water pump MERCEDES-BENZ ML320 1997 Complete User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MERCEDES-BENZ, Model Year: 1997, Model line: ML320, Model: MERCEDES-BENZ ML320 1997Pages: 4133, PDF Size: 88.89 MB
Page 2610 of 4133
21
Detach rear brake cables
Unclip at underfloor of vehicle and
unscrew brake cable holder on right and left
at frame.
22.1
Unbolt check strap of rear axle carrier from
underfloor of vehicle
As of VIN A145273, X708319.
23
Remove left rear stone shield
24
Remove lower tensioning straps (80/2) and
loosen the upper tensioning straps
Tensioning straps are color-coded and
cannot be mixed up.
Support fuel tank using assembly jack.
*BA47.10-P-1001-01D
25
Remove longitudinal strut for tensioning
straps (80/18)
*BA47.10-P-1002-01D
26.1
Unscrew linkage for headlamp range
adjustment
at the top
If installed.
27
Unscrew nuts on bottom of the shock
absorbers at the transverse control arm
Installation:
Install new self-locking nuts.
*BA32.25-P-1001-03D
28
Unscrew rear axle carrier from floor of vehicle
and lower as far as possible
Support rear axle carrier.
Installation:
Install new self-locking bolts.
*BA35.10-P-1001-01C
29
Lower fuel tank
Support fuel tank.
30
Remove upper tensioning strap
at the rear
The tensioning strap at the top at the front.
31.1
Unclip lines from side of fuel tank
As of VIN A289565, X754620.
Installation:
The lines must not be
damaged.
32
Disconnect fuel pump electrical plug
connection
33
Disconnect fuel feed line (90/12) and fuel
return line (90/11)
Fuel lines must not be bent.
Pliers
*163589003700
34
Remove fuel tank (80)
Installation:
Ensure that the sealing
rubbers (5) seat correctly in the body floor to
prevent water entry.
Do not damage fuel lines at filler neck.
Guide filler neck with its chamfered side
(arrow) through between frame and body.
Filler neck and fuel tank cannot be separated
from each other.
35
Install in the reverse order
36.1
Dispose of fuel tank
Ony when replacing the fuel tank.
o
Disposal of fuel tanks
OS47.10-P-0001-01A
Rear axle carrier
Number
Designation
Model
Series 163
BA35.10-P-1001-01C
Self-locking bolt, rear axle carrier at front and rear
to frame floor
Nm
200
Propeller shaft
Number
Designation
Model
Series 163
BA41.10-P-1002-01C
Self-locking bolt, rear propsharft
at rear axle center section
Nm
50
Copyright DaimlerChrysler AG 28.05.2006 CD-Ausgabe G/10/04 . This WIS print-out will not be recorde
d by Modification services.
Page 3
Page 2665 of 4133
ASSESSMENT OF DAMAGE IN WIRING HARNESSES - AH00.19-P-1000-05A
Model 124, 126, 129, 140, 163, 164, 168, 169, 170, 171, 199, 202, 203, 208, 209, 210, 211, 215, 216, 219, 220,
221, 230, 240, 245, 251, 414, 461, 463
Always assess the damage thoroughly before repairing the wiring harnesses.
The following criteria must be observed:
Type of damage:
Damage caused by scorching/overheating, chafing, clamping, crushing, severing, fatigue, corrosion, cable
chewed by an animal, assembly fault.
