light NISSAN ALMERA N16 2003 Electronic Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2003, Model line: ALMERA N16, Model: NISSAN ALMERA N16 2003Pages: 3189, PDF Size: 54.76 MB
Page 6 of 3189

The security indicator is located on the combi meter. The indicator
blinks when the ignition switch is in “OFF” or “ACC” position.
Therefore, NATS warns outsiders that the vehicle is equipped with
the anti-theft system.
When NATS detects trouble, the security indicator lamp lights
up while ignition switch is in “ON” position.
This lighting up indicates that the anti-theft is not functioning,
so prompt service is required.
When servicing NATS (trouble diagnoses, system initialization
and additional registration of other NATS ignition key IDs),
CONSULT-II hardware and CONSULT-II NATS software is
necessary.
Regarding the procedures of NATS initialization and NATS
ignition key ID registration, refer to CONSULT-II operation
manual, NATS.
Therefore, CONSULT-II NATS software (program card and
operation manual) must be kept strictly confidential to main-
tain the integrity of the anti-theft function.
When servicing NATS (trouble diagnoses, system initialization
and additional registration of other NATS ignition key IDs), it
may be necessary to re-register original key identification.
Therefore, be sure to receive all keys from vehicle owner. A
maximum of five key IDs can be registered into NATS.
When failing to start the engine first time using the key of
NATS, start as follows.
a) Leave the ignition key in “ON” position for approximately 5
seconds.
b) Turn ignition key to “OFF” or “LOCK” position and wait approxi-
mately 5 seconds.
c) Repeat step 1 and 2 again.
d) Restart the engine while keeping the key separate from any
others on key-chain.
SGI285
GENERAL PRECAUTIONSNJGI0001S03Do not operate the engine for an extended period of time
without proper exhaust ventilation.
Keep the work area well ventilated and free of any inflammable
materials. Special care should be taken when handling any
inflammable or poisonous materials, such as gasoline, refrig-
erant gas, etc. When working in a pit or other enclosed area,
be sure to properly ventilate the area before working with haz-
ardous materials.
