rod OPEL 1900 1973 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: 1900, Model: OPEL 1900 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 498 of 625
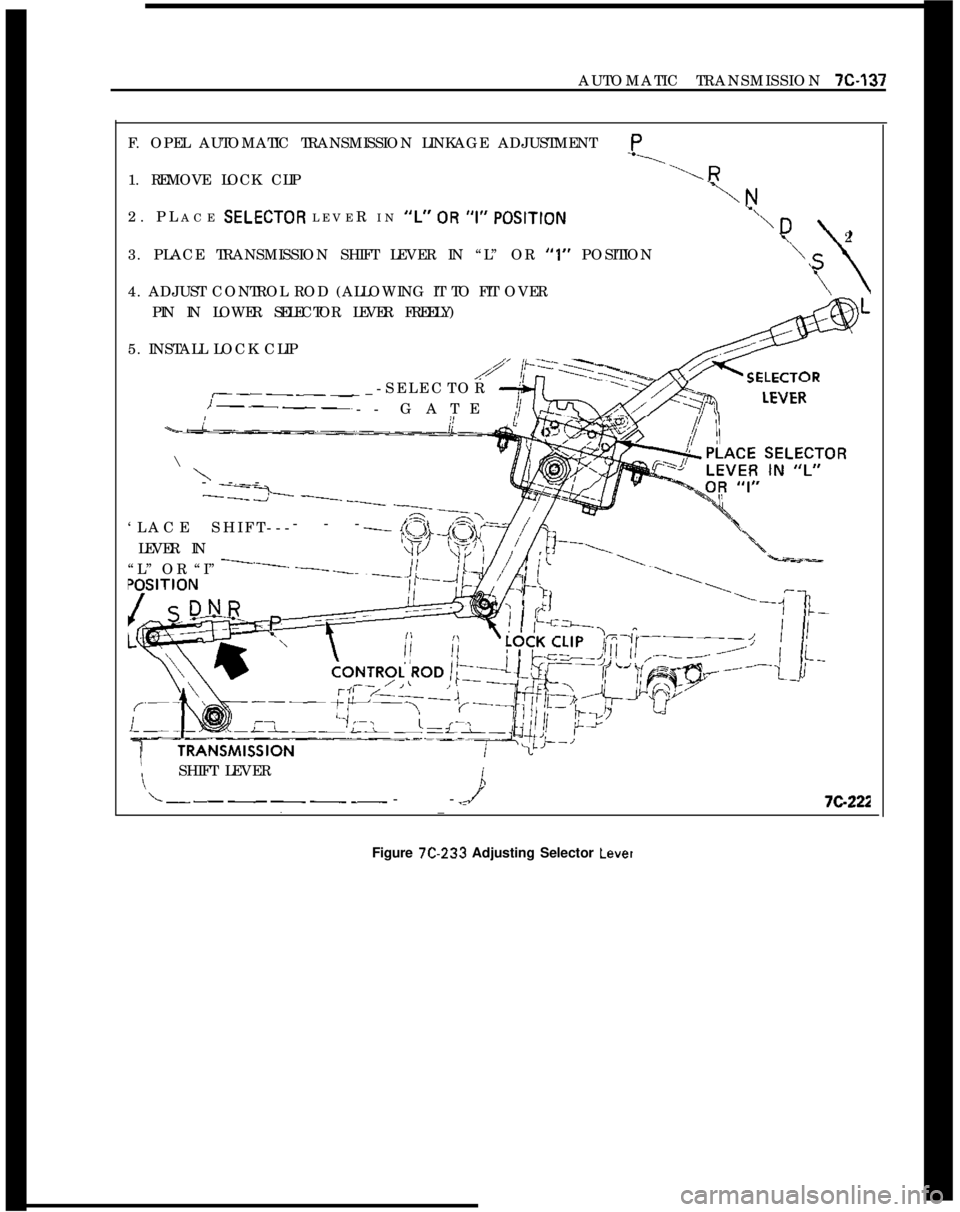
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION X-137F. OPEL AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION LINKAGE ADJUSTMENTP
1. REMOVE LOCK CLIP
-‘\R
l2. PLACE SELECTOR LEVER IN
“r’ 0~ “1” POSITION
23. PLACE TRANSMISSION SHIFT LEVER IN “L” OR “1” POSITION
4. ADJUST CONTROL ROD (ALLOWING IT TO FIT OVER
PIN IN LOWER SELECTOR LEVER FREELY)
5. INSTALL LOCK CLIP
--_--_-SELECTORi--_-~-- GATE
\
\---
-x---i -__‘LACE SHIFT------
LEVER IN
“L” OR “I”
-.-
\/\SHIFT LEVER
L--________--7C-222Figure 7C-233 Adjusting Selector
Level
Page 503 of 625

8A-2 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
HOOD, FENDERS, AND GRILLE
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
GTHeadlampOperation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .DIAGNOSIS: (Not Applicable)
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
GTHeadlampMechanism
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAJOR REPAIR:
Removal and Installation
Hood (1900
- Manta). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fender(1900-Manta). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Headlamp Covering (1900
- Manta). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Headlamp Assembly
(GT). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Headlamp
CableAssembly(GT). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Grille
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .SPECIFICATIONS: (Not Applicable)
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OF GT
HEADLAMP MECHANISMThe concealed headlamps are moved mechanically.
Pushing actuating lever on left side of console opens
headlamps, pulling lever closes headlamps. Two
meshing gear segments convert the movement of the
lever to a rotation of 180 degrees. The pivots of the
headlamps lie below the centerline so that with head-
lamps in closed position the headlamp housing is
flush with front sheet metal.
