fuel pressure MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007Pages: 1449, PDF Size: 56.82 MB
Page 743 of 1449

ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Charging System16-11
1
234
5
8.8±1.0 N·m 22±4 N·m
23±3 N·m11±1 N·m
13±1 N·m
8
(Engine oil)
679
10
20±2 N·m 36±6 N·m
1211
44±10 N·m
14±3 N·m
13
1415 18
1617
9.0±1.0 N·m
9.0±1.0 N·m5.0±1.0 N·m
Removal steps
1. Oil level gauge and guide assembly
2. O-ring
3. Fuel pressure solenoid valve
connector
4. Fuel pressure solenoid valve
assembly
5. Detonation sensor connector
6. Purge control solenoid valve
connector
7. Purge control solenoid valve assembly
8. Injector connector
AA"9. Delivery pipe, injector, and fuel
pressure regulator assembly10. Insulator
11. Insulator
AB"12. Drive belt
13. Alternator connector
DEngine mounting
(Refer to GROUP 32.)
AC"14. Alternator
15. Water pump pulley
16. Alternator brace
17. Oxygen sensor connector
18. Alternator brace stay
Page 744 of 1449
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Charging System16-12
REMOVAL SERVICE POINTS
AA"DELIVERY PIPE, INJECTOR, AND FUEL
PRESSURE REGULATOR ASSEMBLY REMOVAL
After loosening the installed parts, set the related parts
aside to make some space for removing the alternator.
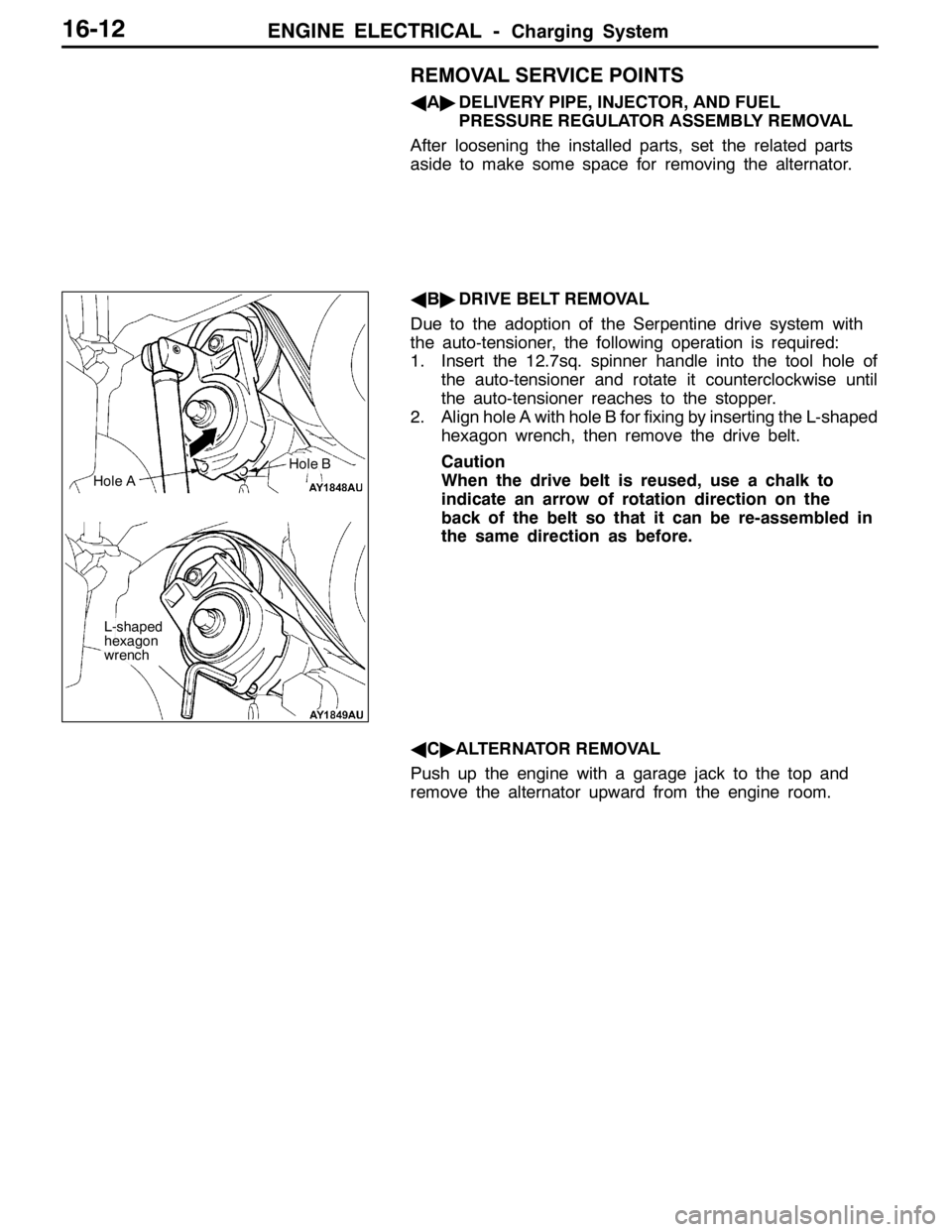
AB"DRIVE BELT REMOVAL
Due to the adoption of the Serpentine drive system with
the auto-tensioner, the following operation is required:
1. Insert the 12.7sq. spinner handle into the tool hole of
the auto-tensioner and rotate it counterclockwise until
the auto-tensioner reaches to the stopper.
2. Align hole A with hole B for fixing by inserting the L-shaped
hexagon wrench, then remove the drive belt.
Caution
When the drive belt is reused, use a chalk to
indicate an arrow of rotation direction on the
back of the belt so that it can be re-assembled in
the same direction as before.
AC"ALTERNATOR REMOVAL
Push up the engine with a garage jack to the top and
remove the alternator upward from the engine room.
Hole A
L-shaped
hexagon
wrench
Hole B
Page 758 of 1449
