inflation pressure LINCOLN AVIATOR 2023 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LINCOLN, Model Year: 2023, Model line: AVIATOR, Model: LINCOLN AVIATOR 2023Pages: 681, PDF Size: 9.33 MB
Page 328 of 681

Why is the feature not available (line markings are gray) when I can see the lane markings on the road?
You are driving too close to the vehicle in front of you.
Transitioning between no lane markings to lane markings or vice versa.
There is standing water on the road.
Faint lane markings, for example partial yellow lane markings on concrete roads.
Lane width is too narrow or too wide.
The camera has not been calibrated after a windshield replacement.
Driving on tight roads or on uneven roads.
Why does the vehicle not come back toward the middle of the lane, as expected, in the Aid or Aid and Alert mode?
High cross winds are present.
There is a large road crown.
Rough roads, grooves or shoulder drop-offs.
Heavy uneven loading of the vehicle or improper tire inflation pressure.
The tires have been changed, or the suspension has been modified.
325
Driving Aids
Page 432 of 681
Plugging in Your HYBRID
We recommend the following options for
your plug-in vehicle (PHEV) :
• Leave your vehicle plugged in. The 12
volt battery maintains power if left
plugged in. However, this periodically
uses electricity from the household
outlet.
• Connect a battery charger to your 12 volt
battery and leave it on a continuous, slow
charge.
• Disconnect the 12 volt battery. If your 12
volt battery is located in the luggage
compartment, do not fully shut the
luggage compartment after
disconnecting the 12 volt battery. Only
leave the luggage compartment open if
your vehicle is stored in a locked
location.
Brakes
• Make sure the brakes and parking brake
release fully.
Tires
• Maintain recommended air pressure.
Miscellaneous
• Make sure all linkages, cables, levers and
pins under your vehicle are covered with
grease to prevent rust.
• Move vehicles at least 25 ft (7.5 m) every
15 days to lubricate working parts and
prevent corrosion.
Removing Vehicle From Storage
When your vehicle is ready to come out of
storage, do the following:
• Wash your vehicle to remove any dirt or
grease film build-up on window surfaces.
• Check windshield wipers for any
deterioration.
• Check under the hood for any foreign
material that may have collected during
storage such as mice or squirrel nests.
• Check the exhaust for any foreign
material that may have collected during
storage.• Check tire pressures and set tire inflation
per the Tire Label.
• Check brake pedal operation. Drive your
vehicle 15 ft (4.5 m) back and forth to
remove rust build-up.
• Check fluid levels (including coolant, oil
and gas) to make sure there are no leaks,
and fluids are at recommended levels.
• If you remove the battery, clean the
battery cable ends and check for
damage.
Contact an authorized dealer if you have any
concerns or issues.
BODY STYLING KITS (IF EQUIPPED)
The distance between the underside of your
vehicle and the ground is less than that of
other models. Drive with extreme care to
avoid damage to your vehicle.
429
Vehicle Care
Page 433 of 681
GENERAL INFORMATION
The recommended tire inflation pressures
are found on the Tire Label which is located
on the B-pillar or the edge of the driver door.
This information can also be found on the
Safety Compliance Certification Label, affixed
to either the door hinge pillar, door-latch
post, or the door edge that meets the
door-latch post; next to the driver’s seating
position.
We strongly recommend maintaining these
tire pressures at all times. Failure to follow
the tire pressure recommendations can
cause uneven treadwear patterns, reduced
fuel economy, and adversely affect the way
your vehicle handles.
Note:Check and set the tire pressure at the
ambient temperature in which you are
intending to drive your vehicle and when the
tires are cold.
Note:Check your tire pressures at least once
per month.
If your vehicle has a spare tire, set the
pressure to the highest value given for your
vehicle and tire size combination.Use only approved wheels and tire sizes,
using other sizes could damage your vehicle.
If you change the diameter of the factory
installed tires, the speedometer may not
display the correct speed. This could effect
the functionality of the All Wheel Drive (AWD)
system, if equipped. Take your vehicle to an
authorized dealer and have the engine
management system reprogrammed.
If you intend to change the size of the factory
installed tires, check the suitability with an
authorized dealer.
Additional information related to the
functionality and maintenance of your tires
can be found in the Wheels and Tire section.
See Tire Care (page 432).
Notice to utility vehicle and truck
owners
WARNING: Vehicles with a higher
center of gravity (utility and four-wheel
drive vehicles) handle differently than
vehicles with a lower center of gravity
(passenger cars). Avoid sharp turns,
excessive speed and abrupt steering in
these vehicles. Failure to drive cautiously
increases the risk of losing control of your
vehicle, vehicle rollover, personal injury
and death.
WARNING: In a rollover crash, an
unbelted person is significantly more likely
to die than a person wearing a seatbelt.
