dimensions MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1998 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1998, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1998Pages: 1501, PDF Size: 25.81 MB
Page 548 of 1501

ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION
1998 Mitsubishi Montero
Engine Overhaul Procedures - General Information
ALL PISTON ENGINES
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
Examples used in this article are general in nature and do
not necessarily relate to a specific engine or system. Illustrations
and procedures have been chosen to guide mechanic through engine
overhaul process. Descriptions of processes of cleaning, inspection,
assembly and machine shop practice are included.
Always refer to appropriate engine overhaul article in the
ENGINES section for complete overhaul procedures and specifications
for the vehicle being repaired.
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
The engine may be identified from its Vehicle Identification
Number (VIN) stamped on a metal tab. Metal tab may be located in
different locations depending on manufacturer. Engine identification
number or serial number is located on cylinder block. Location varies
with manufacturer.
INSPECTION PROCEDURES
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
NOTE: Always refer to appropriate engine overhaul article in the
ENGINES section for complete overhaul procedures and
specifications for the vehicle being repaired.
GENERAL
Engine components must be inspected to meet manufacturer's
specifications and tolerances during overhaul. Proper dimensions and
tolerances must be met to obtain proper performance and maximum engine
life.
Micrometers, depth gauges and dial indicator are used for
checking tolerances during engine overhaul. Magnaflux, Magnaglo, dye-
check, ultrasonic and x-ray inspection procedures are used for parts
inspection.
MAGNETIC PARTICLE INSPECTION
Magnaflux & Magnaglo
Magnaflux is an inspection technique used to locate material
flaws and stress cracks. The part in question is subjected to a strong
magnetic field. The entire part, or a localized area, can be
magnetized. The part is coated with either a wet or dry material that
contains fine magnetic particles.
Cracks which are outlined by the particles cause an
interruption in the magnetic field. The dry powder method of Magnaflux
can be used in normal light. A crack will appear as an obvious bright
line.
Fluorescent liquid is used in conjunction with a blacklight
in a second Magnaflux system called Magnaglo. This type of inspection
demands a darkened room. The crack will appear as a glowing line in
this process. Both systems require complete demagnetizing upon
Page 558 of 1501
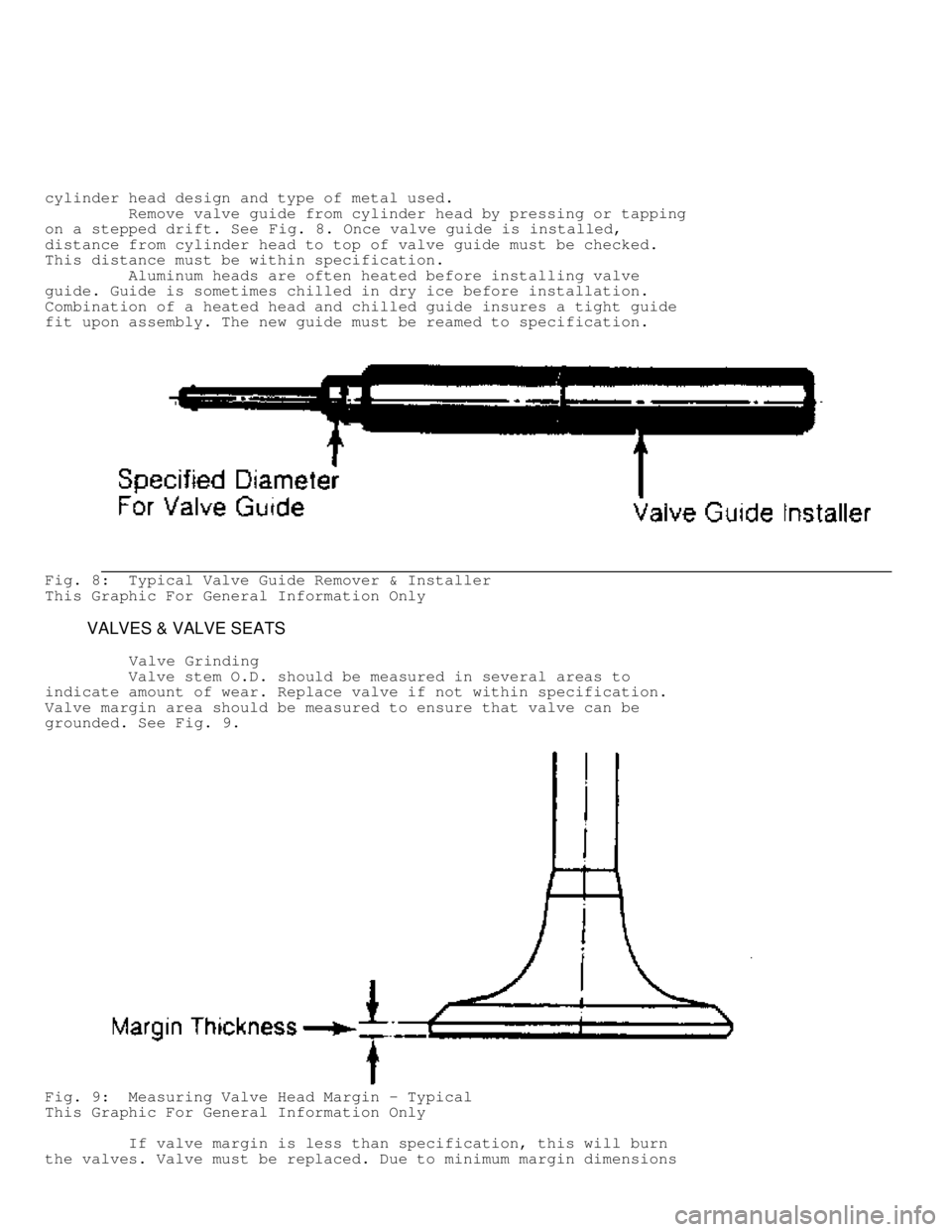
cylinder head design and type of metal used.
