air condition MAZDA 323 1992 Suplement User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 1992, Model line: 323, Model: MAZDA 323 1992Pages: 279, PDF Size: 24.15 MB
Page 119 of 279

P CONVENTIONAL BRAKE SYSTEM
1 t3EOPX.314
@ 66.7 kPa
Iso0 mmHg.
19.7 inHg)
16EOPX-05t
1
13EOPX.315
P-8
POWER BRAKE UNIT
Quick Inspection (On-vehicle)
Power brake unit function check
(Method-using tester)
Connect the SST, vacuum gauge A, and pedal depression
force gauge B as shown in the figure. After bleeding the
air from the SST, conduct the test as described in the 3steps
below.
Note l
Use commercMty available vacuum gauge and ped.
al depression force gauge.
a) Checking for vacuum loss
Unloaded condition
1. Start the engine.
2. Stop the engine when the vacuum gauge reading reaches
66.7 kPa (500 mmHg, 19.7 inHg ) .
3. Observe the vacuum gauge for 15 seconds. If the gauge
shows 63.3-66.7 kPa [475--500 mmHg, 18.7-19.7
inHg 1, the unit is operating.
Loaded condition
1. Start the engine.
2. Depress the brake pedal with a fdrrce of 196 N I20 kgf,
44 Ibfj.
3. With the brake pedal depressed, stop the engine when the
vacuum gauge reading reaches 66.7 kPa {SO0 mmlig,
19.7 inHg].
4. Observe the vacuum gauge for 15 seconds. If the gauge
shows 63.3-66.7 kPa I475--500 mmHg; 18.7-l 9.7
inHg 1, the unit is operating.
b) Checking for hydraulic pressure
1, If with the engine stopped (vacuum 0 kPa (0 mmHg, 0
hltlg 1) the fluid pressure is within specification, the unit is
operating.
Pedal force N fkgf. Ibf]
Fluid pressure kPa (kgf/cm2, psi)
196 LZO. 441 1080 111. 1561 min.
2, Start the engine. Depress the brake pedal when.the vacu-
urn reaches 66.7 kPa 1500 mmHg, 19.7 intlg 1. If the flu-
id pressure is within specification, the unit is operating.
Pedal force N 1 kgf, fbf I Fluid pressure .kPa { kgflcm’. ps 1
196 I20,441 6670 {68, 967
1 min.
-- WlTHOU
&
d
I=-
-
1 MASTER CYUh
.
i_
Page 179 of 279

SYSTEM INDEX
ENGINE-RELATED SYSTEMS STARTING SYSTEM...............2 4
CHARGING SYSTEM...............2 6
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM.........2 8
