fuel cap release OPEL MANTA 1973 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: MANTA, Model: OPEL MANTA 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 40 of 625

IIIGNITION SYSTEMlC- 19
11. (Startx position.) The ignition key must be
released as soon as engine starts. The switch then
returns aujomatically to the on position.
IGNITION
GOILThe ignition coil consists of a laminated non- mag-
netic iron
(core enclosed by two coils; the primary
winding and the secondary winding.
The prim+y circuit consists of the power source
(battery), the ignition switch, the ignition coil pri-
mary winding, the distributor breaker points with
ignition condenser connected in parallel, and all con-
necting
lo& tension wiring.
The secondary circuit consists of the ignition coil
secondary ‘winding, the spark plugs, all connecting
high tens@ wiring, the distributor cap and the
ro-tor.
When the’ ignition switch is turned on and the
breaker pdints are closed, current flows through the
ignition
c&l primary winding and produces a mag-
netic field wound the coil windings.
When the breaker points are separated by the revolv-
ing distributor cam, the magnetic field collapses and
induces a high voltage surge in the secondary wind-
ing,
produ;cing a spark between the spark plug elec-
trodes. ,
The ignitidn condenser which is connected in paral-
lel with the breaker points, prevents arcing between
the
separa’ted breaker contacts, and current flow
after~ the breaker points have been separated, thus
causing a kery rapid collapse of the magnetic field
around th$ Ignition coil.
/
IGNITION ‘DISTRIBUTORThe ignitidn distributor breaks the primary current,distributeslthe high voltage surges induced in the coil
secondary winding to the spark plugs according to
the engin< tiring order and sets ignition timing in
relation to. engine RPM and load.
The housi+g of the distributor contains the centrifu-
gal advance mechanism and the movable breaker
plate with’s breaker lever and contact support. The
vacuum advance mechanism is attached to the
breaker plate and mounted on the outside of the
distributor, housing. See Figure lC-1.
The distributor shaft is driven by a helical gear on the
camshaft and in turn drives the engine oil pump. The
ignition condenser is mounted on the outside of the
housing. The engine output is to a large extent in-
fluenced b) the ignition timing. Maximum engine
performance is obtained when the combustion proc-
ess is well underway as the piston starts down on thepower stroke. The air-fuel charges are, however, not
burned instantly, so it is necessary to advance the
spark in relation to the piston top dead center as
engine speed increases or as engine load decreases.
If the spark is too far advanced, the engine knocks,
causing a drop in engine power output and overheat-
ing. If the spark is retarded, part of the energy deve-
loped during combustion is wasted which will result
in reduced engine power output, excessive fuel con-
sumption and overheating.
The ignition distributor has a double acting double
diaphragm vacuum unit. See Figure lC-1. The ad-
vance unit is supplied with “ported” vacuum. That
is, vacuum is supplied from a port in the primary
barrel of the carburetor located just above the closed
throttle valve. This port supplies no vacuum during
idling nor during closed throttle deceleration, but
supplies full intake manifold vacuum at all speeds
where the throttle valve is opened enough to uncover
the port.
Figure lC-1 Ignition Distributor
The retard unit is supplied with intake manifold
vacuum at all times by means of a line connected
directly to the intake manifold. During idling and
deceleration, when there is no vacuum to the ad-
vance unit, the retard unit will cause the timing to be
retarded 5 degrees. However, during part throttle
operation when there is vacuum to the advance unit,
the advance unit will overpower the retard unit so
that the retard unit has no effect on timing.
The purpose of the retard unit is to reduce hydrocar-
bon and carbon monoxide emissions during idling
and deceleration, where they are especially bad.
In order to avoid voltage losses for easier starting, a
plastic cover has been inserted in the distributor be-
low the rotor as a seperator to keep the inside of the
distributor cup free from condensation.
Page 328 of 625
FUEL SYSTEMSC- 37
must always be removed before the distributor can be
removed.
EVAPORATION CONTROL SYSTEM1. The function of the fuel evaporation control sys-
tem is to absorb the fuel vapors developing in the fuel
tank, especially when vehicle is parked, due to at-
mospheric pressure and temperature influences, and
to release these fuel vapors during vehicle operation.
2. This system utilizes the property of the activated
carbon to absorb and expel fuel vapors. The activated
carbon container is installed on the left front side of
the engine compartment. The fuel tank has a
non-vented tiller cap. Vent hoses are joined in the area of
the tank. A plastic evaporation line leads from there
along vehicle underbody to the activated carbon con-
tainer.
3. A small tube above the throttle valve body con-
nects the carburetor to the activated carbon con-
tainer. In this way, the fuel vapor collected in the
activated carbon container is fed through the carbu-
retor into the combustion chambers during engine
operation.
4. The carburetor is provided with an internal and
outside ventilation, the activated carbon container is
also connected to the outside ventilation (only effec-
tive when engine is idling). In this way, the fuel
vapors escaping to the outside during engine idle are
collected by the activated carbon container and fed
into the combustion chambers.
