Gear ratio LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 632 of 1529

AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24
REPAIRS 44-35
32.Remove 'C' clip securing selector cable to
gearbox bracket.
33.Remove nut securing selector lever to inhibitor
switch and release lever.
34.Disconnect multiplug from inhibitor switch.
35.Loosen gearbox multiplug locking ring and
disconnect plug.
36.Lower gearbox sufficiently to access bell
housing bolts, take care not to trap any pipes or
cables when lowering gearbox.
37.Remove 14 bolts securing gearbox to engine.
38.With assistance remove gearbox from engine.39.Fit suitable strap to retain torque converter.
Refit
1.Clean gearbox to engine mating faces.
2.Remove torque converter retaining strap.
3.With assistance position gearbox to engine.
4.Fit gearbox bell housing bolts and tighten to 46
Nm (34 lbf.ft)..
5.Connect multiplug to gearbox and tighten
locking ring.
6.Connect inhibitor switch multiplug.
7. If fitted: Connect and adjust differential lock
selector cable.
+ TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE,
ADJUSTMENTS, Cable - selector -
differential lock - adjust.
8.Position selector lever to inhibitor switch and
tighten nut to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
9.Position selector cable to gearbox and secure
with 'C' clip.
10.Clean oil pipe unions and fit new 'O' rings.
11.Position and tighten pipe unions to gearbox.
12.Position and tighten oil cooler pipe clamps.
13.Position and tighten oil cooler pipe clip to
engine sump.
14.Position engine RH and LH rear mountings
and tighten bolts to 85 Nm (63 lbf.ft) and nuts to
85 Nm (63 lbf.ft).
15.Secure gearbox breather pipes to bulkhead
clip.
16. Up to 03 Model Year - If fitted: Connect 2
Lucars to differential lock warning lamp switch
and multiplugs to high/low ratio switch and
neutral sensor.
17. 03 Model Year onwards - If fitted: Connect
differential lock warning lamp switch multiplugs
to main harness.
18.Position cable tie and multiplug to transfer
gearbox bracket.
19.Connect high/low ratio selector cable to
selector lever and secure with clevis pin.
20.Position high/low ratio selector cable to
abutment bracket and secure with 'C' clip.
Page 697 of 1529
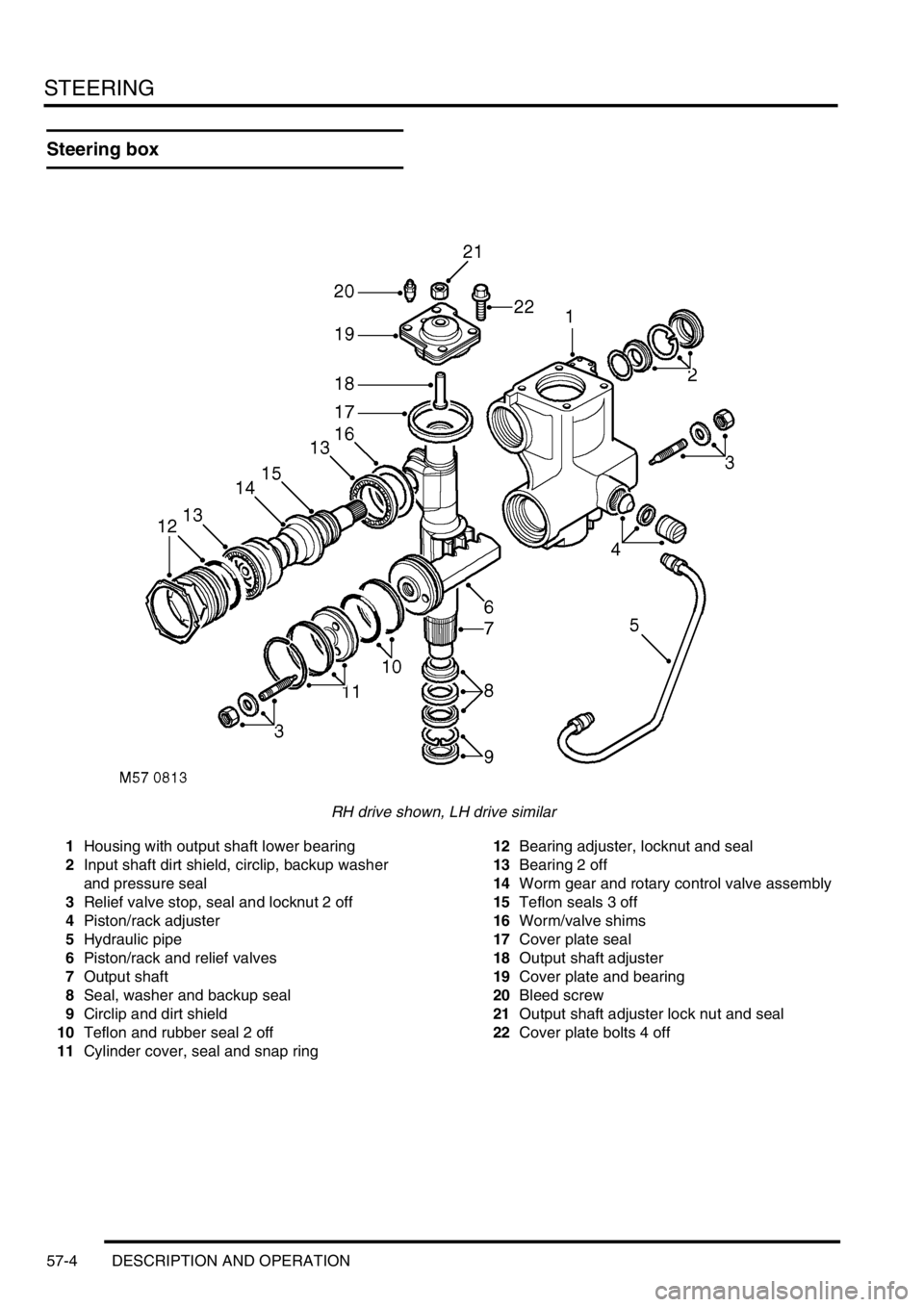
STEERING
57-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Steering box
RH drive shown, LH drive similar
1Housing with output shaft lower bearing
2Input shaft dirt shield, circlip, backup washer
and pressure seal
3Relief valve stop, seal and locknut 2 off
4Piston/rack adjuster
5Hydraulic pipe
6Piston/rack and relief valves
7Output shaft
8Seal, washer and backup seal
9Circlip and dirt shield
10Teflon and rubber seal 2 off
11Cylinder cover, seal and snap ring12Bearing adjuster, locknut and seal
13Bearing 2 off
