tires LINCOLN NAVIGATOR 2013 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LINCOLN, Model Year: 2013, Model line: NAVIGATOR, Model: LINCOLN NAVIGATOR 2013Pages: 481, PDF Size: 5.29 MB
Page 246 of 481

•Allow more distance for stopping with a trailer attached; anticipate
stops and brake gradually.
•Avoid parking on a grade. However, if you must park on a grade:
1. Turn the steering wheel to point the vehicle tires away from
traffic flow.
2. Set the vehicle parking brake.
3. Place the automatic transmission in positionPor manual
transmission in a high gear.
4. Place wheel chocks in front and back of the trailer wheels.
(Chocks not equipped with vehicle.)
Your vehicle may be equipped with a temporary or conventional spare
tire. If the spare tire is different in size (diameter and/or width), tread
type (All-Season or All-Terrain) or is from a different manufacturer other
than the road tires on your vehicle, your spare tire is considered
“temporary”. Consult information on the tire label or Safety Compliance
label for limitations when using.
Launching or Retrieving a Boat or Personal Watercraft (PWC)
Note:Disconnect the wiring to the trailerbeforebacking the trailer into
the water.
Note:Reconnect the wiring to the trailer after the trailer is removed
from the water.
When backing down a ramp during boat launching or retrieval:
•Do not allow the static water level to rise above the bottom edge of
the rear bumper.
•Do not allow waves to break higher than 6 inches (15 centimeters)
above the bottom edge of the rear bumper.
Exceeding these limits may allow water to enter vehicle components:
•Causing internal damage to the components.
•Affecting driveability, emissions, and reliability.
Replace the rear axle lubricant anytime the rear axle has been
submerged in water. Water may have contaminated the rear axle
lubricant, which is not normally checked or changed unless a leak is
suspected or other axle repair is required.
246Towing
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 249 of 481

BREAKING-IN
You need to break in new tires for approximately 300 miles
(480 kilometers). During this time, your vehicle may exhibit some unique
driving characteristics. Avoid driving too fast during the first 1000 miles
(1600 kilometers). Vary your speed frequently and change up through
the gears early. Do not labor the engine. Do not tow during the first
1000 miles (1600 kilometers).
ECONOMICAL DRIVING
Fuel economy is affected by several things such as how you drive, the
conditions you drive under and how you maintain your vehicle.
There are some things to keep in mind that may improve your fuel
economy:
•Accelerate and slow down in a smooth, moderate fashion.
•Drive at steady speeds without stopping.
•Anticipate stops; slowing down may eliminate the need to stop.
•Combine errands and minimize stop-and-go driving.
•Close the windows for high-speed driving.
•Drive at reasonable speeds (traveling at 55 mph [88 km/h] uses 15%
less fuel than traveling at 65 mph [105 km/h]).
•Keep the tires properly inflated and use only the recommended size.
•Use the recommended engine oil.
•Perform all regularly scheduled maintenance.
There are also some things you may not want to do because they may
reduce your fuel economy:
•Sudden or hard accelerations.
•Rev the engine before turning it off.
•Idle for periods longer than one minute.
•Warm up your vehicle on cold mornings.
•Use the air conditioner or front defroster.
•Use the speed control in hilly terrain.
•Rest your foot on the brake pedal while driving.
•Drive a heavily loaded vehicle or tow a trailer.
Driving Hints249
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 305 of 481

Engine
•The engine oil and filter should be changed prior to storage, as used
engine oil contain contaminates that may cause engine damage.
•Start the engine every 15 days. Run at fast idle until it reaches normal
operating temperature.
•With your foot on the brake, shift through all the gears while the
engine is running.
Fuel system
•Fill the fuel tank with high-quality fuel until the first automatic shutoff
of the fuel pump nozzle.
Note:During extended periods of vehicle storage (30 days or more),
fuel may deteriorate due to oxidation. Add a quality gas stabilizer
product to the vehicle fuel system whenever actual or expected storage
periods exceed 30 days. Follow the instructions on the additive label.
The vehicle should then be operated at idle speed to circulate the
additive throughout the fuel system.
Cooling system
•Protect against freezing temperatures.
•When removing vehicle from storage, check coolant fluid level.
Confirm there are no cooling system leaks, and fluid is at the
recommended level.
Battery
•Check and recharge as necessary. Keep connections clean.
•If storing your vehicle for more than 30 days without recharging the
battery, it may be advisable to disconnect the battery cables to ensure
battery charge is maintained for quick starting.
Note:If battery cables are disconnected, it will be necessary to reset
memory features.
Brakes
•Make sure brakes and parking brake are fully released.
Tires
•Maintain recommended air pressure.
Vehicle Care305
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 307 of 481