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Ignition System16-26
IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
This system is equipped with two ignition coils (A
and B) with built-in power transistors for the No.
1 and No. 4 cylinders and the No. 2 and No. 3
cylinders respectively.
Interruption of the primary current flowing in the
primary side of ignition coil A generates a high
voltage in the secondary side of ignition coil A.
The high voltage thus generated is applied to the
spark plugs of No. 1 and No. 4 cylinders to generate
sparks. At the time that the sparks are generated
at both spark plugs, if one cylinder is at the
compression stroke, the other cylinder is at the
exhaust stroke, so that ignition of the compressed
air/fuel mixture occurs only for the cylinder which
is at the compression stroke.
In the same way, when the primary current flowing
in ignition coil B is interrupted, the high voltage
thus generated is applied to the spark plugs of
No. 2 and No. 3 cylinders.
The Engine-ECU turns the two power transistors
inside the ignition coils alternately on and off. Thiscauses the primary currents in the ignition coils
to be alternately interrupted and allowed to flow
to fire the cylinders in the order 1-3-4-2.
The Engine-ECU determines which ignition coil
should be controlled by means of the signals from
the camshaft position sensor which is incorporated
in the camshaft and from the crank angle sensor
which is incorporated in the crankshaft. It also
detects the crankshaft position in order to provide
ignition at the most appropriate timing in response
to the engine operation conditions. It also detects
the crankshaft position in order to provide ignition
at the most appropriate timing in response to the
engine operation conditions.
When the engine is cold or operated at high
altitudes, the ignition timing is slightly advanced
to provide optimum performance.
When the automatic transmission shifts gears, the
ignition timing is also retarded in order to reduce
output torque, thereby alleviating shifting shocks.
