brakes OPEL VECTRA 1988 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1988, Model line: VECTRA, Model: OPEL VECTRA 1988Pages: 525, PDF Size: 58.26 MB
Page 132 of 525

9
System type
Models without ABS:
1.4, 1.6 and 1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Front discs and rear drums, with vacuum servo assistance, dual
hydraulic circuit split diagonally, pressure-proportioning valves in rear
hydraulic circuit. Cable-operated handbrake on rear wheels
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Front and rear discs, with vacuum servo assistance, dual hydraulic
circuit split diagonally, pressure-proportioning valves in rear hydraulic
circuit. Cable-operated handbrake on rear wheels
All models with Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Front and rear discs, with vacuum servo assistance, operated via
hydraulic modulator, dual hydraulic circuit split front/rear, pressure-
proportioning valves in rear hydraulic circuit. Cable-operated
handbrake on rear wheels
Front discs
Type:
1.4, 1.6 and 1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Solid or ventilated (as from 10/91)
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ventilated
Diameter:
1.4, 1.6 and early 1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236 mm
Late (as from 10/91) 1.8 and 2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256 mm
Maximum disc run-out (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 mm
Minimum pad friction material thickness (including backing plate):
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0 mm
Minimum disc thickness after machining: *
1.4, 1.6 and 1.8 litre models (with solid discs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.7 mm
1.4, 1.6 and 1.8 litre models (with vented discs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18.0 mm
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22.0 mm
* When this dimension is reached, only one further new set of brake pads is permissible, then renew the discs
Chapter 9
Braking system
ABS electronic control module - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .22
ABS hydraulic modulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
ABS relays (ABS-2E systems only) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . .23
ABS wheel sensors - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Anti-lock braking system (ABS) - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Brake disc - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Brake drum - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Brake fluid pipes and hoses - general, removal and refitting . . . . . . .25
Brake pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Front brake disc shield - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Front disc caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Front disc pads - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Handbrake - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Handbrake cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27Handbrake lever - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Handbrake shoes (rear disc brakes) - inspection, removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Master cylinder - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Master cylinder (ABS) - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Master cylinder (non-ABS) - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Rear brake backplate - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Rear brake pressure-proportioning valves - removal and refitting . . .24
Rear brake shoes (drum brakes) - inspection, removal and refitting . .6
Rear disc caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Rear disc pads - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Rear wheel cylinder (drum brakes) - removal, overhaul and refitting .12
Vacuum servo - description and testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Vacuum servo - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
9•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 133 of 525

Rear discs
Type (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Solid
Diameter (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260 mm
Maximum disc run-out (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.1 mm
Minimum pad friction material thickness (including backing plate):
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7.0 mm
Minimum disc thickness after machining (all models) * . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.0 mm
* When this dimension is reached, only one further new set of disc pads is permissible, then renew the discs
Minimum handbrake shoe friction material thickness (lining only)
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.0 mm
Rear drums
Internal diameter (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .200 mm
Minimum shoe friction material thickness (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.5 mm above rivet heads
Brake fluid type/specification:
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Lubricants and fluidsin “Weekly checks”
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
ABS hydraulic modulator mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
ABS wheel sensor mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
ABS control unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.51
Brake fluid line unions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1612
Caliper and wheel cylinder bleed screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Front brake disc securing screw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Front brake fluid hose to caliper union . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4030
Front caliper bracket to hub carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9570
Front caliper guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Front caliper mounting (solid disc models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9570
Front caliper to mounting bracket (vented disc models) . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Handbrake lever securing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Master cylinder mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Master cylinder stop screw (ATE type) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Pressure proportioning valve to master cylinder:
ATE type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
GMF type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4030
Rear brake backplate/stub axle spring:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5037
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle-tighten a further 30º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle-tighten a further 15º
Rear brake disc securing screw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Rear caliper mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8059
Rear drum securing screw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Rear wheel cylinder mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Vacuum servo support bracket to bulkhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Vacuum servo to support bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
1General description
The foot brake operates on all four wheels.
Solid or ventilated disc brakes are fitted at the
front, and self-adjusting drum or solid disc
brakes are fitted at the rear, depending on
model. Actuation is hydraulic, with vacuum
servo assistance. The handbrake is cable-
operated, and acts on the rear wheels only.
The hydraulic system is split into two
circuits. On non-ABS models, the system is
split diagonally, and on ABS models, the
system is split front and rear. If there is a
hydraulic fluid leak in one circuit, the
remaining circuit will still function, so that
some braking capability remains.
The hydraulic fluid supply to the rear brakes
is regulated so that the front brakes alwayslock first under heavy braking. The fluid
pressure to the rear brakes is controlled by
two valves, one for each brake, which are
either screwed into the master cylinder or
mounted on the rear underbody of the vehicle,
depending on model.
The brake servo is of the direct-acting type,
fitted between the pedal and the master
cylinder. The servo is powered by vacuum
developed in the inlet manifold. Should the
servo fail, the brakes will still operate, but
increased pedal pressure will be required.
2Anti-lock braking system
(ABS) - general
1ABS is available as an option for all models.
When the ignition is switched on, an ‘ABS’
symbol illuminates in the instrument panel for
a short time. 2The system comprises an electronic control
unit, roadwheel sensors, hydraulic modulator,
and the necessary valves and relays. Disc
brakes are fitted to all four wheels. The
purpose of the system is to stop wheel(s)
locking during heavy brake applications. This
is achieved by automatic release of the brake
on the locked wheel, followed by re-
application of the brake. This procedure is
carried out several times a second by the
hydraulic modulator.
3The modulator is controlled by the
electronic control unit, which itself receives
signals from the wheel sensors, which monitor
the locked or unlocked state of the wheels.
The two front brakes are modulated
separately, but the two rear brakes are
modulated together.
4The ABS unit is fitted between the brake
master cylinder and the brakes, the vacuum
servo and master cylinder being of similar
type for both non-ABS and ABS models.