A white indicator lamp in the instrument panel lights
if the headlamps are not completely opened and
locked. The switches of the headlamp electrical sys-
tem are located behind the left headlamp operating
mechanism.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT OF HEADLAMP MECHANISMBoth headlamp assemblies must operate in unison in
order to lock in either the open or closed position.
Page No.
8A-2
8A-2
8A-3
8A-3
8A-4
8A-4
8A-6
8A-61. Adjust headlamps to be parallel in any position by
changing length of right headlamp operating rod.
For adjustment loosen clamp bolt (A). See Figure
8A-1.Figure
8A-l Headlamp Operation Adjustments
Page 531 of 625
9B-22 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
We can change a vapor back into a liquid by chilling
it, or do the same thing with pressure. When we
condense a vapor we will find that the heat removed
just exactly equals the amount of heat that was neces-
sary to make the substance vaporize in the first place.
At last the lost is found! The latent heat of vaporiza-
tion the heat that apparently disappeared when
a liquid boiled into a vapor again reappears on
the scene when that same vapor reverts back into a
liquid. It is just like putting air into a balloon to
expand it and then letting the same amount of air out
again to return the balloon to its original condition.
We know that any substance will condense at the
same temperature at which it boiled. This tempera-
ture point is a clear-cut division like a fence. On one
side, a substance is a liquid. Immediately on the
other side it is a vapor. Whichever way a substance
would go, from hot to cold or cold to hot, it will
change its character the moment it crosses over thefence.But pressure moves the fence! Water will boil at 212
degrees under normal conditions. Naturally, we ex-
pect steam to condense at the same temperature. But
whenever we put pressure on steam, it doesn’t! It will
condense at some temperature higher than 212 de-
grees. The greater the pressure, the higher the boiling
point and the temperature at which a vapor will
condense. This is the reason why pressure cookers
cook food faster, since the pressure on the water
permits it to boil out at a higher temperature. We
know that R-12 boils at 21.7 degrees below zero. A
thermometer will show us that the rising vapors,
even though they have soaked up lots of heat, are
only slightly warmer. But the vapors must be made
warmer than the room air if we expect heat to flow
out of them. Also, the condensing point temperature
must be above that of room air or else the vapors
won’t condense.This is where pressure comes to the rescue. With
pressure, we can compress the vapor, thereby con-
centrating the heat it contains. When we concentrate
heat in a vapor that way, we increase the intensity of
the heat or, in other words, we increase the tempera-ture;because temperature is merely a measurement
of heat intensity. And the most amazing part of it all
is that we’ve made the vapor hotter without actually
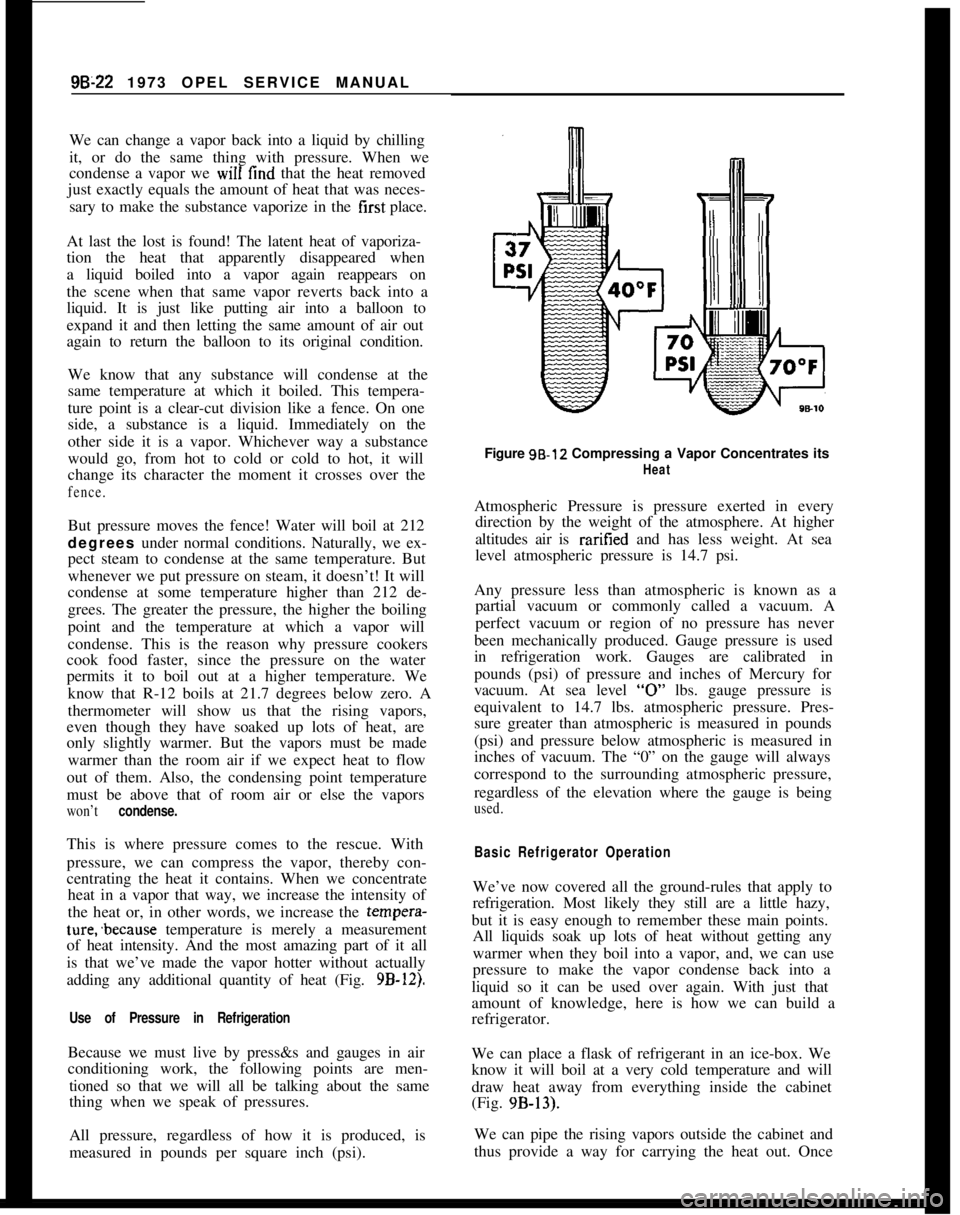
adding any additional quantity of heat (Fig.