Remove valve guide from cylinder head by pressing or tapping
on a stepped drift. See Fig. 8. Once valve guide is installed,
distance from cylinder head to top of valve guide must be checked.
This distance must be within specification.
Aluminum heads are often heated before installing valve
guide. Guide is sometimes chilled in dry ice before installation.
Combination of a heated head and chilled guide insures a tight guide
fit upon assembly. The new guide must be reamed to specification.
Fig. 8: Typical Valve Guide Remover & Installer
This Graphic For General Information Only
VALVES & VALVE SEATS
Valve Grinding
Valve stem O.D. should be measured in several areas to
indicate amount of wear. Replace valve if not within specification.
Valve margin area should be measured to ensure that valve can be
grounded. See Fig. 9.
Fig. 9: Measuring Valve Head Margin - Typical
This Graphic For General Information Only
If valve margin is less than specification, this will burn
the valves. Valve must be replaced. Due to minimum margin dimensions
Page 571 of 1501
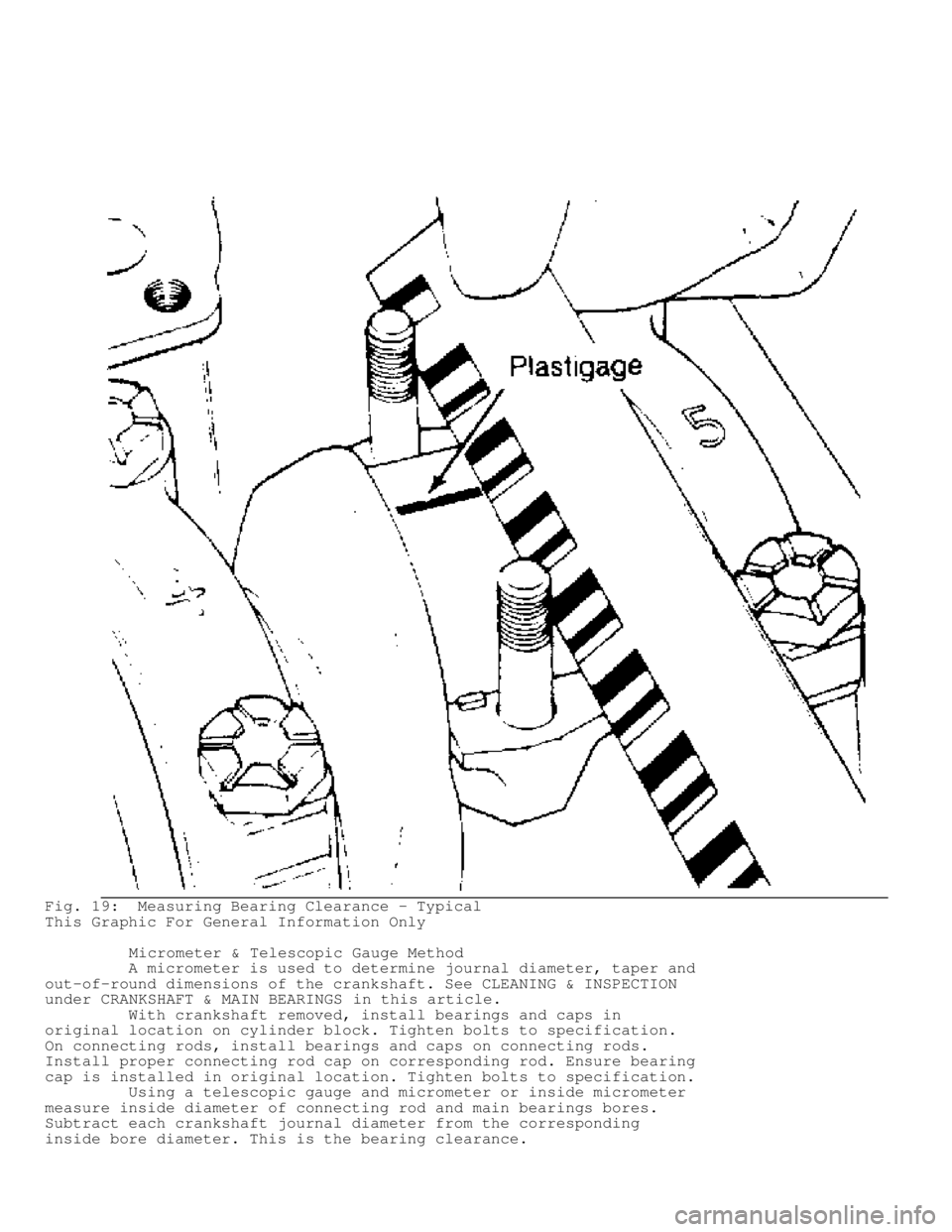
Fig. 19: Measuring Bearing Clearance - Typical
This Graphic For General Information Only
Micrometer & Telescopic Gauge Method
A micrometer is used to determine journal diameter, taper and
out-of-round dimensions of the crankshaft. See CLEANING & INSPECTION
under CRANKSHAFT & MAIN BEARINGS in this article.
With crankshaft removed, install bearings and caps in
original location on cylinder block. Tighten bolts to specification.
On connecting rods, install bearings and caps on connecting rods.
Install proper connecting rod cap on corresponding rod. Ensure bearing
cap is installed in original location. Tighten bolts to specification.
Using a telescopic gauge and micrometer or inside micrometer
measure inside diameter of connecting rod and main bearings bores.
Subtract each crankshaft journal diameter from the corresponding
inside bore diameter. This is the bearing clearance.
Page 577 of 1501

NOTE: Always refer to appropriate engine overhaul article in the
ENGINES section for complete overhaul procedures and
specifications for the vehicle being repaired.
CLEANING & INSPECTION
Clean camshaft with solvent. Ensure all oil passages are
clear. Inspect cam lobes and bearing journals for pitting, flaking or
scoring. Using micrometer, measure bearing journal O.D.