9•2Braking system
Page 134 of 525

5If the ‘ABS’ symbol, in the instrument panel
stays lit after approximately 4 seconds, or if it
comes on sporadically or stays on whilst
driving, there is a fault in the system. Should
this occur, it is recommended that a complete
test is carried out by a Vauxhall dealer, who
will have the necessary specialist diagnostic
equipment. Due to the special equipment
required, it is not practical for the DIY
mechanic to carry out the test procedure.
6To prevent possible damage to the
electronic control unit, always disconnect the
control unit wiring plug before carrying out
electrical welding work.
7It is recommended that the control unit is
removed if the vehicle is being subjected to
high temperatures, like for instance, during
certain paint-drying processes.
8If using steam cleaning equipment, do not
aim the water/steam jet directly at the control
unit.
9Do not disconnect the control unit wiring
plug with the ignition switched on.
10Do not use a battery booster to start the
engine.
11After working on the ABS components,
ensure that all wiring plugs are correctly
reconnected, and have the complete system
tested by a Vauxhall dealer, at the earliest
opportunity.
12All models up to 1991 that were fitted with
ABS, used the ABS-2E system. From 1992
onwards an ABS-2EH system was fitted,
which can be identified by the location of the
electronic control module, which is bolted to
the hydraulic modulator.
13The main differences between the two
systems are in the electrical components and
circuits, the most obvious of these being
omission of the surge arrester relay on the
2EH system.
3Hydraulic system - bleeding
2
General
1If any of the hydraulic components in the
braking system have been removed or
disconnected, or if the fluid level in the
reservoir has been allowed to fall appreciably,
it is certain that air will have entered into the
system. The removal of all this air from the
hydraulic system is essential if the brakes are
to function correctly, and the process of
removing it is known as bleeding.
2Where an operation has only affected one
circuit of the hydraulic system (the system issplit diagonally on non-ABS models, and front
and rear on ABS models), then it will only be
necessary to bleed the relevant circuit. If the
master cylinder has been disconnected and
reconnected, or the fluid level has been
allowed to fall appreciably, then the complete
system must be bled.
3One of three methods can be used to bleed
the system, although Vauxhall recommend
the use of a pressure bleeding kit.
Bleeding - two-man method
4Obtain a clean jar, and a length of rubber or
plastic bleed tubing that will fit the bleed
screws tightly. The help of an assistant will be
required.
5Remove the dust cap and clean around the
bleed screw on the relevant caliper of wheel
cylinder (see illustration), then attach the
bleed tube to the screw. If the complete
system is being bled, start at the front of the
vehicle. When bleeding the complete system
on models with ABS, the front brakes must be
bled before the rears.
6Check that the fluid reservoir is topped up,
and then destroy the vacuum in the brake
servo by giving several applications of the
brake pedal.
7Immerse the open end of the bleed tube in
the jar, which should contain two or three
inches of hydraulic fluid. The jar should be
positioned about 300 mm (12.0 in) above the
bleed screw to prevent any possibility of air
entering the system down the threads of the
bleed screw when it is slackened.
8Open the bleed screw half a turn, and have
the assistant depress the brake pedal slowly
to the floor. With the brake pedal still
depressed, retighten the bleed screw, and
then have the assistant quickly release the
pedal. Repeat the procedure.
9Observe the submerged end of the tube in
the jar. When air bubbles cease to appear,
tighten the bleed screw when the pedal is
being held fully down by the assistant.
10Top-up the fluid reservoir. It must be kept
topped up throughout the bleeding
operations. If the connecting holes to the
master cylinder are exposed at any time due
to low fluid level, the air will be drawn into the
system, and the whole bleeding process will
have to start again.
11If the complete system is being bled, the
procedure should be repeated on the
diagonally opposite rear brake. Then on the
front and rear brakes of the other circuit on
non-ABS models, or on the remaining front
brake and then on the rear brakes on ABS
models.
12On completion, remove the bleed tube,
and discard the fluid that has been bled from
the system, unless it is required to make up
the level in the bleed jar. Never re-use old fluid.
13On completion of bleeding, top-up the
fluid level in the reservoir. Check the action ofthe brake pedal, which should be firm, and
free from any “sponginess” that would
indicate that air is still present in the system.
Bleeding - with one-way valve
14There are a number of one-man brake
bleeding kits currently available from motor
accessory shops. It is recommended that one
of these kits should be used whenever
possible, as they greatly simplify the bleeding
operations. They also reduce the risk of
expelled air or fluid being drawn back into the
system.
15Proceed as described in paragraphs 5
and 6.
16Open the bleed screw half a turn, then
depress the brake pedal to the floor, and
slowly release it. The one-way valve in the
bleeder device will prevent expelled air from
returning to the system at the completion of
each stroke. Repeat the operation until clear
hydraulic fluid, free from air bubbles, can be
seen coming through the tube. Tighten the
bleed screw.
17Proceed as described in paragraphs 11
to 13 inclusive.
Bleeding - with pressure
bleeding kit
18These are also available from motor
accessory shops, and are usually operated by
air pressure from the spare tyre.
19By connecting a pressurised container to
the master cylinder fluid reservoir, bleeding is
then carried out by simply opening each bleed
screw in turn and allowing the fluid to run out.
Like turning on a tap, until no air bubbles are
visible in the fluid being expelled.
20Using this method, the large reserve of
fluid provides a safeguard against air being
drawn into the master cylinder during the
bleeding operations.
21This method of bleeding is recommended
by Vauxhall.
22Begin bleeding with reference to
paragraphs 5 and 6, and continue as
described in paragraphs 11 to 13 inclusive.
Braking system 9•3
3.5 Removing the dust cap from a rear
caliper bleed screw - models with
ventilated discs
9
If brake fluid is spilt on the
paintwork, the affected area
must be washed down with
cold water immediately.
