flat tire PONTIAC GRAND AM 2003 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND AM, Model: PONTIAC GRAND AM 2003Pages: 354, PDF Size: 16.3 MB
Page 203 of 354

Here are some things you can check before a trip:
Windshield Washer Fluid: Is the resewior full? Are
all windows clean inside and outside?
Wiper Blades: Are they in good shape?
Fuel, Engine Oil, Other Fluids: Have you checked
all levels?
Lamps: Are they all working? Are the lenses clean?
Tires: They are vitally important to a safe,
trouble-free trip.
Is the tread good enough for
long-distance driving? Are the tires all inflated to the
recommended pressure?
Weather Forecasts: What’s the weather outlook
along your route? Should you delay your trip a
short time
to avoid a major storm system?
Maps: Do you have up-to-date maps?
Highway Hypnosis
Is there actually such a condition as “highway
hypnosis”? Or is it just plain falling asleep at the wheel?
Call it highway hypnosis, lack of awareness, or
whatever. There
is something about an easy stretch
of road with
the same scenery, along with the hum of the tires on the
road, the drone of the engine, and the rush of the
wind against the vehicle that can make you sleepy. Don’t
let
it happen to you! If it does, your vehicle can leave
the road in
less than a second, and you could crash and
be injured.
What can you
do about highway hypnosis? First, be
aware that it can happen.
Then here are some tips:
Make sure your vehicle is well ventilated, with a
comfortably cool interior.
Keep your eyes moving. Scan the road ahead and
to the sides. Check your rearview mirrors and your
instruments frequently.
service or parking area and take a nap, get some
exercise, or both. For safety, treat drowsiness
on the highway as an emergency.
If you get sleepy, pull off the road into a rest,
4-24
Page 204 of 354

Hill and Mountain Roads
Driving on steep hills or mountains is different from
drivina
w in flat or rollinq terrain.
If you drive regularly in steep country, or if you’re
planning to visit there, here are some tips that can make
your trips safer and more enjoyable.
Keep your vehicle in good shape. Check all fluid
levels and
also the brakes, tires, cooling system
and transaxle. These parts can work hard on
mountain roads.
Know how to go down hills. The most important
thing
to know is this: let your engine do some of
the
slowing down. Shift to a lower gear when you go
down a steep or lom hill.
If you don’t shift down, your brakes could get
so hot that they wouldn’t work well. You would
then have poor braking or even none going
down a
hill. You could crash. Shift down to let
your engine assist your brakes
on a steep
downhill
slope.
i
Coasting downhill in NEUTRAL (N) or with the
ignition
off is dangerous. Your brakes will have
to
do all the work ai siowing down. I ney cwdd
get so hot that they wouldn’t work well. You
would then have poor braking or even none going down a hill. You could crash. Always have your engine running and your vehicle in
I.
4-25
Page 214 of 354
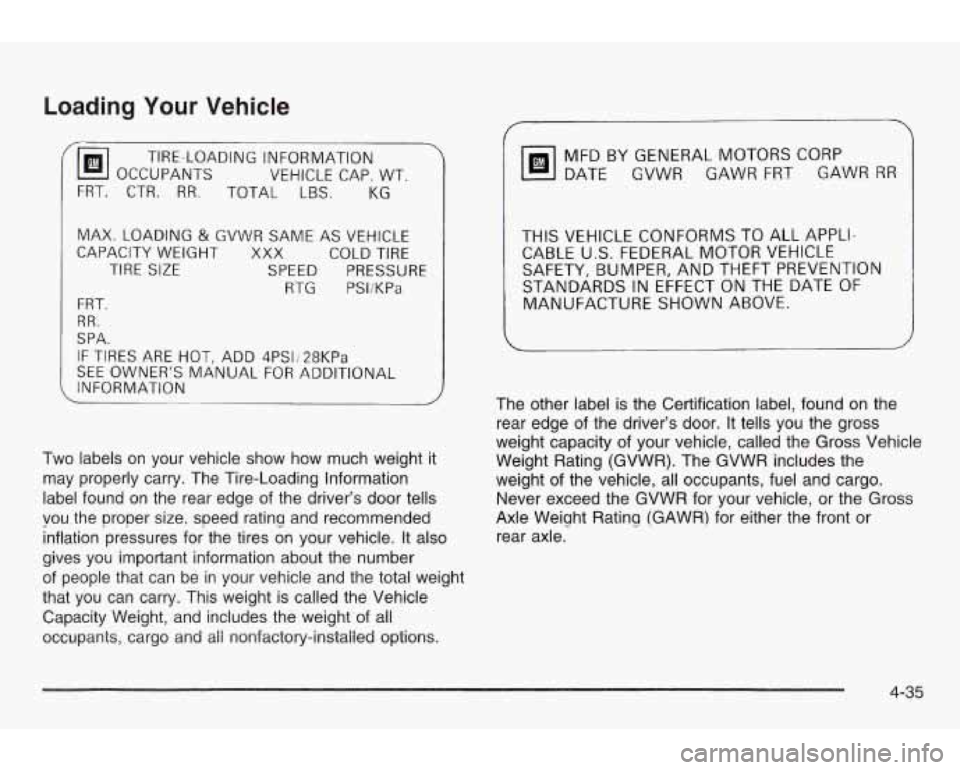
Loading Your Vehicle
'
OCCUPANTS VEHICLE CAP. WT.
