Rear seats LINCOLN TOWN CAR 2003 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LINCOLN, Model Year: 2003, Model line: TOWN CAR, Model: LINCOLN TOWN CAR 2003Pages: 272, PDF Size: 2.19 MB
Page 7 of 272

Special instructions
For your added safety, your vehicle is fitted with sophisticated electronic
controls.
Please read the sectionSupplemental Restraint System (SRS)
in theSeating and safety restraintschapter. Failure to follow
the specific warnings and instructions could result in personal injury.
Front seat mounted rear facing child or infant seats should
NEVERbe used in front of a passenger side air bag unless the
air bag can be and is turned OFF.
MIDDLE EAST/NORTH AFRICA VEHICLE SPECIFIC INFORMATION
For your particular global region, your vehicle may be equipped with
features and options that are different from the ones that are described
in this Owner Guide; therefore, a supplement has been supplied that
complements this book. By referring to the pages in the provided
supplement, you can properly identify those features, recommendations
and specifications that are unique to your vehicle.Refer to this Owner
Guide for all other required information and warnings.
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Introduction
7
Page 19 of 272

8.REW (Rewind):Works in tape
and CD modes.
In tape mode, radio play continues
until rewind is stopped (with the TAPE control) or the beginning of the
tape is reached.
In CD mode, REW control reverses the CD within the current track.
FF (fast forward):Works in tape
and CD modes.
In the tape mode, tape direction
automatically reverses when the end of the tape is reached.
In CD mode, FF advances the CD within the current track.
9.Digital signal processing
(if equipped):Press to adjust the
occupancy modes between the
following:.
•ALL SEATS
•DRIVER SEAT
•REAR SEATS
RDS:(Radio Data System): Allows
you to access FM stations which are
RDS- equipped. Press RDS then
SEL to select from:
Traffic—Allows you to receive traffic announcements and control their
volume level.Traffic information is not available in most U.S.
markets.
Show—Allows you to view the frequency and program type of the
chosen radio station.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the Canadian Radio
and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) recommend that FM radio
broadcasters use RDS technology to transmit information. FM radio
stations are independently operated and individually elect to use RDS
technology to transmit station ID and program type as desired.
10.Autoset:Press to set first six
strong stations into AM, FM1 or
FM2 memory buttons; press again to
return to normal stations.
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Entertainment Systems
19
Page 37 of 272