Brake fluid is an effective paint
stripper!
Page 137 of 525

outboard pad and anti-squeal shim that fits
between the pad and the caliper body.
7Withdraw the inboard pad and anti-squeal
shim.
Refitting
8Proceed as described in Section 4,
paragraphs 10 and 11.
9Check that the cutaway recesses in the
pistons are positioned downwards, at
approximately 23°to the horizontal. A
template made of card may be used to check
the setting (see illustration). If necessary,
carefully turn the pistons to their correct
positions.
10Apply a little brake grease to the top and
bottom edges of the backplates on the new
brake pads.
11Locate the new pads and the anti-squeal
shims in the caliper. Ensure that the friction
material faces the disc, and check that the
pads are free to move slightly.
12Locate the anti-rattle spring on the pads,
then insert the pad retaining pins from the
inside edge of the caliper, while depressing
the spring. Tap the pins firmly into the caliper.
13Repeat the operations on the remaining
side of the vehicle.
14Proceed as described in Section 4,
paragraphs 17 to 20 inclusive.
6Rear brake shoes (drum
brakes) - inspection, removal
and refitting
3
Note: When working on the brake
components, take care not to disperse brake
dust into the air, or to inhale it, since it may
contain asbestos, which can damage your
health.
Inspection
1It is recommended that the brake shoes are
inspected when necessary by removing the
drums. This will enable a proper inspection of
the linings to be made, and additionally, the
wheel cylinders can be inspected for leaks. If
preferred, however, a provisional inspection of
the state of wear of the rear shoe linings can
be made by removing the plugs from the
inspection holes in the brake backplates.2Use a torch or inspection lamp, and if
necessary a mirror, to check that the friction
material has not worn down to less than the
specified minimum.
3If any one of the shoes has worn below the
specified limit, all four rear brake shoes must
be renewed as a set, as follows.
Removal
4Where applicable, remove the wheel trims,
then loosen the rear roadwheel bolts and
chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear of the
vehicle, and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”) positioned
under the body side members. Remove the
roadwheels.
5Fully release the handbrake.
6Extract the drum securing screw and
remove the drum. If the drum is tight, remove
the plug from the inspection hole in the brake
backplate, and push the handbrake operating
lever towards the brake shoe to move the
shoes away from the drum. If necessary,
slacken the handbrake cable adjuster (see
illustrations).
7Note the location and orientation of all
components before dismantling, as an aid to
reassembly.
8Clean the dust and dirt from the drum and
shoes, but take care not to inhale it.
9Remove the shoe hold-down pins, springs
and cups by depressing the cups and turning
them through 90°using a pair of pliers (see
illustrations). Note that the hold-down pins
are removed through the rear of the brake
backplate.
10Disconnect the handbrake cable from the
operating lever.11The upper and lower return springs may
now be unhooked and the shoes removed
separately, or the assembly of shoes, adjuster
strut and springs may be removed together.
Remove the hub, refer to Chapter 10, if
necessary. Take care not to damage the
wheel cylinder rubber boots. Before removing
the return springs, note the position and
orientation of the springs and adjuster strut.
12If the shoes are to be removed for some
time, fit a stout rubber band or a spring clip to
the wheel cylinder, to prevent the pistons from
being pushed out of their bores. In any event,
do not press the brake pedal while the drum is
removed.
Refitting
13Clean the dust and dirt from the brake
backplate, but take care not to inhale it.
14Apply a small amount of brake grease to
the shoe rubbing areas on the backplate.
15Investigate and rectify any source of
contamination of the linings (wheel cylinder or
hub bearing oil seal leaking).
16Although linings are available separately
(without shoes), renewal of the shoes
complete with linings is to be preferred,
unless the reader has the necessary skills and
equipment to fit new linings to the old shoes.
17If not already done, dismantle the shoes,
strut and springs. Note the position and
orientation of the components. On later
models (1992-on), the brake shoe lower
anchorage has been modified so that it is now
rectangular, necessitating modified brake
shoes and a modified lower return spring (see
illustration).
9•6Braking system
5.9 Checking a rear caliper piston cut
away recess angle with a card template6.6B Push the handbrake operating lever
to move the shoes away from the drum
6.9B . . . then withdraw the cup and spring6.9A Release the shoe hold-down cup . . .
