wiring OPEL MANTA 1973 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: MANTA, Model: OPEL MANTA 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 5 of 625

The 1973 Opel Chassis Service MayI has been completely revised with respect to layout, format and information content
in a” attempt
to provide you “The Technician” with a tiore logical and usable publication. An example of the new grouping
layout 6 exhibited on the preceding
page. Each wow is rubdivided as follows:
Grouo 1
_. _
Subiect IIContents.
0
General InformationIGeneral InformationLifting
Maintenance and Lubrication
1ElectricalBattery
Starting System
lgriition System
Charging System
Washers and Wipers
Lighting Systems
Signal SystemI
Instrument Panel
Gauges
Wiring Diagrams
2
Body and Bumpers:General Body InformationI
Frame & Body Mountings
Windows
& Window Moldings
DONS
Rear Compartment LidRoof &Sun Roof
Seat?., Interior Trim & Headlining
Bumpers.
3Suspension and Steering
Front Suspension
Steering Linkages1Front End Alignment
Steering Gear
Steering Column
Rear Suspension
Wheels and Tires
4
Propelley Shaft & Rear AxlePropeller Shaft & Central Joint
Differential
5Brakes ~Power Booster and Master Cylinder
Front Disc BrakeI
Rear Drum Brake
6EngineEngine Mechanical and Mounts
Cooling System
Fuel System
Exhaust Systems
Carburetor and Throttle Linkage
Emission Control Systems
Tune-up
7TransmissionClutch
Manual Transmission
Automatic Transmission
BChassis Sheet MetalHood, Fenders and Grille
9
Accessol;iesHeaterAirConditioning
Radio
Page 22 of 625
ELECTRICALGROUP 1
Section
IAIBICIDIE
IFIGIH
II
IJTitle
Battery and Cables. . . . . .
StartingSystem. . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition System, .
ChargingSystemWashers and Wipers
.,
LightingSystems
SignalSystems
instrument Panel.........
Gauges...........................Wiring Circuit Diagram:
Page No.
lA- 2lB-10lC-18
1 D-28
1 E-37
1 F-45
1 G-54
1 H-57
1 l-65
1 J-72
Page 29 of 625
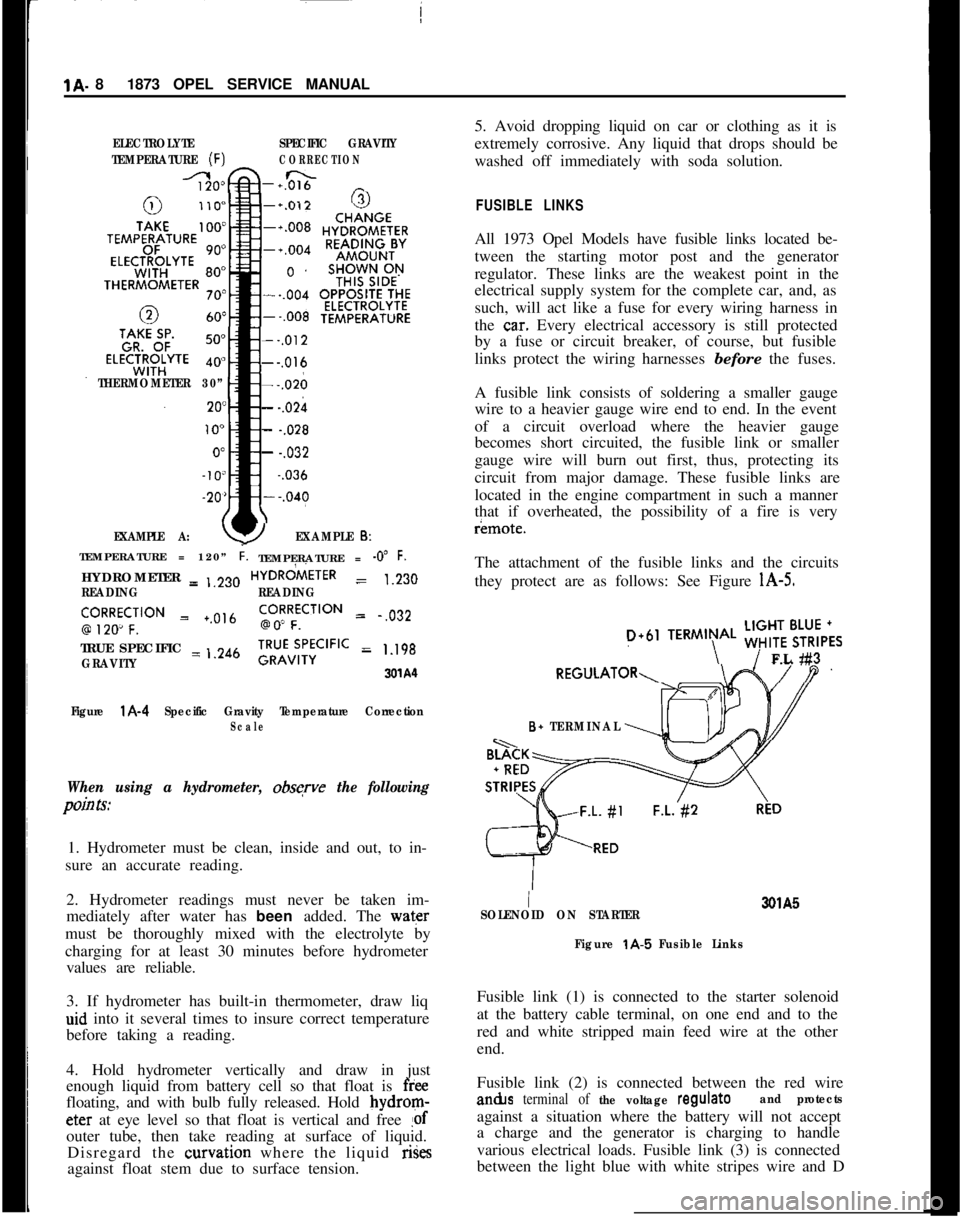
1A. 81873 OPEL SERVICE MANUALELECTROLYTESPECIFIC GRAVITY
TEMPERATURE
(F)CORRECTION
-+0&&n _
THERMOMETER 30”
EXAMPLE A:
--,012---,016---,026
- -.02h
- -.028
- -.032~
-.036
YEXAMPLE 6:TEMPERATURE = 120”
i.TEMPERATURE = -0” F.HYDROMETER = ,,230HYDRdiETER
= 1.230
READINGREADING
‘,9R2Ro~CF;‘“” = +.0,6go!RFfCilON = .,032