COOLING FAN SYSTEM............3 6
CHASSIS-RELATED SYSTEMS ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM........82
INSTFUJMENT CLUSTER-RELATED SYSIEMS IrS$;MENT CLUSTER 6 WARNING
........................ 38
BODY-F&LATEX) SYSTEMS
WINDSHIELD WIPER 6 WASHER.....4 0
HEADLIGHT CLEANER.............4 0
REAR WIPER & WASHER...........4 2
HORNS...................,......6 0
REAR WINDOW DEFROSTER.........6 4
SOUND WARNING SYSTEM..........6 6
POWER WINDOWS.................7 4
POWER DOOR LOCK...............7 6
POWER OUTSIDE MIRRORS.........7 8
SLIDING SUNROOF...............8 0
SEAT WARMERS..................8 4
INTERIOR LIGHTING SYSTEMS IG KEY CYLINDER LAMP..........6 6
INTERIOR 6 SPOT LAMPS.........6 6
COURTESY LAMPS................6 8
TRUNK COMPARTMENT LAMP........6 8
ILLUMINATION LAMPS............7 0
EXTERIOR LIGHTING SYSTEMS
HEADLIGHTS
EXCEPT F.R.GERMANY...........44
F.R.GERMANY..................46
HEADLIGHT LEVELING SYSTEM.....46
TAILLIGHTS
EXCEPT F.R.GERMANY...........48
F.R.GERMANY..................5 0
LICENSE PLATE LIGHTS
EXCEPT F.R.GERMANY...........4 8
F.R.GERMANY..................5 0
POSITION LIGHTS
EXCEPT F.R.GERMANY...........4 4
F.R.GERMANY..................!i? 0
FRONT 6 REAR FOG LIGHTS.......52
TURN 6 HAZARD FLASHER
LIGHTS.......................54
STOPLIGHTS
F.R.GERMANY.a................5 6
EXCEPT F.R.GERMANY...........5 8
BACK-UP LIGHTS................6 0
AIR CONDITIONING-RELATED SYSTEMS HEATER........................6 2
ACCESSORIES CIGARETTE LIGHTER.........<....64
DIGITAL CLOCK.................64
AUDIO SYSTEM..................72
OTHER DIAGNOSIS CONNECTOR...........86
Page 185 of 279
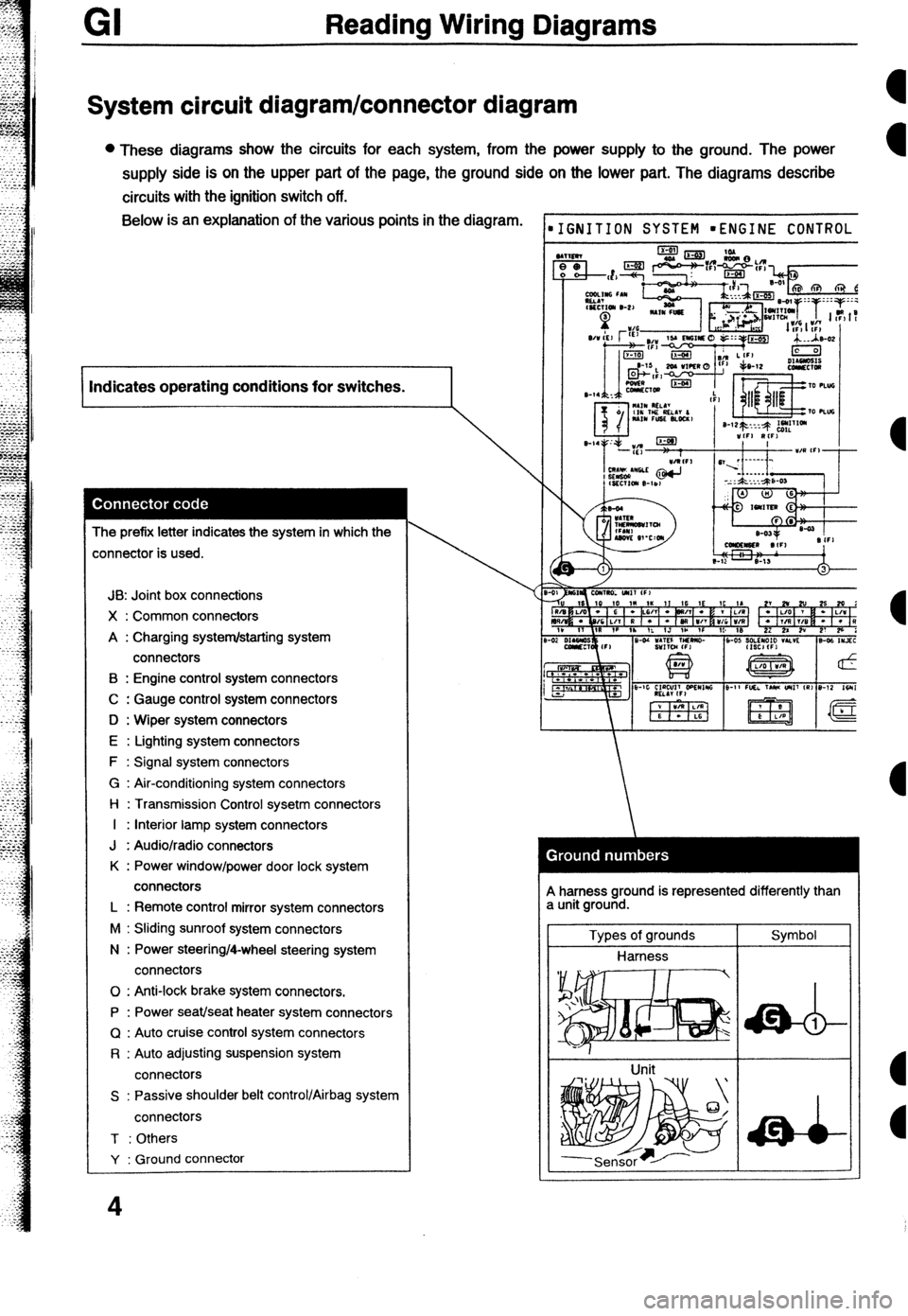
GI Reading Wiring Diagrams
System circuit diagram/connector diagram
l These diagrams show the circuits for each system, from the power supply to the ground. The power
supply side is on the upper part of the page, the ground side on the lower part. The diagrams describe
circuits with the ignition switch off. Below is an explanation of the various points in the diagram.