6.6A Extracting a brake drum securing
screw
Page 138 of 525
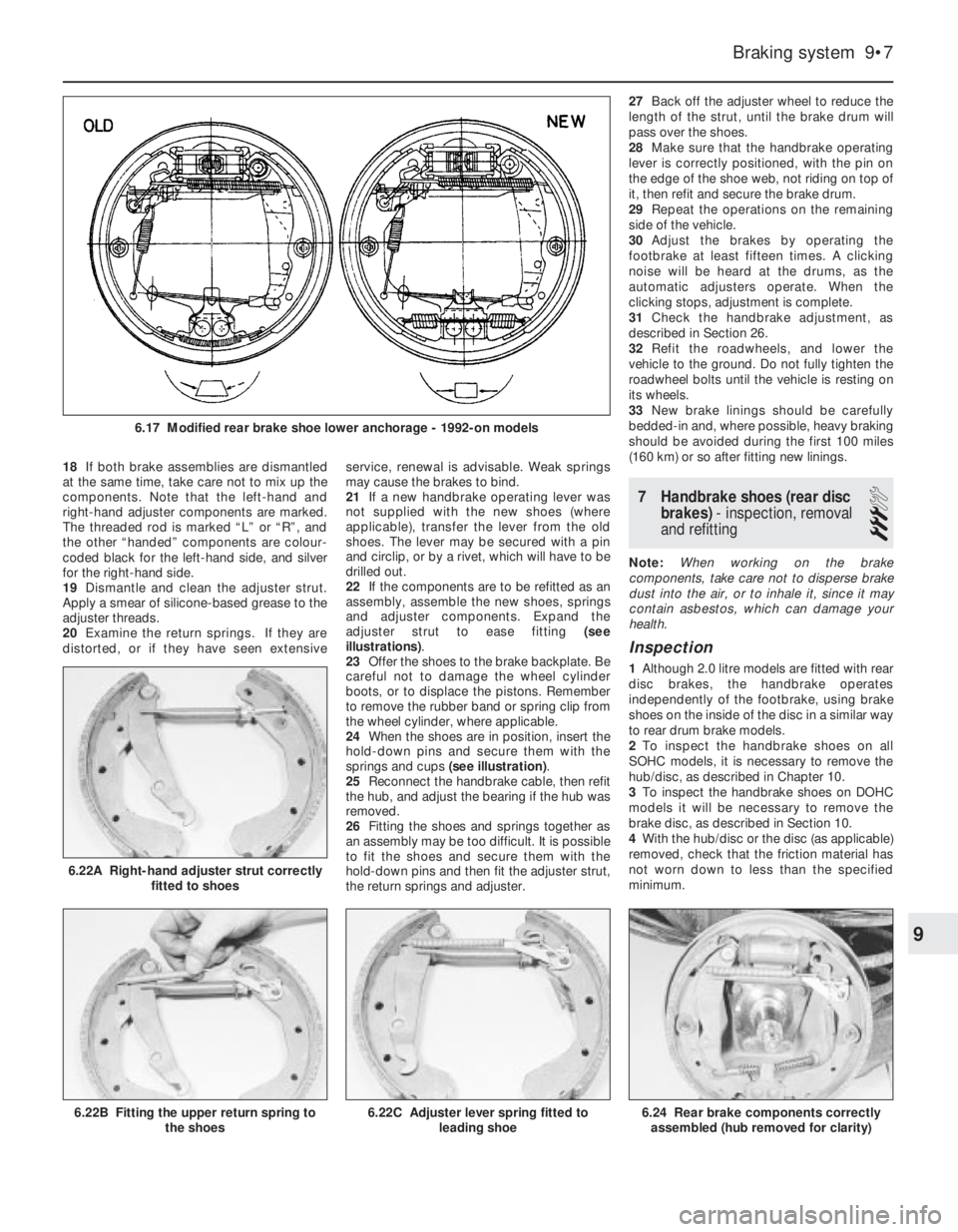
18If both brake assemblies are dismantled
at the same time, take care not to mix up the
components. Note that the left-hand and
right-hand adjuster components are marked.
The threaded rod is marked “L” or “R”, and
the other “handed” components are colour-
coded black for the left-hand side, and silver
for the right-hand side.
19Dismantle and clean the adjuster strut.
Apply a smear of silicone-based grease to the
adjuster threads.
20Examine the return springs. If they are
distorted, or if they have seen extensiveservice, renewal is advisable. Weak springs
may cause the brakes to bind.
21If a new handbrake operating lever was
not supplied with the new shoes (where
applicable), transfer the lever from the old
shoes. The lever may be secured with a pin
and circlip, or by a rivet, which will have to be
drilled out.
22If the components are to be refitted as an
assembly, assemble the new shoes, springs
and adjuster components. Expand the
adjuster strut to ease fitting (see
illustrations).
23Offer the shoes to the brake backplate. Be
careful not to damage the wheel cylinder
boots, or to displace the pistons. Remember
to remove the rubber band or spring clip from
the wheel cylinder, where applicable.
24When the shoes are in position, insert the
hold-down pins and secure them with the
springs and cups (see illustration).
25Reconnect the handbrake cable, then refit
the hub, and adjust the bearing if the hub was
removed.
26Fitting the shoes and springs together as
an assembly may be too difficult. It is possible
to fit the shoes and secure them with the
hold-down pins and then fit the adjuster strut,
the return springs and adjuster.27Back off the adjuster wheel to reduce the
length of the strut, until the brake drum will
pass over the shoes.
28Make sure that the handbrake operating
lever is correctly positioned, with the pin on
the edge of the shoe web, not riding on top of
it, then refit and secure the brake drum.
29Repeat the operations on the remaining
side of the vehicle.
30Adjust the brakes by operating the
footbrake at least fifteen times. A clicking
noise will be heard at the drums, as the
automatic adjusters operate. When the
clicking stops, adjustment is complete.
31Check the handbrake adjustment, as
described in Section 26.
32Refit the roadwheels, and lower the
vehicle to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
33New brake linings should be carefully
bedded-in and, where possible, heavy braking
should be avoided during the first 100 miles
(160 km) or so after fitting new linings.
7Handbrake shoes (rear disc
brakes) - inspection, removal
and refitting
3
Note: When working on the brake
components, take care not to disperse brake
dust into the air, or to inhale it, since it may
contain asbestos, which can damage your
health.
Inspection
1Although 2.0 litre models are fitted with rear
disc brakes, the handbrake operates
independently of the footbrake, using brake
shoes on the inside of the disc in a similar way
to rear drum brake models.
2To inspect the handbrake shoes on all
SOHC models, it is necessary to remove the
hub/disc, as described in Chapter 10.
3To inspect the handbrake shoes on DOHC
models it will be necessary to remove the
brake disc, as described in Section 10.
4With the hub/disc or the disc (as applicable)
removed, check that the friction material has
not worn down to less than the specified
minimum.
Braking system 9•7
6.22A Right-hand adjuster strut correctly
fitted to shoes
6.24 Rear brake components correctly
assembled (hub removed for clarity)6.22C Adjuster lever spring fitted to
leading shoe6.22B Fitting the upper return spring to
the shoes
6.17 Modified rear brake shoe lower anchorage - 1992-on models
9
Page 142 of 525

Rear disc - DOHC models
Removal
15Where applicable, remove the roadwheel
bolt and spacer used when checking the disc.
16Remove the disc pads, as described in
Section 5.
