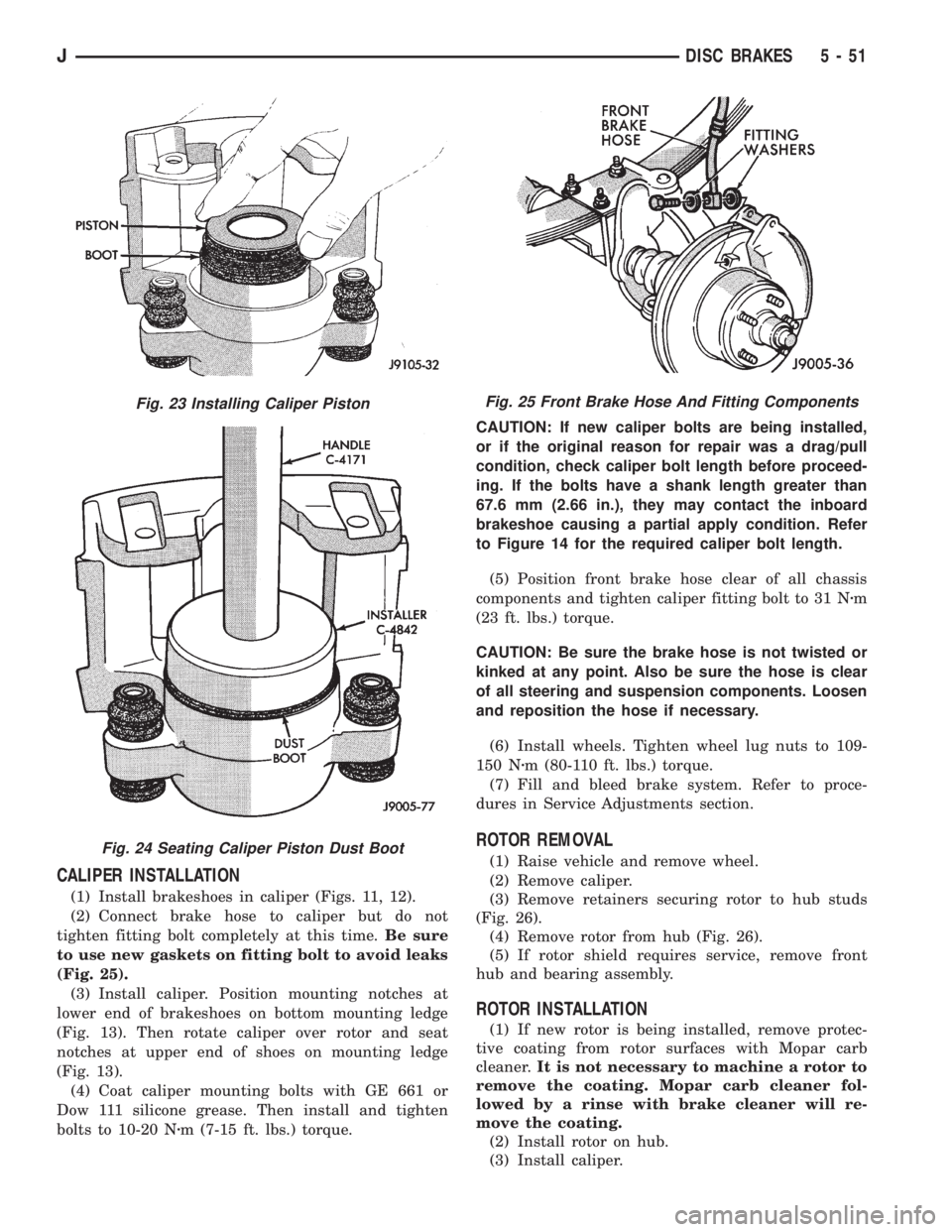
CALIPER INSTALLATION
(1) Install brakeshoes in caliper (Figs. 11, 12).
(2) Connect brake hose to caliper but do not
tighten fitting bolt completely at this time.Be sure
to use new gaskets on fitting bolt to avoid leaks
(Fig. 25).
(3) Install caliper. Position mounting notches at
lower end of brakeshoes on bottom mounting ledge
(Fig. 13). Then rotate caliper over rotor and seat
notches at upper end of shoes on mounting ledge
(Fig. 13).
(4) Coat caliper mounting bolts with GE 661 or
Dow 111 silicone grease. Then install and tighten
bolts to 10-20 Nzm (7-15 ft. lbs.) torque.CAUTION: If new caliper bolts are being installed,
or if the original reason for repair was a drag/pull
condition, check caliper bolt length before proceed-
ing. If the bolts have a shank length greater than
67.6 mm (2.66 in.), they may contact the inboard
brakeshoe causing a partial apply condition. Refer
to Figure 14 for the required caliper bolt length.
(5) Position front brake hose clear of all chassis
components and tighten caliper fitting bolt to 31 Nzm
(23 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: Be sure the brake hose is not twisted or
kinked at any point. Also be sure the hose is clear
of all steering and suspension components. Loosen
and reposition the hose if necessary.
(6) Install wheels. Tighten wheel lug nuts to 109-
150 Nzm (80-110 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Fill and bleed brake system. Refer to proce-
dures in Service Adjustments section.
ROTOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and remove wheel.
(2) Remove caliper.
(3) Remove retainers securing rotor to hub studs
(Fig. 26).
(4) Remove rotor from hub (Fig. 26).
(5) If rotor shield requires service, remove front
hub and bearing assembly.
ROTOR INSTALLATION
(1) If new rotor is being installed, remove protec-
tive coating from rotor surfaces with Mopar carb
cleaner.It is not necessary to machine a rotor to
remove the coating. Mopar carb cleaner fol-
lowed by a rinse with brake cleaner will re-
move the coating.
(2) Install rotor on hub.
(3) Install caliper.
Fig. 23 Installing Caliper Piston
Fig. 24 Seating Caliper Piston Dust Boot
Fig. 25 Front Brake Hose And Fitting Components
JDISC BRAKES 5 - 51
Page 354 of 2158
spring loaded to release when the key is released.
The maximum voltage drop between any two con-
nected terminals should not exceed 12.5 millivolts
per amp. For example: If a 10 amp load is drawn
through the switch, maximum voltage drop should be
10 x 0.0125 or 0.125 volt.
INSTALLATION/ADJUSTMENT
(1) Place the key lock switch in the ACCESSORY
position.
(2) Place the slider bar (in the ignition switch)
(Fig. 12) into the ACCESSORY detent position.
(3) Connect the wiring to the switch as follows: In-
stall the non-black (colored) connector first and then
the black (colored) connector to the ignition switch.
One connector will interlock the other connector.
(4) Slip the remote actuator rod into the access
hole on the switch (Fig. 12). Install the switch to the
steering column. Be careful not to move the slider
bar (on the switch) out of the ACCESSORY detent
position. Remove the ignition switch actuator rod se-
curing-tape from steering column.
(5) Install the two ignition switch-to-steering col-
umn screws finger tight.Do not tighten screws at
this time.
(6) Adjust ignition switch as follows:
(a) Non-tilt steering column: While holding key
lock switch in ACCESSORY position, gently slide
ignition switchup(towards steering wheel). This
will remove slack from switch. Tighten attaching
screws. Do not allow the ignition switch to move
from the ACCESSORY detent position.
(b) Tilt steering column: While holding the key
lock switch in the ACCESSORY position, gently
slide the ignition switchdown(away from steering
wheel) to remove slack from switch. Tighten at-
taching screws. Do not allow the ignition switch to
move from the ACCESSORY detent position.
Because the ignition switch and the headlamp dim-
mer switch share the same two mounting screws, oneof the screws must be removed from the ignition
switch. This must be doneafterthe ignition switch
has been adjusted andbeforethe dimmer switch
has been installed. Remove one screw.Do notre-
move the stud/nut.
(7) Install the headlamp dimmer switch as follows:
Slip switch into actuator rod and position over the ig-
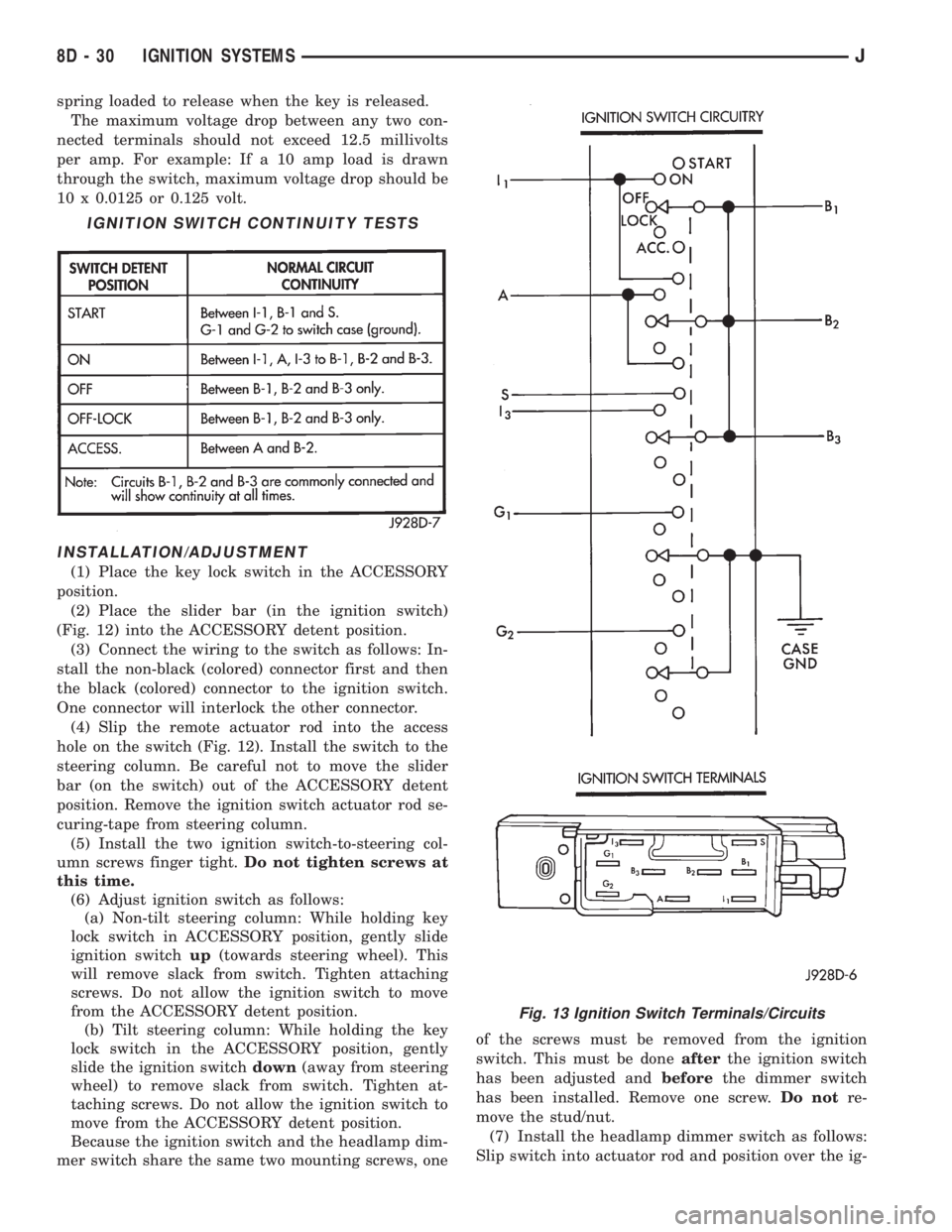
IGNITION SWITCH CONTINUITY TESTS
Fig. 13 Ignition Switch Terminals/Circuits
8D - 30 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 355 of 2158
nition switch. Install screws finger tight. Remove the
dimmer switch actuator rod securing-tape from steer-
ing column.
(8) Adjust dimmer switch as follows: Depress the
switch slightly and insert a 3/32-inch drill bit into
the adjustment hole (Fig. 11). This is done to prevent
horizontal switch movement.
(9) Move switch toward steering wheel to remove
any lash from switch actuator rod. Tighten dimmer
and ignition switch fasteners to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.)
torque.(10) Install the windshield wiper intermittent con-
trol module and its bracket (if equipped).
(11) Install the negative battery cable.
Test dimmer switch. Test ignition switch operation
in all switch positions. If equipped with a tilt steer-
ing column, test operation of dimmer switch and ig-
nition switch in all tilt positions.
Fig. 14 Detent PositionsÐNon-Tilt Steering Column
Fig. 15 Detent PositionsÐTilt Steering Column
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 31
