LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996Pages: 455, PDF Size: 6.44 MB
Page 301 of 455

70BRAKES
2
OVERHAUL MASTER CYLINDER
Service repair no - 70.30.09
Before starting overhaul procedure refer to general
brake service practice
See Repair, General brake
service practice
.
Dismantling master cylinder
1.Disconnect battery and remove master cylinder
from servo
See Repair, Master cylinder.
2.Before commencing overhaul procedure
thoroughly clean master cylinder and inspect
outer surfaces for damage and condition, renew
complete assembly if necessary.
3.The reservoir is a push fit in master cylinder and
secured by seals. Carefully ease reservoir from
master cylinder by rolling it from seals as
illustrated.
4.Using soft jaws, one either side of master
cylinder flange and clamp flange in a suitable
vice. Remove water ingress 'O' ring seal from
master cylinder to servo flange and discard.
5.Hold outside of transfer housing with a suitable
pair of grips, carefully pull, while working pliers in
a backwards and forwards rocking motion to
ease housing off master cylinder, discard
housing and vacuum seal.
6.Withdraw 2 reservoir seals from master cylinder
and note their positions in inlet ports for
reassembly. Discard both seals.
7.Remove retaining ring and 'O' ring seal from
machined outer surface of master cylinder,
discard both seal and retaining ring.
Page 302 of 455

BRAKES
3
OVERHAUL
8.Remove guide ring from mouth of master
cylinder which supports primary plunger
assembly and place to one side, this component
is not part of master cylinder service kit and is to
be refitted on assembly of unit.
9.Pull primary plunger assembly out of master
cylinder.
NOTE: The primary plunger assembly
cannot be broken down any further and is
serviced as a complete unit. Discard
assembly.
10.The secondary plunger assembly will remain at
bottom of master cylinder bore, plunger can be
easily expelled by tapping assembly on a piece
of timber until plunger appears at cylinder mouth,
carefully pull plunger from master cylinder.
11.If swirl tube was not expelled at same time as
secondary plunger, repeat above operation to
expel it from bottom of master cylinder bore and
discard.12.Clean all parts with Girling cleaning fluid or
unused brake fluid and place cleaned parts on to
a clean sheet of paper. Inspect cylinder bore and
plungers for signs of corrosion, ridges and score
marks. Provided working surfaces are in perfect
condition, new seals from a Girling Service
repair kit may be used.
Renewing secondary plunger seals
A.Springs
B.Seal retainer
C.Recuperating seal (primary cup)
D.Washer
E.'L' seal
13.Remove components above from secondary
plunger and discard:
NOTE: A small screwdriver with end
rounded and polished is required to
remove 'L' seal. DO NOT damage
secondary plunger.
14.Coat new seals in unused brake fluid and firstly
fit 'L' seal to plunger.
15.Fit washer followed by recuperating seal. Fit seal
retainer and springs, ensure springs are
correctly seated.
Page 303 of 455

70BRAKES
4
OVERHAUL Assembling master cylinder
CAUTION: It is important that the following
instructions are carried out precisely,
otherwise damage could be caused to new
seals when inserting plungers into cylinder bore.
Generous amounts of new brake fluid should be
used to lubricate parts during assembly.
NOTE: Thoroughly check that no debris is
lodged in fluid passageways and drillings.
If debris is found, carefully remove,
re-clean cylinder and re-check.
16.Fit new swirl tube to bottom of cylinder bore.
17.Lubricate secondary plunger and cylinder bore.
Offer plunger assembly to cylinder until
recuperation seal is resting centrally in mouth of
bore. Gently introduce plunger with a circular
rocking motion, as illustrated. Ensuring that seal
does not become trapped, ease seal into bore
and slowly push plunger down bore in one
continuous movement.
18.Fit primary plunger assembly using same
method as for secondary plunger, push plunger
down bore.
19.Fit original guide ring to support primary plunger.
20.Coat a new 'O' ring with brake fluid and fit to its
respective groove on outer location surface of
master cylinder.
CAUTION: 'O' ring should not be rolled
down outer location surface of master
cylinder but should be slightly stretched
and eased down cylinder and into its groove. Do
not over stretch seal.21.Fit a new retaining ring on outer surface of
master cylinder ensuring that serrations of ring
are facing mounting flange.
22.Fit two new reservoir seals in their respective
ports.
23.Fit a new vacuum seal to either primary plunger
or to bottom of transfer housing bore, open face
of seal towards primary plunger guide ring.
24.Lubricate vacuum seal with brake fluid, fit
transfer housing to master cylinder, push
housing fully up to cylinder mounting flange. Do
not adjust transfer housing after fitting.
25.Lubricate a new water ingress seal with brake
fluid, slightly stretch seal and ease it down
housing until seal is in correct position between
housing and flange.
26.Roll reservoir into top of master cylinder,
reversing procedure described in instruction 3.
27.Fit master cylinder to servo
See Repair,
Master cylinder
.
28.Reconnect battery, and road test vehicle.
Page 304 of 455