Cause of damage:
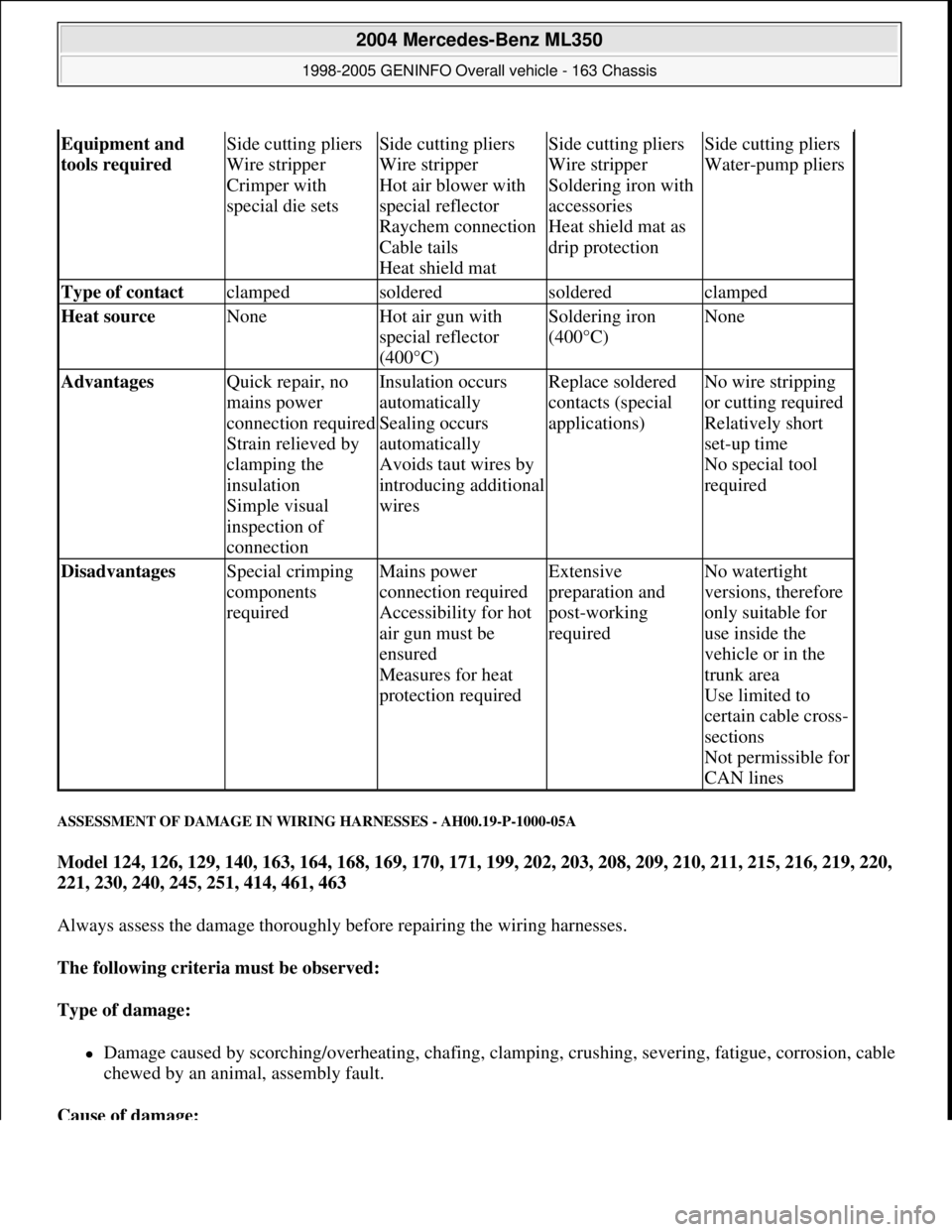
Equipment and
tools required Side cutting pliers
Wire stripper
Crimper with
special die setsSide cutting pliers
Wire stripper
Hot air blower with
special reflector
Raychem connection
Cable tails
Heat shield matSide cutting pliers
Wire stripper
Soldering iron with
accessories
Heat shield mat as
drip protectionSide cutting pliers
Water-pump pliers
Type of contact clampedsolderedsolderedclamped
Heat source NoneHot air gun with
special reflector
(400°C)Soldering iron
(400°C)None
Advantages Quick repair, no
mains power
connection required
Strain relieved by
clamping the
insulation
Simple visual
inspection of
connectionInsulation occurs
automatically
Sealing occurs
automatically
Avoids taut wires by
introducing additional
wiresReplace soldered
contacts (special
applications)No wire stripping
or cutting required
Relatively short
set-up time
No special tool
required
Disadvantages Special crimping
components
requiredMains power
connection required
Accessibility for hot
air gun must be
ensured
Measures for heat
protection requiredExtensive
preparation and
post-working
requiredNo watertight
versions, therefore
only suitable for
use inside the
vehicle or in the
trunk area
Use limited to
certain cable cross-
sections
Not permissible for
CAN lines
2004 Mercedes-Benz ML350
1998-2005 GENINFO Overall vehicle - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:47:44 PMPage 20 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3287 of 4133
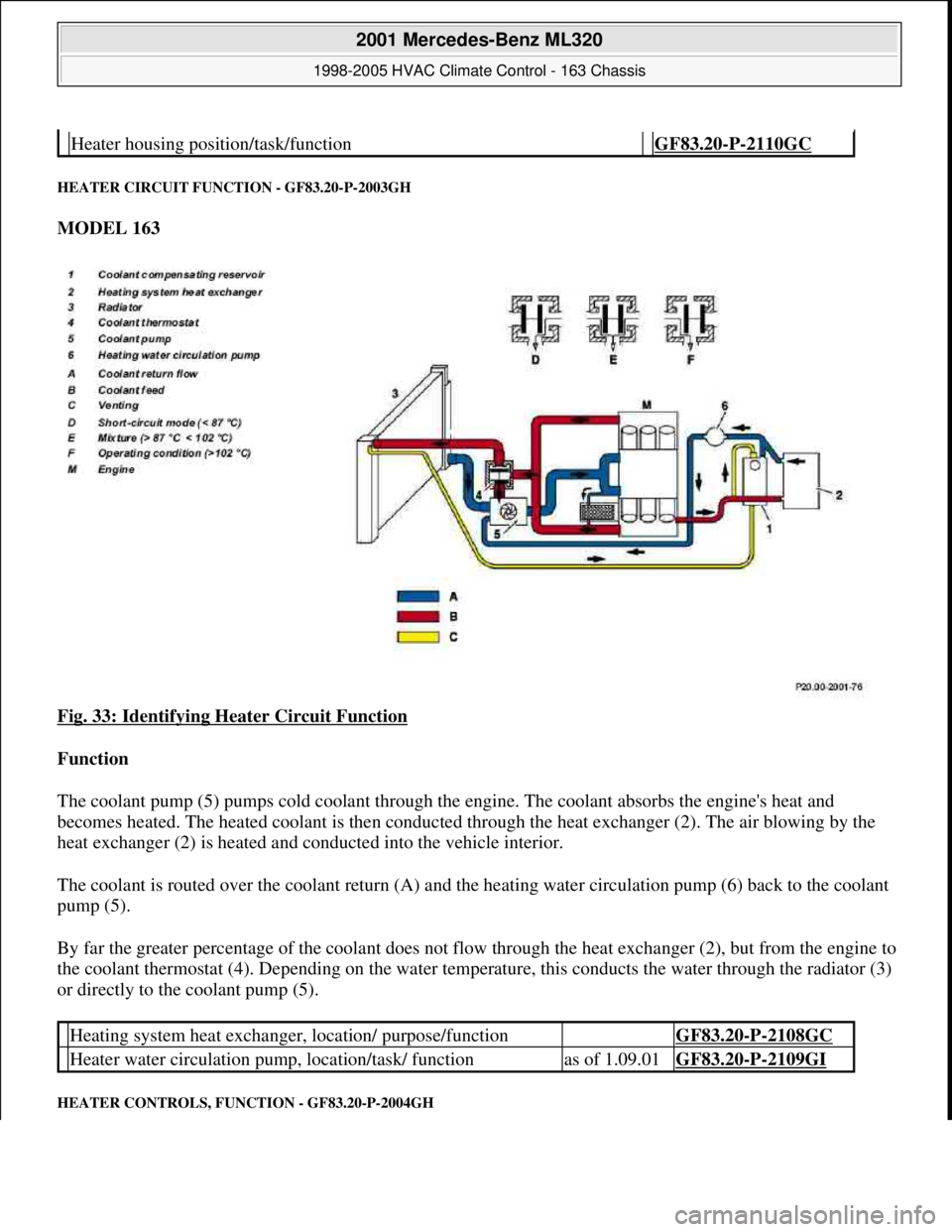
HEATER CIRCUIT FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2003GH