9B-12).
Use of Pressure in RefrigerationBecause we must live by press&s and gauges in air
conditioning work, the following points are men-
tioned so that we will all be talking about the same
thing when we speak of pressures.
All pressure, regardless of how it is produced, is
measured in pounds per square inch (psi).Figure 98.12 Compressing a Vapor Concentrates its
HeatAtmospheric Pressure is pressure exerted in every
direction by the weight of the atmosphere. At higher
altitudes air is raritied and has less weight. At sea
level atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psi.
Any pressure less than atmospheric is known as a
partial vacuum or commonly called a vacuum. A
perfect vacuum or region of no pressure has never
been mechanically produced. Gauge pressure is used
in refrigeration work. Gauges are calibrated in
pounds (psi) of pressure and inches of Mercury for
vacuum. At sea level
“0” lbs. gauge pressure is
equivalent to 14.7 lbs. atmospheric pressure. Pres-
sure greater than atmospheric is measured in pounds
(psi) and pressure below atmospheric is measured in
inches of vacuum. The “0” on the gauge will always
correspond to the surrounding atmospheric pressure,
regardless of the elevation where the gauge is being
used.
Basic Refrigerator OperationWe’ve now covered all the ground-rules that apply to
refrigeration. Most likely they still are a little hazy,
but it is easy enough to remember these main points.
All liquids soak up lots of heat without getting any
warmer when they boil into a vapor, and, we can use
pressure to make the vapor condense back into a
liquid so it can be used over again. With just that
amount of knowledge, here is how we can build a
refrigerator.
We can place a flask of refrigerant in an ice-box. We
know it will boil at a very cold temperature and will
draw heat away from everything inside the cabinet
(Fig. 9B-13).
We can pipe the rising vapors outside the cabinet and
thus provide a way for carrying the heat out. Once
Page 534 of 625
REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS9B- 2596.15
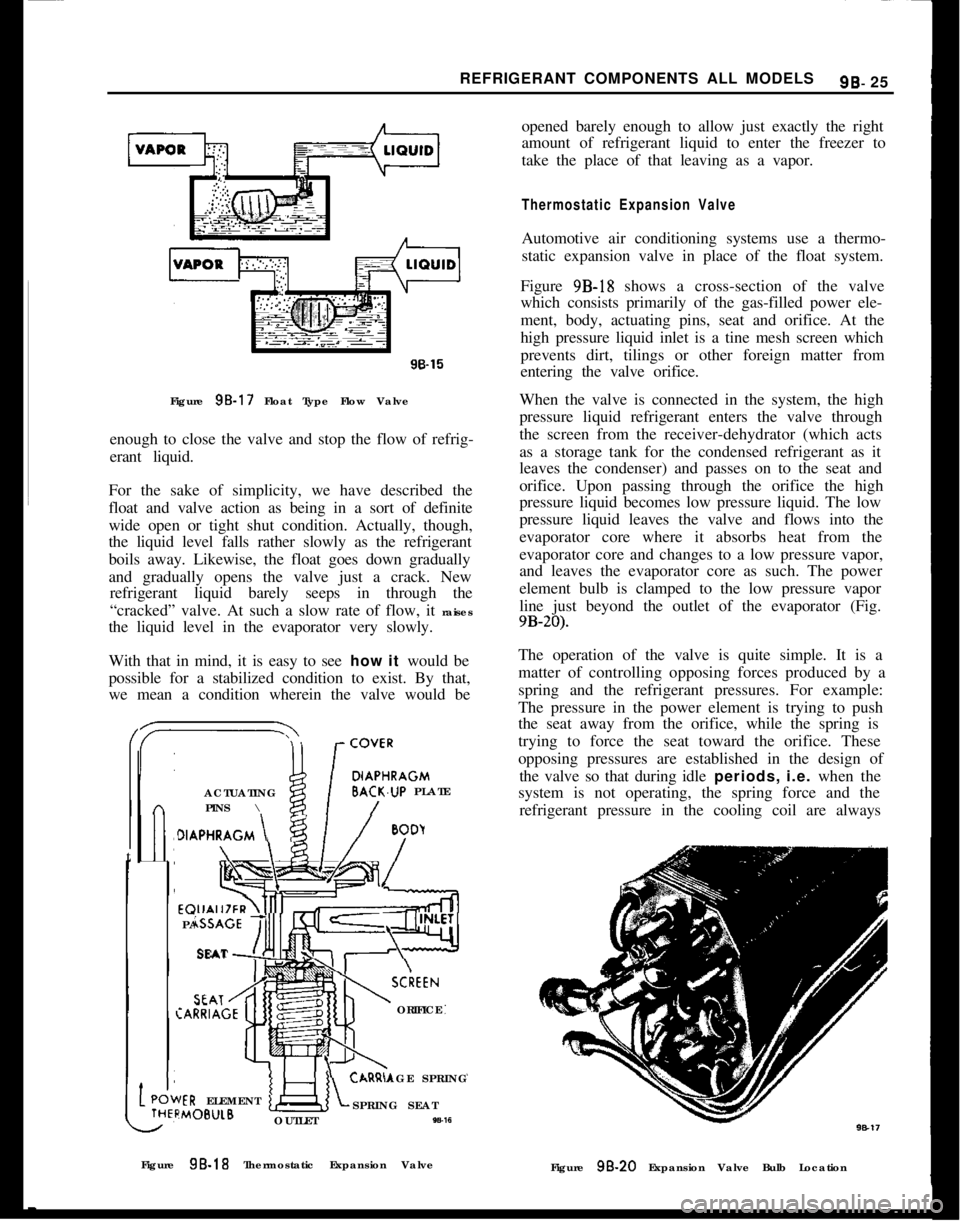
Figure 95.17 Float Type Flow Valve
enough to close the valve and stop the flow of refrig-
erant liquid.