GENERAL INFORMATION
Notice to Utility Vehicle, Van and Truck Owners
WARNING:Utility vehicles have a significantly higher rollover
rate than other types of vehicles. To reduce the risk of serious
injury or death from a rollover or other crash you must:
•Avoid sharp turns and abrupt maneuvers;
•Drive at safe speeds for the conditions;
•Keep tires properly inflated;
•Never overload or improperly load your vehicle; and
•Make sure every passenger is properly restrained.
WARNING:In a rollover crash, an unbelted person is
significantly more likely to die than a person wearing a seat belt.
All occupants must wear seat belts and children/infants must use
appropriate restraints to minimize the risk of injury or ejection.
Utility vehicles, vans and trucks handle
differently than passenger cars in the
various driving conditions that are
encountered on streets, highways and
off-road. Utility vehicles, vans and
trucks are not designed for cornering
at speeds as high as passenger cars
any more than low-slung sports cars
are designed to perform satisfactorily
under off-road conditions.
Wheels and Tires307
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 308 of 481

Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) System (if equipped)
WARNING:Do not become overconfident in the ability of 4WD
vehicles. Although a 4WD vehicle may accelerate better than
two-wheel drive vehicle in low traction situations, it won’t stop any
faster than two-wheel drive vehicles. Always drive at a safe speed.
A vehicle equipped with four-wheel drive (when selected) has the ability
to use all four wheels to power itself. This increases traction which may
enable you to safely drive over terrain and road conditions that a
conventional two-wheel drive vehicle cannot.
Power is supplied to all four wheels through a transfer case or power
transfer unit. Four-wheel drive vehicles allow you to select different drive
modes as necessary. Information on transfer case operation and shifting
procedures can be found in theTransmissionchapter. Information on
transfer case maintenance can be found in theMaintenancechapter.
You should become thoroughly familiar with this information before you
operate your vehicle.
On some four-wheel drive models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive
to four-wheel drive while the vehicle is moving can cause a momentary
clunk and ratcheting sound. These sounds are normal as the front
drivetrain comes up to speed and is not cause for concern.
308Wheels and Tires
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 309 of 481
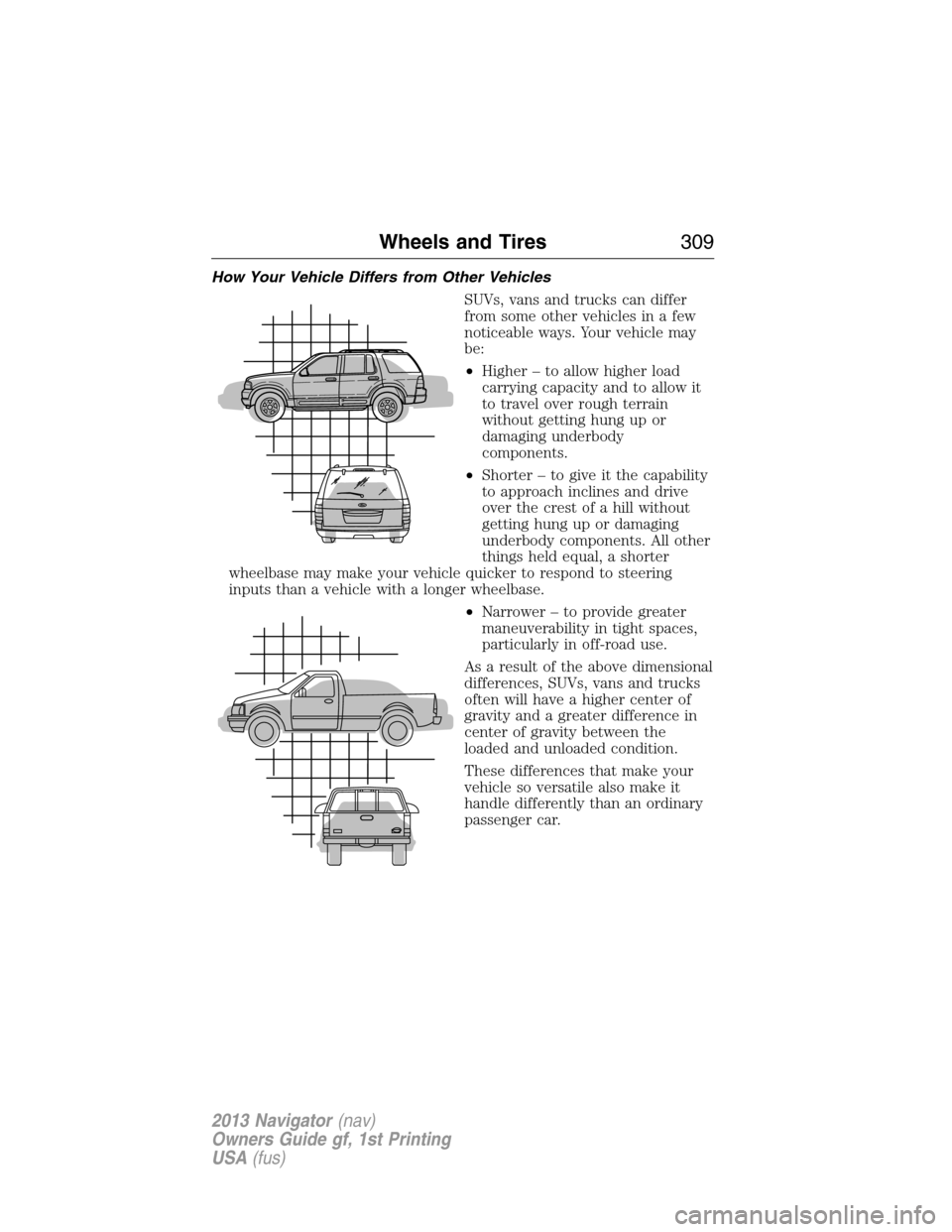
How Your Vehicle Differs from Other Vehicles