TRUE SPECIFIC = ,.246
GRAVITY;RU”v;,‘;CIFIC = 1.198
3xA‘l
Figure
l A-4 Specific Gravity Temperature CorrectionScale
When using a hydrometer, obsqve the following
pain Is:1. Hydrometer must be clean, inside and out, to in-
sure an accurate reading.
2. Hydrometer readings must never be taken im-
mediately after water has been added. The water
must be thoroughly mixed with the electrolyte by
charging for at least 30 minutes before hydrometer
values are reliable.
3. If hydrometer has built-in thermometer, draw liq
aid into it several times to insure correct temperature
before taking a reading.
4. Hold hydrometer vertically and draw in just
enough liquid from battery cell so that float is
freefloating, and with bulb fully released. Hold bydrom-eter at eye level so that float is vertical and free
!ofouter tube, then take reading at surface of liquid.
Disregard the curvation where the liquid rises
against float stem due to surface tension.5. Avoid dropping liquid on car or clothing as it is
extremely corrosive. Any liquid that drops should be
washed off immediately with soda solution.
FUSIBLE LINKSAll 1973 Opel Models have fusible links located be-
tween the starting motor post and the generator
regulator. These links are the weakest point in the
electrical supply system for the complete car, and, as
such, will act like a fuse for every wiring harness in
the
ca.r. Every electrical accessory is still protected
by a fuse or circuit breaker, of course, but fusible
links protect the wiring harnesses before the fuses.
A fusible link consists of soldering a smaller gauge
wire to a heavier gauge wire end to end. In the event
of a circuit overload where the heavier gauge
becomes short circuited, the fusible link or smaller
gauge wire will burn out first, thus, protecting its
circuit from major damage. These fusible links are
located in the engine compartment in such a manner
that if overheated, the possibility of a fire is veryr¬e.
The attachment of the fusible links and the circuits
they protect are as follows: See Figure
l A-5.
D+61TERMIN\AL ;;!$6,,FL #3
B+ TERMINAL
I3QlA5
SOLENOID ON STARTER
Figure
t A-5 Fusible LinksFusible link (1) is connected to the starter solenoid
at the battery cable terminal, on one end and to the
red and white stripped main feed wire at the other
end.