Page 417 of 2158

VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS............................. 2
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1SERVICE PROCEDURES................... 9
GENERAL INFORMATION
The vehicle speed control system (Fig. 1) is an
available option on all XJ (Cherokee) models. The
system is electronically controlled and vacuum oper-
ated. Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the vehicle speed control system. Re-
fer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams for complete cir-
cuit descriptions and diagrams.
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
The speed control servo is mounted to a bracket on
the right side inner fender shield in the engine com-
partment. The servo unit consists of a solenoid valve
body, a vacuum servo and the mounting bracket. The
PCM controls the solenoid valve body. The solenoid
valve body controls the application and release of
vacuum to the diaphragm of the vacuum servo. The
servo unit cannot be repaired and is serviced only as
a complete assembly.
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
The speed control switch module is mounted to the
center of the steering wheel below the driver's airbag
module. The PCM monitors the state of the speed
control switches. The individual switches are labeled:
OFF/ON, RESUME/ACCEL, SET/COAST. Refer to
the owner's manual for more information on speed
control switch functions and setting procedures. The
individual switches cannot be repaired. If one switch
fails, the entire switch module must be replaced.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
Vehicles with the speed control option use a dual
function stop lamp switch. The switch is mounted in
the same location as the conventional stop lamp
switch, on the brake pedal mounting bracket under
the instrument panel. The PCM monitors the state of
the dual function stop lamp switch. Refer to Group 5
- Brakes for more information on stop lamp switch
service and adjustment procedures.
SERVO CABLE
The speed control servo cable is connected betweenthe speed control vacuum servo diaphragm and the
throttle control linkage. This cable causes the throt-
tle control linkage to open or close the throttle valve
in response to movement of the vacuum servo dia-
phragm.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The speed control electronic control circuitry is in-
tegrated into the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The PCM is located in the engine compartment on
the left side inner fender shield. The PCM speed con-
trol functions are monitored by the On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems are
monitored by the PCM. Each monitored circuit is as-
signed a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM
will store a DTC in electronic memory for any failure
it detects. See Using On-Board Diagnostic System in
this group for more information. The PCM cannot be
repaired and must be replaced if faulty.
VACUUM RESERVOIR
The vacuum reservoir is mounted behind the left
end of the front bumper bar. The reservoir contains a
one-way check valve to trap engine vacuum in the
reservoir. When engine vacuum drops, as in climbing
a grade while driving, the reservoir supplies the vac-
uum needed to maintain proper speed control opera-
tion. The vacuum reservoir cannot be repaired and
must be replaced if faulty.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) is a pulse genera-
tor mounted to an adapter near the transmission
(two-wheel drive) or transfer case (four-wheel drive)
output shaft. The sensor is driven through the
adapter by a speedometer pinion gear. The VSS pulse
signal to the speedometer/odometer is monitored by
the PCM speed control circuitry to determine vehicle
speed and to maintain speed control set speed. Refer
to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual for testing of this component. Refer to Group
14 - Fuel System for service of this component.
JVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1
Page 422 of 2158
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AN AIR-
BAG, REFER TO GROUP 8M - RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING STEERING WHEEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT
IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POS-
SIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable. Remove
speed control switch from steering wheel.
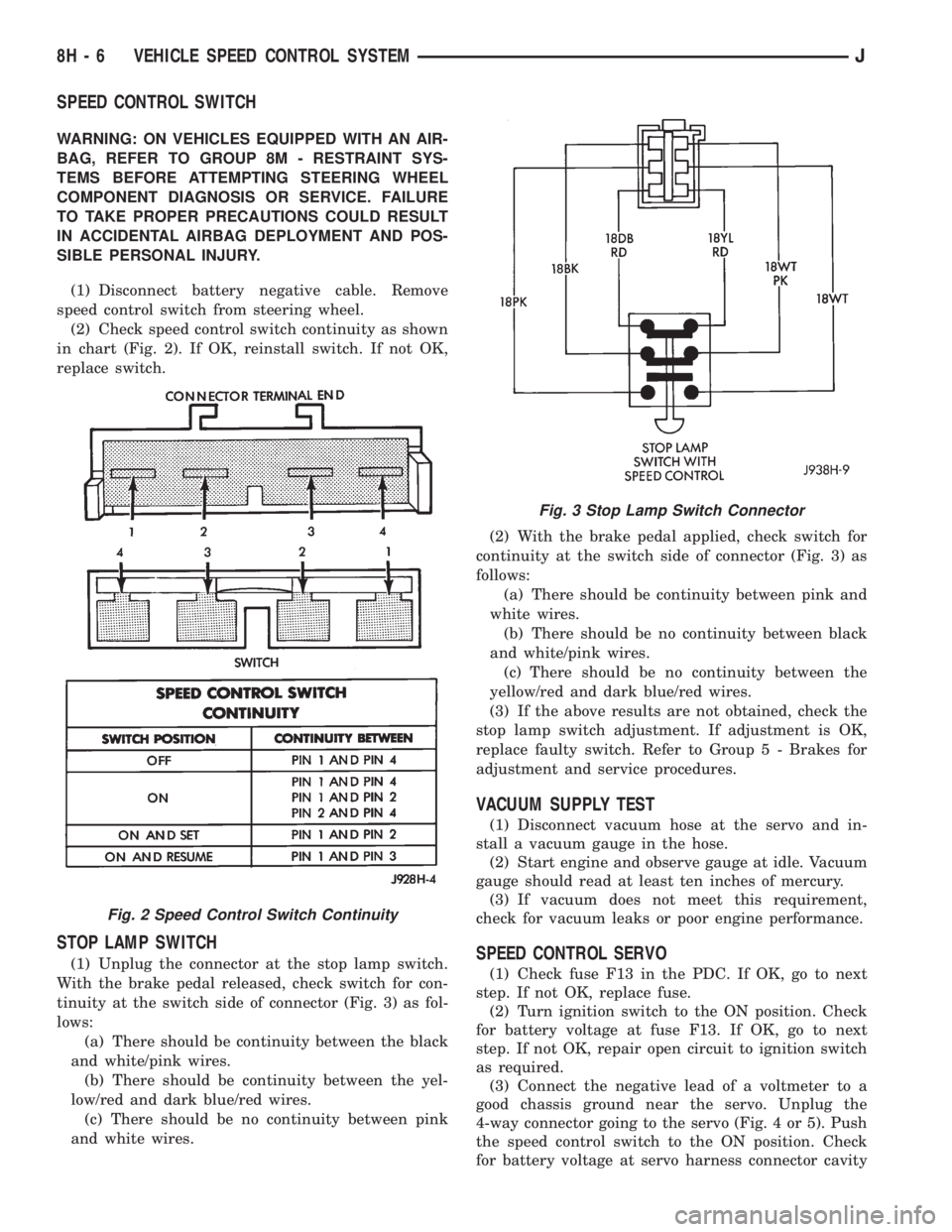
(2) Check speed control switch continuity as shown
in chart (Fig. 2). If OK, reinstall switch. If not OK,
replace switch.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
(1) Unplug the connector at the stop lamp switch.
With the brake pedal released, check switch for con-
tinuity at the switch side of connector (Fig. 3) as fol-
lows:
(a) There should be continuity between the black
and white/pink wires.
(b) There should be continuity between the yel-
low/red and dark blue/red wires.
(c) There should be no continuity between pink
and white wires.(2) With the brake pedal applied, check switch for
continuity at the switch side of connector (Fig. 3) as
follows:
(a) There should be continuity between pink and
white wires.
(b) There should be no continuity between black
and white/pink wires.
(c) There should be no continuity between the
yellow/red and dark blue/red wires.
(3) If the above results are not obtained, check the
stop lamp switch adjustment. If adjustment is OK,
replace faulty switch. Refer to Group 5 - Brakes for
adjustment and service procedures.
VACUUM SUPPLY TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at the servo and in-
stall a vacuum gauge in the hose.