14Worm gear and rotary control valve assembly
15Teflon seals 3 off
16Worm/valve shims
17Cover plate seal
18Output shaft adjuster
19Cover plate and bearing
20Bleed screw
21Output shaft adjuster lock nut and seal
22Cover plate bolts 4 off
Page 698 of 1529

STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-5
Description
General
The major steering components comprise an impact absorbing telescopic steering column, a Power Assisted Steering
(PAS) box, a PAS pump, and fluid reservoir. Hydraulic fluid from the fluid reservoir is filtered and then supplied
through the suction line to the inlet on the PAS pump. The PAS pump supplies fluid to the steering box through a
pressure line routed above the front cross member. Fluid returns to the reservoir along the same route through a
return line. On LH drive vehicles the pipe route above the front cross member is still used, the length of pipe acting
as an oil cooler.
To minimise driver's injury in the event of an accident the steering system has a number of safety features including
a collapsible steering column. An additional safety feature is an air bag located in the steering wheel.
+ RESTRAINT SYSTEMS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SRS.
Steering column assembly and intermediate shaft
The steering column central shaft comprises of two shafts, the upper shaft is splined to accept the steering wheel and
located in bearings in the column tube. A universal joint is located on the bottom of the upper shaft, the joint allows
for angular movement between the upper and lower shafts. The lower shaft is made in two parts, the top section of
the lower shaft is located outside of the lower section. The two sections of the lower shaft are connected by two nylon
injection moulded shear pins. The lower shaft goes through a lower bearing attached to the bulkhead, the lower shaft
is connected by a universal joint to the intermediate shaft in the engine compartment.
Steering column
An upper column tube provides for the location of the steering lock and ignition switch and also the steering switch
gear and a rotary coupler. The rotary coupler provides the electrical connection for the steering wheel mounted airbag,
switches and horn. The upper mounting bracket has two slots, a slotted metal bracket is held in each slot by four resin
shear pins.
The column is mounted on four captive studs which are located on a column mounting bracket. The captive studs
pass through the metal brackets, locknuts secure the steering column to the bulkhead. The two lower mountings are
fixed and cannot move when loads are applied to them. The upper mounting is designed to disengage or deform when
a load is applied, allowing the column to collapse in the event of an accident. The steering column must be replaced
as a complete assembly if necessary.