For the sake of simplicity, we have described the
float and valve action as being in a sort of definite
wide open or tight shut condition. Actually, though,
the liquid level falls rather slowly as the refrigerant
boils away. Likewise, the float goes down gradually
and gradually opens the valve just a crack. New
refrigerant liquid barely seeps in through the
“cracked” valve. At such a slow rate of flow, it raises
the liquid level in the evaporator very slowly.
With that in mind, it is easy to see how it would be
possible for a stabilized condition to exist. By that,
we mean a condition wherein the valve would be/
DIAPHRAGMACTUATINGBACK.UP PLATE
PINS \
t
>IAPHRAGM \
/
BoDyEQUALIZER\4]
PASSAGE
‘!!!ISEATSCkEEN:ARRIAGEORIFICE
AGE SPRINGIER ELEMENT:MOB”LBSPRING SEAT
OUTLET
W-16opened barely enough to allow just exactly the right
amount of refrigerant liquid to enter the freezer to
take the place of that leaving as a vapor.
Thermostatic Expansion ValveAutomotive air conditioning systems use a thermo-
static expansion valve in place of the float system.
Figure 9B-18 shows a cross-section of the valve
which consists primarily of the gas-filled power ele-
ment, body, actuating pins, seat and orifice. At the
high pressure liquid inlet is a tine mesh screen which
prevents dirt, tilings or other foreign matter from
entering the valve orifice.
When the valve is connected in the system, the high
pressure liquid refrigerant enters the valve through
the screen from the receiver-dehydrator (which acts
as a storage tank for the condensed refrigerant as it
leaves the condenser) and passes on to the seat and
orifice. Upon passing through the orifice the high
pressure liquid becomes low pressure liquid. The low
pressure liquid leaves the valve and flows into the
evaporator core where it absorbs heat from the
evaporator core and changes to a low pressure vapor,
and leaves the evaporator core as such. The power
element bulb is clamped to the low pressure vapor
line just beyond the outlet of the evaporator (Fig.
9B-20).The operation of the valve is quite simple. It is a
matter of controlling opposing forces produced by a
spring and the refrigerant pressures. For example:
The pressure in the power element is trying to push
the seat away from the orifice, while the spring is
trying to force the seat toward the orifice. These
opposing pressures are established in the design of
the valve so that during idle periods, i.e. when the
system is not operating, the spring force and the
refrigerant pressure in the cooling coil are always
Figure 9B-18 Thermostatic Expansion Valve
Figure
98.20 Expansion Valve Bulb Location
Page 536 of 625

REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS99.27that line, they still hadn’t gotten anywhere. So, they
started from scratch and juggled molecules around
to make an entirely new refrigerant. Eventually they
succeeded by remodeling the molecules in carbon
tetrachloride. This is the same fluid that is used in
fire extinguishers and dry-cleaners’ solvents.
From this fluid, the chemists removed two chlorine
atoms and replaced them with two fluorine atoms.
This newly-formed fluid carried the technical chemi-
cal name of dichlorodifluoromethane. Today, we
know it as Refrigerant-12 or R-12.
Fluorine is an extremely temperamental substance.
Under most conditions it is toxic and highly corro-
sive, and after is is manufactured, it has to be stored
in special containers because it will eat through glass
and will dissolve most metals in short order.
Despite its rambunctious character though, fluorine
is completely tamed when it is combined with the
other substances that go to make up the refrigerant.
Each is non-toxic, non-inflammable, non-explosive,
and non- poisonous; however, breathing large quan-
tities of R-12 should be avoided.
Pressure. Temperature Relationship of R-12A definite pressure and temperature relationship ex-
ists in the case of liquid refrigerants and their satu-
rated vapors. Increasing the temperature of a
substance causes it to expand. When the substance is
confined in a closed container, the increase in tem-
perature will be accompanied by an increase in pres-
sure, even though no mechanical device was used.
For every temperature, there will be a corresponding
pressure within the container of refrigerant. A table
of the temperature-pressure relationship of R-12 is
presented below. Pressures are indicated in gauge
pressure, either positive pressure (above atmos-
pheric) m pounds or negative pressure (below atmos-
pheric) in inches of vacuum.
“F-40
-35
i#Pressure
11.0*
8.3*
“F
50
50#Pressure
46.1
52.0
-30~
5.5*6057.7
-252.3*6s67 7__.
-200.6
io70.1
-152.4
76.9
-104.584.1
1;6.8 9.2tz99.6 91.71;
11.8 14.712116.9 108.1
1517.7105126.2
2021.1110136.0
2524.6115146.5
3028.5120157.1
;:
30.1
125167.5
32.6
131)179n
4037.0
4541.7*Inches of Vacuum.-. _.-
1402045
150232.0Thus if a gauge is attached to a container of R- 12 and
the room temperature is 70 degrees, the gauge will
register 70 psi pressure; in a 100 degrees room the
pressure will be 117
ps~
AIR CONDITIONINGBecause air conditioning has always been very
closely allied with mechanical refrigeration, most of
us are apt to think of it only as a process for cooling
room air.