I Indicates operating conditions for switches.
I
The prefix letter indicates the system in which the
:onnector is used.
JB: Joint box connections
X : Common connectors
A : Charging system/starting system
connectors
B : Engine control system connectors
C : Gauge control system connectors
D : Wiper system connectors
E : Lighting system connectors
F : Signal system connectors
G : Air-conditioning system connectors
l-l : Transmission Control sysetm connectors
I : Interior lamp system connectors
J : Audio/radio connectors
K : Power window/power door lock system
connectors
L : Remote control mirror system connectors
M : Sliding sunroof system connectors
N : Power steering/4-wheel steering system
connectors
0 : Anti-lock brake system connectors.
P : Power seat/seat heater system connectors
Q : Auto cruise control system connectors
R : Auto adjusting suspension system
connectors
S : Passive shoulder belt control/Airbag system
connectors
T : Others
Y : Ground connector
4
IGNITION SYSTEM mENGINE CONTROL
A harness ground is represented differently than
a unit ground.
Types of grounds
Harness
Unit Symbol
Page 191 of 279
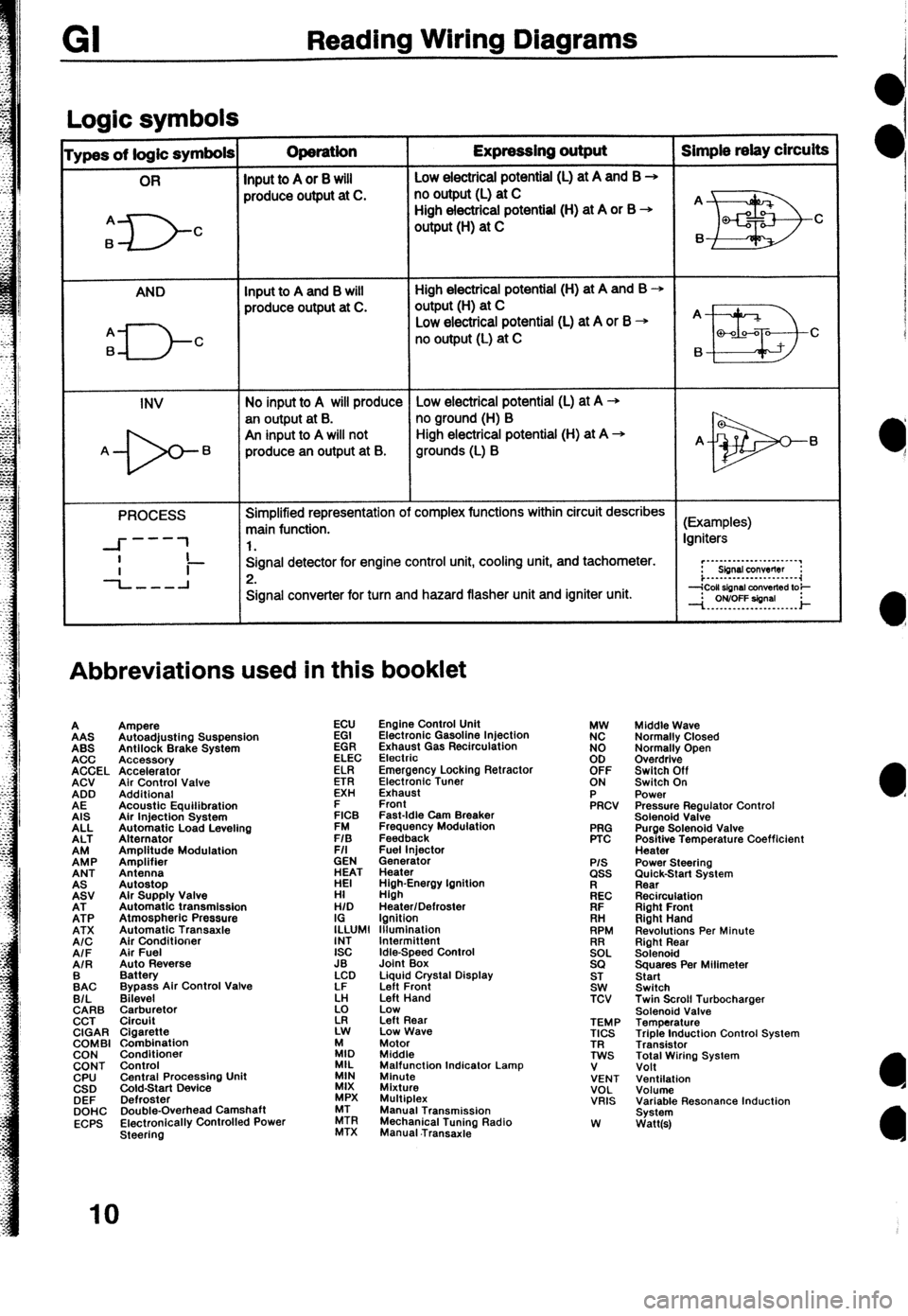
Reading Wiring Diagrams
Loaic symbols I
ypes of logic symbols Operation Expressing output Simple relay circuits
OR
Input to A or 8 will Low electricai potential (L) at A and B +
produce output at C. no output (L) at C
A
6
D- High electrical potential (H) at A or B +
C output (H) at C
AND Input to A and B will High electrical potential (H) at A and B +
produce output at C. output(H) at C
q---J-c
Low electrical potential (L) at A or B + A
no output (L) at C
B a-00-a C
6
INV No input to A will produce Low electrical potential (L) at A -+
an output at B. no ground (H) B
An input to A will not High electrical potential (H) at A +
