PONTIAC G3 2010 Owners Manual
Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 2010, Model line: G3, Model: PONTIAC G3 2010Pages: 368, PDF Size: 3.94 MB
Page 191 of 368

An MP3/WMA CD that was recorded using no file
folders can also be played. The system can support
up to eight folders in depth, though, keep the depth of
the folders to a minimum in order to keep down the
complexity and confusion in trying to locate a particular
folder during playback. If a CD contains more than the
maximum of 50 folders, five sessions, and 999 files,
the player lets you access and navigate up to the
maximum, but all items over the maximum are ignored.
Root Directory
The root directory is treated as a folder. If the root
directory has compressed audio files, the directory is
displayed as ROOT. All files contained directly under
the root directory are accessed prior to any other
directory.
Empty Directory or Folder
If a root directory or a folder exists somewhere in the
file structure that contains only folders/subfolders and
no compressed files directly beneath them, the player
advances to the next folder in the file structure that
contains compressed audio files. The empty folder
does not display.
No Folder
When a CD contains only compressed files, the files are
located under the root folder. The next and previous
folder function does not function on a CD that was
recorded without folders or playlists. When displaying
the name of the folder the radio displays ROOT.
When a CD contains only compressed audio files, but
no folders, all files are located under the root folder.
When the radio displays the name of the folder, the
radio displays ROOT.
Order of Play
The player play will begin from the first track under the
root directory. When all tracks from the root directory
have been played, play will continue from files
according to their numerical listing. After playing the last
track from the last folder, the player will begin playing
again at the first track of the first folder or root directory.
File System and Naming
The song name in the ID3 tag is displayed. If the song
name is not present in the ID3 tag, then the radio
displays the file name without the extension (such as
MP3/WMA) instead.
Track names longer than 32 characters or four pages
are shortened. Parts of words on the last page of text
and the extension of the filename does not display.
4-49
Page 192 of 368