MODEL 163
Fig. 33: Identifying Heater Circuit Function
Function
The coolant pump (5) pumps cold coolant through the engine. The coolant absorbs the engine's heat and
becomes heated. The heated coolant is then conducted through the heat exchanger (2). The air blowing by the
heat exchanger (2) is heated and conducted into the vehicle interior.
The coolant is routed over the coolant return (A) and the heating water circulation pump (6) back to the coolant
pump (5).
By far the greater percentage of the coolant does not flow through the heat exchanger (2), but from the engine to
the coolant thermostat (4). Depending on the water temperature, this conducts the water through the radiator (3)
or directly to the coolant pump (5).
HEATER CONTROLS, FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2004GH
Heater housing position/task/function GF83.20-P-2110GC
Heating system heat exchanger, location/ purpose/function GF83.20-P-2108GC
Heater water circulation pump, location/task/ functionas of 1.09.01GF83.20-P-2109GI
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:15 PMPage 43 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3289 of 4133

Fig. 35: Identifying Heater Core
HEATING WATER CIRCULATION PUMP FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2102-01GI
Function
The quantity of coolant delivered to the heat exchanger when the engine is running is dependent on the coolant
pump. The heating water circulation pump ensures that a constant and bubble-free flow of water is present at
the heat exchanger during residual engine heat utilization, even at low engine speeds.