But true air conditioning goes beyond the mere cool-
ing of the air. It controls the humidity, cleanliness,
and circulation of the air as well.
Whenever it gets warm and muggy in the summer-
time, someone is almost sure to say, “It’s not the heat
it’s the humidity.” But that is only partly right.
Actually it is a combination of the two that makes us
feel so warm temperature alone is not the only
thing that makes us uncomfortable.
Humidity is nothing more nor less that the moisture
content of the air. To a certain extent, it is tied in
with the temperature of the air. Warm air will hold
more moisture than will cold air. When air contains
all the moisture it can hold, we say it is saturated,
and the relative humidity is 100 percent. If the air
contains only half as much water as it could possibly
hold at any given temperature, we say that the rela-
tive humidity is 50 percent. If it contains only a fifth
of its maximum capacity, we say that the relative
humidity is 20 percent and so on. This amount
of water vapor, or relative humidity, affects the way
we perspire on hot days.
Nature has equipped our bodies with a network of
sweat glands that carry perspiration to the skin
sur-faces. Normally, this perspiration evaporates and, in
doing so, absorbs heat just like a refrigerant absorbs
heat when it is vaporized in a freezer. Most of the
heat thus absorbed is drawn from our bodies, giving
us a sensation of coolness. A drop of alcohol on the
back of your hand will demonstrate this principle
very convincingly. Because it is highly volatile, al-
cohol will evaporate very rapidly and absorb quite a
bit of heat in doing so, thereby making the spot on
your hand feel unusually cool.
The ease and rapidity with which evaporation takes
place, whether it be alcohol or perspiration, governs
our sensation of coolness and to a certain extent,
independently of the temperature. Of even more im-
portance, the ease and rapidity of the evaporation are
directly affected by the relative humidity or com-
parative dampness of the air. When the air is dry,
perspiration will evaporate quite readily. But when
the air contains a lot of moisture, perspiration will
evaporate more slowly; consequently less heat is car-
ried away from our body.
Page 538 of 625
REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS99.29
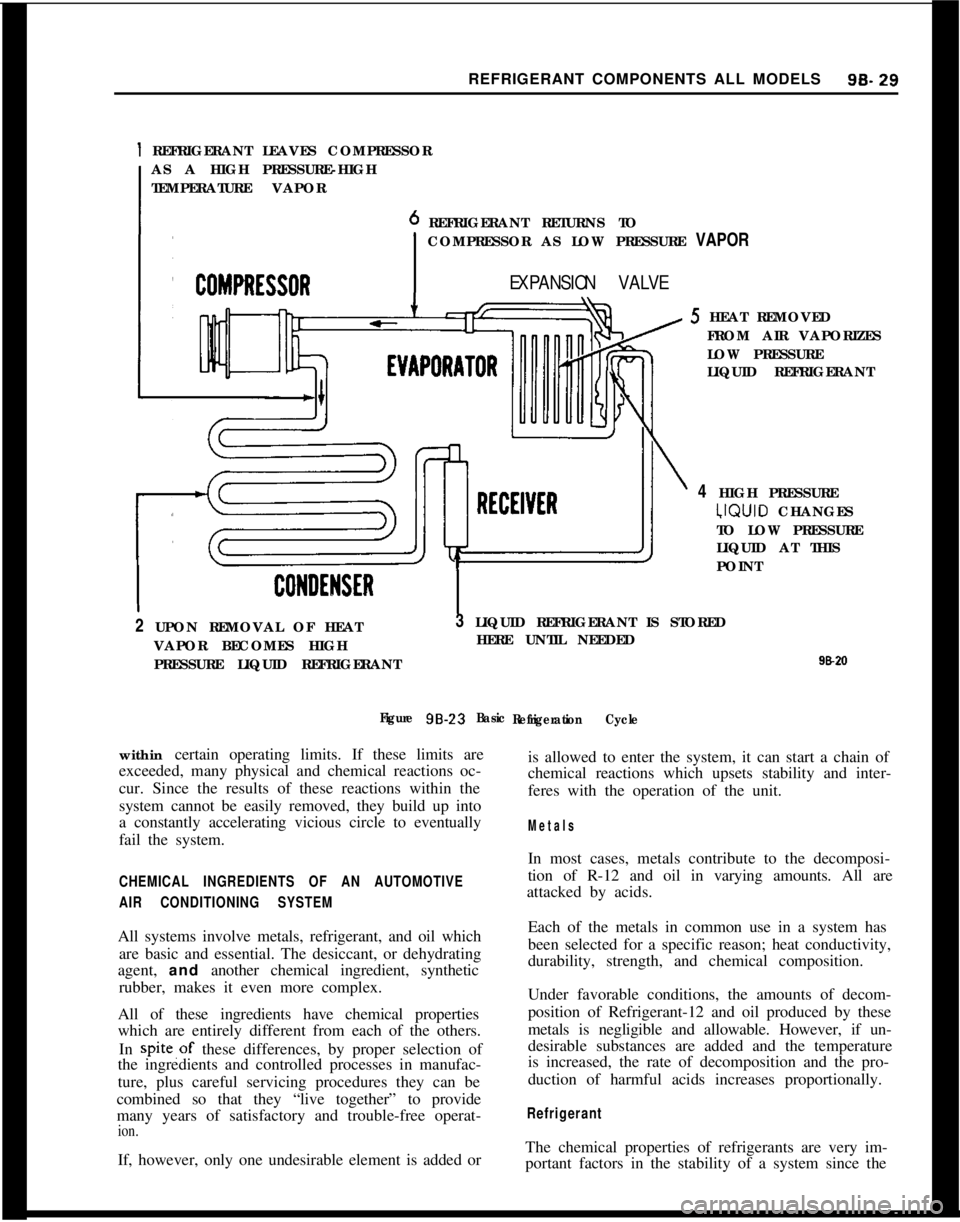
1 REFRIGERANT LEAVES COMPRESSOR
AS A HIGH PRESSURE-HIGH
TEMPERATURE VAPOR
REFRIGERANT RETURNS TO
COMPRESSOR AS LOW PRESSURE VAPOR
EXPANSION VALVE5 HEAT REMOVED
FROM AIR VAPORIZES
LOW PRESSURE
LIQUID REFRIGERANT
4 HIGH PRESSURE‘JQUID CHANGES
TO LOW PRESSURE
LIQUID AT THIS
POINT
2 UPON REMOVAL OF HEAT
VAPOR BECOMES HIGH
PRESSURE LIQUID REFRIGERANT3 LIQUID REFRIGERANT IS STORED
HERE UNTIL NEEDED
98*II
Figure 98-23
Basic
Refrigeration Cyclewithin certain operating limits. If these limits are
exceeded, many physical and chemical reactions oc-
cur. Since the results of these reactions within the
system cannot be easily removed, they build up into
a constantly accelerating vicious circle to eventually
fail the system.is allowed to enter the system, it can start a chain of
chemical reactions which upsets stability and inter-
feres with the operation of the unit.