When an axial load is applied to the upper column tube, energy absorption is achieved by the following mechanism:
lthe mounting bracket deforms,
lthe resin shear pins holding the slotted metal brackets shear,
lthe top mounting bracket slides out of the slotted metal brackets.
The slotted metal brackets remain on the captive studs on the bulkhead. If the column mounting moves, injection
moulded shear pins retaining the two sections of the lower column shaft will shear. This allows the two sections of the
lower shaft to 'telescope' together.
In the event of a collision where the steering box itself moves, two universal joints in the column allow the intermediate
shaft to articulate, minimising movement of the column towards the driver. If movement continues energy absorption
is achieved by the following mechanism:
lthe decouple joint in the intermediate shaft will disengage,
lthe lower section of the steering column shaft will move through the lower bearing,
lthe injection moulded shear pins retaining the two sections of the lower column shaft will shear.
This allows the two sections of the lower shaft to 'telescope' together reducing further column intrusion. Protection to
the drivers face and upper torso is provided by an SRS airbag module located in the centre of the steering wheel.
+ RESTRAINT SYSTEMS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SRS.
Page 701 of 1529
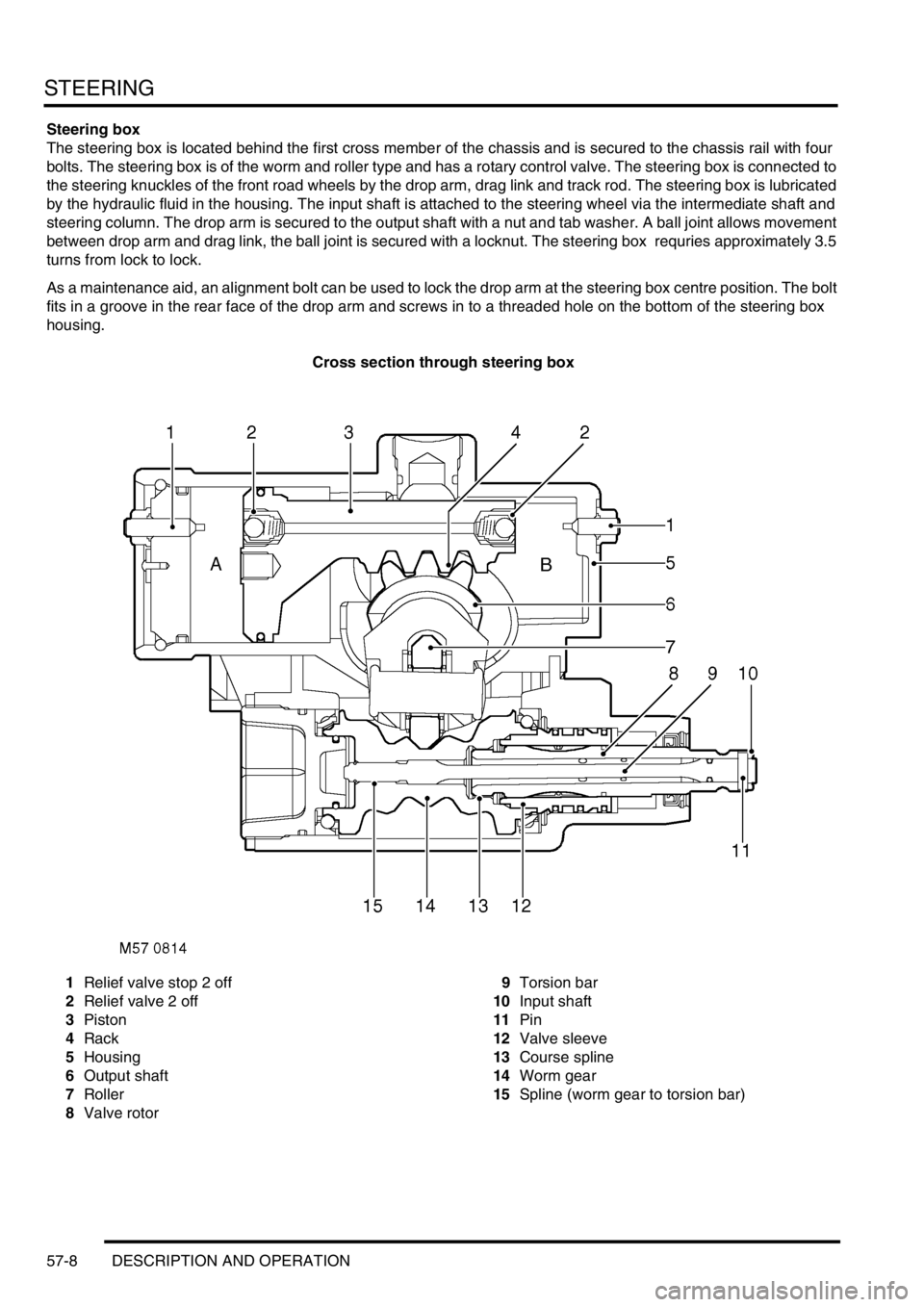
STEERING
57-8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Steering box
The steering box is located behind the first cross member of the chassis and is secured to the chassis rail with four
bolts. The steering box is of the worm and roller type and has a rotary control valve. The steering box is connected to
the steering knuckles of the front road wheels by the drop arm, drag link and track rod. The steering box is lubricated
by the hydraulic fluid in the housing. The input shaft is attached to the steering wheel via the intermediate shaft and
steering column. The drop arm is secured to the output shaft with a nut and tab washer. A ball joint allows movement
between drop arm and drag link, the ball joint is secured with a locknut. The steering box requries approximately 3.5
turns from lock to lock.