Initialization of the heating water circulation pump is carried out via the AAC push-button control module
(N22).
Switch-on conditions
Ignition ON
Stationary heater/ON
Enable conditions at residual engine heat complied with
Special conditions
At ambient temperatures of less than -20°C several starting attempts are made, in order to ensure that the
heating water circulation pump goes into operation.
To this end the heating water circulation pump is switched off in intervals of 1 minute for 5 seconds, until the
coolant or blow-out temperature is +20°C higher than the ambient temperature.
Switch-off conditions
Ignition OFF and overshoot time expired
Stationary heater OFF
Residual engine heat OFF and overshoot time expired
Enable conditions at residual engine heat no longer complied with
Enable conditions at residual engine heat
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:15 PMPage 45 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3290 of 4133

The heating water circulation pump runs in any event 1 minute after starting residual engine heat operation. The
overshoot conditions at least will be fulfilled.
Overshoot conditions
Coolant temperature 100°C --> overshoot time 5 minutes
Coolant temperature >100°C --> overshoot time 10 minutes
HEATER HOUSING POSITION - GF83.20-P-2103-01GH
The heater housing (1) is located beneath the instrument panel.
Fig. 36: Identifying Heater Housing
HEATER BOX FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2103-02GH
Operating condition: Heating
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:15 PMPage 46 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3295 of 4133
The fresh air/recirculated air flap shuts off the supply of recirculated air.
Fresh air is drawn in.
Recirculation mode
The fresh air/recirculated air flap shuts off the supply of fresh air. Air is drawn in from the passenger
compartment.
HEATER CORE, LOCATION/PURPOSE/FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2108GC
MODEL 163, 168
HEATING WATER CIRCULATION PUMP, LOCATION/TASK/FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2109GI
MODEL 163 as of 1.9.01 with code (580a) Automatic air conditioning
Fig. 41: Identifying Heating Water Circulation Pump
Heater core,
locationModel 168GF83.20-P-
2101-02GC
Model 163GF83.20-P-
2101-02GH
Heater core,
purposeThe heater core serves for heating up the air flowing through on the way
to the various defroster, ventilation and heating nozzles in the vehicle
passenger compartment.
Heater core,
function GF83.20-P-
2101-01GC
Heating water
circulation pump,
positionThe heating water circulation pump (M13) is located at the front
right in the engine compartment next to the coolant compensating
reservoir.
Heating water
circulation pump
taskThe heating water circulation pump (M13) serves to maintain a
constant flow of hot water through the heat exchanger in the event of