Fusible link (2) is connected between the red wirean&s
terminal of the voltage regulateand protectsagainst a situation where the battery will not accept
a charge and the generator is charging to handle
various electrical loads. Fusible link (3) is connected
between the light blue with white stripes wire and D
Page 30 of 625

BATTERY AND CABLES - ALL MODELSlA- 9
plus 61 terminal of the voltage regulator and protects
the circuit to the generator telltale light.
BATTERY RECHARGING
There are two separate methods of recharging batter-
ies which giffer basically in the rate of charge. In the
slow-charge method, the battery is supplied a rela-
tively small amount of current for an extended
period of time. In the quick-charge method, the bat-
tery is supplied with a high current for a short period
of time.
Slow-Charging
Slow charking is the best and only method of com-
pletely ch+rging a battery. The slow-charge method,
properly applied, may be safely used under all possi-
ble conditions of the battery, provided electrolyte is at proper
wl in all cells. The battery may be fully
charged by this method, unless the battery is not
capable of taking a full charge. The normal slow
charging rate for the
12.volt battery is 5 amperes.
Full ch&e of battery is indicated when all cell spe-
cific gravities do not increase when checked at three
intervals
of one hour and all cells are gassing freely.
Due to the low rate during slow charging, plenty of
time must ,be allowed. Charge periods of 24 hours or
more are often required.
Quick-Charging
Since time!is often of most importance to the battery
owner, quick-charging must sometimes be used to
partially charge the battery so that the engine will
start and the owner can be on his way.
Charge at:50 amperes for 20 minutes (50 times 20
equals
100Q ampere minutes). If charger will not give
this rate, charge for an equal number of ampere mi-
nutes at the best rate available. Too high a current
during quick-charging will damage battery plates.
A battery cannot be brought up to a fully charged
condition
by the quick-charge method. The battery
can be substantially recharged or boosted, but in
order to bring the battery to a fully charged condi-
tion, the charging cycle must be finished by charging
at a low
oi normal rate. Some quick-chargers have
a
provisioA for finishing the charging cycle at a low
rate so
tha’t the battery can be brought up to a fully
charged condition.
Used
with:care, and employing all safeguards prov-
ided by the manufacturer, a quick-charger will not
damage a battery
which is in good condition.
BATTERY REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Removal
1. Disconnect battery cables (remove negative cable
first to prevent possible shorting).
2. Remove battery hold down
l&acket.
3. Remove battery.
Installation
‘1. Place battery back in hold down position.
2. Tighten hold down bracket bolts.
3. Connect battery cables (connect positive cable first
to prevent possible shorting).
FUSIBLE LINK REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Replace a burned out fusible link as follows:
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Disconnect connector eye on end of fusible link.
3. Cut off other end of burned out link, along with
solder joint.
4. Strip insulation from end of new fusible link and
from end of wiring harness so that each will slide into
soldering sleeve.
5. Crimp new link in soldering sleeve and solder
carefully.
6. Cover new connection tightly with electrical tape.
I. Install new link connector eye on other end of
fusible link.
A burned out fusible link connected to the starter
solenoid would be indicated by:
1. All electrical accessories dead.
2. Starter dead - will not even click. Even with a
nearly dead battery, the starter solenoid will
gener-
ally engage; therefore, no click means no solenoid
action, possibly due to a burned out fusible link.
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS
Delco-General 12 volt-44 amp hour storage battery
is installed as original equipment. Replace with a
Delco Energizer
Y55.
Page 32 of 625

I
STARTING SYSTEMlB- 11
but also in the condition of related units, such as battery, switches, electrical
wiring and wiring connections.
ConditionPossible Cause
Correction
When ignition switch is1. Battery discharged.1. Charge battery.
on, cranking motor locks
up or
dra’gs.2. Battery defective.1. Test and replace as required.
Battery terminals loose,Retighten terminals, clean battery
corroded or improperlyposts and terminals and coat them
grounded.with acid-proof grease.
3. Cranking motor or brush1. Eliminate grounds.
terminals grounded.
I
4. Cranking motor brushes do
,
1. Check brushes
- clean or replace
not rest on commutator, or
arcas required. Clean guides on brush-
jammed in their guides, wornholders.
out, oily or clogged.
5. Ignition switch damaged1. Replace ignition switch.
(loose parts preventing switch
I
from closing or burnt parts).