As a maintenance aid, an alignment bolt can be used to lock the drop arm at the steering box centre position. The bolt
fits in a groove in the rear face of the drop arm and screws in to a threaded hole on the bottom of the steering box
housing.
Cross section through steering box
1Relief valve stop 2 off
2Relief valve 2 off
3Piston
4Rack
5Housing
6Output shaft
7Roller
8Valve rotor9Torsion bar
10Input shaft
11Pin
12Valve sleeve
13Course spline
14Worm gear
15Spline (worm gear to torsion bar)
Page 702 of 1529

STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-9
Principle of operation
Movement of the input shaft is transferred through the pin to the torsion bar and valve rotor on the input shaft. As the
input shaft turns, the spline of the torsion bar turns the worm gear. This action causes the roller to rotate on its bearings
and move. As the roller is located by a pin to a yoke on the output shaft, the output shaft rotates in the steering box
housing. As the amount of torque acting on the input shaft increases the torsion bar starts to twist. As the torsion bar
twists the valve rotor turns in the valve sleeve. When the ports in the valve rotor and valve sleeve are turned, hydraulic
fluid is directed to chamber 'A' or 'B' in the power cylinder.
With hydraulic fluid in one chamber under high pressure, the piston moves. The return line ports in the rotary valve,
aligned by the movement of the valve rotor, allow the fluid in the opposite chamber to flow to return. The teeth of the
rack move and transfer the force from the piston to the output shaft, giving assistance to move the drop arm. As the
output shaft rotates the torsion bar load is decreased. The rotor on the input shaft will return as the torsion bar
unwinds, the rotary valve will then be in a neutral position and the pressure in chambers 'A' and 'B' will equalise. With
no high pressure acting on the piston, force on the piston and rack is released.
To prevent heat accumulation at full steering lock due to excessive pressure, a relief valve inside the steering box is
opened as the box approaches full lock. The relief valve pins are located in the cylinder cover and housing and are
not to be adjusted.
The steering box design ensures a mechanical link through the course spline on the control valve rotor, the spline will
become engaged if:
lThe hydraulic pressure fails.
lThe steering box rotary control valve fails.
The coarse spline may also engage in some full lock situations if sufficient torque is applied to the input shaft.
Page 703 of 1529

STEERING
57-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Rotary control valve
The rotary valve assembly comprises of three parts. The valve sleeve is fixed inside one end of the worm gear, the
valve sleeve has ports through it to allow the passage of hydraulic fluid. The input shaft has a valve rotor machined
on one end, the valve rotor also has ports through it and can rotate in the valve sleeve. A torsion bar is attached to
the input shaft by a pin, the torsion bar goes through the input shaft and valve rotor and is engaged by a spline into
the worm gear.
The coarse spline on the end of the valve rotor is loosely engaged in the worm gear, the coarse spline can make
contact and drive the worm gear in some full lock and in no pressure conditions. In the event of a torsion bar failure,
power assistance will be lost, the coarse spline will drive the worm gear and enable the vehicle to be steered and
driver control maintained.
Rotary control valve at neutral
1Worm gear
2Torsion bar
3Valve sleeve
4Pin5Input shaft and valve rotor
6Piston/rack
7Coarse spline
8Spline (torque shaft to worm gear)
When there is no demand for assistance the torsion bar holds the ports in the valve sleeve and valve rotor in a neutral
relationship to one another. The ports in the valve sleeve and the valve rotor are so aligned to allow equal (low) fluid
pressure on each side of the piston. Excess fluid flows through ports in the valve rotor through the valve sleeve and
back to the reservoir.