Do not smoke while working on the vehicle.
SGI231
Before jacking up the vehicle, apply wheel chocks or other tire
blocks to the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving. After
jacking up the vehicle, support the vehicle weight with safety
stands at the points designated for proper lifting before work-
ing on the vehicle.
These operations should be done on a level surface.
When removing a heavy component such as the engine or
transaxle, be careful not to lose your balance and drop them.
Also, do not allow them to strike adjacent parts, especially the
brake tubes and master cylinder.
PRECAUTIONS
Precautions (Cont’d)
GI-4
Page 16 of 3189
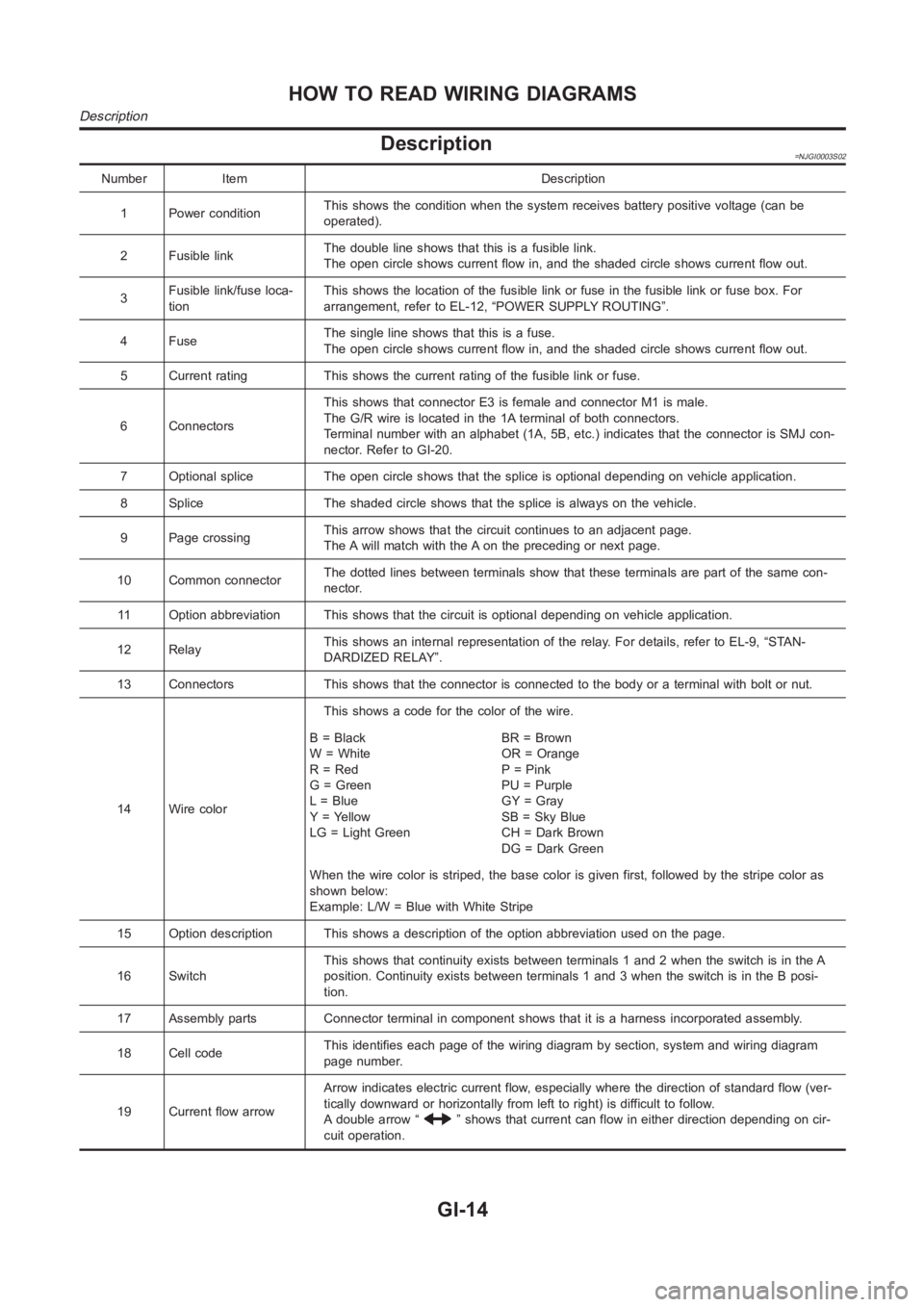
Description=NJGI0003S02
Number Item Description
1 Power conditionThis shows the condition when the system receives battery positive voltage (can be
operated).
2 Fusible linkThe double line shows that this is a fusible link.
The open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
3Fusible link/fuse loca-
tionThis shows the location of the fusible link or fuse in the fusible link or fusebox.For
arrangement, refer to EL-12, “POWER SUPPLY ROUTING”.
4FuseThe single line shows that this is a fuse.
The open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
5 Current rating This shows the current rating of the fusible link or fuse.
6 ConnectorsThis shows that connector E3 is female and connector M1 is male.
The G/R wire is located in the 1A terminal of both connectors.
Terminal number with an alphabet (1A, 5B, etc.) indicates that the connector is SMJ con-
nector. Refer to GI-20.
7 Optional splice The open circle shows that the splice is optional depending on vehicle application.
8 Splice The shaded circle shows that the splice is always on the vehicle.
9 Page crossingThis arrow shows that the circuit continues to an adjacent page.
The A will match with the A on the preceding or next page.
10 Common connectorThe dotted lines between terminals show that these terminals are part of thesamecon-
nector.
11 Option abbreviation This shows that the circuit is optional depending on vehicle application.
12 RelayThis shows an internal representation of the relay. For details, refer to EL-9, “STAN-
DARDIZED RELAY”.