17Remove the brake caliper with reference
to Section 9, but leave the hydraulic fluid pipe
connected. Move the caliper to one side, and
suspend it using wire or string to avoid
straining the pipe.
18Remove the securing screw and withdraw
the disc from the hub (see illustration). If the
disc is tight, collapse the handbrake shoes by
inserting a screwdriver through the adjuster
hole in the disc and turning the adjuster
wheel.
Refitting
19Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
make sure that the mating faces of the disc
and hub are perfectly clean, and apply a little
locking fluid to the threads of the securing
screw. Refit the disc pads, as described in
Section 5.
11Brake drum - removal,
inspection and refitting
3
Note: When working on the brake
components, take care not to disperse brake
dust into the air, or to inhale it, since it may
contain asbestos, which can damage your
health.
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel.
2Fully release the handbrake.
3Extract the drum securing screw and
remove the drum. If the drum is tight, remove
the plug from the inspection hole in the brake
backplate, and push the handbrake operating
lever towards the brake shoe to move theshoes away from the drums. If necessary,
slacken the handbrake cable adjuster.
Inspection
4Brush the dirt and dust from the drum,
taking care not to inhale it.
5Examine the internal friction surface of the
drum. If they are deeply scored, or so worn
that the drum has become ridged to the width
of the shoes, then both drums must be
renewed.
6Regrinding of the friction surface is not
recommended, since the internal diameter of
the drum will no longer be compatible with the
shoe friction material contact diameter.
Refitting
7Refit the brake drum and tighten the
securing screw. If necessary, back off the
adjuster wheel until the drum will pass over
the shoes.
8Adjust the brakes by operating the
footbrake a number of times. A clicking noise
will be heard at the drum as the automatic
adjuster operates. When the clicking stops,
adjustment is complete.
9Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground. Do not fully tighten the roadwheel
bolts until the vehicle is resting on its wheels.
12Rear wheel cylinder (drum
brakes) - removal, overhaul
and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the notes at the beginning of
Sections 3 and 11 before proceeding. Before
dismantling a wheel cylinder, check that
replacement parts can be obtained, and retain
the old components to compare them with the
new ones
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”) positioned
under the body side members. Remove the
roadwheel.
2Fully release the handbrake.3Extract the drum securing screw and
remove the drum. If the drum is tight, remove
the plug from the inspection hole in the brake
backplate, and push the handbrake operating
lever towards the brake shoe to move the
shoes away from the drum. If necessary,
slacken the handbrake cable adjuster.
4Using a pair of pliers, unhook the upper
return spring from the brake shoes, noting its
orientation, then push the upper ends of the
shoes apart until they are clear of the wheel
cylinder (see illustration).
5Working under the bonnet, remove the
brake fluid reservoir cap and secure a piece of
polythene over the filler neck with a rubber
band, or by refitting the cap. This will reduce
the loss of fluid during the following
procedure.
6Unscrew the brake fluid pipe union nut from
the rear of the wheel cylinder, and disconnect
the pipe (see illustration). Take care not to
strain the pipe. Be prepared for fluid spillage,
and plug the open ends to prevent dirt ingress
and further fluid loss.
7Unscrew the two securing bolts from the
rear of the brake backplate, and withdraw the
wheel cylinder.
Overhaul
8If desired, the wheel cylinder can be
overhauled as follows. Otherwise, go on to
paragraph 17 for details of refitting.
9Brush the dirt and dust from the wheel
cylinder, but take care not to inhale it.
10Pull the rubber dust seals from the ends of
the cylinder body.
11The pistons will normally be ejected by
the pressure of the coil spring. If they are not,
tap the end of the cylinder body on a piece of
wood, or apply low air pressure (e.g. from a
foot pump), to the hydraulic fluid union hole in
the rear of the cylinder body, to eject the
pistons from their bores.
12Inspect the surfaces of the pistons and
their bores in the cylinder body for scoring, or
evidence of metal-to-metal contact. If evident,
renew the complete wheel cylinder assembly.
Note that the later type of wheel cylinder can
be used to replace the early type as a
complete unit.
Braking system 9•11