Playing an MP3/WMA
With the ignition in the ON/RUN position, insert a CD
partway into the slot, label side up. The player pulls the
disc in. The CD should begin playing. As each new
track starts to play, the track number, and the song
name will appear on the display. If the ignition or radio
is turned off with a CD in the player, it will stay in the
player. When a CD is in the player and the ignition is
turned on, the radio must be turned on before the CD
will start playback. When the ignition and radio are
turned on, the CD will start playing where it stopped, if it
was the last selected audio source.
The CD player can play the smaller 8 cm (3 in) single
CDs with an adapter ring. Full-size CDs and the smaller
CDs are loaded in the same manner.
Sound quality may be reduced due to CD-R quality, the
method of recording, the quality of the music that has
been recorded, and the way the CD-R has been
handled.
DIR (Directory) :Press to repeat the tracks in the
current directory. DIR displays.
Press DIR again to repeat the tracks in all of the
directories. ALL displays.
Press DIR again to turn off repeat play.
uSEEKt(Next/Previous Folder) (in MP3/WMA
Mode): Press to change the folder. If CD-R does not
have any folders, “ROOT”flashes on the display for a
short time.
[TUNE (Next Track): Press the up TUNE arrow to
go to the next track. The track number displays. The
player continues moving forward through the CD each
time TUNE is pressed.
rTUNE (Previous Track): Press the down TUNE
arrow to go to the start of the current track. The track
number displays. The player continues moving
backward through the CD each time TUNE is pressed.
INFO/DISP (Information/Display) : Press to display
additional text information related to the current
MP3/WMA song. A choice of additional information
such as: Song Title, Album Title, and Artist. Bit rate
might also display.
When information is not available, No Info displays.
Press this button for longer than two seconds to change
display mode.
SCROLL (MP3/WMA Mode Only) : Press the SOUND
button for longer than two seconds. The song title or
other available information of a song scrolls on/off.
The offset is scroll on. The scroll mode can be changed
only when the SOUND button is pressed for longer than
two seconds.
4-50
Page 193 of 368
XM Radio Messages
UPDATING :The encryption code in the receiver is
being updated, and no action is required. This process
should take no longer than 30 seconds.
NO SIGNAL : The system is functioning correctly, but
the vehicle is in a location that is blocking the XM™
signal. When the vehicle is moved into an open area,
the signal should return.
LOADING : The audio system is acquiring and
processing audio and text data. No action is needed.
This message should disappear shortly.
OFF AIR : This channel is not currently in service.
Tune in to another channel.
CH UNAVAILABLE : This previously assigned channel
is no longer assigned. Tune to another station. If this
station was one of the presets, choose another station
for that preset button.
RADIO ID : If tuned to channel 0, this message
alternates with the XM™ Radio 8 digit radio ID label.
This label is needed to activate the service.
CHECK XM TUNER : If this message does not clear
within a short period of time, the receiver could have a
fault. Consult with your dealer/retailer.
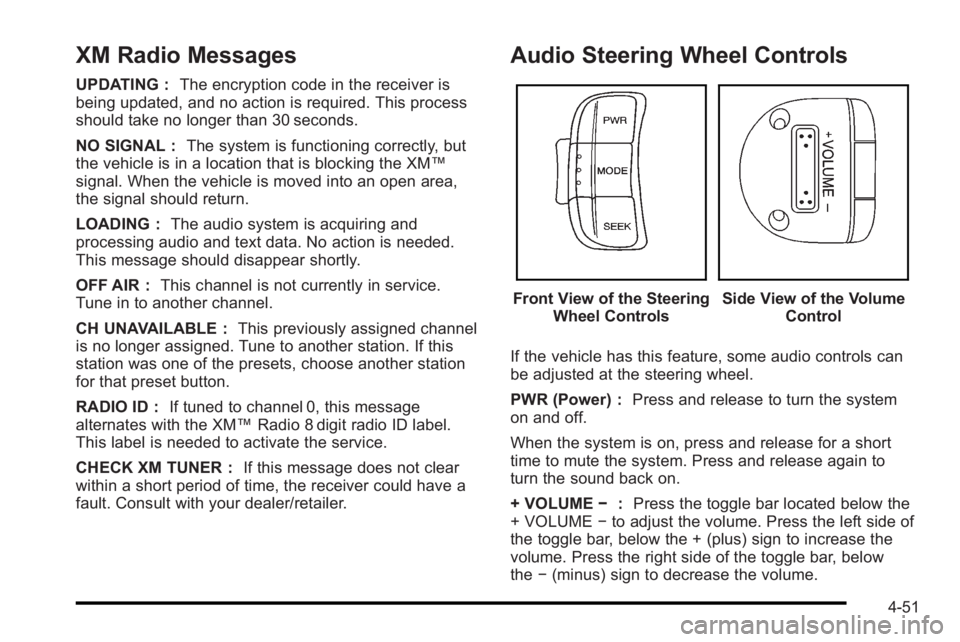
Audio Steering Wheel Controls
Front View of the Steering Wheel ControlsSide View of the Volume Control
If the vehicle has this feature, some audio controls can
be adjusted at the steering wheel.
PWR (Power) : Press and release to turn the system
on and off.
When the system is on, press and release for a short
time to mute the system. Press and release again to
turn the sound back on.
+ VOLUME −:Press the toggle bar located below the
+ VOLUME −to adjust the volume. Press the left side of
the toggle bar, below the + (plus) sign to increase the
volume. Press the right side of the toggle bar, below
the −(minus) sign to decrease the volume.
4-51
Page 194 of 368