Metals
CHEMICAL INGREDIENTS OF AN AUTOMOTIVE
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMAll systems involve metals, refrigerant, and oil which
are basic and essential. The desiccant, or dehydrating
agent, and another chemical ingredient, synthetic
rubber, makes it even more complex.
All of these ingredients have chemical properties
which are entirely different from each of the others.
In spite,of these differences, by proper selection of
the ingredients and controlled processes in manufac-
ture, plus careful servicing procedures they can be
combined so that they “live together” to provide
many years of satisfactory and trouble-free operat-
ion.If, however, only one undesirable element is added orIn most cases, metals contribute to the decomposi-
tion of R-12 and oil in varying amounts. All are
attacked by acids.
Each of the metals in common use in a system has
been selected for a specific reason; heat conductivity,
durability, strength, and chemical composition.
Under favorable conditions, the amounts of decom-
position of Refrigerant-12 and oil produced by these
metals is negligible and allowable. However, if un-
desirable substances are added and the temperature
is increased, the rate of decomposition and the pro-
duction of harmful acids increases proportionally.
RefrigerantThe chemical properties of refrigerants are very im-
portant factors in the stability of a system since the
Page 540 of 625

REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS9B- 31
When adding oil, the container should be exception-
ally clean and dry due to the fact that the refrigera-
tion oil in the container is as moisture-free as it is
possible to make it. Therefore, it will quickly absorb
any moisture with which it comes in contact. For this
same reason the oil container should not be opened
until ready for use and it should be capped immedi-
ately afte;r use.
When it is necessary to open a system, have every-
thing you will need ready and handy so that as little
time as possible will be required to perform the oper-
ation. Don’t leave the system open any longer than
is necessary.
Finally, after the operation has been completed and
the system sealed again, air and moisture should be
evacuated from the system before recharging.
THE PRIMARY CAUSES OF SYSTEM FAILURES
LeaksA shortage of refrigerant causes oil to be trapped in
the evaporator. Oil may be lost with the refrigerant
at point of leakage. Both of these can cause compres-
sor seizure.
Oil circulates in the system with the refrigerant; in
solution with the liquid and in globules with the
vapor. It leaves the compressor by the action of the
pistons and mixes with the refrigerant liquid in the
condenser. The oil then enters the evaporator with
the liquid and, with the evaporator properly flooded,
is returned to the compressor through the low pres-
sure line. Some of the oil returns as globules in the
vapor, but more important, it is swept as a liquid
along the walls of the tubing by the velocity of the
vapor. If the evaporator is starved, the oil cannot
return in sut?icient quantities to keep the compressor
properly lubricated.
High Temperature and PressureAn increase in temperature causes an increase in
pressure. This accelerates chemical instability due to
existing contaminants in the system, and initiates
chemical instability in clean systems. Other results
are brittle hoses,
“0” ring gaskets, and valve dia-
phragms with possible decomposition, broken com-
pressor discharge reeds, and seized compressor
bearings.
A fundamental law of nature accounts for the fact
that when a substance, such as a refrigerant, is in-
creased in temperature, its pressure is also increased.
Any chemical reactions caused by contaminants al-
ready in the system are greatly accelerated as the
temperature increases. A 15 degree rise in tempera-
ture doubles the chemical action. Even in a goodclean system, heat alone can start a chain of harmful
chemical reactions.
While temperature alone can cause the synthetic rub-
ber parts to become brittle and possibly to decom-
pose, the increased pressure can cause them to
rupture or blow.
As the temperature and pressure increases the stress
and strain on the compressor discharge reeds also
increases. This can result in broken reeds. Due to the
effect of the contaminants caused by high tempera-
ture and pressure, compressor bearings can be
caused to seize.
High temperature and pressure are also caused by air
in the system.
Air in the SYstemAir results from a discharged system or careless ser-
vicing procedures. This reduces system capacity and
efficiency and causes oxidation of oil into gum and
varnish.
When a leak causes the system to become dis-
charged, the resulting vacuum within the system will
cause air to be drawn in. Air in the system is a
non-condensable gas and will build up in the con-
denser as it would in an air compressor tank. The
resultant heat produced will contribute to the condi-
tions discussed previously.
Many systems are contaminated and also reduced in
capacity and efficiency by servicemen who either do
not know or are careless regarding proper servicing
procedures.