12.6 Unscrewing rear wheel cylinder brake
fluid pipe union12.4 Rear brake assembly
1 Wheel cylinder
2 Upper shoe return spring (note
orientation)
10.18 Withdrawing the rear brake disc -
DOHC model
9
Page 143 of 525
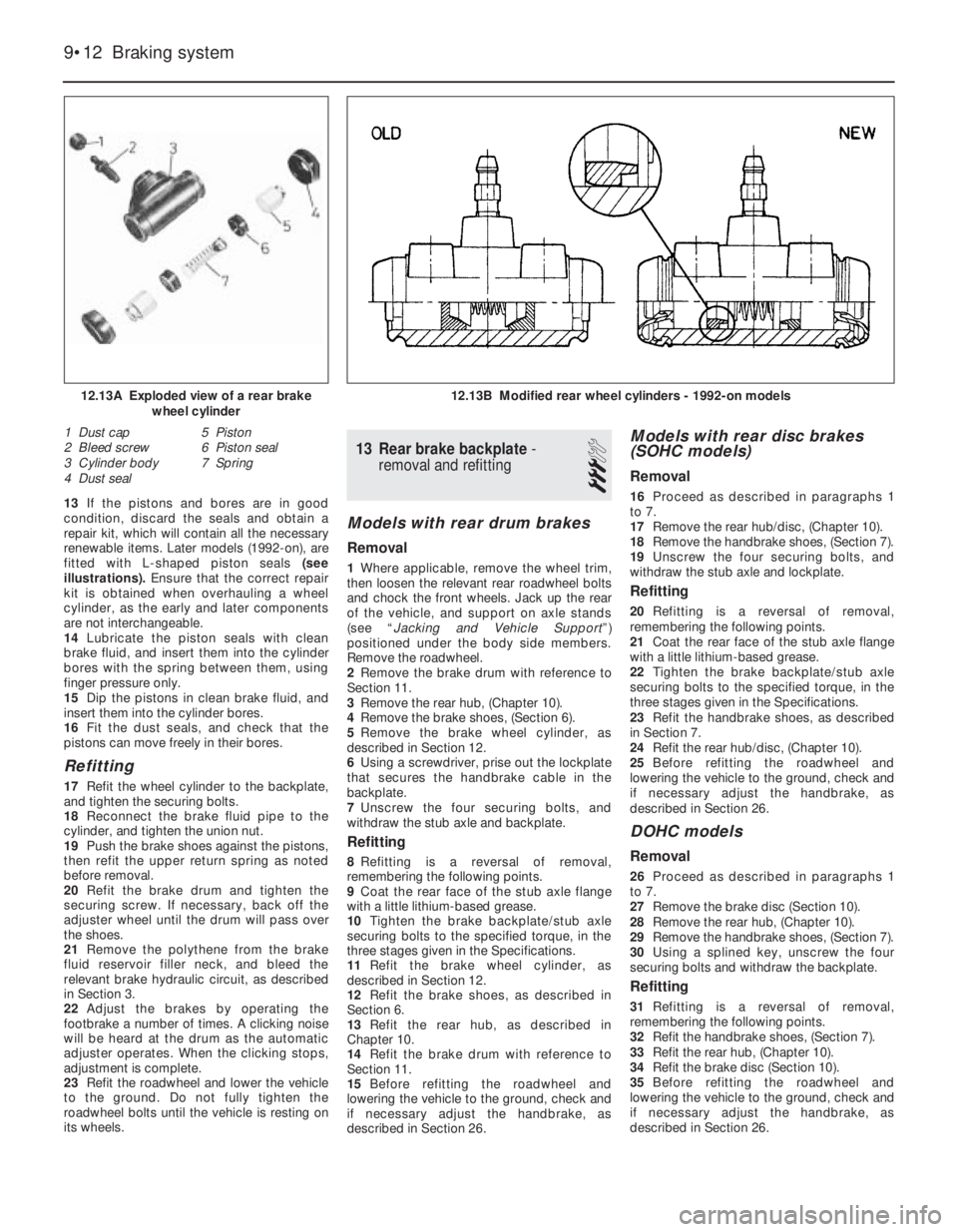
13If the pistons and bores are in good
condition, discard the seals and obtain a
repair kit, which will contain all the necessary
renewable items. Later models (1992-on), are
fitted with L-shaped piston seals (see
illustrations). Ensure that the correct repair
kit is obtained when overhauling a wheel
cylinder, as the early and later components
are not interchangeable.
14Lubricate the piston seals with clean
brake fluid, and insert them into the cylinder
bores with the spring between them, using
finger pressure only.
15Dip the pistons in clean brake fluid, and
insert them into the cylinder bores.
16Fit the dust seals, and check that the
pistons can move freely in their bores.
Refitting
17Refit the wheel cylinder to the backplate,
and tighten the securing bolts.
18Reconnect the brake fluid pipe to the
cylinder, and tighten the union nut.
19Push the brake shoes against the pistons,
then refit the upper return spring as noted
before removal.
20Refit the brake drum and tighten the
securing screw. If necessary, back off the
adjuster wheel until the drum will pass over
the shoes.
21Remove the polythene from the brake
fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed the
relevant brake hydraulic circuit, as described
in Section 3.
22Adjust the brakes by operating the
footbrake a number of times. A clicking noise
will be heard at the drum as the automatic
adjuster operates. When the clicking stops,
adjustment is complete.
23Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
13Rear brake backplate -
removal and refitting
3
Models with rear drum brakes
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel.
2Remove the brake drum with reference to
Section 11.
3Remove the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
4Remove the brake shoes, (Section 6).
5Remove the brake wheel cylinder, as
described in Section 12.
6Using a screwdriver, prise out the lockplate
that secures the handbrake cable in the
backplate.
7Unscrew the four securing bolts, and
withdraw the stub axle and backplate.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
9Coat the rear face of the stub axle flange
with a little lithium-based grease.
10Tighten the brake backplate/stub axle
securing bolts to the specified torque, in the
three stages given in the Specifications.
11Refit the brake wheel cylinder, as
described in Section 12.
12Refit the brake shoes, as described in
Section 6.
13Refit the rear hub, as described in
Chapter 10.
14Refit the brake drum with reference to
Section 11.
15Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
Models with rear disc brakes
(SOHC models)
Removal
16Proceed as described in paragraphs 1
to 7.
17Remove the rear hub/disc, (Chapter 10).
18Remove the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
19Unscrew the four securing bolts, and
withdraw the stub axle and lockplate.
Refitting
20Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
21Coat the rear face of the stub axle flange
with a little lithium-based grease.
22Tighten the brake backplate/stub axle
securing bolts to the specified torque, in the
three stages given in the Specifications.
23Refit the handbrake shoes, as described
in Section 7.
24Refit the rear hub/disc, (Chapter 10).
25Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
DOHC models
Removal
26Proceed as described in paragraphs 1
to 7.
27Remove the brake disc (Section 10).
28Remove the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
29Remove the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
30Using a splined key, unscrew the four
securing bolts and withdraw the backplate.
Refitting
31Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
32Refit the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
33Refit the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
34Refit the brake disc (Section 10).
35Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
9•12Braking system
12.13A Exploded view of a rear brake
wheel cylinder
1 Dust cap
2 Bleed screw
3 Cylinder body
4 Dust seal5 Piston
6 Piston seal
7 Spring
12.13B Modified rear wheel cylinders - 1992-on models
Page 146 of 525

42Where applicable, screw the pressure-
proportioning valves into the base of the
cylinder.
43Refit the master cylinder, as described in
Section 15.
17Master cylinder (ABS) -
general
The master cylinder fitted to models with
ABS cannot be dismantled, and no attempt
should be made at overhaul.