A- 6 produce an output at B. grounds (L) B A- 6
PROCESS Simplified representation of complex functions within circuit describes
main function. (Examples)
---
--I- 1 1. Igniters
I
-L-l Signal detector for engine control unit, cooling unit, and tachometer.
Ii- 2. r”~“-‘-‘-““‘~~‘.“’
Sbnsl conwflw :
i...-..--.---......-.~~
Signal converter for turn and hazard flasher unit and igniter unit.
Abbreviations used in this booklet
A
AAS
ABS
ACC
ACCEL
ACV
ADD
AE
AIS
ALL
ALT
EP
ANT
EV
EP
ATX
A/C
AIF
AIR
:AC
B/L
CARB
CCT
CIGAR
COMBI
CON
CONT
CPU
CSD
DEF
DOHC
ECPS Ampere
Autoadjusting Suspension
Antilock Brake System
Accessory
Accelerator
Air Control Valve
Additional
Acoustic Equilibration
Air Injection System
Automatic Load Leveling
Alternator
Amplitude Modulation
Amplifier
Antenna
Autostop
Alr Supply Valve
Automatic transmission
Atmospheric Pressure
Automatic Transaxle
Air Conditioner
Air Fuel
Auto Reverse
Battery
Bypass Air Control Valve
Bilevel
$rr$:,tor
Cigarette
Combination
Conditioner
Control
Central Procassino Unit
&Id-Start Device -
Defroster
Double-Overhead Camshaft
Electronically Controlled Power
Steering ECU
EGI
EGR
ELEC
ELR
ETR
EXH
E
FICB
FM
F/S
F/I
GEN
ET
HI
H/D
I;LUMl
INT
ISC
JB
LCD
LF
k!
z Engine Control Unit
Electronic Gasoline Injection
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Electrio
Emergency Locking Retractor
Electronic Tuner
Exhaust
Front
Fast-Idle Cam Breaker
Frequency Modulation
Feedback
Fuel lniector
Generator
Heater
High-Energy Ignition
High
Heater/Defroster
Ignition
lllumlnation
Idle-Speed Control
Joint Box
Liquid Crystal Display
Left Front
Left Hand
Low
Left Rear
Low Wave
:I, Motor
Middle
MIL
MIN Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Minute
MIX
Mixture
MPX Multiplex
ZR Manual Transmission
MTX Mechanical Tuning Radio
Manual .Transaxie PRG
PTC
P/S ass
kc
FIF
. . .