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vacuum
gauge should read at least ten inches of mercury.
(3) If vacuum does not meet this requirement,
check for vacuum leaks or poor engine performance.
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
(1) Check fuse F13 in the PDC. If OK, go to next
step. If not OK, replace fuse.
(2) Turn ignition switch to the ON position. Check
for battery voltage at fuse F13. If OK, go to next
step. If not OK, repair open circuit to ignition switch
as required.
(3) Connect the negative lead of a voltmeter to a
good chassis ground near the servo. Unplug the
4-way connector going to the servo (Fig. 4 or 5). Push
the speed control switch to the ON position. Check
for battery voltage at servo harness connector cavity
Fig. 2 Speed Control Switch Continuity
Fig. 3 Stop Lamp Switch Connector
8H - 6 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMJ
Page 487 of 2158
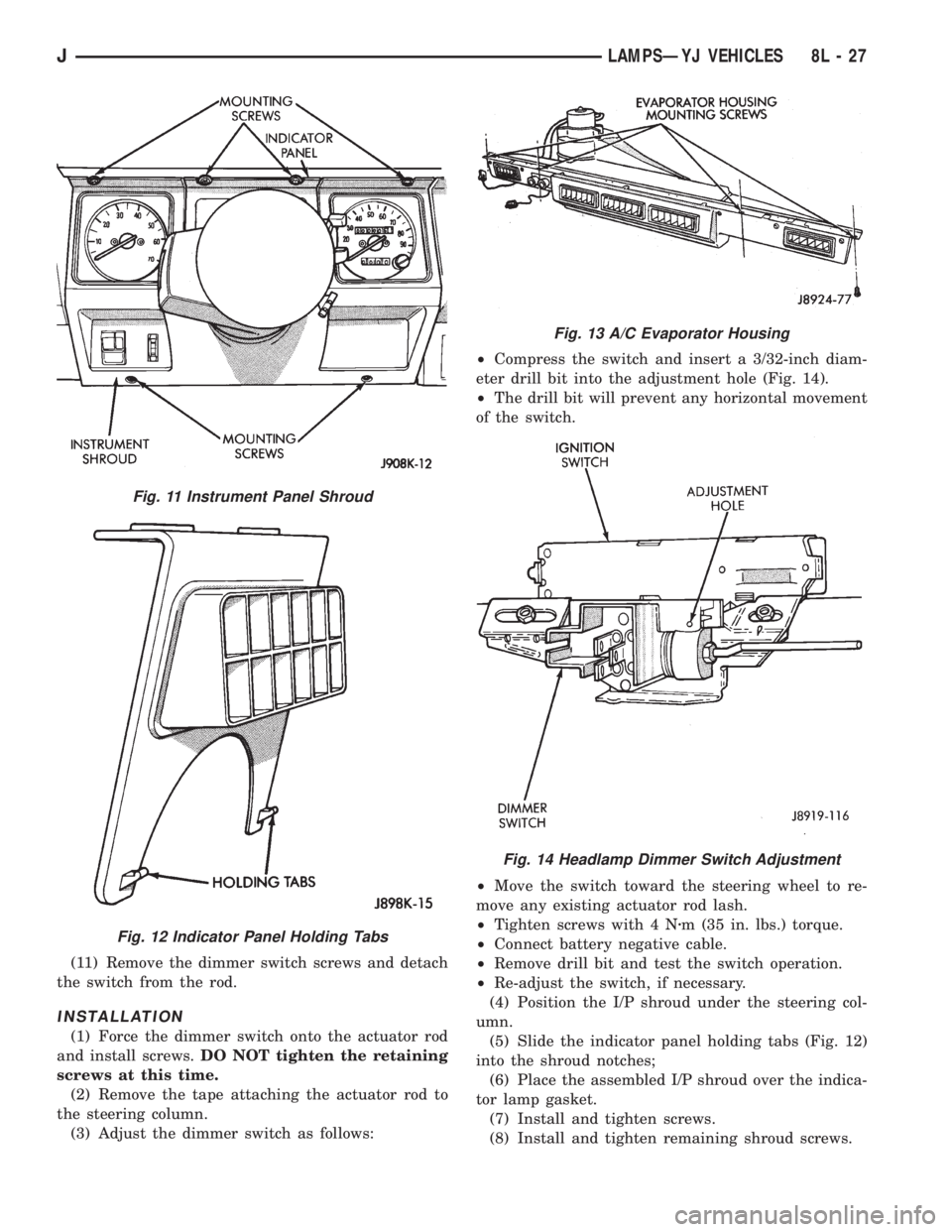
(11) Remove the dimmer switch screws and detach
the switch from the rod.
INSTALLATION
(1) Force the dimmer switch onto the actuator rod
and install screws.DO NOT tighten the retaining
screws at this time.
(2) Remove the tape attaching the actuator rod to
the steering column.
(3) Adjust the dimmer switch as follows:²Compress the switch and insert a 3/32-inch diam-
eter drill bit into the adjustment hole (Fig. 14).
²The drill bit will prevent any horizontal movement
of the switch.
²Move the switch toward the steering wheel to re-
move any existing actuator rod lash.