If faulty, the complete unit must be
renewed, as described in Section 15.
18Vacuum servo - description
and testing
Description
1The vacuum servo is fitted between the
brake pedal and the master cylinder, and
provides assistance to the driver when the
pedal is depressed, reducing the effort required
to operate the brakes. The unit is operated by
vacuum from the inlet manifold. With the brake
pedal released, vacuum is channelled to both
sides of the internal diaphragm. However,
when the pedal is depressed, one side of the
diaphragm is opened to atmosphere, resulting
in assistance to the pedal effort. Should the
vacuum servo develop a fault, the hydraulic
system is not affected, but greater effort will be
required at the pedal.
Testing
2The operation of the servo can be checked
as follows.
3With the engine stopped, destroy the
vacuum in the servo by depressing the brake
pedal several times.
4Hold the brake pedal depressed and start
the engine. The pedal should sink slightly as
the engine is started.
5If the pedal does not sink, check the servo
vacuum hose for leaks.
6If no defects are found in the vacuum hose,
the fault must lie in the servo itself.7No overhaul of the servo is possible, and if
faulty, the complete unit must be renewed.
19Vacuum servo - removal and
refitting
4
Note: During the 1989 model year, some
vehicles were produced with the brake pedal
height incorrectly set, resulting in the brake
pedal resting approximately 15.0 mm (0.6 in)
above the clutch pedal instead of 4.0 mm
(0.16 in below). The correct pedal height can
be set by adjusting the vacuum servo
operating fork dimension, as described in
paragraphs 15 and 16
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Working inside the vehicle, remove the
lower trim panel from the driver’s footwell.
3Disconnect the wiring plug from the brake
lamp switch, then twist the switch anti-
clockwise and remove it from its bracket.
4Pull the spring clip from the right-hand end
of the servo fork-to-pedal pivot pin.
5Using a pair of pliers, pull back the end of
the pedal return spring from the pedal, to
enable the servo fork-to-pedal pivot pin to be
removed. Withdraw the pivot pin.
6Remove the windscreen cowl panel, as
described in Chapter 11, then remove the
windscreen wiper motor and linkage as
described in Chapter 12.7Remove the coolant expansion tank as
described in Chapter 3.
8Pull the vacuum pipe from the brake servo.
9Unscrew the two securing nuts, and
carefully withdraw the brake master cylinder
from the studs on the servo. Move the master
cylinder forwards slightly, taking care not to
strain the brake pipes.
10Remove the two plugs covering the servo
securing bolts from the cowl panel (see
illustrations).
11Using a Allen key or hexagon bit, unscrew
the servo securing bolts and remove them
completely, then lift the servo from the
bulkhead (see illustrations).
12If desired, the mounting bracket can be
removed from the servo by unscrewing the
four securing nuts. Note that the bracket will
stick to the servo, as it is fitted with sealing
compound.
13The servo cannot be overhauled, and if
faulty, the complete unit must be renewed.
Refitting
14Before refitting the servo, check that the
operating fork dimension is correct as follows.
15Measure the distance from the end face of
the servo casing to the centre of the pivot pin
hole in the end of the operating fork. The
distance should be 144.0 mm (5.6 in). To
make accurate measurement easier, insert a
bolt or bar of similar diameter through the
pivot pin hole, and measure to the centre of
the bolt or bar (see illustration).
Braking system 9•15
19.11A Unscrew the securing bolts . . .19.15 Measuring the servo operating fork
dimension using a bolt inserted through
the pivot pin hole19.11B . . . and withdraw the servo
19.10B . . . to expose the servo securing
bolts19.10A Remove the plugs . . .
9
Page 149 of 525

8Disconnect the battery negative lead.
9Unclip the lid and open the relay box, then
pull out the relay (see illustration).
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, with
reference to paragraph 6.
24Rear brake pressure-
proportioning valves -
removal and refitting
4
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3 before proceeding. Note also that
the valve must only be renewed in pairs, and
both valves must be of the same calibration.
Ensure that correct type of valves are fitted.
The bodies have been stamped for easier
identification.
Master cylinder-mounted valves
Removal
1Remove the brake fluid reservoir cap, and
secure a piece of polythene over the filler
neck with a rubber band, or by refitting the
cap. This will reduce the loss of fluid during
the following procedure.
2Locate a container beneath the master
cylinder, to catch the brake fluid that will be
released.
3Identify the two lower brake pipes for
position, then unscrew the union nuts and
disconnect the pipes from the proportioning
valves in the base of the master cylinder. Plug
the open ends of the pipes to prevent dirt
ingress.
4Unscrew the proportioning valves from the
master cylinder, and plug the open ends of
the cylinder to prevent dirt ingress.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but on
completion, remove the polythene from the
brake fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed the
complete hydraulic system, as described in
Section 3.
Rear underbody-mounted valves
Removal
6Proceed as described in paragraph 1.
7Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle, and support securely on
axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) positioned under the body side
members.
8Working under the rear of the vehicle,
unscrew the union nut and disconnect the
brake pipe from one of the valves. Be
prepared for fluid spillage, and plug the open
end of the pipe to prevent dirt ingress and
further fluid spillage.
9Similarly, disconnect the flexible hose from
the valve.
10Pull the valve retaining clip from the
bracket on the underbody, noting that on
certain models, the retaining clip also secures
the ABS sensor wiring, and withdraw the valve
(see illustration).
11Repeat the procedure for the other valve.
Refitting
12Proceed as described in paragraph 5.
25Brake fluid pipes and hoses
- general, removal and refitting
4
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3, before proceeding.
General
1When checking the condition of the
system’s pipes and/or hoses, carefully check
that they do not foul other components such
as the power steering gear pipes (where
applicable), so that there is no risk of the
pipes chafing. If necessary use clips or ties to
secure braking system pipes and hoses well
clear of other components.