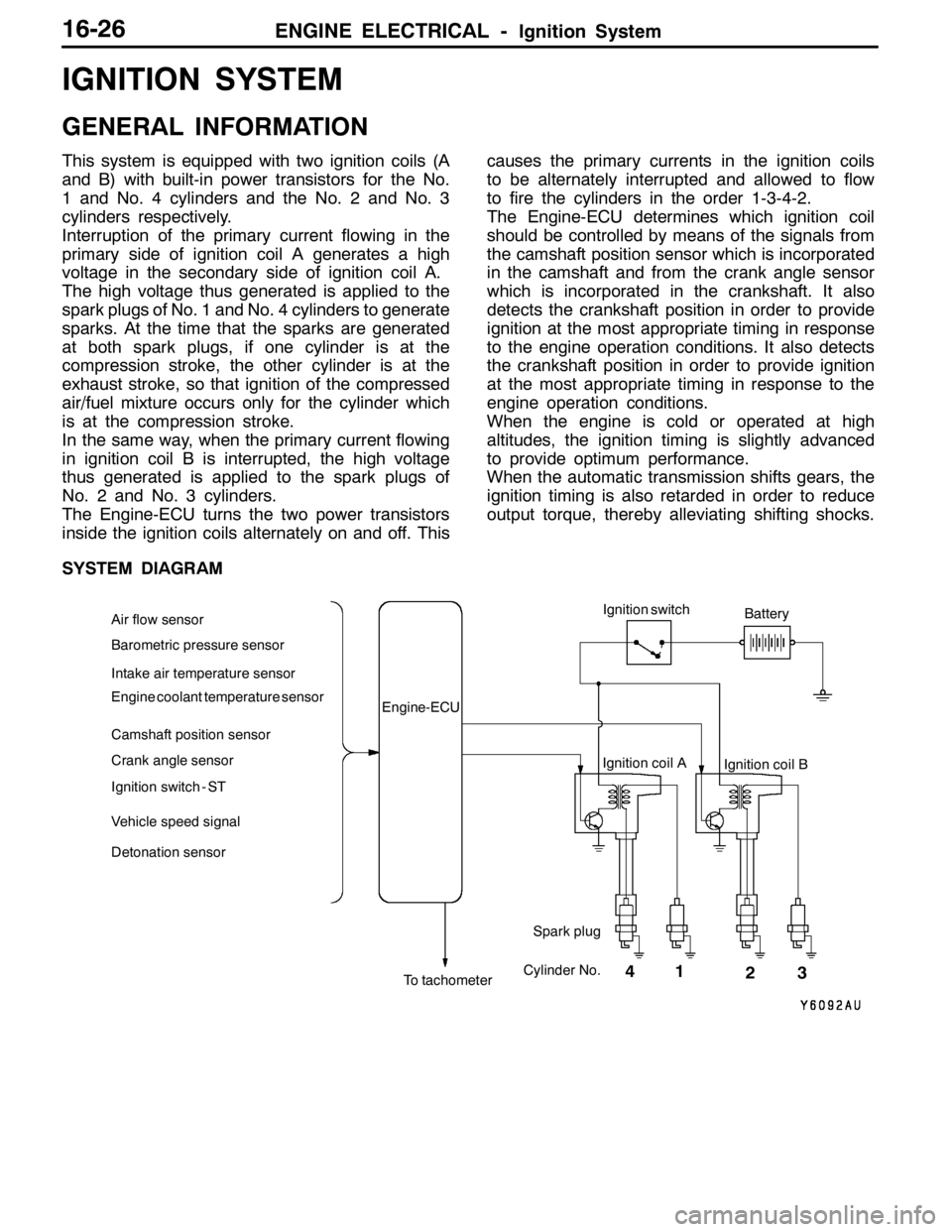
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Barometric pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Crank angle sensor
Ignition switch - ST
Vehicle speed signalEngine-ECU
Ignition coil A
Ignition coil B Ignition switch
Spark plugBattery
To tachometerCylinder No. Air flow sensor
1 4
23
Detonation sensor
Page 775 of 1449
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-5
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard value
Purge control solenoid valve coil resistance (at 20_C)Ω30 - 34
EGR control solenoid valve coil resistance (at 20_C)Ω29 - 35
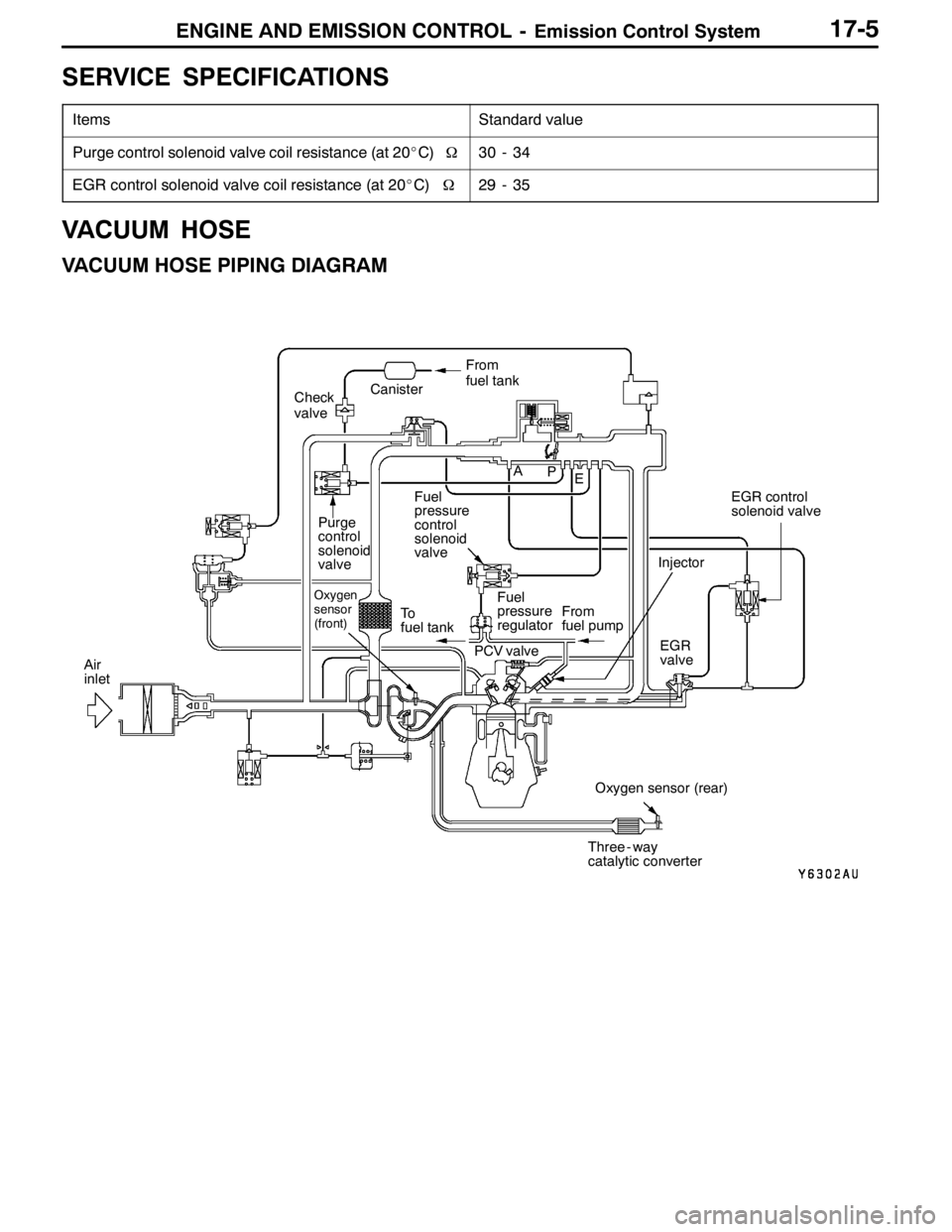
VACUUM HOSE
VACUUM HOSE PIPING DIAGRAM
Fuel
pressure
control
solenoid
valve
Oxygen
sensor
(front)
Check
valve
Fuel
pressure
regulator
PCV valve To
fuel tank
Oxygen sensor (rear) From
fuel pump
Air
inletEGR control
solenoid valve
Purge
control
solenoid
valveCanisterFrom
fuel tank
EGR
valve Injector
Three - way
catalytic converter A
P
E
Page 776 of 1449

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-6
VACUUM CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Vacuum hose colour
B: Black
G: Green