Fade: Allows you to adjust the
amount of sound emitted from the
front and rear speakers.
Balance: Allows you to adjust the
sound distribution between the right
and left speakers.
SCV(Speed Compensated Volume):
Automatically compensates for road
wind and noise. Refer toSpeed
compensated volumeearlier in this
chapter.
DSP Occupancy mode:Use to
optimize the sound based upon the
occupants in the vehicle. Select
from ALL SEATS, REAR SEATS or
DRIVER SEAT.
Setting memory preset stations
The radio is equipped with six station memory preset controls. These
controls can be used to select up to six preset AM stations and twelve
FM stations (six in FM1 and six in FM2).
1. Select the frequency band with the AM/FM1/FM2 touch controls.
2. Select a station.
3. Press and hold a memory preset until the sound returns. The
frequency will appear in the preset.
CD mode
CD units are designed to play commercially pressed 12 cm (4.75 in)
audio compact discs only. Due to technical incompatibility, certain
recordable and re-recordable compact discs may not function
correctly when used in Ford CD players. Irregular shaped CDs,
CDs with a scratch protection film attached, and CDs with
homemade paper (adhesive) labels should not be inserted into
the CD player. The label may peel and cause the CD to become
jammed. It is recommended that homemade CDs be identified
CNTR
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Entertainment Systems
37
Page 128 of 272
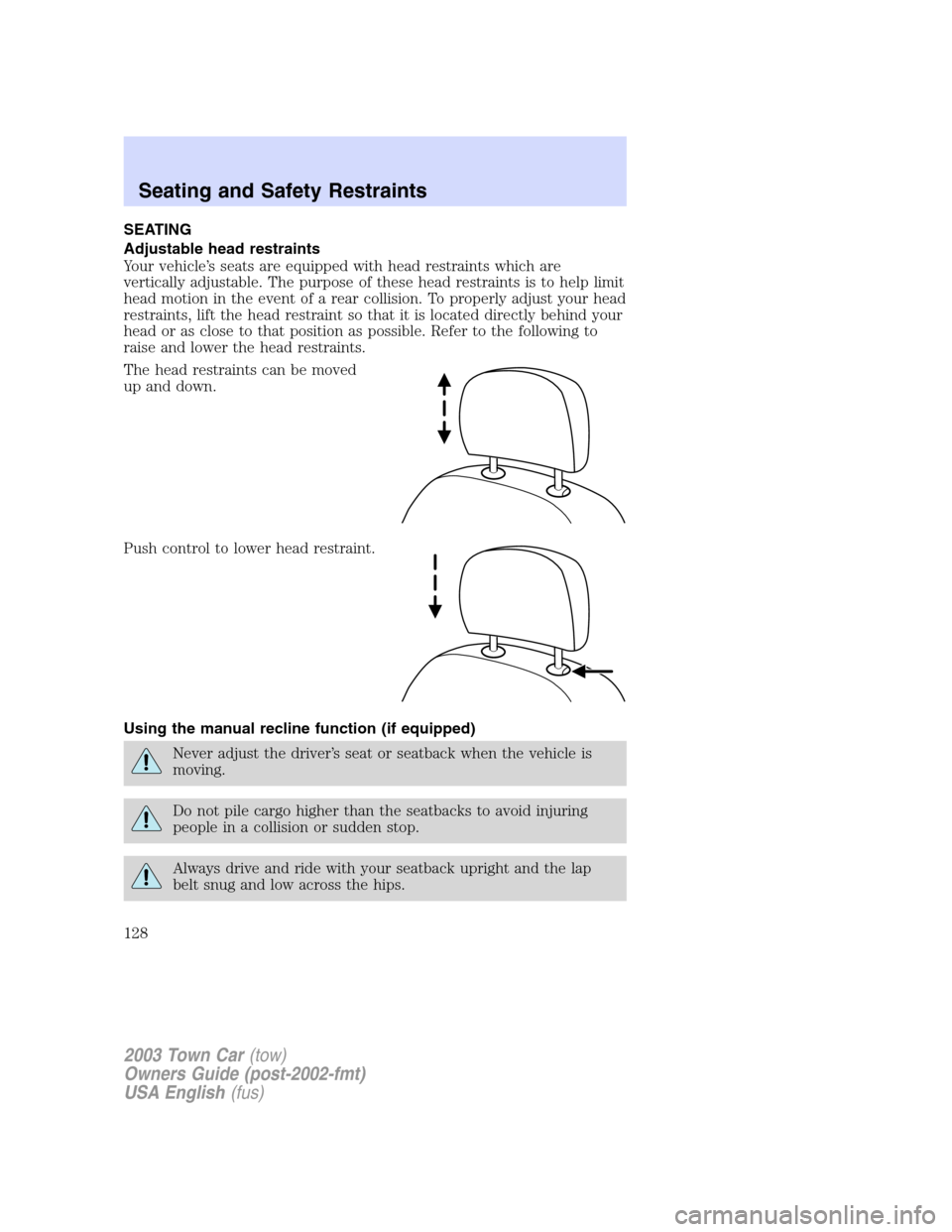
SEATING
Adjustable head restraints
Your vehicle’s seats are equipped with head restraints which are
vertically adjustable. The purpose of these head restraints is to help limit
head motion in the event of a rear collision. To properly adjust your head
restraints, lift the head restraint so that it is located directly behind your
head or as close to that position as possible. Refer to the following to
raise and lower the head restraints.
The head restraints can be moved
up and down.
Push control to lower head restraint.
Using the manual recline function (if equipped)
Never adjust the driver’s seat or seatback when the vehicle is
moving.
Do not pile cargo higher than the seatbacks to avoid injuring
people in a collision or sudden stop.
Always drive and ride with your seatback upright and the lap
belt snug and low across the hips.
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Seating and Safety Restraints
128
Page 131 of 272