²Tighten screws with 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.) torque.
²Connect battery negative cable.
²Remove drill bit and test the switch operation.
²Re-adjust the switch, if necessary.
(4) Position the I/P shroud under the steering col-
umn.
(5) Slide the indicator panel holding tabs (Fig. 12)
into the shroud notches;
(6) Place the assembled I/P shroud over the indica-
tor lamp gasket.
(7) Install and tighten screws.
(8) Install and tighten remaining shroud screws.
Fig. 11 Instrument Panel Shroud
Fig. 12 Indicator Panel Holding Tabs
Fig. 13 A/C Evaporator Housing
Fig. 14 Headlamp Dimmer Switch Adjustment
JLAMPSÐYJ VEHICLES 8L - 27
Page 1500 of 2158

STEERING LINKAGEÐXJ
INDEX
page page
Drag Link............................... 16
Pitman Arm.............................. 17
Service Information........................ 16Steering Damper.......................... 17
TieRod ................................ 16
SERVICE INFORMATION
The steering linkage consists of a pitman arm, drag
link, tie rod, and steering damper. Adjustment
sleeves are used on the tie rod and drag link for toe
and steering wheel alignment.
Refer to Group 2, Front Suspension and Axle for
additional information.
The tie-rod end ball stud seals should be inspected
during all oil changes.
A damaged ball stud seal requires removal of the
seal. Inspect the tie-rod end ball stud at the throat
opening. Check for lubricant loss, contamination, ball
stud wear or corrosion. If these conditions exist, re-
place the tie-rod. A replacement seal can be installed
if lubricant is in good condition. Otherwise, a com-
plete replacement ball stud end should be installed.
Lubricate the tie-rod end with MOPARtMulti-Mile-
age Lubricant, or equivalent product.
Use a Puller tool C-3894-A for tie rod removal.
Failure to use this tool could damage the ball
stud and seal (Fig. 1).
TIE ROD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cotter pins and nuts at the tie rod
ball studs and drag link (Fig. 2).
(2) Loosen the ball studs with a puller tool to re-
move the tie rod.(3) If necessary, loosen the end clamp bolts and re-
move the tie rod ends from the tube.
INSTALLATION
(1) If necessary, install the tie rod ends in the tube
(Fig. 2). Position the tie rod clamp as shown (Fig. 3)
and tighten to 27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the tie rod on the drag link and steering
knuckle. Install the retaining nuts.
(3) Tighten the ball stud nut on the steering
knuckle to 47 Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the
ball stud nut to drag link to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.)
torque. Install new cotter pins.
DRAG LINK
REMOVAL
The drag link ball stud cannot be disassem-
bled for service.
(1) Remove the steering damper ball stud from the
drag link with a puller tool.
(2) Remove the drag link from the steering knuckle
with a puller tool. Remove the same for tie rod and
pitman arm.
(3) If necessary, loosen the end clamp bolts and re-
move the tie rod end from the link.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the drag link adjustment sleeve and tie
rod end. Position clamp bolts as shown (Fig. 3).
(2) Position the drag link at the steering linkage
(Fig. 2).
Install the nut that attach the drag link to the
steering knuckle. Do the same for the tie rod and pit-
man arm.
(3) Tighten the nut at the steering knuckle to 47
Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the pitman and tie
rod ball stud nuts to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque. In-
stall new cotter pins.
(4) Install the steering damper onto the drag link.