WHEELS AND TYRES
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION TYPES OF WHEEL RIMS AND TYRES
Description
Dependent on specification and model type, the
vehicle is equipped with pressed steel or alloy wheel
rims, both using tubeless radial ply tyres.
Tyre codes
The text, codes and numbers moulded into the tyre
wall vary between tyre manufacturers, however most
tyres are marked with the information shown in the
illustrated example.
NOTE: The illustration is an example of the
type of markings moulded into tyres and is
for guidance only. For specific tyre
specifications
See GENERAL SPECIFICATION
DATA, Information, Tyre size and pressures
.1.Type of tyre construction -Radial Ply
2.Load index -104
3.Speed symbol -SorT
4.USA Tyre quality grading -Tread wear 160
Traction A temperature B
5.Tread wear indicators moulded into tread pattern
are located at intervals around the tyre and
marked by a code -E66 103S6
6.Tyres with 'Mud Snow' type tread pattern are
marked -M&S
7.Tyre reinforcing mark -Reinforced
8.USA Load and pressure secification -
(900Kg(1984LBS) at 340KA (50PSI) MACS
PRESS
9.Tyre size -205 16 ot 235/70 R16
10.Type of tyre -TUBELESS
11.Country of manufacture -MADE IN GREAT
BRITAIN
12.USA Compliance symbol and identification -
DOT AB7C DOFF 267
13.European type approval identification -E11
01234
14.Tyre construction -SIDE WALL 2 PLIES
RAYON. TREAD 2 RAYON 2 STEEL
15.Manufacturers brand name/type -TRACTION
PLUS mzx M
Page 305 of 455