low engine speeds and residual engine heat utilization.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:15 PMPage 51 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3296 of 4133
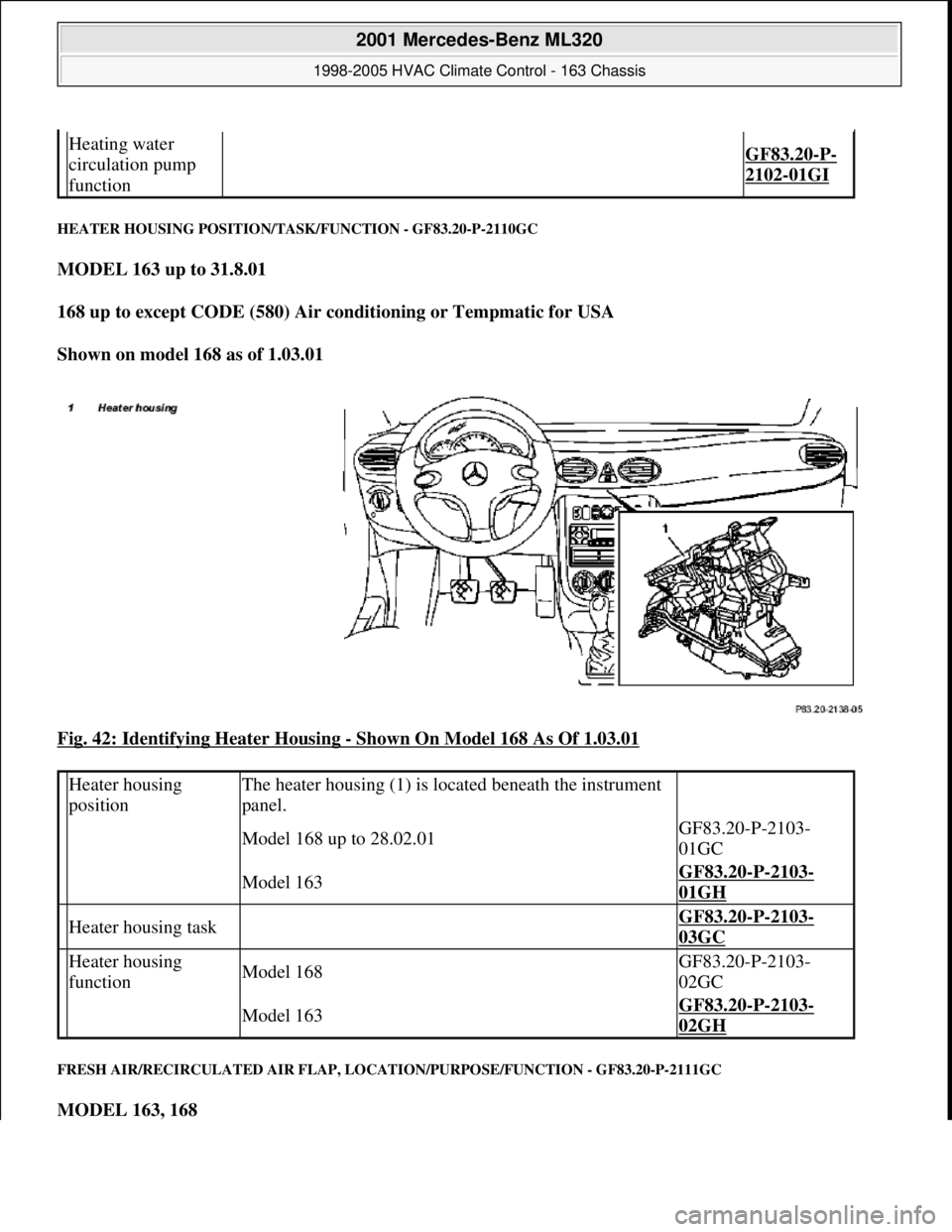
HEATER HOUSING POSITION/TASK/FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2110GC
MODEL 163 up to 31.8.01
168 up to except CODE (580) Air conditioning or Tempmatic for USA
Shown on model 168 as of 1.03.01
Fig. 42: Identifying Heater Housing
- Shown On Model 168 As Of 1.03.01
FRESH AIR/RECIRCULATED AIR FLAP, LOCATION/PURPOSE/FUNCTION - GF83.20-P-2111GC
MODEL 163, 168
Heating water
circulation pump
function
GF83.20-P-
2102-01GI
Heater housing
positionThe heater housing (1) is located beneath the instrument
panel.
Model 168 up to 28.02.01GF83.20-P-2103-
01GC
Model 163GF83.20-P-2103-
01GH
Heater housing task GF83.20-P-2103-
03GC
Heater housing
functionModel 168GF83.20-P-2103-
02GC
Model 163GF83.20-P-2103-
02GH
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:15 PMPage 52 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3325 of 4133

The residual engine heat utilization system allows the vehicle to be heated even when the ignition is
switched OFF. To do so the system utilizes the residual heat from the engine and guides it via the
blower into the passenger compartment. The heating water circulation pump ensures that the
coolant is properly circulated.
Automatic air conditioning push-button control module
The automatic air conditioning can be operated by the driver using various tip switches. Apart from this
the push-
button control module reads in different sensor signals, processes them and controls components
in the automatic air conditioning.
Rear ventilation control panel
The operator can intervene in the automatic regulation of the rear ventilation through the automatic air
conditioning by using the rear ventilation control panel and adjust it accordingly to suit needs at any
given time. With the aid of the air distribution switch and blower switch the operator can accommodate
his/her own wishes. The correspondingly altered function is then no longer regulated by the automatic air
conditioning.
By pressing the automatic control button the manually initiated settings can be reset and thus regulated
again by the automatic air conditioning.
Regulation of the air quantity and air distribution ensues thus solely by way of the automatic air
conditioning push-button control module.
Heater circuit
Coolant is heated by the engine. Subsequently, the heated coolant is then routed through the heat exchanger,
where the heat is dissipated to the air in the passenger compartment. The heater return line, in which the heating
water circulation pump is located, takes the coolant back to the coolant pump.
The heating water circulation pump ensures that the coolant is properly circulated.
The coolant flows through the heat exchanger permanently.