Support camshaft at each end with "V" blocks. Position dial
indicator with tip resting on center bearing journal. Rotate camshaft
and note reading. If reading exceeds specification, replace camshaft.
Check cam lobe lift by measuring base circle of camshaft
using micrometer. Measure again at 90 degrees to tip of cam lobe. Cam
lift can be determined by subtracting base circle diameter from tip of
cam lobe measurement.
Different lift dimensions are given for intake and exhaust
cam lobes. Reading must be within specifications. Replace camshaft if
cam lobes or bearing journals are not within specifications.
Inspect camshaft gear for chipped, eroded or damaged teeth.
Replace gear if damaged. On camshafts using thrust plate, measure
distance between thrust plate and camshaft shoulder. Replace thrust
plate if not within specification.
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
Removal & Installation
Remove the camshaft rear plug. The camshaft bearing remover
is assembled with its shoulder resting on the bearing to be removed
according to manufacturer's instructions. Tighten puller nut until
bearing is removed. Remove remaining bearings, leaving front and rear
bearings until last. These bearings act as guide for camshaft bearing
remover.
To install new bearings, puller is rearranged to pull
bearings toward the center of block. Ensure all lubrication passages
of bearing are aligned with cylinder block. Coat new camshaft rear
plug with sealant. Install camshaft rear plug. Ensure plug is even
in cylinder block.
CAMSHAFT INSTALLATION
Lubricate bearing surfaces and cam lobes with ample amount of
Molykote or camshaft lubricant. Carefully install camshaft. Use care
not to damage bearing journals during installation. Install thrust
plate retaining bolts (if equipped). Tighten bolts to specification.
On overhead camshafts, install bearing caps in original location.
Tighten bolts to specification. Check end play.
CAMSHAFT END PLAY
Using dial indicator, check end play. Position dial indicator
on front of engine block. Position indicator tip against camshaft.
Push camshaft toward rear of engine and adjust indicator to zero.
Move camshaft forward and note reading. Camshaft end play
must be within specification. End play may be adjusted by relocating
gear, shimming thrust plate or replacing thrust plate depending on
manufacturer.
TIMING CHAINS & BELTS