service indicator LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 253 of 1529
EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
For NAS vehicles with positive pressure, EVAP system leak detection capability, the atmosphere vent line from the
EVAP canister connects to a port on the fuel leak detection pump via a short, large bore hose which is secured to the
component ports by crimped metal clips at each end. A large bore plastic hose from the top of the leak detection pump
is routed to the RH side of the engine bay where it connects to an air filter canister. Under normal operating conditions
(when the fuel leak detection solenoid valve is not energised), the EVAP canister is able to take in clean air via the
air filter, through the pipework and past the open solenoid valve to allow normal purge operation to take place and
release any build up of EVAP system pressure to atmosphere.
The EVAP system pipes are clipped at various points along the pipe runs and tied together with tie straps at suitable
points along the runs.
The NAS and ROW EVAP canisters are of similar appearance, but use charcoal of different consistency. The ROW
vehicles use granular charcoal of 11 bwc (butane working capacity) and NAS vehicles use pelletised charcoal with a
higher absorption capacity of 15 bwc. All canisters are of rectangular shape and have capacities of 1.8 litres (3 1/8
imp. pts) with purge foam retention.
Purge Valve
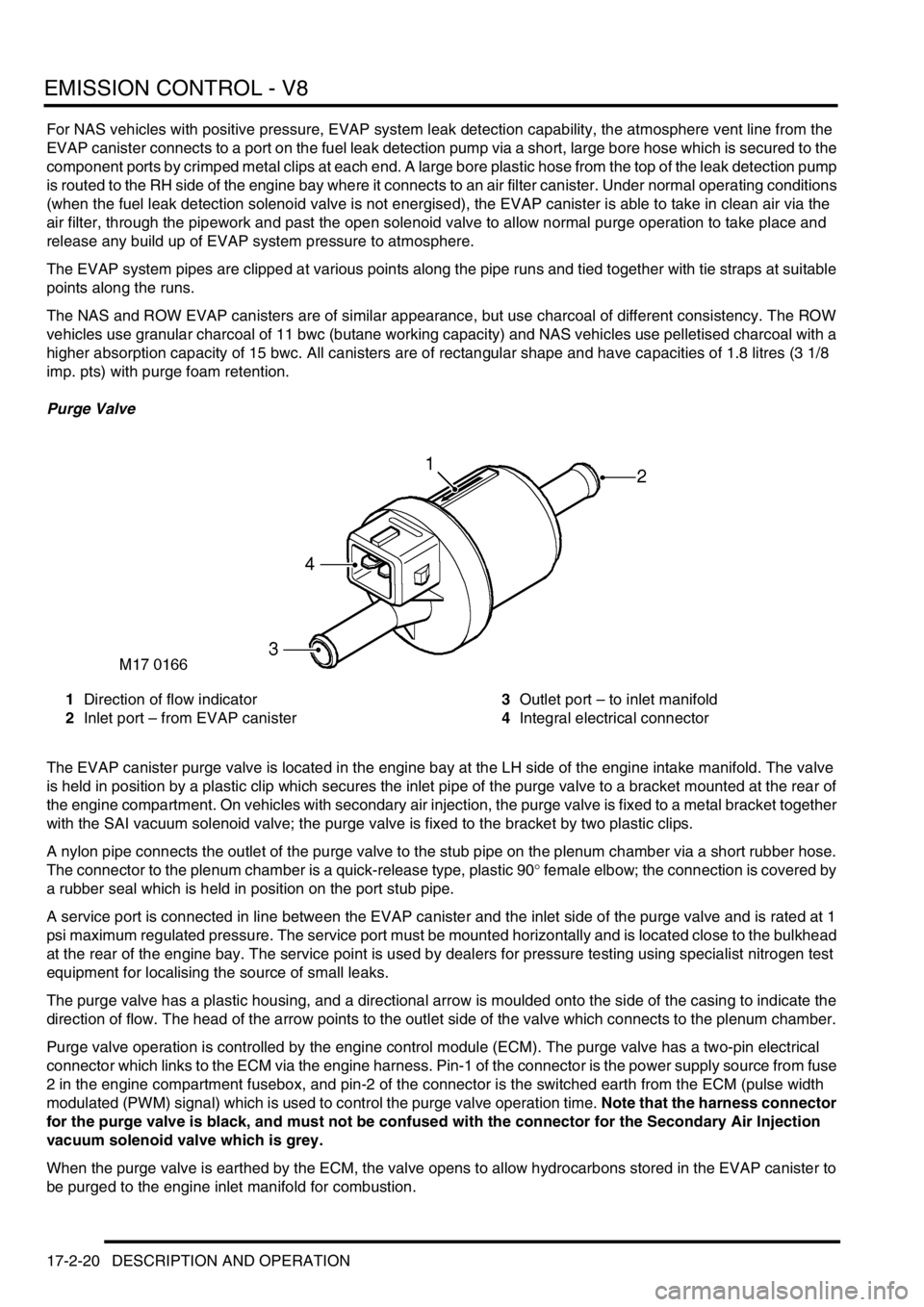
1Direction of flow indicator
2Inlet port – from EVAP canister3Outlet port – to inlet manifold
4Integral electrical connector
The EVAP canister purge valve is located in the engine bay at the LH side of the engine intake manifold. The valve
is held in position by a plastic clip which secures the inlet pipe of the purge valve to a bracket mounted at the rear of
the engine compartment. On vehicles with secondary air injection, the purge valve is fixed to a metal bracket together
with the SAI vacuum solenoid valve; the purge valve is fixed to the bracket by two plastic clips.
A nylon pipe connects the outlet of the purge valve to the stub pipe on the plenum chamber via a short rubber hose.
The connector to the plenum chamber is a quick-release type, plastic 90° female elbow; the connection is covered by
a rubber seal which is held in position on the port stub pipe.
A service port is connected in line between the EVAP canister and the inlet side of the purge valve and is rated at 1
psi maximum regulated pressure. The service port must be mounted horizontally and is located close to the bulkhead