Depending upon the desired in-car temperature, regulation is conducted over the blending air flaps, which are
operated by the blending air flap actuator motor.
Heater operation with heater booster in vehicles with OM 612.963
In vehicles equipped with direct-injection diesel engines, an electrical heater booster is additionally installed in
the evaporator housing downstream of the heat exchanger, in order to compensate the heater output deficit
which occurs in the case of certain operating conditions.
The 3 heating elements in the heater booster are supplied with current, as a result of which they are heated and
start to glow. As a result of the structural conditions, it is ensured that the drawn in fresh air flows directly past
the electric heater booster, and is therefore heated.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 81 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3328 of 4133
The control module integrated in the AAC push-button control module (N22) looks after all system regulation
and control functions such as:
comparing preselected and actual temperatures and controlling the air temperature at the air outlets
automatic switchover from fresh air to recirculated air mode
electrical control of refrigerant compressor
controlling the auxiliary fan or the electric suction-type fan motor/ air conditioning with integrated
control
The AAC push-button control module (N22) has a diagnostic capability. Consequently, any faults which occur
are stored in the fault memory which can be read with the help of the diagnosis assistant system (DAS).
When the AAC push-button control module is replaced (N22), variant coding must be carried out using the
Diagnosis Assistant System (DAS).
The AAC push-button control module (N22) also performs the following actuations:
direct: refrigerant compressor; heating water circulation pump; PTC heater booster (OM 612 only), rear
window heater
via the CAN BUS: auxiliary fan, electric suction-type fan motor/air conditioning with integrated control,
blower control and air distribution in the rear compartment (automatic mode)
via the AC bus: blower motor; 8 stepping motors for air distribution
The following sensor signals are read in by the AAC push-button control module (N22):
direct: temperature sensor evaporator, pressure and temperature sensor refrigerant, in-car temperature
sensor, center nozzle vent air temperature sensor, footwell and rear passenger compartment, sun sensor
via the CAN BUS: Ambient temperature display temperature sensor, sensor for specified values in rear
control panel
REFRIGERANT CIRCUIT FUNCTION - GF83.40-P-2001GH
MODEL 163 up to 31.8.01 with CODE (580) Air conditioning or Tempmatic for USA
Blower switch, location/task/design/function GF83.25-P-2100GI
Temperature selector wheel, location/task/ design/function GF83.25-P-2102GI
Air distribution switch, location/task/design/ function GF83.25-P-2101GI
Defroster button, location/task/function GF83.40-P-2139GI
Recirculating air push-button, location/task/ function GF83.40-P-2145GI
Auto button, location/task/function GF83.40-P-2147GI
AC OFF button, location/task/function GF83.40-P-2107GI
Rest push-button, location/task/function GF83.40-P-2148GI
Rear passenger compartment air distribution button, location/task/function GF83.40-P-2173GI
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 84 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3362 of 4133
function 2146GI
Blower motor,
location/purpose/design/function GF83.10-P-
2170GI
Blower regulator, location/purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2141GI
Rear blower motor, location/purpose/design/
function GF83.10-P-
2168GI
Rear electronic blower regulator, location/
purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2176GI
Combination filter, location/purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2128GI
Defroster vent flap actuator motor, location/
purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2175GI
Footwell flap actuator,
location/purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2132GI
Actuator motor, center nozzle flap, location/
purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2172GI
Actuator motor, rear shut-off flap, location/
purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2171GI
Actuator motor, rear air distribution flap,
location/purpose/function GF83.10-P-
2173GI
Heating system heat exchanger, location/
purpose/function GF83.20-P-
2108GC
Heating water circulation pump, location/
purpose/function GF83.20-P-
2109GI
Fresh air/recirculation flap, location/purpose/
function GF83.20-P-
2111GC
Fresh air/recirculation flap actuator, location/
purpose/function GF83.30-P-
2116GC
Blower switch,
location/purpose/design/function GF83.25-P-
2100GI
Blower button, location/purpose/functionRear ventilation operating moduleGF83.40-P-
2144GI
Air distribution switch,
location/purpose/design/ function GF83.25-P-
2101GI
Air distribution button,
location/purpose/functionRear ventilation operating moduleGF83.40-P-
2159GI
Temperature selector wheel, location/purpose/
design/function GF83.25-P-
2102GI
Defroster button, location/purpose/function GF83.40-P-
2139GI
Recirculating air push-button,
location/purpose/ function GF83.40-P-
2145GI
GF83.40-P-
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 118 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.