Utility vehicles and trucks handle differently
than passenger cars in the various driving
conditions that are encountered on streets,
highways and off-road. Utility vehicles and
trucks are not designed for cornering at
speeds as high as passenger cars any more
than low-slung sports cars are designed to
perform satisfactorily under off-road
conditions.
430
Wheels and Tires
Page 436 of 681
The traction grades, from highest to
lowest are AA, A, B, and C. The grades
represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet
pavement as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test
surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire
marked C may have poor traction
performance.
Temperature A B C
WARNING: The temperature
grade for this tire is established for a
tire that is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinflation, or excessive loading,
either separately or in combination,
can cause heat buildup and possible
tire failure.
The temperature grades are A (the
highest), B and C, representing the tire’s
resistance to the generation of heat and
its ability to dissipate heat when tested
under controlled conditions on a
specified indoor laboratory test wheel.
Sustained high temperature can causethe material of the tire to degenerate
and reduce tire life, and excessive
temperature can lead to sudden tire
failure. The grade C corresponds to a
level of performance which all
passenger car tires must meet under the
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 139. Grades B and A represent
higher levels of performance on the
laboratory test wheel than the minimum
required by law.
Glossary of Tire Terminology
*Tire label: A label showing the original
equipment tire sizes, recommended
inflation pressure and the maximum
weight the vehicle can carry.
*Tire Identification Number (TIN): A
number on the sidewall of each tire
providing information about the tire
brand and manufacturing plant, tire size
and date of manufacture. Also referred
to as DOT code.
*Inflation pressure: A measure of the
amount of air in a tire.*Standard load: A class of P-metric or
Metric tires designed to carry a
maximum load at set pressure. For
example: For P-metric tires 35 psi
(2.4 bar) and for Metric tires 36 psi
(2.5 bar). Increasing the inflation
pressure beyond this pressure will not
increase the tire’s load carrying
capability.
*Extra load: A class of P-metric or Metric
tires designed to carry a heavier
maximum load at 42 psi (2.9 bar).
Increasing the inflation pressure beyond
this pressure will not increase the tire’s
load carrying capability.
*kPa: Kilopascal, a metric unit of air
pressure.
*PSI: Pounds per square inch, a standard
unit of air pressure.
*Cold tire pressure: The tire pressure
when the vehicle has been stationary
and out of direct sunlight for an hour or
more and prior to the vehicle being
driven for 1 mi (1.6 km).
433
Wheels and Tires
Page 437 of 681
*Recommended inflation pressure: The
cold inflation pressure found on the
Safety Compliance Certification Label
(affixed to either the door hinge pillar,
door-latch post, or the door edge that
meets the door-latch post, next to the
driver's seating position), or Tire Label
located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the
driver door.
*B-pillar: The structural member at the
side of the vehicle behind the front door.
*Bead area of the tire: Area of the tire
next to the rim.
*Sidewall of the tire: Area between the
bead area and the tread.
*Tread area of the tire: Area of the
perimeter of the tire that contacts the
road when mounted on the vehicle.
*Rim: The metal support (wheel) for a
tire or a tire and tube assembly upon
which the tire beads are seated.Information Contained on the Tire
Sidewall
Both United States and Canada Federal
regulations require tire manufacturers
to place standardized information on the
sidewall of all tires. This information
identifies and describes the fundamental
characteristics of the tire and also
provides a U.S. DOT Tire Identification
Number for safety standard certification
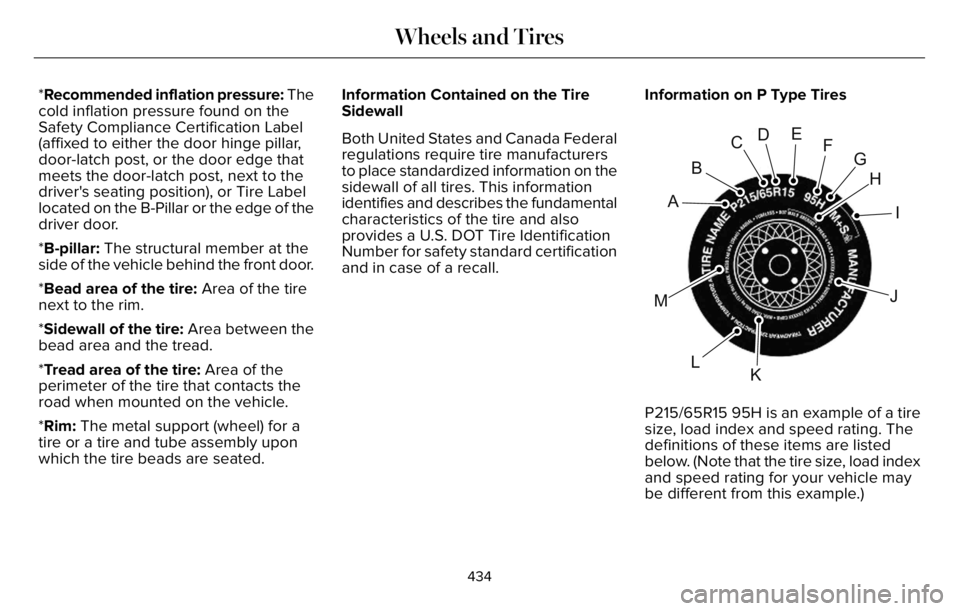
and in case of a recall.Information on P Type Tires
H
I
J
KL
M
A
B
CDEFG
E142543
P215/65R15 95H is an example of a tire
size, load index and speed rating. The
definitions of these items are listed
below. (Note that the tire size, load index
and speed rating for your vehicle may
be different from this example.)