WHEELS AND TYRES
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS TYRE WEAR CHART
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
Rapid wear at Tyres under-inflated Inflate to correct pressure
shoulders Worn suspension components Replace worn components
i.e. ball joints, panhard
rod bushes, steering damper
Excessive cornering speeds
Rapid wear at
centreTyres over-inflated Inflate to correct pressure
of tread
Wear at one
shoulderTrack out of adjustment Adjust track to correct figure
Bent panhard rod Check and replace worn or damaged
components
Bald spots or tyre Wheel out of balance Balance wheel and tyre
cupping assembly
Excessive radial runout Check runout and replace tyre
if necessary
Shock absorber worn Replace shock absorber
Excessive braking
Tyre scalloped Track out of adjustment Adjust toe to correct figure
Worn suspension components Replace tyre as necessary
Excessive cornering speeds
CAUTION: This diagnosis chart is for general guidance only and does not necessarily include
every cause of abnormal tyre wear.
Page 306 of 455
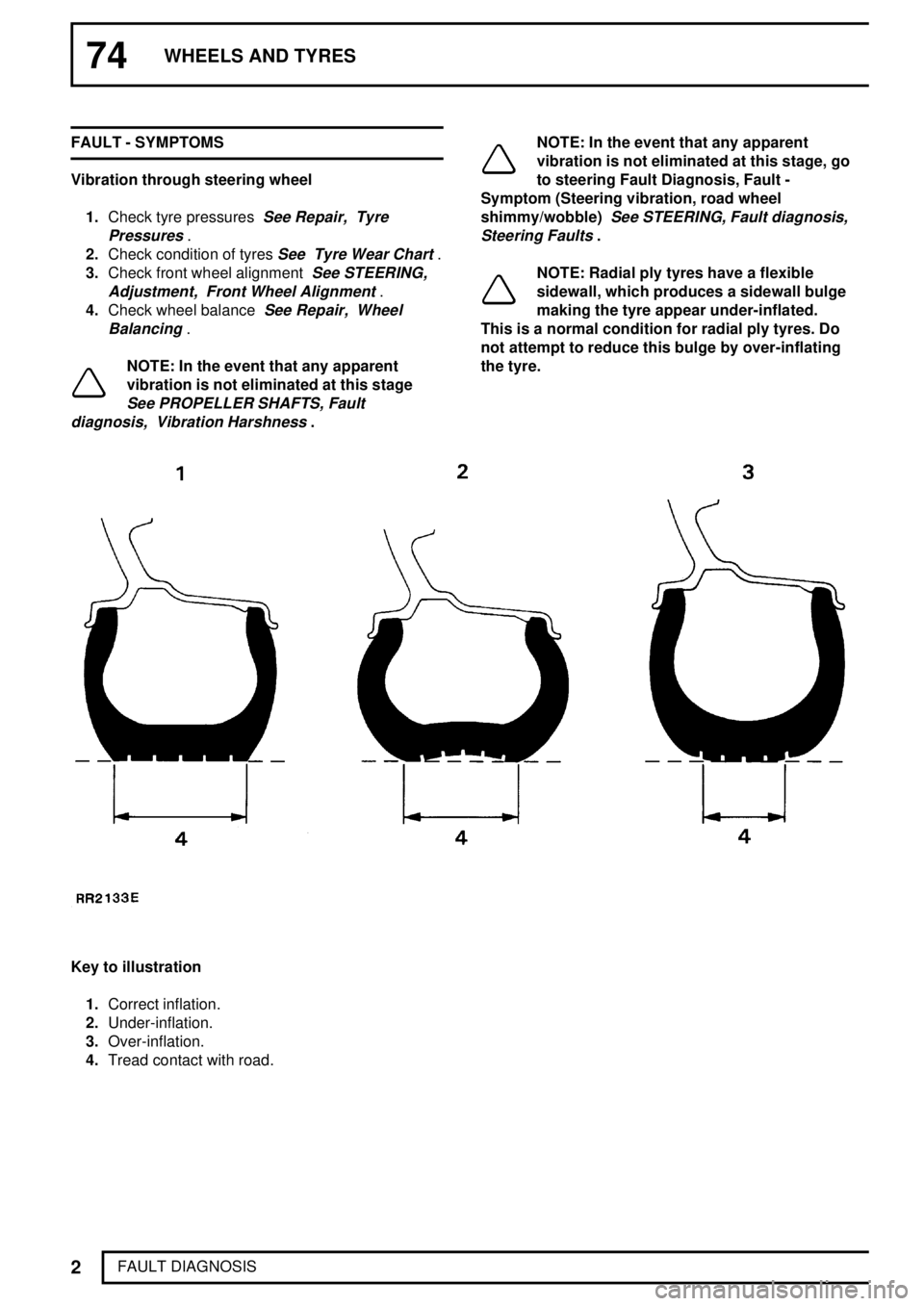
74WHEELS AND TYRES
2
FAULT DIAGNOSIS FAULT - SYMPTOMS
Vibration through steering wheel
1.Check tyre pressures
See Repair, Tyre
Pressures
.
2.Check condition of tyres
See Tyre Wear Chart.
3.Check front wheel alignment
See STEERING,
Adjustment, Front Wheel Alignment
.
4.Check wheel balance
See Repair, Wheel
Balancing
.
NOTE: In the event that any apparent
vibration is not eliminated at this stage
See PROPELLER SHAFTS, Fault
diagnosis, Vibration Harshness
.
NOTE: In the event that any apparent
vibration is not eliminated at this stage, go
to steering Fault Diagnosis, Fault -
Symptom (Steering vibration, road wheel
shimmy/wobble)
See STEERING, Fault diagnosis,
Steering Faults
.
NOTE: Radial ply tyres have a flexible
sidewall, which produces a sidewall bulge
making the tyre appear under-inflated.
This is a normal condition for radial ply tyres. Do
not attempt to reduce this bulge by over-inflating
the tyre.
Key to illustration
1.Correct inflation.
2.Under-inflation.
3.Over-inflation.
4.Tread contact with road.
Page 307 of 455
WHEELS AND TYRES
1
REPAIR REV: 05/99 GENERAL INFORMATION
WARNING: This is a multi-purpose vehicle
with wheels and tyres designed for both
on and off road usage. Only use wheels
and tyres specified for use on the vehicle.
The vehicle is equipped with tubeless 'S','T' or 'H'
rated radial ply tyres as standard equipment. The
tyres are of European metric size and must not be
confused with the "P" size metric tyres available in
North America.
Vehicle wheel sets, including spare wheel, must be
fitted with the same make and type of tyre to the
correct specification and tread pattern. Under no
circumstances must cross-ply or bias-belted tyres be
used.
For tyre specification and pressures
See GENERAL
SPECIFICATION DATA, Information, Wheels and
Tyres
.
Steel wheels
Tubeless tyres are mounted on 7.0 inch wide by 16
inch diameter steel wheels.
Alloy Wheels
Tubeless tyres are mounted on 7.0 inch wide by 16
inch diameter cast aluminium alloy wheels. The
surface has a paint finish covered with a clear
polyurethane lacquer. Care must be taken when
handling the wheel to avoid scratching or chipping the
finish.
The alloy wheel rim is of the asymmetric hump
type incorporating a safety hump to improve
location of the tyre bead in its seat. If difficulty is
experienced in fitting tyres to this type of rim
See
Tyre Fitting
.
WARNING: DO NOT fit an inner tube to an
alloy wheel.TYRE INSPECTION
Inspect tyres at weekly intervals to obtain maximum
tyre life and performance and to ensure compliance
with legal requirements. Check for signs of incorrect
inflation and uneven wear, which may indicate a need
for balancing or front wheel alignment,
See Fault
diagnosis, Tyre Wear Chart
, if the tyres have
abnormal or uneven wear patterns.
Check tyres at least weekly for cuts, abrasions, bulges
and for objects embedded in the tread. More frequent
inspections are recommended when the vehicle is
regularly used in off road conditions.
To assist tyre inspection, tread wear indicators are
moulded into the bottom of the tread grooves, as
shown in the illustration above.
When the tread has worn to a depth of 1.6 mm the
indicators appear at the surface as bars which
connect the tread pattern across the width of the tread
as shown in the illustration above.
Page 308 of 455