at the rear of the engine bay. The service point is used by dealers for pressure testing using specialist nitrogen test
equipment for localising the source of small leaks.
The purge valve has a plastic housing, and a directional arrow is moulded onto the side of the casing to indicate the
direction of flow. The head of the arrow points to the outlet side of the valve which connects to the plenum chamber.
Purge valve operation is controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The purge valve has a two-pin electrical
connector which links to the ECM via the engine harness. Pin-1 of the connector is the power supply source from fuse
2 in the engine compartment fusebox, and pin-2 of the connector is the switched earth from the ECM (pulse width
modulated (PWM) signal) which is used to control the purge valve operation time. Note that the harness connector
for the purge valve is black, and must not be confused with the connector for the Secondary Air Injection
vacuum solenoid valve which is grey.
When the purge valve is earthed by the ECM, the valve opens to allow hydrocarbons stored in the EVAP canister to
be purged to the engine inlet manifold for combustion.
Page 306 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-7
The ECM controls the following outputs:
lFuel injectors (1 per cylinder).
lIgnition coils/ high tension leads/ spark plugs.
lFuel pump relay.
lIdle air control valve.
lHeated oxygen sensors.
lEVAP canister purge valve.
lEVAP canister vent solenoid (CVS) valve (where fitted).
lMalfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ service engine soon lamp (where fitted).
lHill descent control (via SLABS interface).
lEVAP system fuel leak detection pump (where fitted)
lSecondary air injection pump (where fitted)
The ECM also interfaces with the following:
lDiagnostics via diagnostic connector with TestBook.
lController Area Network (CAN) link to EAT ECU.
lAir conditioning system.
lSelf Levelling & Anti-lock Braking System (SLABS) ECU.
lImmobilisation system via the body control unit (BCU).
lInstrument cluster.
lCruise control ECU
lActive Cornering Enhancement (ACE) ECU
Page 344 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-45
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ service engine soon warning lamp
The MIL/ service engine soon warning lamp is located in the instrument cluster. It illuminates to alert the driver to
system malfunctions. Service engine soon warning lamp is the name for this warning lamp in NAS only, it is called
MIL in all other markets.