Press to move the rear portion of
the seat cushion up or down.
Heated seats (if equipped)
To operate the heated seats:
•Push the indicated side of the
control for maximum heat.
•Push again to deactivate.
•Push the indicated side of the
control for minimum heat.
•Push again to deactivate.
The heated seat module resets at every ignition run cycle. While the
ignition is in the run position, activating the high or low heated seat
switch enables heating mode. When activated, they will turn off
automatically when the ignition is turned to the OFF position.
The indicator light will illuminate when the heated seats have been
activated.
Rear heated seats (if equipped)
The rear seat heat controls are located on the rear door panels and
operate like the front heated seats. Refer to theHeated Seatssection in
this chapter for instructions on operating the rear heated seats.
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
131
Page 132 of 272

Easy-access/easy-out feature (if equipped)
This feature automatically moves the driver’s seat backward when:
•the transmission is in N (Neutral) or P (Park)
•the key is removed from the ignition cylinder
The seat will move 5 cm (2 inches) forward (to the original position) when:
•the transmission is in N (Neutral) or P (Park)
•the key is placed in the ignition cylinder
Seat mounted cup holders
Your vehicle may be equipped with cupholders in the cushion of the
front center seat and the rear seat . The rear seat cupholder is designed
to over rotate from the seat when subjected to a heavy load. The rear
seat cupholder can be reset by rotating to the closed position.
Use only soft cups in the cupholder. Hard objects can injure you
in a collision.
Memory seats/rearview mirrors/adjustable pedals (if equipped)
This system allows automatic
positioning of the driver seat,
outside rearview mirrors, and
adjustable pedals to three
programmable positions.
The memory seat control is located on the driver door.
•To program position one, move the driver seat to the desired position
using the seat controls. Press the SET control. The SET control
indicator light will briefly illuminate. While the light is illuminated,
press control 1.
•
To program position two, repeat the previous procedure using control 2.
•To program position three, repeat the previous procedure but press
controls 1 and 2 simultaneously.
A position can only be recalled when the transmission gearshift is in
Park. A memory seat position may be programmed at any time.
The memory seat positions are also recalled when you press your remote
entry transmitter UNLOCK control.
To program the memory seat to remote entry transmitter, refer to
Remote entry systemin theLocks and security chapter.
SET
12
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
132
Page 134 of 272

Driver and passenger dual-stage air bag supplemental restraints
The dual-stage air bags offer the capability to tailor the level of air bag
inflation energy. A lower, less forceful energy level is provided for more
common, moderate-severity impacts. A higher energy level is used for
the most severe impacts. Refer toAir bag supplemental restraints
section in this chapter.
Front crash severity sensor
The front crash severity sensor enhances the ability to detect the
severity of an impact. Positioned up front, it provides valuable
information early in the crash event on the severity of the impact. This
allows your Personal safety system to distinguish between different levels
of crash severity and modify the deployment strategy of the dual-stage
air bags and safety belt pretensioners.
Driver’s seat position sensor
The driver’s seat position sensor allows your Personal safety system to
tailor the deployment level of the driver dual-stage air bag based on seat
position. The system is designed to help protect smaller drivers sitting
close to the driver air bag by providing a lower air bag output level.
Passenger occupant classification sensor (OCS)
For air bags to do their job they must inflate with great force, and this
force can pose a potentially deadly risk to occupants that are very close
to the air bag when it begins to inflate. For some occupants, this occurs
because they are initially sitting very close to the air bag. For other
occupants, this occurs when the occupant is not properly restrained by
seat belts or child safety seats and they move forward during pre-crash
braking. The most effective way to reduce the risk of unnecessary
injuries is to make sure all occupants are properly restrained. Accident
statistics suggest that children are much safer when properly restrained
in the rear seating positions than in the front.
Air bags can kill or injure a child in a child seat.NEVERplace a
rear-facing child seat in front of an active air bag. If you must
use a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move the seat all the
way back.
Always transport children 12 years old and under in the back
seat and always properly use appropriate child restraints.
The passenger occupant classification sensor can automatically turn off
the passenger front air bag and side air bag (if equipped). The system is
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
134
Page 138 of 272