TIRE-LOADING
INFORMATION
FRT. CTR.
RR. TOTAL LBS. KG
MAX. LOADING & GVWR SAME AS VEHICLE
CAPACITY WEIGHT
XXX COLD TIRE
TIRE
SIZE SPEED PRESSURE
RTG PSI/KPa
FRT.
RR.
SPA.
IF TIRES ARE HOT, ADD 4PS1128KPa
SEE OWNER'S MANUAL FOR ADDITIONAL
, INFORMATION
Two labels on your vehicle show how much weight it
may properly carry. The Tire-Loading Information
label found on the rear edge of the driver's door tells
you the proper size. speed ratinu and recommended
inflation pressures for the tires on your vehicle. It also
gives you important information about the number
of people that can be in your vehicle and the total weight
that you can carry. This weight is called the Vehicle
Capacity Weight, and includes the weight of all
occUpanfs, cargo and nonfac~ory~~ns~a~~e~ options.
7
MFD BY GENERAL MOTORS CORP
DATE GVWR GAWR FRT GAWR
RR
THIS VEHICLE CONFORMS TO ALL APPLI-
CABLE U.S. FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE
SAFETY, BUMPER, AND THEFT PREVENTION
STANDARDS
IN EFFECT ON THE DATE OF
MANUFACTURE SHOWN ABOVE.
The other label is the Certification label, found
on the
rear edge of the driver's door. It tells you the gross
weight capacity of your vehicle, called the Gross Vehicle
Weight Rating (GVWR). The GVWR includes the
weight of the vehicle, all occupants, fuel and cargo.
Never exceed the GVWR for your vehicle, or the Gross
Axle Weiqht Ratinq (GAWR) for either the front or
rear axle.
4-35
Page 218 of 354
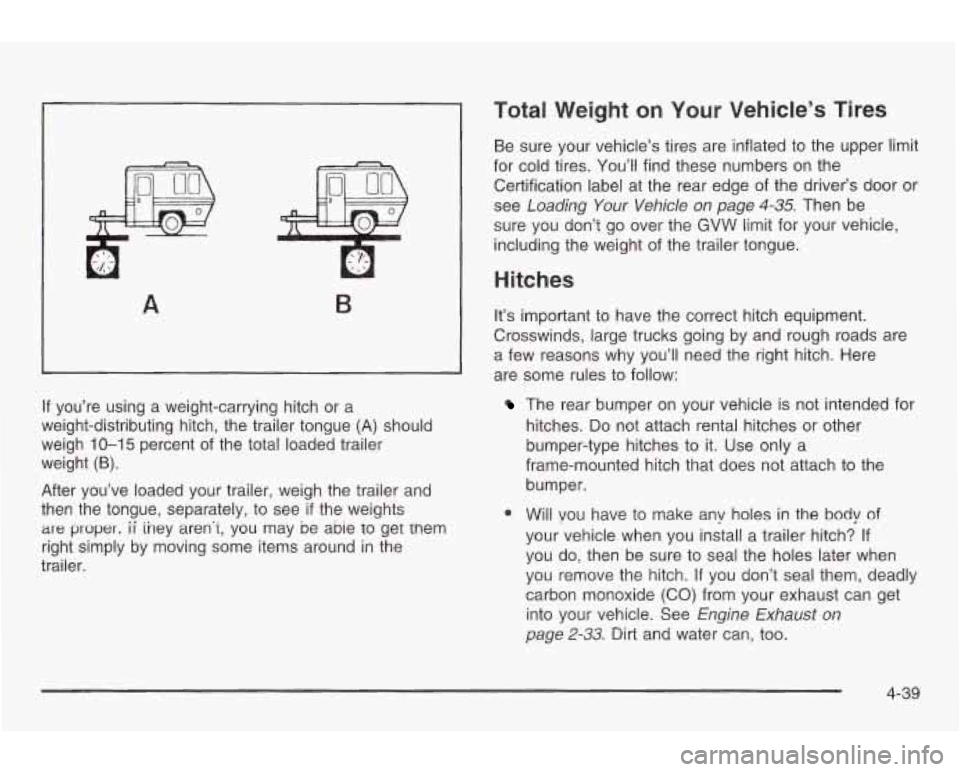
A B
If you’re using a weight-carrying hitch or a
weight-distributing hitch, the trailer tongue (A) should
weigh
10-15 percent of the total loaded trailer
weight
(6).