Page 704 of 1529
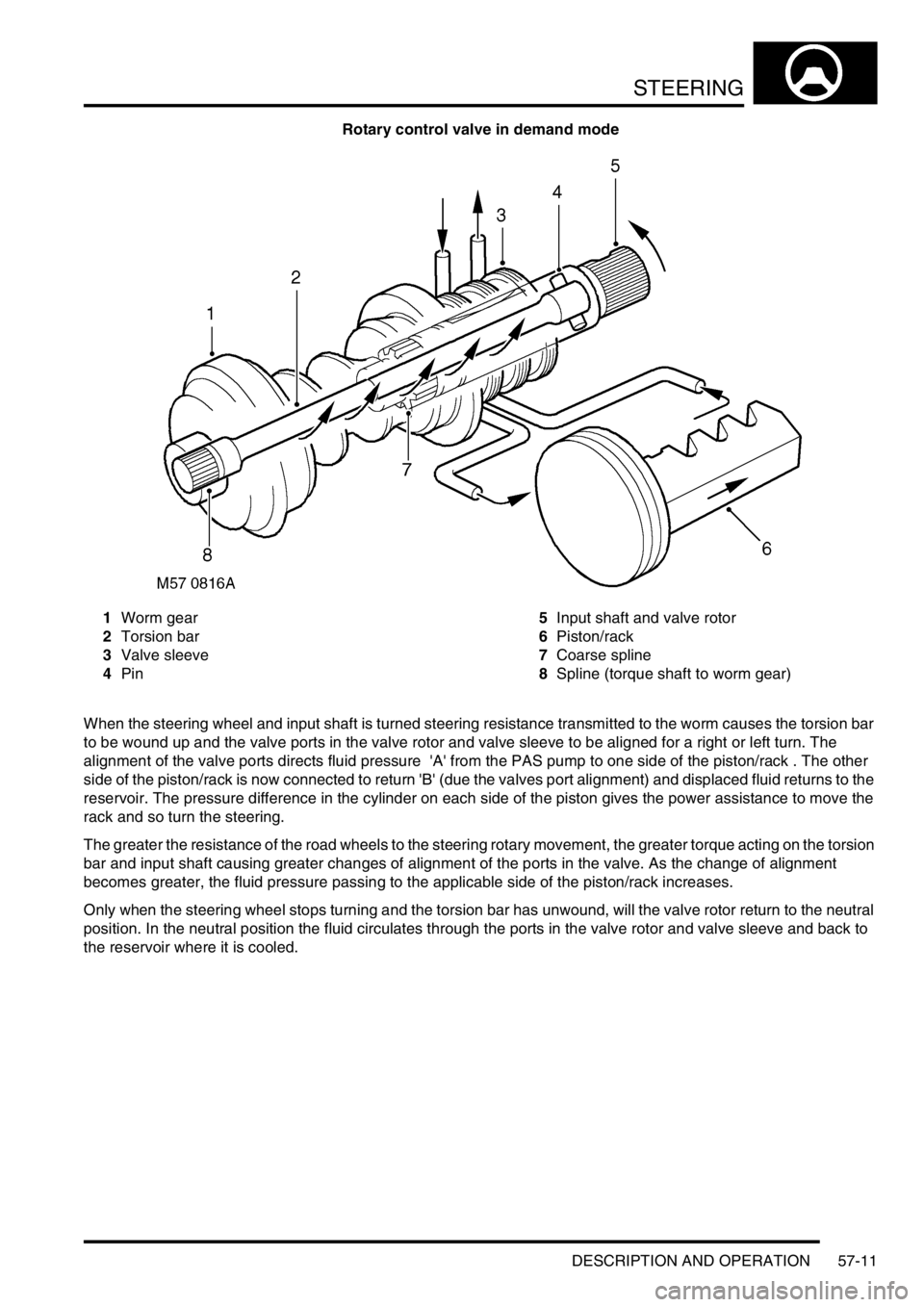
STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-11
Rotary control valve in demand mode
1Worm gear
2Torsion bar
3Valve sleeve
4Pin5Input shaft and valve rotor
6Piston/rack
7Coarse spline
8Spline (torque shaft to worm gear)
When the steering wheel and input shaft is turned steering resistance transmitted to the worm causes the torsion bar
to be wound up and the valve ports in the valve rotor and valve sleeve to be aligned for a right or left turn. The
alignment of the valve ports directs fluid pressure 'A' from the PAS pump to one side of the piston/rack . The other
side of the piston/rack is now connected to return 'B' (due the valves port alignment) and displaced fluid returns to the
reservoir. The pressure difference in the cylinder on each side of the piston gives the power assistance to move the
rack and so turn the steering.