13 Connectors This shows that the connector is connected to the body or a terminal with bolt or nut.
14 Wire colorThis shows a code for the color of the wire.
B=Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light GreenBR = Brown
OR = Orange
P = Pink
PU = Purple
GY = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG=DarkGreen
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as
shown below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option description This shows a description of the option abbreviationused on the page.
16 SwitchThis shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switchis in the A
position. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is inthe B posi-
tion.
17 Assembly parts Connector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell codeThis identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram
page number.
19 Current flow arrowArrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction ofstandard flow (ver-
tically downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
A double arrow “
” shows that current can flow in either direction depending on cir-
cuit operation.
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Description
GI-14
Page 25 of 3189

Incident Simulation TestsNJGI0005S02INTRODUCTIONNJGI0005S0201Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought
in for service. If possible, re-create the conditions present at the
time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found
Diagnoses. The following section illustrates ways to simulate the
conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
Vehicle vibration
Heat sensitive
Freezing
Water intrusion
Electrical load
Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is
important for simulating the conditions of the problem.
VEHICLE VIBRATIONNJGI0005S0202The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough
road or when engine is vibrating (idle with A/C on). In such a case,
you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the
illustration below.
Connectors & Harness
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the
electrical system you are inspecting.Gentlyshake each connec-
tor and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you
are trying to duplicate. This test may indicate a loose or poor elec-
trical connection.
Hint
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin
film of corrosion on the connector terminals. A visual inspection
may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the
problem occurs intermittently, perhaps the problem is caused by
corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
Sensors & Relays
Gentlyapply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system
you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
SGI839
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests
GI-23
Page 31 of 3189
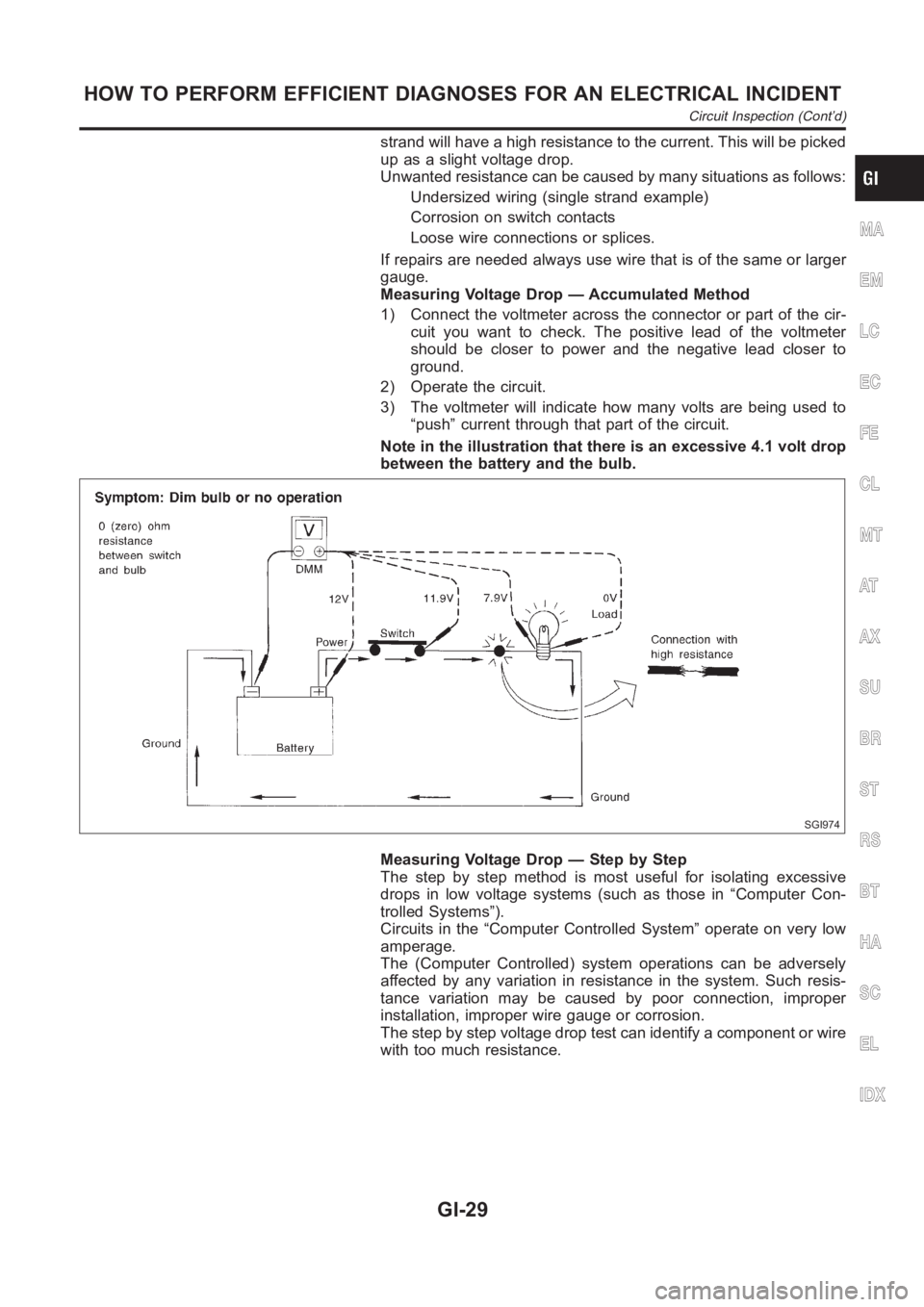
strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
Undersized wiring (single strand example)
Corrosion on switch contacts
Loose wire connections or splices.
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger
gauge.
Measuring Voltage Drop — Accumulated Method
1) Connect the voltmeter across the connector or part of the cir-
cuit you want to check. The positive lead of the voltmeter
should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to
ground.
2) Operate the circuit.
3) The voltmeter will indicate how many volts are being used to
“push” current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop
between the battery and the bulb.
SGI974
Measuring Voltage Drop — Step by Step
The step by step method is most useful for isolating excessive