MODE :Press and release this button multiple times
to cycle through the audio playback options that are
available on the vehicle. Options may include FM, AM,
XM, CD, and AUX.
SEEK : Press and release to go to the next preset
station.
Press and hold for a long time to go to the next AM, FM,
or XM station. The radio seeks stations only with a
strong signal that are in the selected band.
When playing a CD, press and release to go to the next
track. Press and hold to fast forward through the tracks.
Radio Reception
Frequency interference and static can occur during
normal radio reception if items such as cell phone
chargers, vehicle convenience accessories, and
external electronic devices are plugged into the
accessory power outlet. If there is interference or static,
unplug the item from the accessory power outlet.
AM
The range for most AM stations is greater than for FM,
especially at night. The longer range can cause station
frequencies to interfere with each other. For better radio
reception, most AM radio stations boost the power
levels during the day, and then reduce these levels
during the night. Static can also occur when things like
storms and power lines interfere with radio reception.
When this happens, try reducing the treble on the radio.
FM Stereo
FM signals only reach about 10 to 40 miles
(16 to 65 km). Although the radio has a built-in electronic
circuit that automatically works to reduce interference,
some static can occur, especially around tall buildings
or hills, causing the sound to fade in and out.
XM™ Satellite Radio Service
XM Satellite Radio Service gives digital radio reception
from coast-to-coast in the 48 contiguous United States,
and in Canada. Just as with FM, tall buildings or hills
can interfere with satellite radio signals, causing the
sound to fade in and out. In addition, traveling or
standing under heavy foliage, bridges, garages,
or tunnels may cause loss of the XM signal for a period
of time.
4-52
Page 195 of 368
Cellular Phone Usage
Cellular phone usage may cause interference with the
vehicle's radio. This interference may occur when
making or receiving phone calls, charging the
phone's battery, or simply having the phone on.
This interference causes an increased level of static
while listening to the radio. If static is received while
listening to the radio, unplug the cellular phone and
turn it off.
Fixed Mast Antenna (Hatchback)
Vehicles without OnStar®have a fixed mast antenna
that can withstand most car washes without being
damaged. If the mast should ever become slightly bent,
straighten it out by hand. If the mast is badly bent,
replace it.
Check occasionally to make sure the mast is still
tightened to the antenna base located on the roof of the
vehicle. If tightening is required, tighten by hand.
Backglass Antenna (Sedan)
Vehicles without OnStar®have the AM-FM antenna
integrated with the rear window defogger, located in the
rear window. Make sure that the inside surface of the
rear window is not scratched and that the lines on
the glass are not damaged. If the inside surface is
damaged, it could interfere with radio reception. Also,
for proper radio reception, the antenna connector at the
top-center of the rear window needs to be properly
attached to the post on the glass.
Notice: Using a razor blade or sharp object to clear
the inside rear window can damage the rear window
antenna and/or the rear window defogger. Repairs
would not be covered by the vehicle warranty. Do
not clear the inside rear window with sharp objects.
Notice: Do not apply aftermarket glass tinting with
metallic film. The metallic film in some tinting
materials will interfere with or distort the incoming
radio reception. Any damage caused to your
backglass antenna due to metallic tinting materials
will not be covered by the vehicle warranty.
Because this antenna is built into the rear window, there
is a reduced risk of damage caused by car washes and
vandals.
4-53
Page 196 of 368

If static is heard on the radio, when the rear window
defogger is turned on, it could mean that a defogger
grid line has been damaged. If this is true, the grid line
must be repaired.
If adding a cellular telephone to the vehicle, and the
antenna needs to be attached to the glass, make sure
that the grid lines for the AM-FM antenna are not
damaged. There is enough space between the grid
lines to attach a cellular telephone antenna without
interfering with radio reception.Multi-Band Antenna
Vehicles with OnStar®have a multi-band antenna that is
located on the roof of the vehicle. The antenna is used
for the AM/FM radio, OnStar
®and the XM™ Satellite
Radio Service System. Keep the antenna clear of
obstructions for clear reception. If the vehicle has a
sunroof, the performance of the AM/FM radio, OnStar
®,
and the XM system may be affected if the sunroof
is open.
4-54
Page 197 of 368

Section 5 Driving Your Vehicle
Your Driving, the Road, and the Vehicle. . . . . . . . . .5-2
Defensive Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Drunk Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Control of a Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Braking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Antilock Brake System (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Braking in Emergencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
Off-Road Recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Passing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Loss of Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Driving at Night . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9 Before Leaving on a Long Trip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
Highway Hypnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
Hill and Mountain Roads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
Winter Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
If Your Vehicle is Stuck in Sand, Mud, Ice,
or Snow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
Rocking Your Vehicle to Get It Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-14
Loading the Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-14
Towing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-25
Towing Your Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-25
Recreational Vehicle Towing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-25
Towing a Trailer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-27
5-1
Page 198 of 368