The greater the resistance of the road wheels to the steering rotary movement, the greater torque acting on the torsion
bar and input shaft causing greater changes of alignment of the ports in the valve. As the change of alignment
becomes greater, the fluid pressure passing to the applicable side of the piston/rack increases.
Only when the steering wheel stops turning and the torsion bar has unwound, will the valve rotor return to the neutral
position. In the neutral position the fluid circulates through the ports in the valve rotor and valve sleeve and back to
the reservoir where it is cooled.
Page 709 of 1529

STEERING
57-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Hydraulic fluid is supplied to the PAS pump inlet from the PAS reservoir, the PAS pump draws in and pressurises the
fluid. The PAS pump self regulates internal flow rates and operating pressure, and supplies pressurised fluid from the
PAS pump outlet to a rotary control valve in the steering box. At neutral the fluid is circulated by the PAS pump and
flows around the system at a lower pressure and a constant flow rate. With most of the fluid being returned to the
reservoir the pressure inside the system remains very low. When a control input turns the rotary control valve in the
steering box, pressure in the system will rise as the control valve directs fluid to give power assistance.
The action of turning the steering wheel turns the steering column and intermediate shaft. The intermediate shaft turns
the input shaft of the steering box. The input shaft moves the rotary control valve in the steering box, the rotary valve
controls the pressure used inside the steering box for power assistance. The input shaft also turns a worm gear, the
worm gear acts on a roller attached to the output shaft. As the worm gear turns the roller, the roller travels along the
lands of the worm gear. As the roller is attached to the output shaft the output shaft turns.
As the output shaft of the steering box turns, hydraulic pressure is supplied via the rotary control valve to the steering
box. The hydraulic pressure acts on a rack that assists with the movement of the output shaft of the steering box. A
drop arm is attached to the output shaft of the steering box. The drop arm is connected to a drag link by a ball joint.
The drag link is connected via ball joints to one front steering knuckle and road wheel. A track rod connected to this
steering knuckle links the two steering knuckles together. As one steering knuckle and road wheel is turned by the
