inflation pressure MITSUBISHI MIRAGE G4 2018 (in English) User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2018, Model line: MIRAGE G4, Model: MITSUBISHI MIRAGE G4 2018Pages: 263, PDF Size: 37.9 MB
Page 221 of 263
Tires 9-12 Vehicle care and maintenance
9
N00939201635
It is important to familiarize yourself with the following terms: Cold tire pressure: • The measured pressure after the vehicle has been parked for
at least three hours,
or• The measured pressure when the vehicle is driven less than 1 mile (1.6 km) after having been parked for three hours.
Maximum pressure: the maximum per- missible cold tire inflation pressure for this tire.
WA R N I N G Never disconnect the battery while the engine is running, or you could damagethe vehicle’s electrical parts. Never short-circuit the battery. This could cause it to overheat and be damaged. Keep sparks, cigarette
s, and flames away
from the battery because the battery couldexplode. Electrolyte (battery acid) is made of corro- sive diluted sulfuric acid. If it spills on nearby parts, it can crack, stain, or dis- color them. And if it gets on your skin orin your eyes, it can cause burns or blind- ness. Please observe the following han- dling instructions:• If electrolyte gets on plastic parts orother nearby parts, wipe it off with a softcloth or chamois soak
ed in a solution of
water and neutral detergent then imme- diately rinse the affected parts withplenty of water.• If electrolyte gets on your hands orclothes, rinse thoroughly with water. If electrolyte gets in
your eyes, flush them
with water immediately and get immedi-ate medical attention.
Open doors and wind
ows in any closed
space where you may be charging or working with the battery. Always wear protective clothing and gog- gles when working with the battery, or have a skilled automobi
le technician do it.
If you are quick-charging your battery, first disconnect the battery cables. In order to prevent a short-circuit, be sure to disconnect the negative (-) terminal first, and reconnect it last. Battery posts, termin
als and related acces-
sories contain lead
and lead compounds.
Wash hands after handling.NOTE
Check each battery terminal for corrosion. You can stop more corrosion by washing with a solution of baking soda and water. Grease the posts and cl
amps after cleaning or
tightening them. Check to see that the battery is securely installed and cannot be
moved. Also check
each terminal for tightness. If you will not be driv
ing your vehicle for a
long period of time, re
move the battery and
store it in a place where the battery fluid willnot freeze. The batter
y only should be stored
with a full charge. Before cleaning the ba
ttery, tighten all the
filler port caps to keep
dirt and moisture out.
WA R N I N G
Tires
WA R N I N GDriving with tires that are worn, damaged or improperly inflated is dangerous.These type tire conditions will adversely affect vehicle performance. These type tire conditions can also cause atread separation or blowout which may result in an accide
nt causing serious
injury or death. Tires, including spar
e tire, degrade over
time with age even when they are notbeing used. It is recommended that tires over 6 years generally be replaced even if damage isnot obvious.
BK0249600US.book 12 ページ 2017年4月20日 木曜日 午後1時36分
Page 222 of 263
Tires
Vehicle care and maintenance 9-13
9
Recommended inflation pressure: the inflation pressure for optimum tire perfor-mance. Intended outboard sidewall: • The sidewall that c
ontains a whitewall,
bears white letteri
ng or bears manufac-
turer, brand, and/or model name molding that is higher or deeper than the samemolding on the other sidewall of the tire, or • The outward facing si
dewall of an asym-
metrical tire that has a particular side that must always face outward whenmounted on a vehicle.
Passenger car tire: a
tire intended for use
on passenger cars, multipurpose passen-ger vehicles, and trucks that have a gross vehicle weight rati
ng (GVWR) of 10,000
pounds or less. Light truck (LT) tire: a tire designated by its manufacturer as primarily intended for use on lightweight truc
ks or multipurpose
passenger vehicles. Tread: portion of a tire that comes into contact with the road. Tread rib: a tread se
ction running circum-
ferentially around a tire. Tread separation: pulling away of the tread from the tire carcass. Carcass: the tire structure, except tread and sidewall rubber which, when inflated,bears the load.