6. Solenoid switch damaged.
1. Repair or replace as required.
7. Excessive voltage drop in1. Check wiring and connections.
wiring switches damaged,Repair or replace switches.
connections loose.
The armature revolves but
1. Drive pinion clogged.1. Clean drive pinion.
the drive binion does not
come into; mesh.
2. Drive pinion or ring gear1. Replace ring gear and
,
teeth flattened or burred.overrunning clutch.
I
3. Poor condition of shaft1. Replace armature and overrunningsplines.clutch.
4. Voltage drop.1. Replace shift lever.
When ignjtion switch is
1. Battery discharged.1. Charge battery.
on, armature revolves
until drive pinion engages
and then
Btops.2. Brush spring tension too1. Check brushes - clean or replace
weak.as required.
3. Cranking motor solenoid or
1. Replace or repair solenoid or
switch defective.
switch.
Page 33 of 625

19- 12 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL :ConditionPosiible CauseCorrection4. Voltage drop.1. Check wiring and wiring
connections.
5. Overrun&g clutch slips.1. Replace overrunning clutch.
The cranking motor keeps
on rotating after ignition
switch is off.1. Ignition
{witch does not
cut off or solenoid switch
sticks.
1, Immediately disconnect cranking
motor cable from battery. Inspect
and/or replace or repair ignition and
solenoid switches as required.
The drive pinion does notdemesh after engine has
been cranked.1. Drive pinion or ring gear
1. Clean components as specified.
teeth clogged or flattened.Replace as required.
Return spring slack or broken.MAlNTEilANCE AND ADJUSTMENT
/
STARTING SYSTEM CHECKS
Voltage Loss ChecksWhen the starter cranks too slowly, check the bat-
tery state of charge and all electrical connections
between the battery and starter.
1. Turn on headlights and
opera’te starter. If head-
lights dim considerably when starter is engaged, the
battery may be discharged or be defective. Check the
battery.
2. If the headlights stay bright but the starter d&s
not turn over, the starter cables may be faulty or the
starter defective.
(a) Test battery voltage while cranking engine
1(9volts minimum).
(b) Check voltage from starter tkrminal of solenoid
to starter frame while cranking engine.
3. The difference in readings taken in Operations 2a
and 2b above represents the
volt& drop through the
cables and solenoid switch. Voltdge drop should
Gotexceed
.5 volt.
4. Locate excessive resistance as follows:
(a) Turn voltmeter to scale above 12 volts and con-
nect voltmeter leads
across connection or switch: to
be checked.
(b) With starter switch closed, turn voltmeter switch
to lowest scale and take reading as quickly as possi-
ble, then turn switch back to higher scale and stop
cranking engine.(c) Voltmeter must not read more than
.2 volt across
any
c:onnection. If voltmeter reads more than .2 volt,
the
d~efect must be corrected.
Starter Current Draw - Lock Test1. Make sure battery is fully charged and in good
condition.
2. Connect a volt ampere starter tester according to
manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Pull parking brake on securely, shift transmission
into 4th (direct) gear and actuate starter. (Starter will
not
t,urn engine because engine is locked through
transmission.)
4. While starter is actuated, read voltage and current.
Refer to Specification Chart.
(a) Voltage low
_ poor battery or a voltage loss in the
starter circuit.
(b) Current high
- short circuit in starter. Overhaul
starter.
(c) Current low
- commutator dirty, brushes worn,
solenoid switch contacts defective or open circuit in
starter. Overhaul starter.
Starter Current Draw. On Car1. Bring engine to normal operating temperature.
2. Stop engine and disconnect coil wire from dis-
tributor.
3. Ground coil wire to prevent excessive coil voltage
build up.
Page 34 of 625

STARTING SYSTEMlB- 13
4. Connect test equipment and, with transmission in
neutral, turn engine over until voltage stabilizes.
Note read.ings.5. Current draw should be between 90-130 amperes.
I3. Remove end frame from field frame and pull both
insulating tubes out of field frame.
4. To prevent brushes from coming out when remov-
ing the field frame, place a 29 millimeter socket over
commutator while lifting up on the field frame. The
brushes will be held in place by the socket. See FigurelB-4.
STARTER
:OVERHAULStarter
R&~moval1.
Dixon&t starter wiring.
2. Remove starter support bracket.
3. Removk two starter bolts, one nut and lockwash-en.
4. Removi starter.
Starter
Di+assembly1. Hold starter in a vise, as shown in Figure
lB- 3.