drops in low voltage systems (such as those in “Computer Con-
trolled Systems”).
Circuits in the “Computer Controlled System” operate on very low
amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely
affected by any variation in resistance in the system. Such resis-
tance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper
installation, improper wire gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire
with too much resistance.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont’d)
GI-29
Page 32 of 3189
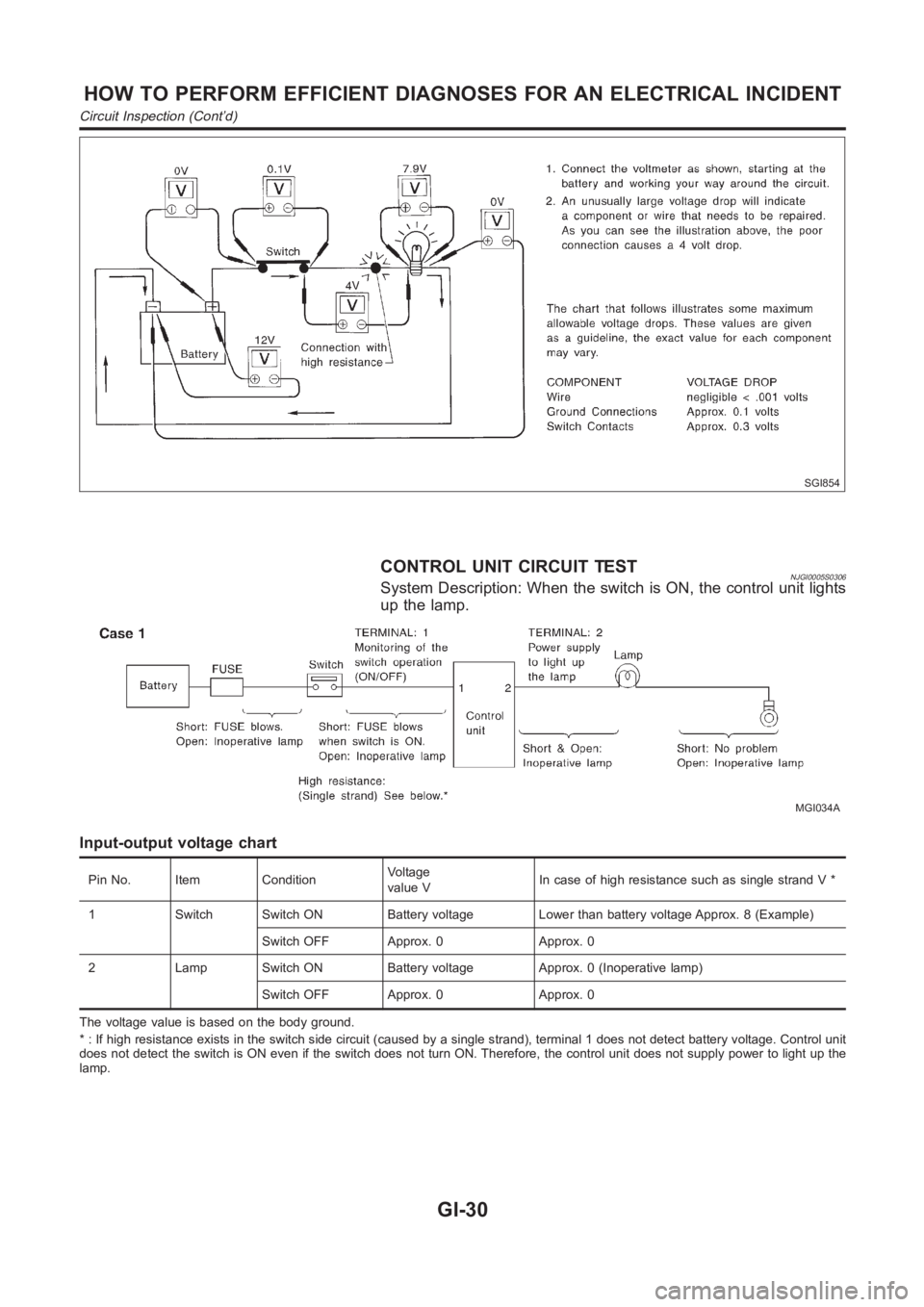
SGI854
CONTROL UNIT CIRCUIT TESTNJGI0005S0306System Description: When the switch is ON, the control unit lights
up the lamp.
MGI034A
Input-output voltage chart
Pin No. Item ConditionVoltage
value VIn case of high resistance such as single strand V *
1 Switch Switch ON Battery voltage Lower than battery voltage Approx. 8 (Example)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
2 Lamp Switch ON Battery voltage Approx. 0 (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
The voltage value is based on the body ground.
* : If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 1 does not detect battery voltage. Control unit
does not detect the switch is ON even if the switch does not turn ON. Therefore, the control unit does not supply power to light up the
lamp.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont’d)
GI-30
Page 33 of 3189

MGI035A
Input-output voltage chart
Pin No. Item ConditionVoltage
value VIn case of high resistance such as single strand V *
1 Lamp Switch ON Approx. 0 Battery voltage (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF Battery voltage Battery voltage
2 Switch Switch ON Approx. 0 Higher than 0 Approx. 4 (Example)
Switch OFF Approx. 5 Approx. 5
The voltage value is based on the body ground.