Sidewall: portion of a tire between the tread and bead. Section width: the line
ar distance between
the exteriors of the sidewalls of an inflated tire, excluding elevations due tolabeling, decoration, or protective bands. Bead: the part of the tire that is made of steel wires, wrapped
or reinforced by ply
cords and that is shaped to fit the rim. Ply: a layer of rubber-coated parallel cords. Cord: the strands forming the plies in the tire. Rim: a metal support for a tire or a tire and tube assembly upon which the tire beads are seated. Rim diameter: nominal diameter of the bead seat. Groove: the space between two adjacent tread ribs.
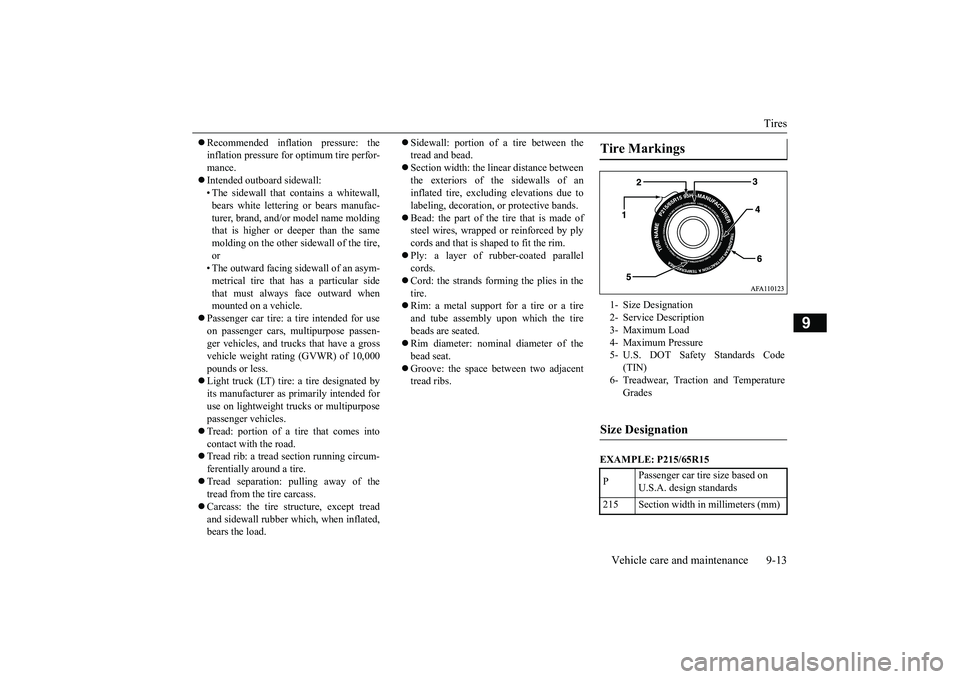
EXAMPLE: P215/65R15Tire Markings 1- Size Designation 2- Service Description 3- Maximum Load 4- Maximum Pressure5- U.S. DOT Safety Standards Code
(TIN)
6- Treadwear, Traction and Temperature
Grades
Size Designation P
Passenger car tir
e size based on
U.S.A. design standards
215 Section width in millimeters (mm)
BK0249600US.book 13 ページ 2017年4月20日 木曜日 午後1時36分
Page 223 of 263
Tires 9-14 Vehicle care and maintenance
9
EXAMPLE: 95H Maximum load indicates the maximum load this tire is designed to carry.
Maximum Pressure i
ndicates the maximum
permissible cold tire inflation pressure for this tire. The TIN may be found on one or both sides of the tire but the date code may only be onone side. Look for the TIN on the outboard side of tires as mounted on the vehicle. If the TIN is not found on the outboard side thenyou will find it on the inboard side of the tire. EXAMPLE: DOT MA L9 ABCD 1504
65
Aspect ratio in percent (%) Ratio of section height to section width of tire.