Tighten the nut to 47 Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Install
a new cotter pin.
Fig. 1 Ball Stud Removal
19 - 16 STEERINGJ
Page 1503 of 2158
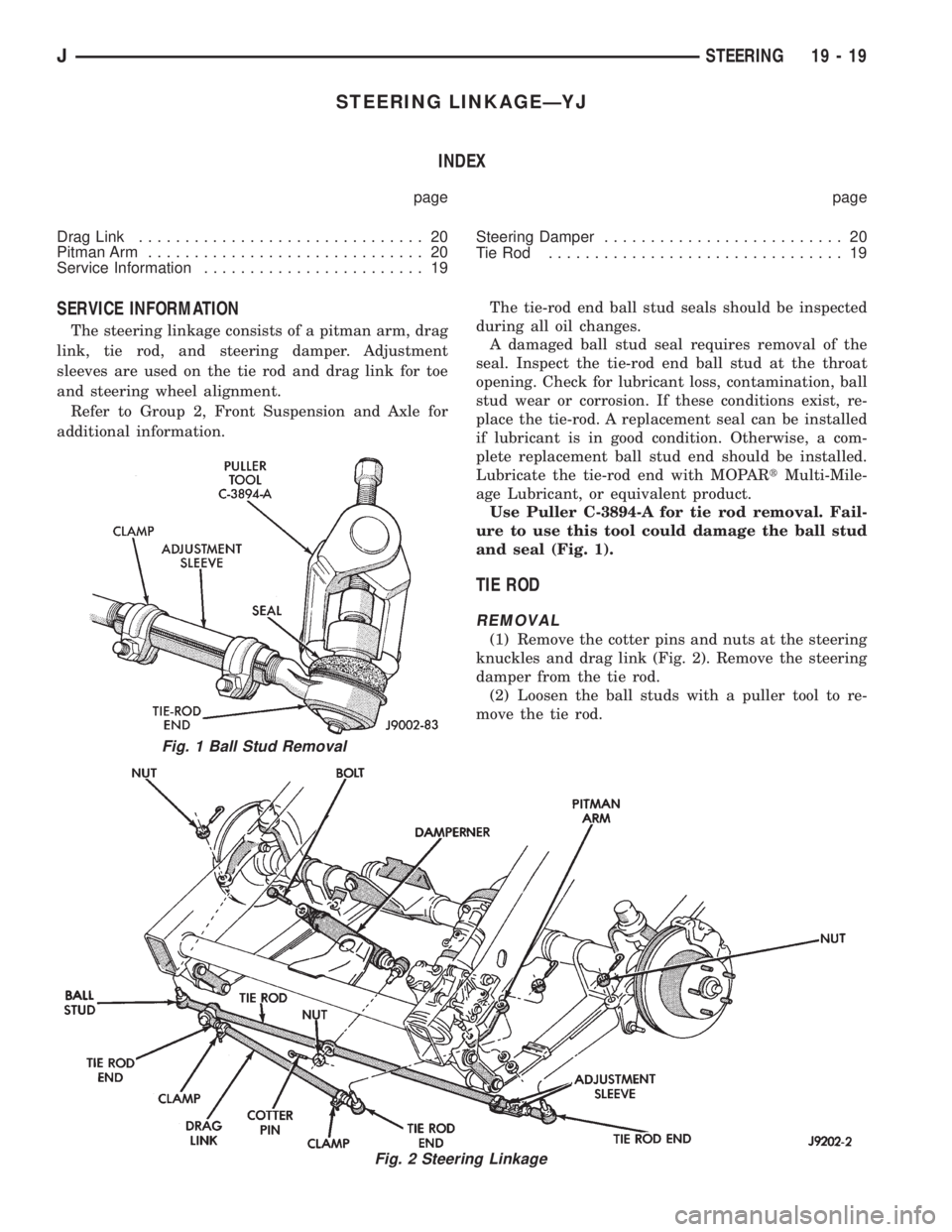
STEERING LINKAGEÐYJ
INDEX
page page
Drag Link............................... 20
Pitman Arm.............................. 20
Service Information........................ 19Steering Damper.......................... 20
TieRod ................................ 19
SERVICE INFORMATION
The steering linkage consists of a pitman arm, drag
link, tie rod, and steering damper. Adjustment
sleeves are used on the tie rod and drag link for toe
and steering wheel alignment.
Refer to Group 2, Front Suspension and Axle for
additional information.The tie-rod end ball stud seals should be inspected
during all oil changes.
A damaged ball stud seal requires removal of the
seal. Inspect the tie-rod end ball stud at the throat
opening. Check for lubricant loss, contamination, ball
stud wear or corrosion. If these conditions exist, re-
place the tie-rod. A replacement seal can be installed
if lubricant is in good condition. Otherwise, a com-
plete replacement ball stud end should be installed.
Lubricate the tie-rod end with MOPARtMulti-Mile-
age Lubricant, or equivalent product.
Use Puller C-3894-A for tie rod removal. Fail-
ure to use this tool could damage the ball stud
and seal (Fig. 1).
TIE ROD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cotter pins and nuts at the steering
knuckles and drag link (Fig. 2). Remove the steering
damper from the tie rod.
(2) Loosen the ball studs with a puller tool to re-
move the tie rod.
Fig. 1 Ball Stud Removal
Fig. 2 Steering Linkage
JSTEERING 19 - 19
Page 1504 of 2158

(3) If necessary, loosen the end clamp bolts and re-
move the tie rod end from the tube.
INSTALLATION
(1) If necessary, install the tie rod end in the tube
(Fig. 2). Position the tie rod clamp as shown (Fig. 3).
Tighten the ball-stud end clamp bolts to 49 Nzm (36 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the tie rod on the drag link and steering
knuckles. Install the retaining nuts. Install the steer-
ing damper to the tie rod.
(3) Tighten the ball stud nut on the steering
knuckle to 47 Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the
ball stud nut to drag link to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.)
torque. Tighten the steering damper nut to 74 Nzm
(55 ft. lbs.) torque. Install new cotter pins.
DRAG LINK
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cotter pins and nuts at the tie rod
and pitman arm (Fig. 2).
(2) Remove the drag link from the tie rod and pit-
man arm with a puller tool.
(3) If necessary, loosen the end clamp bolts and re-
move the tie rod ends from the tube.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the drag link adjustment sleeve and tie
rod ends. Position clamp bolts as shown (Fig. 3).
(2) Position the drag link at the steering linkage
(Fig. 2).
Install the drag link to tie rod and pitman arm.
(3) Tighten the nut at the pitman arm to 74 Nzm
(55 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the tie rod ball stud nut
to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque. Install new cotter pins.
STEERING DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Place the front wheels in a straight-ahead position.
(2) Remove the steering damper retaining nut and
bolt from the axle bracket (Fig. 2).
(3) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the ball
stud at the tie rod (Fig. 2).
(4) Remove the steering damper ball stud from the
tie rod with a puller tool.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the steering damper to the axle bracket
and tie rod.