L: Light blue
R: Red
W: White
Y: YellowFrom air
cleaner
Intake manifoldThrottle body
To
combustion
chamber
Fuel pressure
regulator
EGR control
solenoid valve
Canister
EGR valve
Brown
Check valve Vacuum
tank
Fuel pressure
solenoid valve
Air by-pass valve
Secondary air control
solenoid valve
Secondary air
control valvePurge control
solenoid valve
Air cleaner
Waste gate
solenoid valveWaste gate
actuator
Page 780 of 1449

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System
Vacuum tank
Alternator
Purge control solenoid valve
17-10
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The evaporative emission control system prevents
fuel vapours generated in the fuel tank from
escaping into the atmosphere.
Fuel vapours from the fuel tank flow through the
fuel tank pressure control valve and vapour
pipe/hose to be stored temporarily in the canister.
When driving the vehicle, fuel vapours stored in
the canister flow through the purge solenoid and
purge port and go into the intake manifold to be
sent to the combustion chamber.When the engine coolant temperature is low or
when the intake air quantity is small (when the
engine is at idle, for example), the engine control
unit turns the purge solenoid off to shut off the
fuel vapour flow to the intake manifold.
This does not only insure the driveability when the
engine is cold or running under low load but also
stabilize the emission level.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
BatteryIntake air
temperature sensor
Barometric pressure
sensor
Check
valve
Canister
Control
relay
Purge control
solenoid valve
(ON: Open)
Engine-ECUEngine coolant
temperature sensor Air flow sensor
COMPONENT LOCATION
Page 788 of 1449
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-18
CANISTER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Pre-removal and Post-installation Operation
DAir Pipe C, Air Hose D Removal and Installation (Refer to GROUP 15 - Inter Cooler.)
DBattery and Battery Tray Removal and Installation
DAir Cleaner Assembly Removal and Installation (Refer to GROUP 15 - Air Cleaner.)
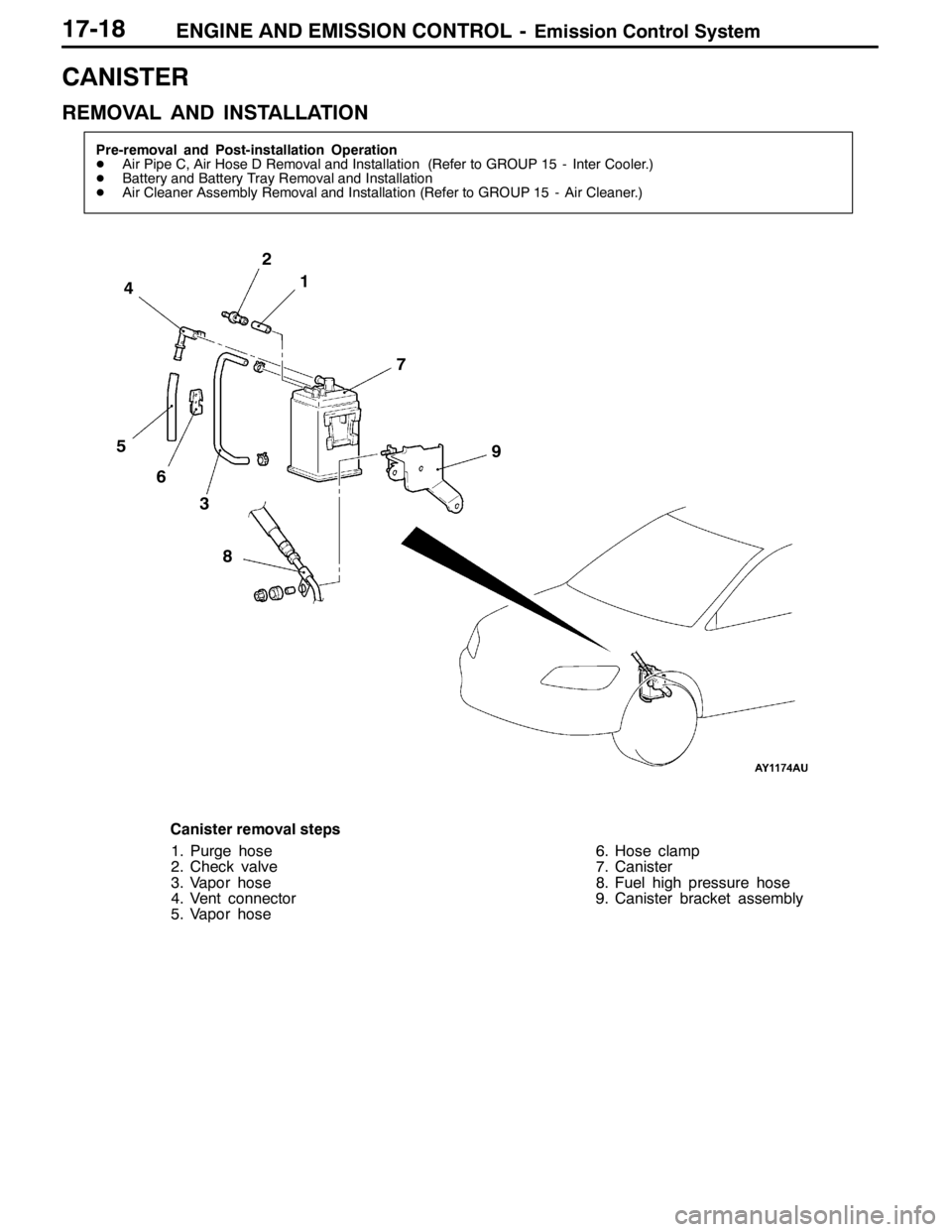
1 2
3 4
5
67
89
Canister removal steps
1. Purge hose
2. Check valve
3. Vapor hose
4. Vent connector
5. Vapor hose6. Hose clamp
7. Canister
8. Fuel high pressure hose
9. Canister bracket assembly
Page 1335 of 1449

CHASSIS ELECTRICAL -Combination Meter54A-15
SPECIAL TOOLS
ToolsNumberNameUse
A
B
C
D
MB991223
A: MB991219
B: MB991220
C: MB991221
D: MB991222Harness set
A: Inspection har-
ness
B: LED Harness
C: LED Harness
Adapter
D: ProbeBrief test for fuel gauge and water temperature
gauge
A: For inspection of connector pin contact
pressure
B: For inspection of power circuit
C: For inspection of power circuit
D: For connecting commercially available
tester
MB990784Ornament removerMeter bezel removal
TROUBLESHOOTING
DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
INPUT SIGNAL INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Connect MUT-IIor voltmeter to diagnostic connector to perform input inspection. (Refer to GROUP 00
- How to Use Troubleshooting and Inspection Procedure.)
INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODES
Trouble symptomInspection procedure No.Reference page
Speedometer inoperative (other meters are operated)154A-16
Tachometer inoperative (other meters are operated)254A-16
Fuel gauge inoperative (other meters are operated)354A-17
Water temperature gauge inoperative (other meters are operated)454A-18
All meters inoperative554A-19