R
Construction code • “R” means radial construction. • “D” means dia
gonal or bias con-
struction.
15 Rim diameter in inches (in)
NOTE
European/Japanese metric tire sizing is based on European/Japanese design standards.Tires designed to these standards have the tire size molded into the sidewall beginning with the section width. The letter “P” isabsent from this ti
re size designation.
Example: 215/65R15 96H. LT (Light Truck) -metric tire sizing is based on U.S.A. design standa
rds. The size desig-
nation for LT-metric tires is the same as forP-metric tires except for the letters “LT” that are molded into the sidewall preceding the size designation.Example: LT235/85R16. Temporary spare tires are high pressure com- pact spares designed
for temporary emer-
gency use only. Tires designed to this standard have the letter “T” molded into thesidewall prec
eding the size designation.
Example: T145/80D18 103M.
Service Description 95
Load index A numerical code associated with the maximum load a tire can carry.
H
Speed symbol A symbol indicating the range of speeds at which a tire can carry a load corresponding to its load index under certai
n operating con-
ditions. The maximum speed correspond-ing to the speed symbol should only be achieved under specified operating conditions
. (i.e. tire pres-
sure, vehicle loading, road condi- tions and posted speed limits)
Maximum Load
WA R N I N G Overloading of your tire is dangerous. Overloading can cause tire failure, affectvehicle handling, and
increase your stop-
ping distance. Use tires of the recom- mended load capaci
ty for your vehicle.
Never overload them.
Maximum Pressure Tire Identification Number (TIN) DOT
Department of Transportation This symbol certifies that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation tire safety standards, and is approved for highway use.
BK0249600US.book 14 ページ 2017年4月20日 木曜日 午後1時36分
Page 224 of 263
Tires
Vehicle care and maintenance 9-15
9
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specifiedgovernment test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and one-half (11/2) times as well on th
e government course
as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon th
e actual conditions of
their use, however, and may depart signifi- cantly from the norm due to variations in driving habits, service
practices and differ-
ences in road characteristics and climate.
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are AA, A, B and C. Those grades representthe tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under contro
lled conditions on
specified government te
st surfaces of asphalt
and concrete. A tire
marked C may have poor
traction performance. The temperature grades
are A (the highest), B
and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and
its ability to dissipate
heat when tested under controlled conditionson a specified indoor laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to
degenerate and reduce
tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corre- sponds to a level of performance which allpassenger car tires must meet under the Fed- eral Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels ofperformance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
N00939301984
Proper tire inflation pressure is essential forthe safe and satisfactory operation of your
vehicle. The wrong tire pressure will cause problems in three major areas: Safety Too little pressure increases flexing in the tire and can cause tire failure. Too much pressure can cause a tire to lose its abilityto cushion shock. Objects on the road and potholes could then ca
use tire damage that
may result in tire failure. Economy The wrong tire pressu
re can cause uneven
wear patterns in the tire tread. These abnormal wear patter
ns will reduce the
tread life, and the tire will have to bereplaced sooner. Too little pressure also makes it harder for the tire to roll, and this uses up more fuel. Ride comfort and vehicle stability The superior riding experience built into your vehicle partly de
pends on the correct
tire pressure. Too much pressure gives an uncomfortable and jarring ride. Too little pressure feels as if
your vehicle is slow to
respond. Unequal tire pressure
s can make steering
your vehicle uneven
and unpredictable.
The tire pressure for your vehicle under nor- mal driving conditions is listed on the placard attached to the driver’s door sill. (Refer to “Tire and loading information plac-ard” on page 11-3.)