Mark end’ frame and field frame to ensure correctinstallatioli of parts on reassembly.
rTHRU BOLTS7Figure
18-4 Removing Field Frame
5. Remove the two (2) solenoid attaching screws and
remove solenoid and spring.
Figure 1 B-3 Cranking Motor in Vise
2. Remove both starter through bolts and field coil
end from solenoid switch lower threaded bolt. See
Figure lB13.Figure
lb5 Driving Retaining Ring Back
Page 39 of 625
1 C- 18 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
IGNITIPN SYSTEM
CbNTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION: Ignition System ..................................................................
Ignition
Switc,h....................................................................
Ignition Coil
..........................................................................\
Distributor
............................I...............................................
DIAGNOSIS: (Not Available)
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS: Contact PointReplacement ............................................
Dwell Angle Adjustment :
................................................
Ignition Timing Adjustment ..........................................
Ignition Wire Inspection :
..................................................
Check Ignition Output ......................................................
Check Distributor
..............................................................
Check Spark Plugs
............................................................
MAJOR REPAIR: Distributor Removal ..........................................................
Disassembly ........................
I...............................................
Reassembly
..........................I...............................................
Distributor Installation
....................................................
SPECIFICATIONS: /
Ignition
Coil ..........................................................................
Distributor
....‘........................i...............................................
Spark Plugs ........................................................................\
..
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INGITION SYSTEM
The ignition system basically consists of an ignitipn
switch, ignition coil, distributor, battery and related
wiring. The ignition switch is located in the steering
column, the ignition coil is located left front inner fender
skirt and the distributor is located at the left
front of the engine.
IGNITION SWITCH
The combined ignition switch and steering lock ian
be switched to any one of the below listed positions.
Insert key with notch pointing upward.
Page No.
lC-18
lC-18
lC-19
lC-19
1 c-20
1 c-20
1 c-20
lC-21 r
lC-21
1 c-22
1 c-22
1 r-23
1 C-23
1 c-24
1 C-25
1 C-26
1 C-26
1 C-26
(Fully counterclockwise) Lock position. Ignition
locked, steering locked, only with key removed.
Electrical circuits disconnected except to main light-
ing switch and dome lamp. The
key can be removed.
0- (First position clockwise from lock) Garage posi-
tion. ‘The key and lock assembly must be pushed “in”
to reach this position from lock. The steering is un-
locked and the ignition is off. The electrical circuits
are the same as in lock position. The key cannot be withdrawn.
l- [Chposition.) All electrical circuits controlled by
ignition switch are completed through the switch.
The key cannot
be removed while switch is in drive
position.
Page 40 of 625

IIIGNITION SYSTEMlC- 19
11. (Startx position.) The ignition key must be
released as soon as engine starts. The switch then
returns aujomatically to the on position.
IGNITION
GOILThe ignition coil consists of a laminated non- mag-
netic iron
(core enclosed by two coils; the primary
winding and the secondary winding.
The prim+y circuit consists of the power source
(battery), the ignition switch, the ignition coil pri-
mary winding, the distributor breaker points with
ignition condenser connected in parallel, and all con-
necting
lo& tension wiring.
The secondary circuit consists of the ignition coil
secondary ‘winding, the spark plugs, all connecting
high tens@ wiring, the distributor cap and the
ro-tor.
When the’ ignition switch is turned on and the
breaker pdints are closed, current flows through the
ignition
c&l primary winding and produces a mag-
netic field wound the coil windings.
When the breaker points are separated by the revolv-
ing distributor cam, the magnetic field collapses and
induces a high voltage surge in the secondary wind-
ing,
produ;cing a spark between the spark plug elec-
trodes. ,
The ignitidn condenser which is connected in paral-
lel with the breaker points, prevents arcing between
the
separa’ted breaker contacts, and current flow
after~ the breaker points have been separated, thus
causing a kery rapid collapse of the magnetic field
around th$ Ignition coil.
/
IGNITION ‘DISTRIBUTORThe ignitidn distributor breaks the primary current,distributeslthe high voltage surges induced in the coil
secondary winding to the spark plugs according to
the engin< tiring order and sets ignition timing in
relation to. engine RPM and load.
The housi+g of the distributor contains the centrifu-
gal advance mechanism and the movable breaker
plate with’s breaker lever and contact support. The
vacuum advance mechanism is attached to the
breaker plate and mounted on the outside of the
distributor, housing. See Figure lC-1.