SUVs, vans and trucks can differ
from some other vehicles in a few
noticeable ways. Your vehicle may
be:
•Higher – to allow higher load
carrying capacity and to allow it
to travel over rough terrain
without getting hung up or
damaging underbody
components.
•Shorter – to give it the capability
to approach inclines and drive
over the crest of a hill without
getting hung up or damaging
underbody components. All other
things held equal, a shorter
wheelbase may make your vehicle quicker to respond to steering
inputs than a vehicle with a longer wheelbase.
•Narrower – to provide greater
maneuverability in tight spaces,
particularly in off-road use.
As a result of the above dimensional
differences, SUVs, vans and trucks
often will have a higher center of
gravity and a greater difference in
center of gravity between the
loaded and unloaded condition.
These differences that make your
vehicle so versatile also make it
handle differently than an ordinary
passenger car.
Wheels and Tires309
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 310 of 481

TIRE CARE
Information About Uniform Tire Quality Grading
Tire Quality Grades apply to new
pneumatic passenger car tires. The
Quality grades can be found where
applicable on the tire sidewall between
tread shoulder and maximum section
width. For example:
•Treadwear 200 Traction AA Temperature A
These Tire Quality Grades are determined by standards that the United
States Department of Transportation has set.
Tire Quality Grades apply to new pneumatic passenger car tires. They do
not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver or
temporary use spare tires, light truck or LT type tires, tires with nominal
rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches or limited production tires as defined in
Title 49 Code of Federal Regulations Part 575.104(c)(2).
U.S. Department of Transportation-Tire quality grades:The U.S.
Department of Transportation requires Ford Motor Company to give you
the following information about tire grades exactly as the government
has written it.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of
the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified
government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one
and one-half (1
1�2) times as well on the government course as a tire
graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual
conditions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the
norm due to variations in driving habits, service practices, and
differences in road characteristics and climate.
310Wheels and Tires
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 311 of 481