MA
Code representing the tire manu- facturing location. (2 digits)
L9 ABCD
Code representing the tire size. (2 digits) Code used by tire manufacturer. (1 to 4 digits)
15
Number representing the week in which the tire was manufactured. (2 digits)
04
Number representing the year in which the tire was manufactured. (2 digits)
Treadwear, Traction and Temper- ature Grades Treadwear
Tr a c t i o n TemperatureTire inflation pressures
BK0249600US.book 15 ページ 2017年4月20日 木曜日 午後1時36分
Page 225 of 263
Tires 9-16 Vehicle care and maintenance
9
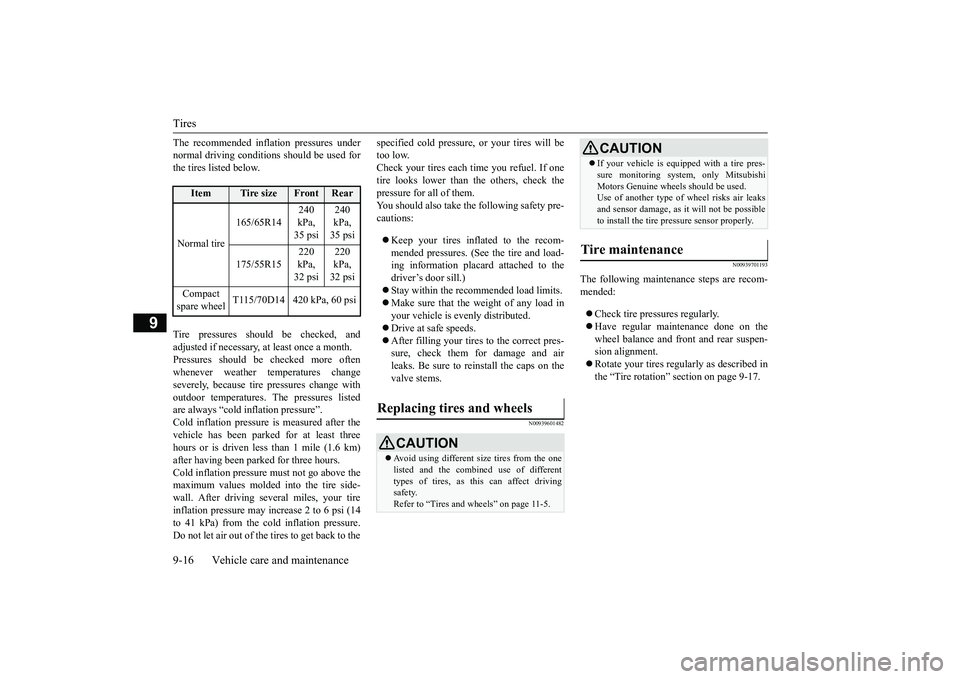
The recommended inflation pressures under normal driving conditions should be used forthe tires listed below. Tire pressures should be checked, and adjusted if necessary, at least once a month. Pressures should be checked more often whenever weather temperatures changeseverely, becaus
e tire pressures change with
outdoor temperatures. The pressures listed are always “cold inflation pressure”.Cold inflation pressure is measured after the vehicle has been parked
for at least three
hours or is driven less than 1 mile (1.6 km)after having been parked for three hours. Cold inflation pressure must not go above the maximum values molded into the tire side-wall. After driving seve
ral miles, your tire
inflation pressure may increase 2 to 6 psi (14 to 41 kPa) from the cold inflation pressure.Do not let air out of the tires to get back to the
specified cold pressure, or your tires will be too low.Check your tires each time you refuel. If one tire looks lower than the others, check the pressure for all of them.You should also take the following safety pre- cautions: Keep your tires inflated to the recom- mended pressures. (See the tire and load-ing information placard attached to the driver’s door sill.) Stay within the recommended load limits. Make sure that the weight of any load in your vehicle is evenly distributed. Drive at safe speeds. After filling your tires to the correct pres- sure, check them for damage and airleaks. Be sure to reinstall the caps on the valve stems.
N00939601482
N00939701193
The following maintenance steps are recom- mended: Check tire pressures regularly. Have regular maintenance done on the wheel balance and front and rear suspen-sion alignment. Rotate your tires regularly as described in the “Tire rotation” section on page 9-17.