After you’ve loaded your trailer, weigh the trailer and
then the tongue, separately, to see
if the weights
are proper. ii iney aren’i, you may be abie to get tnem
right simply by moving some items around in the
trailer.
Total Weight on Your Vehicle’s Tires
Be sure your vehicle’s tires are inflated to the upper limit
for cold tires. You’ll find these numbers on the
Certification label at the rear edge of the driver’s door or
see
Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-35. Then be
sure you don’t go over the GVW limit for your vehicle,
including the weight of the trailer tongue.
Hitches
It’s important to have the correct hitch equipment.
Crosswinds, large trucks going by and rough roads are
a few reasons why you’ll need the right hitch. Here
are some rules
to follow:
The rear bumper on your vehicle is not intended for
hitches. Do not attach rental hitches or other
bumper-type hitches to it. Use only a
frame-mounted hitch that does not attach
to the
bumper.
0 Will vou have to make any holes in the body of
your vehicle when you install a trailer hitch? If
you do, then be sure to seal the holes later when
you remove the hitch.
If you don’t seal them, deadly
carbon monoxide
(CO) from your exhaust can get
into your vehicle. See
Engine Exhaust on
page 2-33. Dirt ana water can, too.
4-39
Page 224 of 354
Section 5 Service and Appearance Care
Service ............................................................ 5.3
Doing Your Own Service Work
......................... 5.3
Adding Equipment to the Outside of Your
Vehicle
...................................................... 5.4
Fuel ................................................................ 5.5
Gasoline Octane
............................................ 5.5
Gasoline Specifications
.................................... 5.5
California Fuel
............................................... 5-6
Additives
....................................................... 5-6
Fuels in Foreign Countries
............................... 5-7
Filling
a Portable Fuel Container ..................... -5-9
Filling Your Tank
............................................ 5-7
Checking Things Under the Hood
.................................................... 5-10
Hood Release
.............................................. 5-10
Engine Compartment Overview
....................... 5-12
Engine Oil
................................................... 5.15
Engine Air CleanedFilter
................................ 5-21
Manual Transaxle Fluid
.................................. 5-22
Hydraulic Clutch
........................................... 5-23
Engine Coolant
............................................. 5-23
Engine Overheating
....................................... 5-26
Cooling System
............................................ 5-29
Power Steering Fiuia
~1-36
I~~ULWIII~LIW I 1ulIaUAlG I lulu J-LL An ntnmntie Trnnr.r-.vln Cln #;PI r on ..............................
- -- ....................................
Windshield Washer Fluid ................................ 5-37
Brakes
........................................................ 5.39
Battery
........................................................ 5.42
Jump Starting
............................................... 5-43
Bulb Replacement .......................................... 5.49
Halogen Bulbs
.............................................. 5.49
Headlamps
.................................................. 5.49
Front Turn Signal and Parking Lamps
.............. 5-50
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp (CHMSL)
......... 5.50
Taillamps, Turn Signal, and Stoplamps
............ 5.51
Replacement Bulbs
....................................... 5.51
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
.............. 5.52
Tires
.............................................................. 5.53
Inflation
.. Tire Pressure ................................ 5-54
Tire Inspection and Rotation
........................... 5-55
When It
Is Time for New Tires ....................... 5-56
Buying New Tires
......................................... 5-56
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
......................... 5-57
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
.................. 5-59
Wheel Replacement
...................................... 5-59
Tire Chains
.................................................. 5-60
If a Tire Goes Flat ........................................ 5-61
Changing
a Flat Tire ..................................... 5-62
Compact Spare Tire
...................................... 5-71
5-
1
Page 276 of 354

Ti res
I
CAUTION: (Continued)
Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by --
a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions
about your tire warranty and where to obtain service, 0 Underinflated tires pose the same danger
see your Pontiac Warranty booklet for details. as overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check
all tires
I
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result
of too much
friction. You could have an air-out and a
serious accident. See “Loading Your
Vehicle” in the Index.
CAUTION: (Continued)
I
I
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked
when your tires are cold.