Your Driving, the Road, and the
Vehicle
Defensive Driving
Defensive driving means“always expect the
unexpected.” The first step in driving defensively is to
wear your safety belt —See Safety Belts: They Are for
Everyone on page 2‑15.
{WARNING:
Assume that other road users (pedestrians,
bicyclists, and other drivers) are going to be
careless and make mistakes. Anticipate what
they might do and be ready. In addition:
.Allow enough following distance between
you and the driver in front of you.
.Focus on the task of driving.
Driver distraction can cause collisions resulting in
injury or possible death. These simple defensive
driving techniques could save your life.
Drunk Driving
{WARNING:
Drinking and then driving is very dangerous. Your
reflexes, perceptions, attentiveness, and judgment
can be affected by even a small amount of
alcohol. You can have a serious —or even
fatal —collision if you drive after drinking. Do not
drink and drive or ride with a driver who has been
drinking. Ride home in a cab; or if you are with a
group, designate a driver who will not drink.
Death and injury associated with drinking and driving is
a global tragedy.
Alcohol affects four things that anyone needs to drive a
vehicle: judgment, muscular coordination, vision, and
attentiveness.
Police records show that almost 40 percent of all motor
vehicle-related deaths involve alcohol. In most cases,
these deaths are the result of someone who was
drinking and driving. In recent years, more than
17,000 annual motor vehicle-related deaths have been
associated with the use of alcohol, with about
250,000 people injured.
5-2
Page 199 of 368

For persons under 21, it is against the law in every
U.S. state to drink alcohol. There are good medical,
psychological, and developmental reasons for
these laws.
The obvious way to eliminate the leading highway
safety problem is for people never to drink alcohol
and then drive.
Medical research shows that alcohol in a person's
system can make crash injuries worse, especially
injuries to the brain, spinal cord, or heart. This means
that when anyone who has been drinking—driver or
passenger —is in a crash, that person's chance of
being killed or permanently disabled is higher than if
the person had not been drinking.
Control of a Vehicle
The following three systems help to control the vehicle
while driving —brakes, steering, and accelerator. At
times, as when driving on snow or ice, it is easy to ask
more of those control systems than the tires and road
can provide. Meaning, you can lose control of the
vehicle.
Adding non‐dealer/non‐retailer accessories can affect
vehicle performance. See Accessories and
Modifications on page 6‑3.
Braking
See Brake System Warning Light on page 4‑26.
Braking action involves perception time and reaction
time. Deciding to push the brake pedal is perception
time. Actually doing it is reaction time.
Average reaction time is about three‐fourths of a
second. But that is only an average. It might be less
with one driver and as long as two or three seconds or
more with another. Age, physical condition, alertness,
coordination, and eyesight all play a part. So do alcohol,
drugs, and frustration. But even in three‐fourths of a
second, a vehicle moving at 100 km/h (60 mph) travels
20 m (66 feet). That could be a lot of distance in an
emergency, so keeping enough space between the
vehicle and others is important.
And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of the road, whether it is pavement or
gravel; the condition of the road, whether it is wet, dry,
or icy; tire tread; the condition of the brakes; the weight
of the vehicle; and the amount of brake force applied.
Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive in
spurts, heavy acceleration followed by heavy braking,
rather than keeping pace with traffic. This is a mistake.
5-3
Page 200 of 368

The brakes might not have time to cool between hard
stops. The brakes will wear out much faster with a lot
of heavy braking. Keeping pace with the traffic and
allowing realistic following distances eliminates a lot
of unnecessary braking. That means better braking
and longer brake life.
If the engine ever stops while the vehicle is being
driven, brake normally but do not pump the brakes.
If the brakes are pumped, the pedal could get harder
to push down. If the engine stops, there will still be
some power brake assist but it will be used when the
brake is applied. Once the power assist is used up,
it can take longer to stop and the brake pedal will be
harder to push.
Adding non‐dealer/non‐retailer accessories can affect
vehicle performance. SeeAccessories and
Modifications on page 6‑3.
Antilock Brake System (ABS)
The vehicle might have the Antilock Brake
System (ABS), an advanced electronic braking
system that helps prevent a braking skid.
If the vehicle has ABS,
this warning light comes
on briefly when the
vehicle is started.
The warning light is on the instrument panel cluster.
See Antilock Brake System (ABS) Warning Light
on
page 4‑27.
Let us say the road is wet and you are driving safely.
Suddenly, an animal jumps out in front of you. You slam
on the brakes and continue braking. Here is what
happens with ABS:
A computer senses that the wheels are slowing down.
If one of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the
computer will separately work the brakes at each wheel.
ABS can change the brake pressure to each wheel, as
required, faster than any driver could. This can help the
driver steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As the brakes are applied, the computer keeps
receiving updates on wheel speed and controls braking
pressure accordingly.
5-4