Energy management feature
•This vehicle has a seat belt system with an energy management
feature at the front outboard seating positions to help further reduce
the risk of injury in the event of a head-on collision.
•This seat belt system has a retractor assembly that is designed to pay
out webbing in a controlled manner. This feature is designed to help
reduce the belt force acting on the occupant’s chest.
The front outboard and rear safety restraints in the vehicle are
combination lap and shoulder belts. The front outboard passenger and
rear seat safety belts have three types of locking modes described below:
Vehicle sensitive mode
This is the normal retractor mode, which allows free shoulder belt length
adjustment to your movements and locking in response to vehicle
movement. For example, if the driver brakes suddenly or turns a corner
sharply, or the vehicle receives an impact of approximately 8 km/h (5
mph) or more, the combination safety belts will lock to help reduce
forward movement of the driver and passengers.
Webbing extraction sensitive mode
The webbing extraction sensitive mode stops the belt webbing from
retracting if it is pulled out too quickly.
Automatic locking mode
In this mode, the shoulder belt is automatically pre-locked. The belt will
still retract to remove any slack in the shoulder belt. The automatic
locking mode is not available on the driver safety belt.
This mode should be usedany timea child safety seat is installed in the
vehicle. Children 12 years old and under should be properly restrained in
the rear seat whenever possible. Refer toSafety restraints for children
orSafety seats for childrenlater in this chapter.
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
138
Page 153 of 272

How does the side air bag system work?
The design and development of the
side airbag system included
recommended testing procedures
that were developed by a group of
automotive safety experts known as
the Side Airbag Technical Working
Group. These recommended testing
procedures help reduce the risk of
injuries related to the deployment of
side airbags.
The side air bag system consists of
the following:
•An inflatable nylon bag (air bag)
with a gas generator concealed
behind the outboard bolster of
the driver and front passenger
seatbacks.
•A special seat cover designed to allow airbag deployment.
•The same warning light, electronic control and diagnostic unit as used
for the front air bags.
•Two crash sensors located near the side of the vehicle.
Side air bags, in combination with seat belts, can help reduce the risk of
severe injuries in the event of a significant side impact collision.
The side air bags are fitted on the outboard side of the seatbacks of the
front seats. In certain lateral collisions, the air bag on the side affected
by the collision will be inflated. The air bag was designed to inflate
between the door panel and occupant to further enhance the protection
provided occupants in side impact collisions.
The air bag SRS is designed to activate when the vehicle sustains lateral
deceleration sufficient to cause the sensors to close an electrical circuit
that initiates air bag inflation.
The fact that the air bags did not inflate in a collision does not mean that
something is wrong with the system. Rather, it means the forces were
not of the type sufficient to cause activation. Side air bags are designed
to inflate in side-impact collisions, not roll-over, rear-impact, frontal or
near-frontal collisions, unless the collision causes sufficient lateral
deceleration.
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
153
Page 155 of 272

SAFETY RESTRAINTS FOR CHILDREN
See the following sections for directions on how to properly use safety
restraints for children. Also seeAir bag supplemental restraint system
(SRS)in this chapter for special instructions about using air bags.
Important child restraint precautions
You are required by law to use safety restraints for children in the U.S.
and Canada. If small children (generally children who are four years old
or younger and who weigh 18 kg [40 lbs] or less) ride in your vehicle,
you must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Check
your local and state or provincial laws for specific requirements
regarding the safety of children in your vehicle. When possible, always
place children under age 12 in the rear seat of your vehicle. Accident
statistics suggest that children are safer when properly restrained in the
rear seating positions than in the front seating position.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the
vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
Always follow the instructions and warnings that come with any infant or
child restraint you might use.
Children and safety belts
If the child is the proper size, restrain the child in a safety seat.
Children who are too large for child safety seats (as specified by your
child safety seat manufacturer) should always wear safety belts.
Follow all the important safety restraint and air bag precautions that
apply to adult passengers in your vehicle.
If the shoulder belt portion of a combination lap and shoulder belt can
be positioned so it does not cross or rest in front of the child’s face or
neck, the child should wear the lap and shoulder belt. Moving the child
closer to the center of the vehicle may help provide a good shoulder belt
fit.
Do not leave children, unreliable adults, or pets unattended in
your vehicle.
2003 Town Car(tow)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
155