Rigid pipes
Removal
2Some of the commonly used brake pipes
can be obtained from Vauxhall parts dealers,
ready-formed and complete with unions, but
other brake pipes must be prepared using
4.75 mm (0.19 in) diameter brake pipe. Kits for
making the brake pipes can be obtained from
certain motor accessory shops.
3Before removing a brake pipe, remove the
brake fluid reservoir cap, and secure a piece
of polythene over the filler neck with a rubber
band, or by refitting the cap. This will reduce
the loss of fluid when the pipe is
disconnected.4Jack up the vehicle, and support securely
on axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) positioned under the body side
members.
5To remove a brake pipe, unscrew the
unions at each end, and release the pipe from
the retaining clips.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, taking
care not to overtighten the unions.
7On completion, remove the polythene from
the brake fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed
the relevant hydraulic circuit(s), as described
in Section 3.
Flexible hoses
Removal
8Proceed as described previously for the
rigid pipes, but note that a flexible pipe must
never be installed twisted, although a slight
“set” is permissible to give it clearance from
adjacent components.
Refitting
9When reconnecting a flexible hose to a
front brake caliper, note that the sealing rings
on the union bolt must be renewed.
26Handbrake - adjustment
2
Models with rear drum brakes
1The handbrake will normally be kept in
correct adjustment by the self-adjusting
action of the rear brake shoes. However, due
to cable stretch over a period of time, the
travel of the handbrake lever may become
excessive, in which case the following
operations should be carried out.
2Chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of
the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
3Fully release the handbrake.
4Turn the knurled nut on the cable adjuster
(mounted on the torsion beam), until the brake
shoes can just be heard to rub when the rear
wheels are turned by hand in the normal
direction of rotation (see illustration).
9•18Braking system
23.9 ABS surge arrester relay (arrowed)
26.4 Handbrake cable adjuster. Knurled
nut arrowed - all SOHC models24.10 Brake pressure-proportioning valve
on rear underbody - DOHC model
1 Valve 2 Retaining clip
Page 150 of 525
5Loosen the adjuster nut until the wheels are
just free to turn.
6The handbrake must start to operate with
the lever on the second notch of the ratchet.
7On completion of adjustment, check the
handbrake cables for free movement, and
apply a little grease to the adjuster threads to
prevent corrosion.
8Lower the vehicle to the ground.
Models with rear disc brakes
9Where applicable, remove the wheel trims,
then loosen the rear roadwheel bolts and
chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear of the
vehicle, and support securely on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheels.
10Pull the handbrake lever as far as the
second notch on the ratchet.
11On DOHC models fitted with a catalytic
converter, unscrew the four securing nuts and
withdraw the exhaust centre box heat shield
by carefully sliding it round the centre box.
12On all SOHC models, loosen the knurled
nut on the cable adjuster (mounted on the
torsion beam).
13On DOHC models, loosen the nut
securing the cable equaliser yoke to the
handbrake lever operating rod.
14Using a screwdriver inserted through the
adjuster hole in one of the discs/hubs (see
illustration), turn the adjuster wheel until the
brake shoes can just be heard to rub when the
disc/hub is turned by hand in the normal
direction of rotation.
15Turn the adjuster wheel back until the
disc/hub is just free to turn.
16Repeat paragraphs 14 and 15 on the
remaining side of the vehicle.
17Tighten the nut on the cable adjuster or
the equaliser, as applicable, until the brakeshoes just begin to operate. Check that the
shoes operate equally on both wheels.
18Fully release the handbrake, then apply it
again.
19The discs/hubs must lock when the
handbrake lever reaches the sixth notch on
the ratchet. If necessary, turn the nut on the
cable adjuster or equaliser, as applicable, to
achieve this.
20Where applicable, refit the exhaust heat
shield.
21Refit the roadwheels and lower the vehicle
to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
27Handbrake cable - removal
and refitting
3
Models with rear drum brakes
Removal
1The handbrake cable is in two sections. The
longer section runs from the handbrake
operating rod, through the adjuster, to the
right-hand brake assembly. The shorter
section runs from the adjuster to the left-hand
brake assembly. The two sections of the cable
can be renewed independently.
2Where applicable, remove the wheel trim(s),
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts.
Chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of the
vehicle, and support securely on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel(s).
3Note the routing of the handbrake cable(s),
as an aid to refitting.
4Remove the relevant brake drum(s), with
reference to Section 11.
Longer cable
Removal
5Note the length of exposed thread at the
handbrake cable adjuster on the torsion
beam, then unscrew the adjuster nut from the
threaded rod.
6Disconnect the cable from the handbrake
lever operating rod on the vehicle underbody
(see illustration).
7Detach the cable from the guides on the
underbody. Note that the cable can be fed
through certain guides, but in some cases, the
guide brackets must be bent away from the
underbody to allow the cable to be withdrawn.
8Detach the cable from the adjuster on the
torsion beam.
9Unhook the cable end from the lever on the
brake shoe, then using a screwdriver, prise
out the lockplate that secures the handbrake
cable in the backplate.
10Withdraw the cable from the vehicle,
releasing it from the guide on the torsion
beam.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
12Screw the adjuster nut onto the threaded
rod to the position noted before removal.
13Ensure that the handbrake cable is routed
as noted before removal.
14Refit the brake drum, (Section 11).
15Before refitting the roadwheel(s) and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, adjust the
handbrake, as described in Section 26.
Shorter cable
Removal
16Note the length of exposed thread at the
handbrake cable adjuster on the torsion
beam, then unscrew the adjuster nut from the
threaded rod. Continue as described in
paragraphs 8 to 10.
Braking system 9•19
27.6 Handbrake cable connection to handbrake lever operating
rod
1 Handbrake cable
2 Connecting link3 Handbrake lever operating rod26.14 Using a screwdriver to turn the handbrake adjuster wheel -
model with rear disc brakes
9