434
Wheels and Tires
Page 438 of 681
A. P: Indicates a tire, designated by the
Tire and Rim Association, that may be
used for service on cars, sport utility
vehicles, minivans and light trucks. Note:
If your tire size does not begin with a
letter this may mean it is designated by
either the European Tire and Rim
Technical Organization or the Japan Tire
Manufacturing Association.
B. 215: Indicates the nominal width of
the tire in millimeters from sidewall edge
to sidewall edge. In general, the larger
the number, the wider the tire.
C. 65: Indicates the aspect ratio which
gives the tire's ratio of height to width.
D. R: Indicates a radial type tire.
E. 15: Indicates the wheel or rim
diameter in inches. If you change your
wheel size, you will have to purchase
new tires to match the new wheel
diameter.F. 95: Indicates the tire's load index. It
is an index that relates to how much
weight a tire can carry. You may find this
information in your owner’s manual. If
not, contact a local tire dealer.
Note:You may not find this information
on all tires because it is not required by
federal law.
G. H: Indicates the tire's speed rating.
The speed rating denotes the speed at
which a tire is designed to be driven for
extended periods of time under a
standard condition of load and inflation
pressure. The tires on your vehicle may
operate at different conditions for load
and inflation pressure. These speed
ratings may need to be adjusted for the
difference in conditions. The ratings
range from 81 mph (130 km/h) to
186 mph (299 km/h). These ratings are
listed in the following chart.
Note:You may not find this information
on all tires because it is not required by
federal law.
Speed rating Letter rating
81 mph (130 km/h) M
87 mph (140 km/h) N
99 mph (159 km/h) Q
106 mph (171 km/h) R
112 mph (180 km/h) S
118 mph (190 km/h) T
124 mph (200 km/h) U
130 mph (210 km/h) H
149 mph (240 km/h) V
435
Wheels and Tires
Page 440 of 681
*Traction: The traction grades, from
highest to lowest are AA, A, B, and C.
The grades represent the tire's ability to
stop on wet pavement as measured
under controlled conditions on specified
government test surfaces of asphalt and
concrete. A tire marked C may have
poor traction performance.
*Temperature: The temperature grades
are A (the highest), B and C,
representing the tire's resistance to the
generation of heat and its ability to
dissipate heat when tested under
controlled conditions on a specified
indoor laboratory test wheel.
M. Maximum Inflation Pressure:
Indicates the tire manufacturers'
maximum permissible pressure or the
pressure at which the maximum load
can be carried by the tire. This pressure
is normally higher than the vehicle
manufacturer's recommended cold
inflation pressure which can be found
on the Safety Compliance Certification
Label (affixed to either the door hinge
pillar, door-latch post, or the door edge
that meets the door-latch post, next tothe driver's seating position), or Tire
Label which is located on the B-Pillar or
the edge of the driver’s door. The cold
inflation pressure should never be set
lower than the recommended pressure
on the vehicle label.
The tire suppliers may have additional
markings, notes or warnings such as
standard load or radial tubeless.
Additional Information Contained on
the Tire Sidewall for LT Type Tires
Note:Tire Quality Grades do not apply
to this type of tire.
A
BC
BD
E142544
LT type tires have some additional
information beyond those of P type tires;
these differences are described below.
A. LT: Indicates a tire, designated by the
Tire and Rim Association, that is
intended for service on light trucks.
437
Wheels and Tires
Page 441 of 681
B. Load Range and Load Inflation
Limits: Indicates the tire's load-carrying
capabilities and its inflation limits.
C. Maximum Load Dual lb (kg) at psi
(kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load
and tire pressure when the tire is used
as a dual, defined as four tires on the
rear axle (a total of six or more tires on
the vehicle).
D. Maximum Load Single lb (kg) at psi
(kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load
and tire pressure when the tire is used
as a single, defined as two tires (total)
on the rear axle.