Item
Tire size
Front
Rear
Normal tire
165/65R14
240 kPa, 35 psi
240 kPa, 35 psi
175/55R15
220 kPa, 32 psi
220 kPa, 32 psi
Compact spare wheel
T115/70D14 420 kPa, 60 psi
Replacing tires and wheels
CAUTION Avoid using different size tires from the one listed and the combined use of different types of tires, as this can affect driving safety.Refer to “Tires and wheels” on page 11-5.
If your vehicle is equippe
d with a tire pres-
sure monitoring system, only MitsubishiMotors Genuine wheels should be used.Use of another type of
wheel risks air leaks
and sensor damage, as
it will not be possible
to install the tire pressure sensor properly.
Tire maintenance
CAUTION
BK0249600US.book 16 ページ 2017年4月20日 木曜日 午後1時36分
Page 261 of 263

Alphabetical index 12-4
12
Power windows
..................................
5-29
Puncture (Tire changing)
.......................
8-6
R
Radio
General information about your radio 7-20
Rear combination lights
Bulb capacity
.................................
9-27
Replacement
..................................
9-31
Rear seat
..............................................
4-5
Rear side-marker lights
Bulb capacity
.................................
9-27
Replacement
..................................
9-31
Rear turn signal lights
Bulb capacity
.................................
9-27
Replacement
..................................
9-31
Rear-view camera
...............................
5-61
Rearview mirror
Inside rearview mirror
.....................
5-33
Outside rearview mirrors
.................
5-35
Replacement of light bulbs
..................
9-26
Replacing tires and wheels
..................
9-16
Reporting Safety Defects
.....................
10-2
S
Safe driving techniques
.........................
6-4
Seat belts
.............................................
4-7
Adjustable seat belt shoulder anchor
.4-12
Child restraint systems
.....................
4-14
Front passenger seat belt warning light
.....
4-11 Maintenance and inspection
.............
4-22
Seat belt extender
............................
4-13
Seat belt force limitter system
..........
4-14
Seat belt instructions
........................
4-8
Seat belt pre-tensioners
....................
4-13
Seat belt use
during pregnancy
.........
4-13
Seats
...................................................
4-2
Arm rest
..........................................
4-5
Front seats
.......................................
4-2
Head restraints
.................................
4-5
Heated seats
.....................................
4-4
Seats and restraint systems
................
4-2
Service brake
......................................
5-46
Service precautions
..............................
9-2
Side turn signal lights
Bulb capacity
..................................
9-27
Snow tires
..........................................
9-18
Spark plugs
.........................................
9-20
Starting the engine
...............................
5-37
Steering
Electric power stee
ring system (EPS) 5-50
Steering wheel height adjustment
......
5-33
Stop lights
Bulb capacity
..................................
9-27
Replacement
...................................
9-31
Storage spaces
....................................
5-92
Sun visors
..........................................
5-85
Supplemental Restraint System
............
4-22
How the Supplementa
l Restraint System
works
..........................................
4-25
Maintenance service
.......................
4-36
T
Tail lights
Bulb capacity
.................................
9-27
Replacement
..................................
9-31
Tank capacity
.....................................
11-6
Tire pressure monitoring system
...........
5-58
Tires
..................................................
9-12
Inflation pressures
..........................
9-15
Maintenance
...................................
9-16
Quality grading
..............................
10-2
Replacing tires and wheels
..............
9-16
Rotation
.........................................
9-17
Size (tire and wheel)
.......................
11-5
Snow tires
......................................
9-18
Tire and loading information placard 11-3Tire chains
.....................................
9-18
To change a tire
................................
8-6
Tread wear indicator
.......................
9-17
Tools
...................................................
8-5
Storage
............................................
8-5
Towing
..............................................
8-12
Trailer towing
.....................................
6-11
Trunk lid
............................................
5-27
BK0249600US.book 4 ページ 2017年4月20日 木曜日 午後1時36分