During ignition a self-test function of the lamp is carried out. The lamp will illuminate for 3 seconds then it will
extinguish if no faults exist.
+ INSTRUMENTS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Input/Output
The MIL is supplied with battery voltage from the instrument cluster. When the ECM detects a fault, it provides an
earth path to illuminate the MIL. Output to the MIL is via pin 20 of connector C0637 of the ECM.
Air Temperature Control (ATC) request
The ATC request comes via the ATC switch located in the facia panel. When the driver operates the switch it acts as
a request from the ATC ECU to engage the ATC clutch to drive the system.
During periods of high driver demand such as hard acceleration or maximum rev/min the ATC clutch will be disabled
for a short time. This is to reduce the load on the engine.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Page 738 of 1529

STEERING
REPAIRS 57-45
Shaft - intermediate and universal joint -
steering column
$% 57.40.22
The intermediate shaft has a red indicator clip
fitted which must be inspected at service, and
after the vehicle has been subject to an impact.
If the clip is not present or is not fully seated
against the clamp plate, a new assembly must be
fitted.
Remove
1. LHD diesel: Loosen 2 clips securing
intercooler to turbocharger hose. Place hose
aside.
2.Remove bolt securing intermediate shaft to
steering column.
3.Remove bolt securing intermediate shaft to
universal joint.
4. Universal joint: Remove the bolt securing the
universal joint to the steering box.
Page 1302 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-15
Electric seats
The BCU controls the logical operation of the electrically operated front seats. Two modes of operation are available:
+ SEATS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - electric seats.
lElectric seat adjustment is enabled if the ignition is on or the driver's door is opened for a short time period.
lElectric seat adjustment is enabled if the ignition is on and the driver's door is closed.
The seats are operated by four electric motors which control the seat cushion rear up/ down, the seat cushion front
up/ down, seat cushion forward/ rearward and seat squab recline. The electrically powered lumbar adjustment in each
seat is operated by a single motorised air pump and a solenoid located on the seat squab frame. The air pump inflates
a cushion in the seat squab and the solenoid operates a valve to deflate the cushion. The seat squab and cushion
may also contain heater elements to provide heated seat operation.
The switches for electrically operated seats are located either side of the centre console.
Direction indicators and hazard warning lamps
The direction indicator lamps are operated from a three position direction indicator switch on the left hand, steering
column stalk. The BCU only allows the lamps to work as direction indicators when the ignition switch is in position II.
The BCU also controls the lamps to operate as hazard warning lamps and as a visual warning for the anti-theft system,
in which cases all lamps flash simultaneously irrespective of the ignition switch position.
System control of the direction indicators and hazard warning lamps is provided by the BCU operating with the IDM
and two electronic relays located in the passenger compartment fuse box. The IDM and relays are integral parts of
the passenger compartment fuse box and cannot be serviced individually. The serial data bus is used for
communication of status and operation requests between the BCU, IDM and instrument pack.
The hazard warning lamps are operated from a latching pushbutton switch located on the fascia.
All direction indicator/ hazard warning lamp bulbs are rated at 5 Watts.
Headlamps
The BCU contains a feature which allow the vehicle headlamps to be turned on when the remote transmitter is
pressed (courtesy headlamps).
For markets with daylight running lamps, the BCU controls the logical operation of the daylight running lamps. Options
are daylight running lamps are on if the main beam headlamps are off, or the daylight running lamps are on with main
and dipped beam off and the gearbox not in Park.
Front fog lamps
For markets with front fog lamps fitted, the BCU controls the operation of the front fog lamps. Options can be selected
so that the fog lamps will operate with or without the headlamps on main beam.
Instrument pack
The BCU communicates with the instrument pack via a serial data bus.