drag link, the other steering knuckle and wheel is moved by the track rod.
Page 763 of 1529
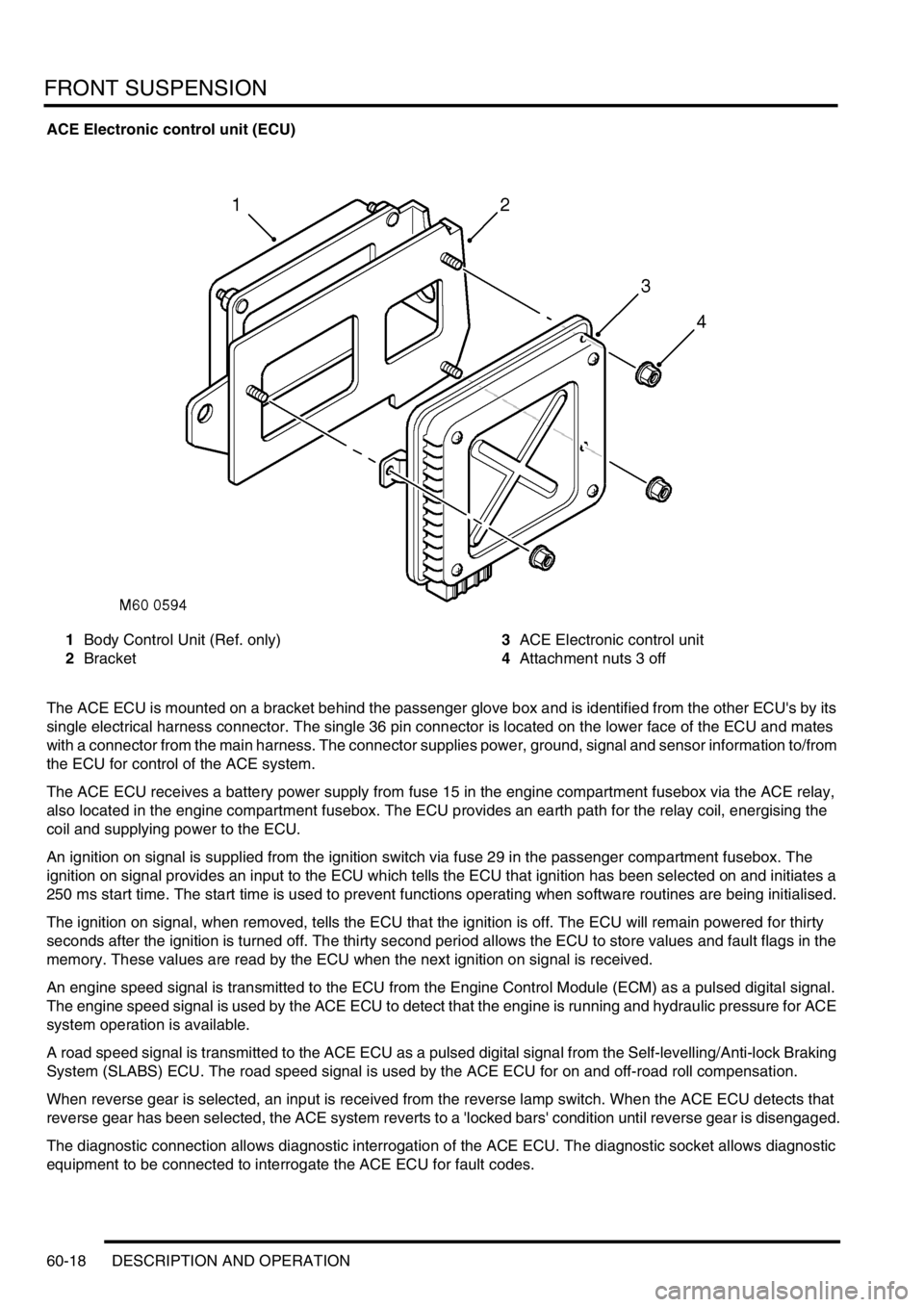
FRONT SUSPENSION
60-18 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ACE Electronic control unit (ECU)
1Body Control Unit (Ref. only)
2Bracket3ACE Electronic control unit
4Attachment nuts 3 off
The ACE ECU is mounted on a bracket behind the passenger glove box and is identified from the other ECU's by its
single electrical harness connector. The single 36 pin connector is located on the lower face of the ECU and mates
with a connector from the main harness. The connector supplies power, ground, signal and sensor information to/from
the ECU for control of the ACE system.
The ACE ECU receives a battery power supply from fuse 15 in the engine compartment fusebox via the ACE relay,
also located in the engine compartment fusebox. The ECU provides an earth path for the relay coil, energising the
coil and supplying power to the ECU.
An ignition on signal is supplied from the ignition switch via fuse 29 in the passenger compartment fusebox. The
ignition on signal provides an input to the ECU which tells the ECU that ignition has been selected on and initiates a
250 ms start time. The start time is used to prevent functions operating when software routines are being initialised.
The ignition on signal, when removed, tells the ECU that the ignition is off. The ECU will remain powered for thirty
seconds after the ignition is turned off. The thirty second period allows the ECU to store values and fault flags in the
memory. These values are read by the ECU when the next ignition on signal is received.
An engine speed signal is transmitted to the ECU from the Engine Control Module (ECM) as a pulsed digital signal.
The engine speed signal is used by the ACE ECU to detect that the engine is running and hydraulic pressure for ACE
system operation is available.
A road speed signal is transmitted to the ACE ECU as a pulsed digital signal from the Self-levelling/Anti-lock Braking
System (SLABS) ECU. The road speed signal is used by the ACE ECU for on and off-road roll compensation.
When reverse gear is selected, an input is received from the reverse lamp switch. When the ACE ECU detects that
reverse gear has been selected, the ACE system reverts to a 'locked bars' condition until reverse gear is disengaged.
The diagnostic connection allows diagnostic interrogation of the ACE ECU. The diagnostic socket allows diagnostic
equipment to be connected to interrogate the ACE ECU for fault codes.