* : If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 2 does not detect approx. 0V. Control unit
does not detect the switch is ON even if the switch turns ON. Therefore, the control unit does not control ground to light up the lamp.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont’d)
GI-31
Page 55 of 3189
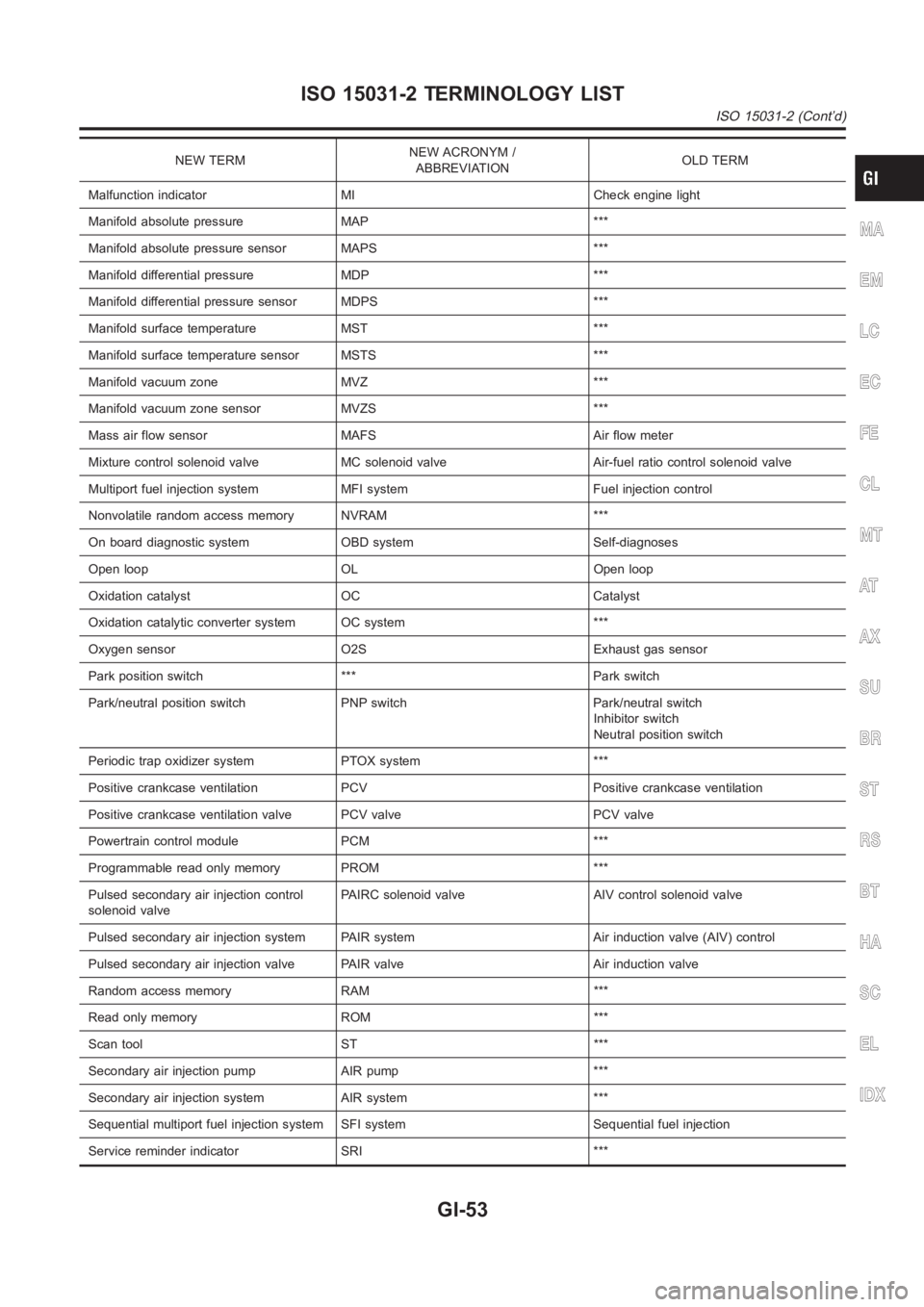
NEW TERMNEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATIONOLD TERM
Malfunction indicator MI Check engine light
Manifold absolute pressure MAP ***
Manifold absolute pressure sensor MAPS ***
Manifold differential pressure MDP ***
Manifold differential pressure sensor MDPS ***
Manifold surface temperature MST ***
Manifold surface temperature sensor MSTS ***
Manifold vacuum zone MVZ ***
Manifold vacuum zone sensor MVZS ***
Mass air flow sensor MAFS Air flow meter
Mixture control solenoid valve MC solenoid valve Air-fuel ratio control solenoid valve
Multiport fuel injection system MFI system Fuel injection control
Nonvolatile random access memory NVRAM ***
On board diagnostic system OBD system Self-diagnoses
Open loop OL Open loop
Oxidation catalyst OC Catalyst
Oxidation catalytic converter system OC system ***
Oxygen sensor O2S Exhaust gas sensor
Park position switch *** Park switch
Park/neutral position switch PNP switch Park/neutral switch
Inhibitor switch
Neutral position switch
Periodic trap oxidizer system PTOX system ***
Positive crankcase ventilation PCV Positive crankcase ventilation
Positive crankcase ventilation valve PCV valve PCV valve
Powertrain control module PCM ***
Programmable read only memory PROM ***
Pulsed secondary air injection control
solenoid valvePAIRC solenoid valve AIV control solenoid valve
Pulsed secondary air injection system PAIR system Air induction valve (AIV) control
Pulsed secondary air injection valve PAIR valve Air induction valve
Random access memory RAM ***
Read only memory ROM ***
Scan tool ST ***
Secondary air injection pump AIR pump ***
Secondary air injection system AIR system ***
Sequential multiport fuel injection system SFI system Sequential fuel injection
Service reminder indicator SRI ***
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
ISO 15031-2 TERMINOLOGY LIST
ISO 15031-2 (Cont’d)
GI-53
Page 58 of 3189

NJMA0036
Shown below are Pre-delivery Inspection Items required for the new vehicle. It is recommended that
necessary items other than those listed here be added, paying due regard tothe conditions in each