+ INSTRUMENTS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
lThe instrument pack provides the BCU and IDM with details of vehicle speed.
lSignals are provided from the IDM to the instrument pack and BCU when the direction indicator lamps are active.
lFor certain markets, the BCU provides a signal to the instrument pack for indicating when the transfer box is in
neutral.
lThe IDM can signal the instrument pack to illuminate a trailer warning lamp. This operates when the IDM senses
that the current drawn by the indicator circuit exceeds a preset threshold.
lThe odometer reading displayed on the instrument pack LCD screen is also stored in non volatile memory in the
BCU. Whenever the ignition is turned from position I to position II, the instrument pack and the BCU compare
their stored values.
lThe gear selector position is displayed on the instrument pack LCD screen under the direction of the BCU.
Starting
The starting system comprises a starter motor and solenoid located at the rear right hand side of the engine. A starter
relay controlled by the BCU is used to supply battery power for starter solenoid operation. The starter motor receives
its feed directly from the battery.
Page 1488 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-5
Description
General
The instrument pack consists of four analogue dials, four warning lamp packs and a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
odometer.
The four dials are used to indicate:
lRoad speed.
lEngine speed.
lFuel tank level.
lEngine coolant temperature.
The dials are driven by a microprocessor from information received from the serial communication link. Information
input is received as either:
lDigital.
lAnalogue.
lPulse train.
lPulse Width Modulation (PWM).
The LCD provides information for:
lOdometer.
lTrip distance.
lSelected gear (on vehicles fitted with an automatic gearbox).
A trip reset button is provided to zero the trip display, this button also allows the selection of "miles" or "kilometres"
for the display. A photocell controls the illumination of the LCD, maintaining contrast of the display during ambient light
changes.
Within the four warning lamp packs there are 28 lamps. A long life bulb illuminates the high beam warning lamp and
the rest of the warning lamps are illuminated by Light Emitting Diodes (LED's). All warning lamp legends are invisible
until lit. When lit the symbols are illuminated on a black background.
The warning lamps illuminate in one of four colours. The colour indicates the level of importance to the driver, as
follows:
lRed = warning.
lAmber = caution.
lGreen = system operative.
lBlue = main beam operative.
The first warning lamp pack is located in the top left-hand side of the instrument pack and contains the following
warning lamps:
lTraction control warning lamp.
lTransfer box in neutral warning lamp.
lDifferential lock warning lamp
lOverspeed warning lamp (activated for gulf market only).
lBrake system warning lamp.
lHill Descent Control (HDC) information warning lamp.
lMalfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ SERVICE ENGINE SOON warning lamp.
The second warning lamp pack is located in the centre of the instrument pack and contains the following warning
lamps:
lDirection indicator warning lamps.
lHigh beam warning lamp.
lAnti-lock brake system warning lamp.
Page 1495 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
88-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)/ SERVICE ENGINE SOON warning lamp
The MIL/service engine soon warning lamp within the instrument pack utilises an amber LED and a clear legend. If
an emission related fault is detected by the engine management system or, on automatic gearbox models, the EAT
ECU, the ECM will illuminate the LED providing the driver with a visible warning.
The warning lamp will illuminate whenever the vehicle is driven until the fault is repaired, and the ECM fault code
memory is cleared using TestBook.
When the ignition is switch on the ECM carries out a self-test function of the lamp. The lamp will illuminate for 3
seconds then extinguish if no faults exist. If a fault is present the lamp will be extinguished for 1 second before
illuminating again to indicate a fault exists.
There are two configurations of the legend for the warning lamp:
lNAS and Canada = SERVICE ENGINE SOON text.
lAll other markets = MIL SAE J1930 symbol.
The power input for the LED is supplied by the instrument pack via fuse 27. The ECM provides a voltage to the
instrument pack Central Processing Unit (CPU) to control the warning lamp:
l< 1.8 volts = warning lamp on.
l> 7.7 volts = warning lamp off.