RH
RPM
!2EL
SQ
ST
SW
TCV
TEMP
TICS
TR
TWS
V
VENT
VOL
VRIS
W Middle Wave
Normally Closed
Normally Open
Overdrive
Switch Off
Switch On
Power
Pressure Regulator Control
Solenoid Valve
Purge Solenoid Valve
Positive Temperature Coefficient
Heater
Power Steering
;im&k-Start System
Recirculation
Right Front
Right Hand
Revolutions Per Minute
Right Rear
Solenoid
Squares Per Milimeter
Start
Switch
Twin Scroll Turbocharger
Solenoid Valve
Temperature
Triple Induction Control System
Transistor
Total Wiring System
Volt
Ventilation
Volume
Variable Resonance Induction
System
Watt(s)
IO
Page 216 of 279

Ve:BenyVdhfp
Test condttton
-roliqc lblwk
lgnhn switch ON
VI3
- bmtm
2A
28
x
2D
2E
2F
26
2H
21
2J
2K
21
2M
2N
20
2P
20
2R Test condtthw
ranabla
2s
2T
2u
2v
2W
2x
2Y
arm-up)
P
P
8°F) P
ov
ov
ov
ov
ov of sv
Approx. 2v
-
ov or 5v
tpplox. 1.5
- connected to
oveftmost warning
tluzz.af
I
I
i”e started wilh cootanl 1 Below 1.5V 1 No&ad engine 1Bo sec. alter eng
temperature is above 90% 1194°F ) and
CondilkJn
iniake air temperature is between 40%
I l@i°F) and So% (122OFj
Other condition at idle
VB
lgrition switch ON
L VE ‘Engine Signd
Idle
VFJ’ Monitor: Green
Engine speed above 2.ooO rpm during
VE and red lamps
Nash Sde”&d valve
m kw tap.)
deceteralion (alter warm-up) -
-
0 -
lanition switch ON -
-
-
-
0 lnjedor (Nos. 1. 3) -
Ignition switch ON
Idle
injector (Nos 2. 4) IgrMon switch ON
I -3 Va
I
ISC valve -
-
0
0
-
0
0
0
0
-
0
0
-
- Idle -
Lpprox. 4.01
4.!--5sv
0 of 5v Knock control unit
Engine speed above 2,GOD rf
Thio#e sensor/
Airllow mder Constant -
0 Solenoid valve
(purge conlro4) Ignition switch ON
II
-
I* I “la I
lgnitlon switch ON .-.- ._
lgnitiin swilch ON VB
-
Idle Below 1.w
210 sec. alter engine started with coolant Below 1.5V No&d engine
temperature above 90% ( 194OF) and
cofditlon
intake air temperature above 50°C
/122OF)
Other condition al idle Va - 0
0 Qrcuit-oparing
relay
sdenoid valve
(PRC high temp.) Accelerator pedal released
Accelerator pedal lully depfesw ,pprox. 0.5L
.pprox. 4.oi 22 -
1 J
Is- r,
L-7 r
2Y Zw 2U 2s 20 20 ZM 2K 21 2G 2E 2C ZA 1U IS 10 10 1M tK I, tG 1E ,C ,A
22 2X ZV 2T ZR 2P 2N 2L 2J 2H ZF 20 28 1V IT IF! ,P IN 1L 1J t” 1F 10 19 lamlion switch ON
Idle (cold engine)
Idle (alter warm-up) ov
o-l.OV
0.5-l.OV
o-0.4v
xpprox. 3.8
tipprox. 3.0
tpprox 2.5
bpprox. 2.5
Bdow 0.5v
V8 -
lncreasmg engine speed (after w
Deceleralion
lgnltro” switch ON Airllow meter -
n airflow meter intake aa
Ambient air temperalure 20°C (6
ErlQl”l? codant temperature 200(
Alter warm-up
Ignition switch ON Water
thermosensor
To&charge
rndlcator
1 I
UI “I
u-1 r
-
2Y ZW ZU ZS 20 20 2M ZK 21 2G 2E 2C ZA lU IS 10 10 1f.I 1K 11 1G 1E tC 1A
22 2X 2V 27 2P 2P 2N 2L 2J 2H ZF 2D 28 IV IT IA 1P IN IL 1.1 1H 1F ID It3
35