country.
Perform applicable items on each model. Consult text of this section for specifications.
UNDER HOOD — engine off
Radiator coolant level and coolant hose connections for leaks
Battery fluid level, specific gravity and conditions of battery terminals
Drive belts tension
Fuel filter for water or dusts (Diesel only), and fuel lines and connections for leaks
Engine oil level and oil leaks
Clutch and brake reservoir fluid level and fluid lines for leaks
Windshield and rear window washer and headlamp cleaner reservoir fluid level
Power steering reservoir fluid level and hose connections for leaks
ON INSIDE AND OUTSIDE
Remove front spring/strut spacer (If applicable)
Operation of all instruments, gauges, lights and accessories
Operation of horn(s), wiper and washer
Steering lock for operation
Check air conditioner for gas leaks
Front and rear seats, and seat belts for operation
All moldings, trims and fittings for fit and alignment
All windows for operation and alignment
Hood, trunk lid, door panels for fit and alignment
Latches, keys and locks for operation
Weatherstrips for adhesion and fit
Headlamp aiming
Tighten wheel nuts (Inc. inner nuts if applicable)
Tire pressure (Inc. spare tire)
Check front wheels for toe-in
Install clock/voltmeter/room lamp fuse (If applicable)
Install deodorizing filter to air conditioner (If applicable)
Remove wiper blade protectors (If applicable)
UNDER BODY
Manual transmission/transaxle, transfer and differential gear oil level
Brake and fuel lines and oil/fluid reservoirs for leaks
Tighten bolts and nuts of steering linkage and gear box, suspension, propeller shafts and drive shafts
Tighten rear body bolts and nuts (Models with wooden bed only)
ROAD TEST
Clutch operation
Parking brake operation
Service brake operation
Automatic transmission/transaxle shift timing and kickdown
Steering control and returnability
Engine performance
Squeaks and rattles
ENGINE OPERATING AND HOT
Adjust idle speed
Automatic transmission/transaxle fluid level
Engine idling and stop knob operation (Diesel only)
FINAL INSPECTION
Install necessary parts (outside mirror, wheel covers, seat belts, mat, carpet or mud flaps)
Inspect for interior and exterior metal and paint damage
Check for spare tire, jack, tools (wheel chock), and literature
Wash, clean interior and exterior
: Not applicable to this model
PRE-DELIVERY INSPECTION ITEMS
MA-2
Page 116 of 3189
![NISSAN ALMERA N16 2003 Electronic Repair Manual EM-38
[QG]