Too frequently, systems which have been open to the
atmosphere during service operations have not been
properly purged or evacuated. Air is also introduced
into the system by unpurged gauge and charging
lines. Remember that any air in the system is too
much air.
Poor ConnectionsHose clamp type fittings must be properly made.
Hoses should be installed over the sealing flanges and
with the end of the hose at the stop flange. The hose
should never extend beyond the stop flange. Locate
the clamp properly and torque as recommended. Be
especially careful that the sealing flanges are not
nicked or scored or a future leak will result.
When compression fittings are used, over tightening
can cause physical damage to the “0” ring gasket
and will result in leaks. The use of torque and back-
ing wrenches is highly recommended. When making
a connection with compression fittings, the gaskets
should always be first placed over the tube before
Page 541 of 625

98-32 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
inserting it in the connection. Another precaution -inspect the fitting for burrs which can cut the
“0”ring.
Restrictions
Restrictions may be due to powdered desiccant or
dirt and foreign matter. This may result in starved
evaporator and loss of cooling, or a seized compres-
SOT.When the amount of moisture in a system sufti-
ciently exceeds the capacity of the desiccant, it can
break down the desiccant and cause it to powder.
The powder passes through the dehydrator screen
with the refrigerant liquid and is carried to the ex-
pansion valve screen. While some of it may pass
through the valve screen into the evaporator, it may
quickly build up to cause a restriction.
Due to the fact that sufftcient oil can not be returned
to the compressor, it may seize.
Dirt
Dirt, which is any foreign material, may come from
cleaner residues, cutting, machining, or preserving
oils, metal dust or chips, lint or dust, loose rust,
soldering or brazing fluxes, paint or loose oxide
scale. These can also cause seized bearings by abra-
sion or wedging, discharge and expansion valve fail-
ure, decomposition of refrigerant and oil, or
corrosion of metal parts.
CorrosionCorrosion and its by-products can restrict valve and
drier screens, rough bearing surfaces or rapid fatigu-
ing of discharge reeds. This can result in high tem-
perature and pressure, decomposition or leaks. In
any event, this means a wrecked compressor.
From this, we can see the vicious circle that can be
produced in a refrigerating system to cause its fail-
ure. Corrosion can be the indirect cause of leaks, and
leaks can be the direct cause of corrosion. We can
also see the important role we as servicemen play in
maintaining chemical stability.
The major cause of corrosion is moisture.
Moisture
Moisture is the greatest enemy of refrigerating sys-
tems. Combined with metal, it produces oxide, Iron
Hydroxide and Aluminum Hydroxide. Combined
with R-12 it produces Carbonic acid, Hydrochloric
acid, and Hydrofluoric acid. Moisture can also cause
freeze-up of expansion valve and powdered desic-
cant.Although high temperature and dirt are responsible
for many difficulties in refrigerating systems, in most
instances it is the presence of moisture in the system
that accelerates these conditions. It can be said,themfore, that moisture is the greatest enemy of all.
The acids that it produces, in combination with both
the metals and the refrigerant, cause damaging
COT-
rosion. While the corrosion may not form as rapidly
with R-12 as with some other refrigerants, the even-
tual formation is as damaging.
If the operating pressure and temperature in the
evaporator is reduced to the freezing point, moisture
in the refrigerant can collect at the orifice of the
expansion valve and freeze. This temporarily re-
stricts the flow of liquid causing erratic cooling.
As previously mentioned, moisture in excess of the
desiccant’s capacity can cause it to powder.
YOU SHOULD KNOW AND REMEMBER..That the inside of the refrigerat,ion system is com-
pletely sealed from the outside world. And if that
seal remains broken at any point
- the system will
soon be destroyed. That complete and positive seal-
ing of the entire system is vitally important and that
this sealed condition is absolutely necessary to retain
the chemicals and keep them in a pure and proper
condition.
That all parts of the refrigeration system are under
pressure at all times, whether operating or idle, and
that any leakage. points are continuously losing re-
frigerant and oil.
That the leakage of refrigerant can be so silent that
the complete charge may be lost without warning.
That refrigerant gas is heavier than air and will rap-
idly drop to the floor as it flows from a point of
leakage.
That the pressure in the system may momentarily
become as high as 400 lbs. per square inch, and that
under such pressure the molecules of refrigerant are
forced out through the smallest opening or pore.
That the compressor is continually giving up some
lubricating oil to the circulating refrigerant and de-
pends upon oil in the returning refrigerant for con-
tinuous replenishment. Any stoppage or major loss
of refrigerant will therefore be fatal to the compres-
SOT.That the extreme internal dryness of a properly proc-
essed system is a truly desert condition, with the
drying material in the receiver holding tightly on to
the tiny droplets of residual moisture.