5. The vent lines are connected to the upper part of
the activated carbon container. Fresh air enters
through a foam rubber filter at the lower part andflows, together with the fuel vapor, to the carburetor.
Metered bores in the hose fittings of the fuel tank
control the air
- and fuel vapor flow through the
activated carbon container to the carburetor, and the
pressure release in the fuel tank and ensure complete
purging of the carbon container.
Care must be taken not to mix up lines at the ac-
tivated carbon container. See Figure
6C-2.6. The metered bores in the fuel tank fitting and an
overflow protection in the fuel tank, which prevents
a complete filling of the tank, prevents fuel flows into
the activated carbon container rendering it useless.
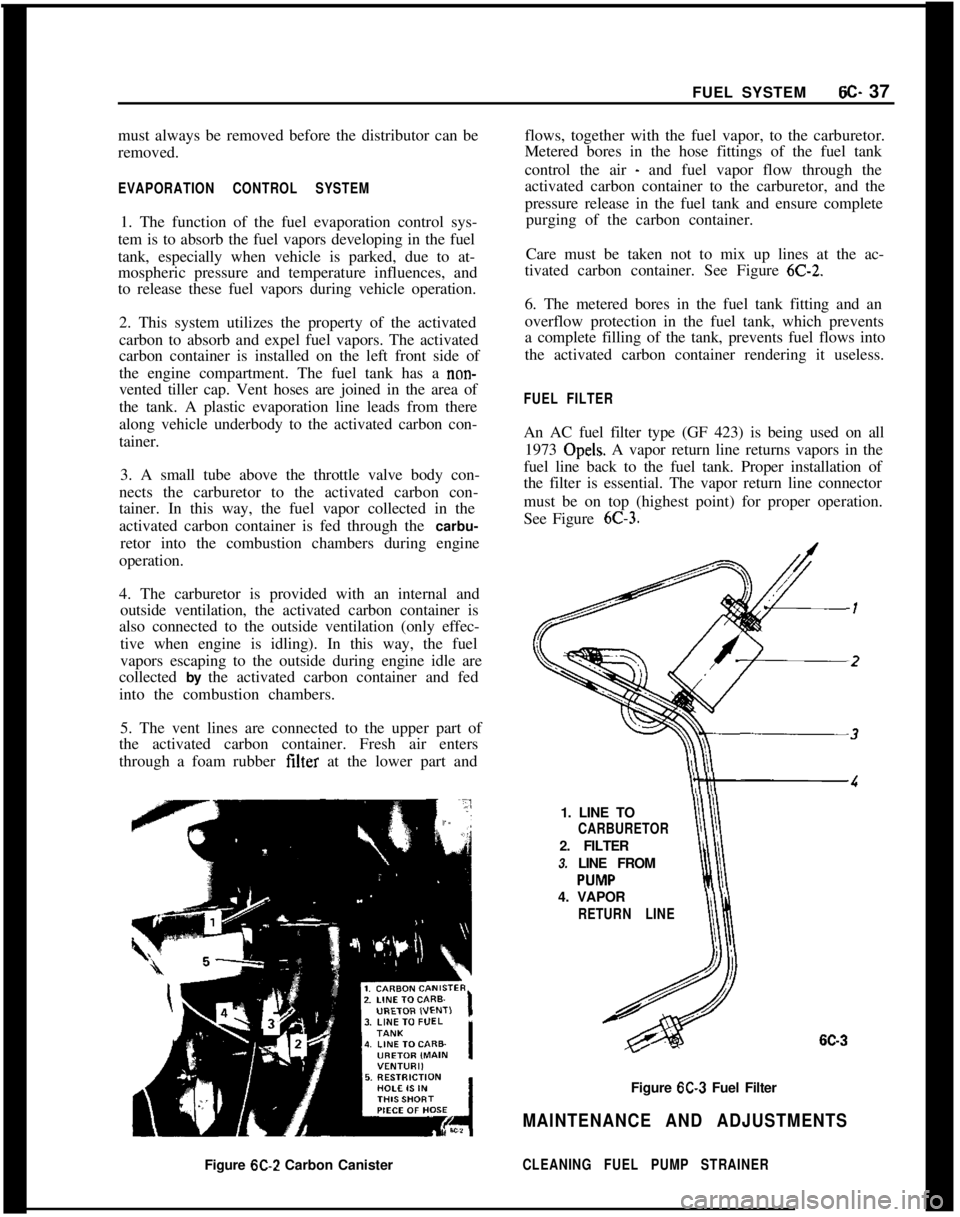
FUEL FILTERAn AC fuel filter type (GF 423) is being used on all
1973 Opels. A vapor return line returns vapors in the
fuel line back to the fuel tank. Proper installation of
the filter is essential. The vapor return line connector
must be on top (highest point) for proper operation.
See Figure
6C-3.1. LINE TO
CARBURETOR2. FILTER
3. LINE FROM
4. VAPOR
RETURN LINE
6C-3Figure
6C-3 Fuel Filter
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTSFigure
6C-2 Carbon CanisterCLEANING FUEL PUMP STRAINER