74WHEELS AND TYRES
2
REPAIRREV: 05/99 When the indicators appear in two or more adjacent
grooves, at three locations around the tyre, a new tyre
must be fitted.
NOTE: DO NOT attempt to interchange
tyres, e.g. from front to rear, as tyre wear
produces characteristic patterns
depending on their position. If tyre position is
changed after wear has occured, the performance
of the tyre will be adversely affected.
NOTE: Territorial vehicle regulations
governing tyre wear MUST be adhered to.
WHEELS INSPECTION
Regularly check the condition of the wheels. Replace
any wheel that is bent, cracked, dented or has
excessive runout.
VALVES INSPECTION
Check condition of inflation valve. Replace any valve
that is worn, cracked, loose, or leaking air.TYRE PRESSURES
Maximum tyre life and performance will be
obtained only if tyres are maintained at the correct
pressures.
Tyre pressures must be checked at least once a week
and preferably daily, if the vehicle is used off road.
The tyre inflation pressure is calculated to give the
vehicle satisfactory ride and steering characteristics
without compromising tyre tread life. For
recommended tyre pressures in all conditions
See
GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA, Information,
Wheels and Tyres
.
Always check tyre inflation pressures using an
accurate gauge and inflate tyres to the
recommended pressures only.
Check and adjust tyre pressuresONLYwhen the
tyres are cold, vehicle parked for three hours or more,
or driven for less than 3.2 km (2 miles) at speeds
below 64 km/h (40 mph). Do not reduce inflation
pressures if the tyres are hot or the vehicle has been
driven for more than 3.2 km (2 miles) at speeds over
64 km/h (40 mph), as pressures can increase by 0.41
bars (6 lb/in
2) over cold inflation pressures.
CheckALLtyre pressures including the spare. Refit
the valve caps as they form a positive seal and keep
dust out of the valve.
Page 309 of 455

WHEELS AND TYRES
3
REPAIR WHEEL BALANCING
CAUTION: It is essential that all wheel
balancing is carried out off the vehicle.
The use of on the vehicle balancing could
cause component damage or personal injury and
MUST NOT be attempted.
NOTE: Before attempting to balance a
wheel and tyre assembly clean all mud and
dirt deposits from both inside and outside
rims and remove existing balance weights.
Remove stones from the tyre tread in order to avoid
operator injury during dynamic balancing and to obtain
the correct balance.
Inspect tyres for damage and correct tyre pressures
and balance according to the equipment
manufacturer's instructions.
Steel wheels
Clean area of wheel rim and attach balance weights in
position shown.
Alloy wheels
Clean area of wheel rim and attach adhesive balance
weights in position shown. Cut through rear face of
weight strip to detach required weights.
CAUTION: Use only correct adhesive
balance weights to avoid damage to
aluminium wheel rim. DO NOT attempt to
use a steel wheel weight on an aluminium wheel.
Page 310 of 455

74WHEELS AND TYRES
4
REPAIR Static balance
Wheel tramp
A- Heavy spot.
B- Add balance weights here.
C- Centre line of spindle.
Static balance is the equal distribution of weight
around the wheel. A statically unbalanced wheel will
cause a bouncing action called wheel tramp. This
condition will eventually cause uneven tyre wear.Dynamic balance
Wheel shimmyA- Heavy spot.
B- Add balance weights here.
C- Centre line of spindle.
Dynamic balance is the equal distribution of weight on
each side of the centre line so that when the wheel
spins there is no tendency for side to side movement.
A dynamically unbalanced wheel will cause wheel
shimmy.