The distributor shaft is driven by a helical gear on the
camshaft and in turn drives the engine oil pump. The
ignition condenser is mounted on the outside of the
housing. The engine output is to a large extent in-
fluenced b) the ignition timing. Maximum engine
performance is obtained when the combustion proc-
ess is well underway as the piston starts down on thepower stroke. The air-fuel charges are, however, not
burned instantly, so it is necessary to advance the
spark in relation to the piston top dead center as
engine speed increases or as engine load decreases.
If the spark is too far advanced, the engine knocks,
causing a drop in engine power output and overheat-
ing. If the spark is retarded, part of the energy deve-
loped during combustion is wasted which will result
in reduced engine power output, excessive fuel con-
sumption and overheating.
The ignition distributor has a double acting double
diaphragm vacuum unit. See Figure lC-1. The ad-
vance unit is supplied with “ported” vacuum. That
is, vacuum is supplied from a port in the primary
barrel of the carburetor located just above the closed
throttle valve. This port supplies no vacuum during
idling nor during closed throttle deceleration, but
supplies full intake manifold vacuum at all speeds
where the throttle valve is opened enough to uncover
the port.
Figure lC-1 Ignition Distributor
The retard unit is supplied with intake manifold
vacuum at all times by means of a line connected
directly to the intake manifold. During idling and
deceleration, when there is no vacuum to the ad-
vance unit, the retard unit will cause the timing to be
retarded 5 degrees. However, during part throttle
operation when there is vacuum to the advance unit,
the advance unit will overpower the retard unit so
that the retard unit has no effect on timing.
The purpose of the retard unit is to reduce hydrocar-
bon and carbon monoxide emissions during idling
and deceleration, where they are especially bad.
In order to avoid voltage losses for easier starting, a
plastic cover has been inserted in the distributor be-
low the rotor as a seperator to keep the inside of the
distributor cup free from condensation.
Page 51 of 625

i
1 D- 301973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
6. Make sure all electrical accessories are turned (lff.
Start engine with battery post adapter switch closed;
open switch as soon as engine
iS: started.
7. Adjust engine speed to 2500 RPM.
8. Turn tester control knob to “LOAD” position
aid
adjust knob to obtain highest possible ammeter r&d-
ing. Output must be 30 amperes minimum. If
outcut
is okay, proceed to voltage regulator test below. j
/.9. If output is low, defect may be in alternator or m
regulator. To eliminate regulator, supply field &-
rent direct to cause full alternat,or output. Unplug
three-way connector from regulator and plug in a
jumper between the red and black leads. See Figure
lD-5. Retest as described in Steps 7 and 8. If output
is still low, generator is faulty and must be
remov&d.
301D5 :
Figure lD-5 Alternator Ouiput Check I
10. If output (using field jumper) is now okay, defect
is in the regulator or wiring harness. Check all wiring
connections. If all wiring is okay, try
replac/~g
regulator; if output now tests okay (without
uslpg
field jumper), you have found the trouble. Always
follow-up with a voltage regulator test.
Test and Adjust Voltage Regulator Setting
1. Always test alternator output first, as describedlin
subparagraph a above. Leave all test
instrumeqts
connected, but make sure field
jumper is removed; if
used.
2. With engine speed at 2500 RPM, turn tester con-
trol
knob to “l/4 OHM” position. Make sure ill
electrical accessories are turned off. After volt&e
reading stabilizes, any reading between 13.5 and 14.5
volts is okay.
3. If voltage reading is out of limits, remove regulator cover and adjust voltage regulator armature spring
tension to obtain a middle reading of 14.0 volts. If
reading fluctuates, voltage contacts are dirty.
4. Replace regulator cover and recheck voltage set- ting. A steady voltage reading between 13.5 and 14.5
volts means voltage regulator is okay.
5. Adjust engine speed to specified idle. Reseal volt-
age regulator cover carefully, using electrical tape.
MAJOR REPAIR
ALTERNATOR OVERHAUL
Always disconnect battery ground cable before mak-
ing any electrical repairs.
Alternator Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground strap.
2. Unplug wiring connector from alternator. 3. Disconnect battery lead from alternator.
4. Remove adjusting brace bolt, lockwasher, plain
washer and nut.
5. Loosen pivot bolt. Push alternator inward and
remove belt from pulley.
6. Drop alternator down and remove pivot bolt, nut,
lockwasher and plain washer.
7. Remove alternator.
Figure 1D-6 Removing Alternator Pulley