Information on T Type Tires
T145/80D16 is an example of a tire size.
Note:The temporary tire size for your
vehicle may be different from this
example. Tire Quality Grades do not
apply to this type of tire.
A
BCD
E
T type tires have some additional
information beyond those of P type tires;
these differences are described below:A. T: Indicates a type of tire, designated
by the Tire and Rim Association, that is
intended for temporary service on cars,
sport utility vehicles, minivans and light
trucks.
B. 145: Indicates the nominal width of
the tire in millimeters from sidewall edge
to sidewall edge. In general, the larger
the number, the wider the tire.
C. 80: Indicates the aspect ratio which
gives the tire's ratio of height to width.
Numbers of 70 or lower indicate a short
sidewall.
D. D: Indicates a diagonal type tire.
R: Indicates a radial type tire.
E. 16: Indicates the wheel or rim
diameter in inches. If you change your
wheel size, you will have to purchase
new tires to match the new wheel
diameter.
438
Wheels and Tires
Page 442 of 681
Recommended Tire Pressures and
Inflating Your Tires
Safe operation of your vehicle requires
that your tires are properly inflated.
Remember that a tire can lose up to half
of its air pressure without appearing flat.
Every day before you drive, check your
tires. If one looks lower than the others,
use a tire gauge to check the pressure
of all tires and adjust if required.
At least once a month and before long
trips, inspect each tire and check the tire
pressure with a tire gauge (including
spare, if equipped). Inflate all tires to the
inflation pressure recommended by the
manufacturer.
WARNING: Under-inflation is the
most common cause of tire failures
and may result in severe tire cracking,
tread separation or blowout, with
unexpected loss of vehicle control and
increased risk of injury. Under-inflation
increases sidewall flexing and rolling
resistance, resulting in heat buildup
and internal damage to the tire. It also
may result in unnecessary tire stress,
irregular wear, loss of vehicle control
and accidents. A tire can lose up to
half of its air pressure and not appear
to be flat!
You are strongly urged to buy a reliable
tire pressure gauge, as automatic
service station gauges may be
inaccurate. We recommend the use of
a digital or dial-type tire pressure gauge
rather than a stick-type tire pressure
gauge. Use the recommended cold
inflation pressure for optimum tire
performance and wear. Under-inflation
or over-inflation may cause uneven
treadwear patterns.Always inflate your tires to the
recommended inflation pressure even
if it is less than the maximum inflation
pressure information found on the tire.
You will find a Tire Label containing the
manufactures recommended tire
inflation pressure by the tire size and
other important information located on
the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s
door.
The recommended tire inflation pressure
is also found on the Safety Compliance
Certification Label (affixed to either the
door hinge pillar, door-latch post, or the
door edge that meets the door-latch on
the B-pillar, or on the edge of the
driver’s door.
Failure to follow the tire pressure
recommendations can cause uneven
treadwear patterns and adversely affect
the way your vehicle handles.
439
Wheels and Tires
Page 443 of 681

Inspecting Your Tires and Wheel Valve
Stems
Periodically inspect the tire treads for
uneven or excessive wear and remove
objects such as stones, nails or glass
that may be wedged in the tread
grooves. Check the tire and valve stems
for holes, cracks, or cuts that may permit
air leakage and repair or replace the tire
and replace the valve stem. Inspect the
tire sidewalls for cracking, cuts, bruises
and other signs of damage or excessive
wear. If internal damage to the tire is
suspected, have the tire demounted and
inspected in case it needs to be repaired
or replaced. For your safety, tires that
are damaged or show signs of excessive
wear should not be used because they
are more likely to blow out or fail.
Improper or inadequate vehicle
maintenance can cause tires to wear
abnormally. Inspect all your tires,
including the spare, frequently, and
replace them if one or more of the
following conditions exist:Tire Wear
E142546
When the tread is worn down to one
sixteenth of an inch (2 mm), tires must
be replaced to help prevent your vehicle
from skidding and hydroplaning. Built-in
treadwear indicators, or wear bars,
which look like narrow strips of smooth
rubber across the tread will appear on
the tire when the tread is worn down to
one sixteenth of an inch (2 mm).
When the tire tread wears down to the
same height as these wear bars, the tire
is worn out and must be replaced.Damage
Periodically inspect the tire treads and
sidewalls for damage (such as bulges in
the tread or sidewalls, cracks in the
tread groove and separation in the tread
or sidewall). If damage is observed or
suspected, have the tire inspected by a
tire professional. Tires can be damaged
during off-road use, so inspection after
off-road use is also recommended.
Age
WARNING: Tires degrade over
time depending on many factors such
as weather, storage conditions, and
conditions of use (load, speed, inflation
pressure) the tires experience
throughout their lives.
440
Wheels and Tires