(2) Install the steering damper bolt in the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 74 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the ball stud nut at the tie rod. Tighten
the nut to 74 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque. Install a new
cotter pin.
PITMAN ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the drag
link at the pitman arm.
(2) Remove the drag link ball stud from the pit-
man arm with a puller.
(3) Remove the nut and washer from the steering
gear shaft. Mark the pitman shaft and pitman arm
for installation reference. Remove the pitman arm
from steering gear with Puller C-4150-A (Fig. 4).
INSTALLATION
(1) Align and install the pitman arm on steering
gear shaft.
(2) Install the washer and nut on the shaft.
Tighten the nut to 251 Nzm (185 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install drag link ball stud to pitman arm (Fig.
4). Install and tighten nut to 74 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.)
torque. Install a new cotter pin.
Fig. 4 Pitman Arm Removal
Fig. 3 Tie Rod/Drag Link Clamp Bolt
19 - 20 STEERINGJ
Page 1523 of 2158

(2) Wrap a single layer of plastic tape around the
pitman shaft threads and splines. This will protect
the replacement seals during installation.
(3) Install the seal with a suitable size socket.
(4) Remove the tape from the shaft.
(5) Center the steering gear.
(6) Align and install the pitman arm.
(7) Install the washer and retaining nut on the pit-
man shaft. Tighten the nut to 251 Nzm (185 ft. lbs.)
torque.
GEAR ADJUSTMENTS IN VEHICLE
REMOVE
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Mark the pitman shaft and pitman arm for in-
stallation reference. Remove the pitman arm from
the shaft.
(3) Loosen the adjuster lock nut then back the ad-
juster plug off 1/4 turn.
(4) Remove the steering wheel horn pad.
(5) Turn the steering wheel in one direction until
stopped by the gear. Then turn back 1/2 turn.
CAUTION: Do not turn the steering wheel hard
against the internal stops when the linkage is re-
moved. This could result in damage to the recircu-
lating ball guides.
MEASURE
Place a low calibration (50 in. lbs.) torque wrench
and socket on the steering wheel nut. Rotate the
wrench and nut through a 90 degree arc (1/4 turn).
This will measure the worm shaft bearing preload.
ADJUST WORMSHAFT BEARING PRELOAD
TORQUE
(1) Adjust the preload by tightening the adjuster
plug. The preload should be 0.6 to 1 Nzm(5to8in.
lbs.) torque.
Steering column/shaft misalignment or damage will
increase the amount of torque required to rotate the
steering wheel. If the rotating torque is exceptionally
high, inspect the steering column/shaft alignment. If
the alignment is correct, remove the steering gear,
determine the cause of the high preload torque, and
repair as necessary.
(2) Tighten the adjuster locknut to 68 Nzm (50 ft.
lbs.) torque. Measure the preload torque. If neces-
sary, adjust the preload torque again.
ADJUST OVERCENTER DRAG TORQUE
(1) Turn the steering wheel from one stop to the
other and count the total numbers of turns. Turn the
wheel back in reverse direction 1/2 the total number
of turns to center the steering gear.(2) Turn the over center adjusting screw in to re-
move all lash between the ball nut and pitman shaft
sector teeth. Hold the adjustment screw and tighten
the lock nut to 34 Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Check the torque at the steering wheel by tak-
ing the highest reading as the wheel is turned
through the center position.
(4) The overcenter drag torque should be 0.5 to 1
Nzm (4 to 10 in. lbs.).
(5) If necessary, loosen the lock nut and adjust the
over center adjuster screw to obtain the proper
torque. Re-tighten the lock nut to the lock nut.
(6) After tightening the locknut, measure the over-
center drag torque again and readjust the torque, if
necessary.
INSTALL
(1) Align the installation reference marks and in-
stall the pitman arm.
(2) Install and tighten the pitman shaft nut and
washer to 251 Nzm (185 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the horn button.
GEAR DISASSEMBLY
(1) Rotate the wormshaft from stop-to-stop and
count the number of rotations. Rotate the wormshaft
in the reverse direction 1/2 of the total number of ro-
tations to center it and the ball nut.
(2) Remove the pitman shaft adjustment screw
locknut. Remove the cover retaining bolts, cover, and
gasket (Fig. 3).
(3) Slide the adjustment screw head (Fig. 3) out of
the pitman shaft T-slot and remove it and the
shim(s).
(4) Retain the shim(s) for end-play measurement
during assembly.
(5) Remove the pitman shaft, the wormshaft bear-
ing preload torque adjustment cap locknut, and the
adjustment cap (Fig. 2).
(6) Remove the wormshaft and the ball nut (Fig.
2).
(7) Remove (pry) the pitman shaft and the worm-
shaft seals from the steering gear housing (Fig. 3).
WORMSHAFT AND BALL NUT DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the upper bearing from the wormshaft
(Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Do not allow the ball nut to rotate freely
and travel to either extreme end of the wormshaft.
This could damage the tangs at the ends of the re-
circulating ball guides (Fig. 3).
(2) Remove the recirculating ball guide clamp re-
taining screws, the clamp and the guides (Fig. 2).
Separate the half-guides and place the recirculating
balls aside in a container.
JSTEERING 19 - 39