Page 619 of 625
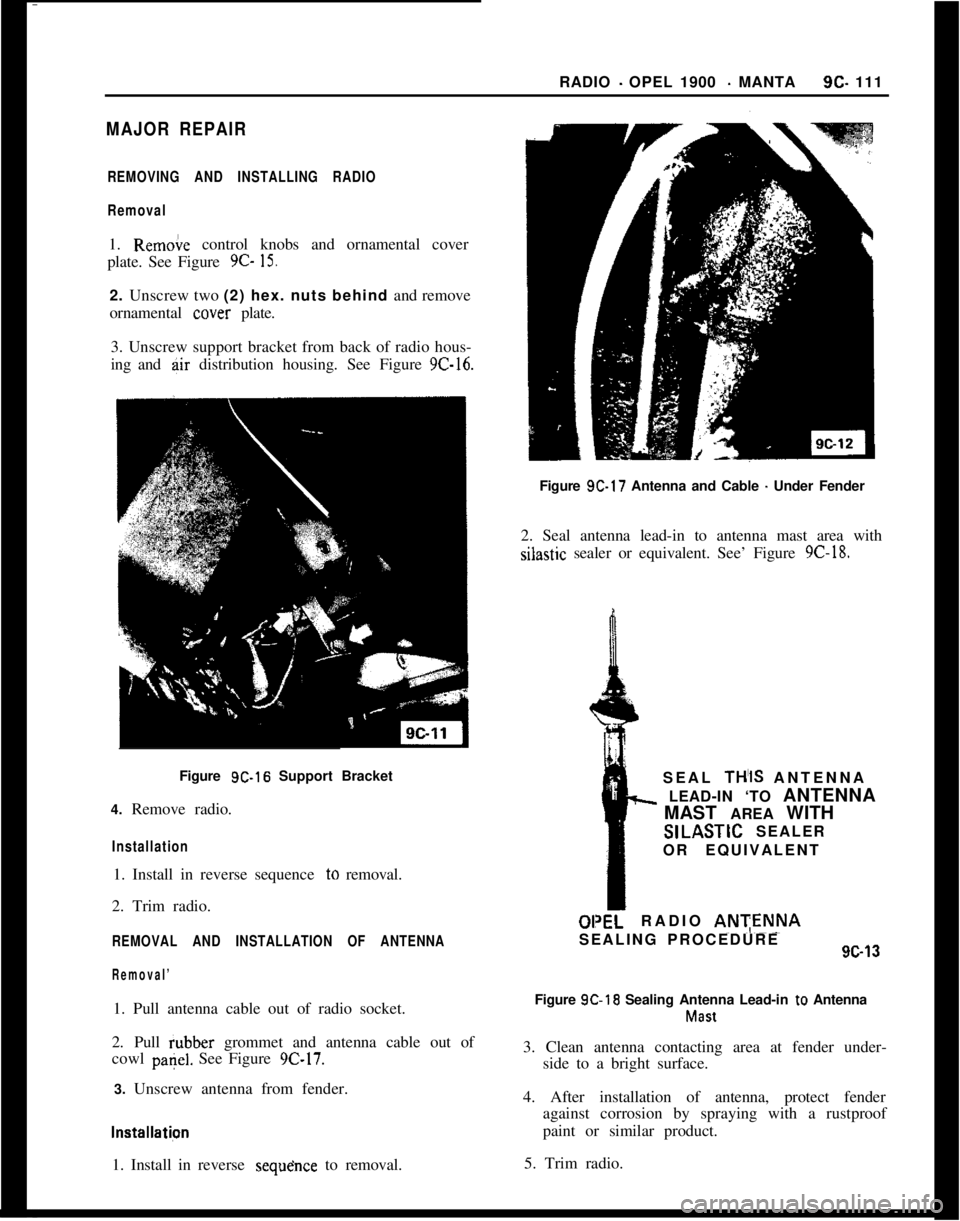
MAJOR REPAIRRADIO
- OPEL 1900 - MANTA9c- 111
REMOVING AND INSTALLING RADIO
Removal ~
1. Rem&e control knobs and ornamental cover
plate. See Figure 9C-
15.2. Unscrew two (2) hex. nuts behind and remove
ornamental cover plate.
3. Unscrew support bracket from back of radio hous-
ing and air distribution housing. See Figure
9C-16.~ Figure 9C-16 Support Bracket
4. Remove radio.
Installation1. Install in reverse sequence to removal.
2. Trim radio.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF ANTENNA
Removal’1. Pull antenna cable out of radio socket.
2. Pull iubber grommet and antenna cable out of
cowl
pa+. See Figure 9C-17.3. Unscrew antenna from fender.
lnstallatipn1. Install in reverse
sequehce to removal.Figure 9C-17 Antenna and Cable
- Under Fender
2. Seal antenna lead-in to antenna mast area withsilastic sealer or equivalent. See’ Figure
9C-18.SEAL
TH’IS ANTENNA
h LEAD-IN ‘TO ANTENNA
MAST AREA WITHSILASTIC SEALER
OR EQUIVALENT
01RADIO ANTENNASEALING PROCEDURE9c-13
Figure 9C-18 Sealing Antenna Lead-in
to AntennaMast
3. Clean antenna contacting area at fender under-
side to a bright surface.
4. After installation of antenna, protect fender
against corrosion by spraying with a rustproof
paint or similar product.
5. Trim radio.
Page 624 of 625

SubjectPage Number1
Throttle Linkage Adjustment........,:.......6E-51
Timing Chain Cover.......................6A-23
Timing Chain and Sprocket.........
':.......6A-23
Tires...................................36-55
Inflation.....................
.;.......3G-62
Rotation.............................36-57
Sizes.........................
........3G-62
Track Rod..............................3F-53
Transmission Oil Pan
Automatic Transmission.................7C-99
Transmission Reassembly
4 Speed Manual. 1.9.....................76-28Tranmission Removal and Installation
4 Speed Manual
Removal...........................7B-22
Installation.........................76-22
Auto&tic............................7c-94Tune’Up Procedure........................66-65
Torque Specifications. Engine...............6A-27
Turn Signal See Directional Signal
Universal Joints..........................4A-3Subject
VPage Number
Vacuum Modulator..7C-101
Valve Body Transmlssmn7C.99
Valve and Seat Reconditioning Engine6A-12
WWater Pump Engine1.9L Engine
Wheels
Wheel Alignment
Whee! Bearing, Adjustment,
Windshield Wiper and Washer:
Trouble Diagnosis:Description and Operation
Removal and Installation
Specifications
Wiring Diagrams Complete
Opel 1900 ._.
Manta
GT
1 E-37
1 E-37
1 E-38
1 E-43
1 J-l 03
1 J-l 05lJ-10768-3436-553C-223A-4