CAMSHAFT
8. Remove stopper pin from intake camshaft sprocket.
9. Slowly turn crankshaft pulley clockwise to set intake camshaft
sprocket to most retarded position.
●Sprocket begin NISSAN ALMERA N16 2003 Electronic Repair Manual EM-38
[QG]
CAMSHAFT
8. Remove stopper pin from intake camshaft sprocket.
9. Slowly turn crankshaft pulley clockwise to set intake camshaft
sprocket to most retarded position.
●Sprocket begin](/img/5/57350/w960_57350-115.png)
EM-38
[QG]
CAMSHAFT
8. Remove stopper pin from intake camshaft sprocket.
9. Slowly turn crankshaft pulley clockwise to set intake camshaft
sprocket to most retarded position.
●Sprocket begins turning after crankshaft does. Once sprocket
starts turning, keep turning crankshaft until the vane (cam-
shaft) also begins turning. Most retarded position should now
be achieved.
●Most retarded position is confirmed when stopper pin groove
is at a clockwise offset from lock pin breathing groove.
●While turning crankshaft slightly more counterclockwise, con-
firm that lock pin is engaged when vane and sprocket turn
together.
10. Install cylinder head front cover.
●Apply liquid gasket (Use Genuine Liquid Gasket or equiva-
lent) continuously as shown in figure.
●Install it by aligning dowel pin on cylinder head.
11. Check and adjust valve clearance. Refer to EM-42, "
Va l v e
Clearance" .
12. From this step, install in the reverse order of removal.
PBIC0966E
MBIB0213E
MBIB0214E
PBIC0968E
Page 123 of 3189
![NISSAN ALMERA N16 2003 Electronic Repair Manual CAMSHAFT
EM-45
[QG]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
5. With valve spring compressed, securely place tip of lifter stopper
(special service tool) onto surroundings of valve spring. Then
remove camsha NISSAN ALMERA N16 2003 Electronic Repair Manual CAMSHAFT
EM-45
[QG]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
5. With valve spring compressed, securely place tip of lifter stopper
(special service tool) onto surroundings of valve spring. Then
remove camsha](/img/5/57350/w960_57350-122.png)
CAMSHAFT
EM-45
[QG]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
5. With valve spring compressed, securely place tip of lifter stopper
(special service tool) onto surroundings of valve spring. Then
remove camshaft pliers (special service tool).
CAUTION:
If camshaft pliers are suddenly turned back, lifter stopper
may contact and damage camshaft journals. Turn back
camshaft pliers carefully to remove.
6. Keep adjusting shim slightly up from valve lifter.
●Insert a slotted screwdriver with extra-thin tip into cutout on
valve lifter for this purpose.
7. Using a magnetic handle, remove adjusting shim.
8. Using a micrometer, measure thickness (t1) of removed adjust-
ing shim at camshaft contact face (around center).
9. Use following formula to select proper replacement adjusting shim.
●Formula to calculate adjusting shim thickness (unit: mm)
Thickness of replacement valve lifter = t1+ ( C1 - C2 )
t1 = Thickness of removed valve lifter
C1 = Measured valve clearance
C2=Standard valve clearance:
PBIC1013E
PBIC1014E
MBIB0229E
Hot engine:
Intake : 0.37 mm (0.015 in)
Exhaust : 0.40 mm (0.016 in)
Reference values with cold engine:
Intake : 0.30 mm (0.012 in)
Exhaust : 0.35 mm (0.014 in)