Traction AA A B C
WARNING:The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on
straight-ahead braking traction tests, and does not include
acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning or peak traction characteristics.
The traction grades, from highest to lowest are AA, A, B, and C. The
grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured
under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction
performance.
Temperature A B C
WARNING:The temperature grade for this tire is established for
a tire that is properly inflated and not overloaded. Excessive
speed, underinflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in
combination, can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C, representing the
tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat
when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory
test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire
to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance
which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard No. 139. Grades B and A represent higher levels of
performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by
law.
Glossary of Tire Terminology
•Tire label:A label showing the OE (Original Equipment) tire sizes,
recommended inflation pressure and the maximum weight the vehicle
can carry.
•Tire Identification Number (TIN):A number on the sidewall of
each tire providing information about the tire brand and
manufacturing plant, tire size and date of manufacture. Also referred
to as DOT code.
•Inflation pressure:A measure of the amount of air in a tire.
Wheels and Tires311
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 312 of 481
![LINCOLN NAVIGATOR 2013 User Guide •Standard load:A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a
maximum load at 35 psi [37 psi (2.5 bar) for Metric tires]. Increasing
the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not inc LINCOLN NAVIGATOR 2013 User Guide •Standard load:A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a
maximum load at 35 psi [37 psi (2.5 bar) for Metric tires]. Increasing
the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not inc](/img/15/7028/w960_7028-311.png)
•Standard load:A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a
maximum load at 35 psi [37 psi (2.5 bar) for Metric tires]. Increasing
the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase the tire’s
load carrying capability.
•Extra load:A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a
heavier maximum load at 41 psi [43 psi (2.9 bar) for Metric tires].
Increasing the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase
the tire’s load carrying capability.
•kPa:Kilopascal, a metric unit of air pressure.
•PSI:Pounds per square inch, a standard unit of air pressure.
•Cold inflation pressure:The tire pressure when the vehicle has
been stationary and out of direct sunlight for an hour or more and
prior to the vehicle being driven for 1 mile (1.6 kilometers).
•Recommended inflation pressure:The cold inflation pressure found
on the Safety Compliance Certification Label (affixed to either the
door hinge pillar, door-latch post, or the door edge that meets the
door-latch post, next to the driver’s seating position), or Tire Label
located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door.
•B-pillar:The structural member at the side of the vehicle behind the
front door.
•Bead area of the tire:Area of the tire next to the rim.
•Sidewall of the tire:Area between the bead area and the tread.
•Tread area of the tire:Area of the perimeter of the tire that
contacts the road when mounted on the vehicle.
•Rim:The metal support (wheel) for a tire or a tire and tube assembly
upon which the tire beads are seated.
312Wheels and Tires
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 313 of 481

INFORMATION CONTAINED ON THE TIRE SIDEWALL
Both U.S. and Canada Federal regulations require tire manufacturers to
place standardized information on the sidewall of all tires. This
information identifies and describes the fundamental characteristics of
the tire and also provides a U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number for
safety standard certification and in case of a recall.
Information on P Type Tires
P215/65R15 95H is an example of a
tire size, load index and speed
rating. The definitions of these
items are listed below. (Note that
the tire size, load index and speed
rating for your vehicle may be
different from this example.)
A.P:Indicates a tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association
(T&RA), that may be used for service on cars, SUVs, minivans and light
trucks.
Note:If your tire size does not begin with a letter, this may mean it is
designated by either ETRTO (European Tire and Rim Technical
Organization) or JATMA (Japan Tire Manufacturing Association).
B.215:Indicates the nominal width of the tire in millimeters from
sidewall edge to sidewall edge. In general, the larger the number, the
wider the tire.
C.65:Indicates the aspect ratio which gives the tire’s ratio of height to
width.
D.R:Indicates a radial type tire.
H
I
J
KL
M
A
B
CDEFG
Wheels and Tires313
2013 Navigator(nav)
Owners Guide gf, 1st Printing
USA(fus)