Page 766 of 1529
FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-21
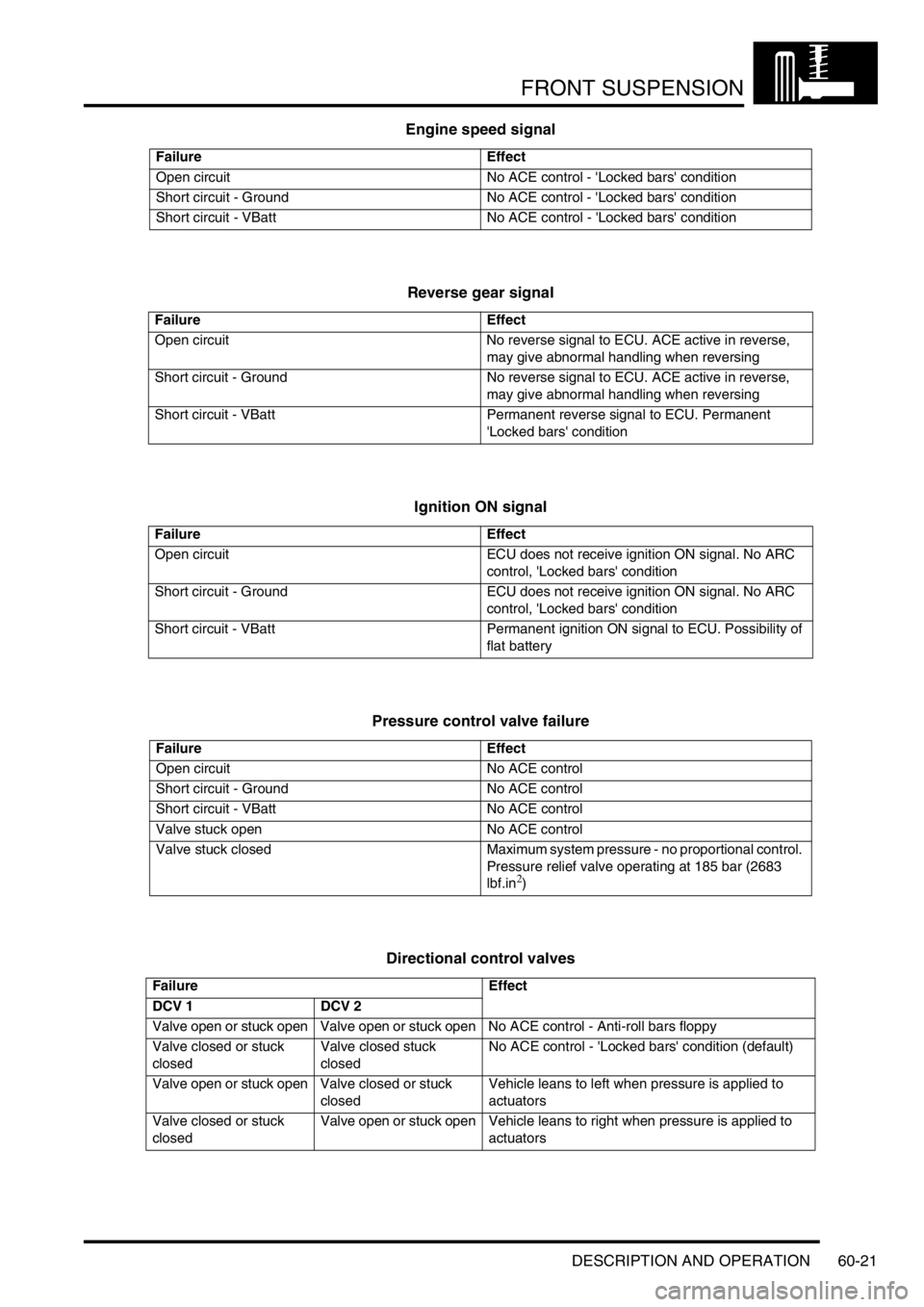
Engine speed signal
Reverse gear signal
Ignition ON signal
Pressure control valve failure
Directional control valves
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit No reverse signal to ECU. ACE active in reverse,
may give abnormal handling when reversing
Short circuit - Ground No reverse signal to ECU. ACE active in reverse,
may give abnormal handling when reversing
Short circuit - VBatt Permanent reverse signal to ECU. Permanent
'Locked bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit ECU does not receive ignition ON signal. No ARC
control, 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground ECU does not receive ignition ON signal. No ARC
control, 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt Permanent ignition ON signal to ECU. Possibility of
flat battery
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control
Valve stuck open No ACE control
Valve stuck closed Maximum system pressure - no proportional control.
Pressure relief valve operating at 185 bar (2683
lbf.in
2)
Failure Effect
DCV 1 DCV 2
Valve open or stuck open Valve open or stuck open No ACE control - Anti-roll bars floppy
Valve closed or stuck
closedValve closed stuck
closedNo ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition (default)
Valve open or stuck open Valve closed or stuck
closedVehicle leans to left when pressure is applied to
actuators
Valve closed or stuck
closedValve open or stuck open Vehicle leans to right when pressure is applied to
actuators