Overinflated tires are more likely to be
cut, punctured or broken by
a sudden
impact
- such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
0 Worn, old tires can cause accidents. If
your tread
is badly worn, or if your tires
have been damaged, replace them.
5-53
Page 277 of 354

Inflation -- Tire Pressure
The Tire-Loading Information label, which is on the rear
edge of the driver’s door, shows the correct inflation
pressures for your tires when they’re cold. “Cold” means
your vehicle has been sitting for at least three hours
or driven no more than
1 mile (1.6 km).
Notice: Don’t let anyone tell you that underinflation
or overinflation is
all right. It’s not. If your tires
don’t have enough air (underinflation), you can get
the following:
Too much flexing
0 Too much heat
Tire overloading
Bad wear
@ Bad handling
0 Bad fuel economy
If your tires have too much air (overinflation), you
can get the following:
0 Unusual wear
Bad handling
Rough ride
0 Needless damage from road hazards
When to Check
Check your tires once a month or more.
Don’t forget your compact spare tire.
It should be at
60 psi (420 kPa).
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure. You can’t tell
if your tires are properly inflated
simply by looking at them. Radial tires may look
properly inflated even when they’re underinflated.
Be sure to put the valve caps back on the valve stems.
They help prevent leaks by keeping out dirt and
moisture.
5-54
Page 278 of 354
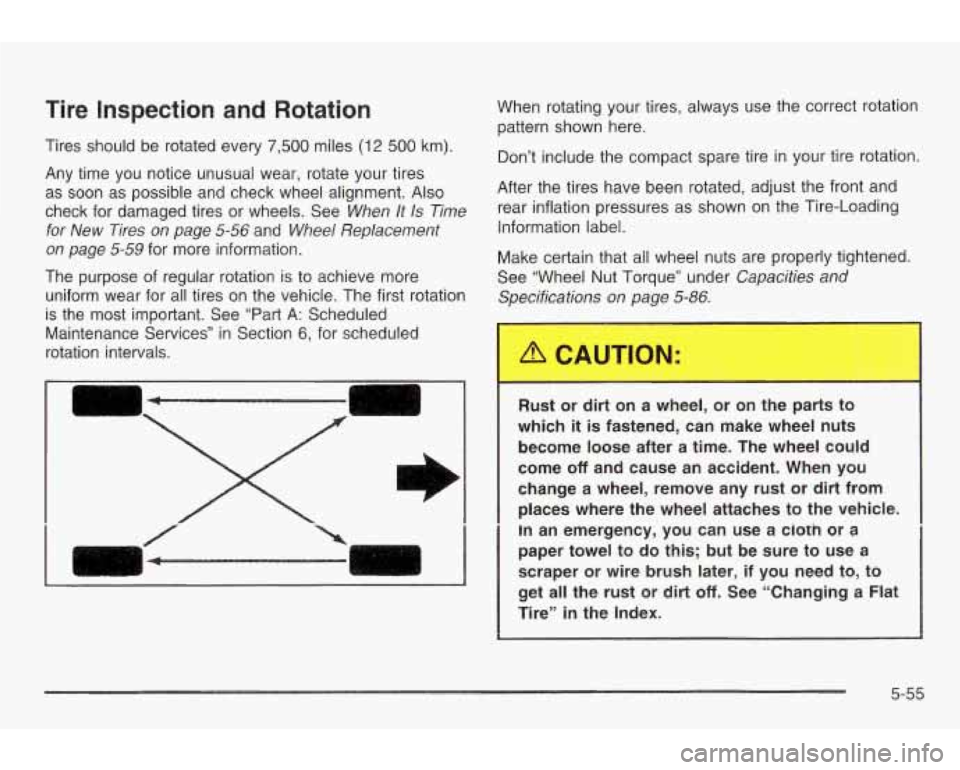
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be rotated every 7,500 miles (12 500 km).
Any time you notice unusual wear, rotate your tires
as soon as possible and check wheel alignment.
Also
check for damaged tires or wheels. See When It Is Time
for New Tires on page 5-56
and Wheel Replacement
on page 5-59
for more information.
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first rotation
is the most important. See “Part A: Scheduled
Maintenance Services” in Section
6, for scheduled
rotation intervals.
n 4 J
1
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Don’t include the compact spare tire in your tire rotation.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown on the Tire-Loading
Information label.
Make certain that all wheel nuts are properly tightened.
See “Wheel Nut Torque” under
Capacities and
Specifications on page 5-86.
.
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to
which
it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change
a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle.
In an emergency, you can use a ciorh or a
paper towel to
do this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later,
if you need to, to
get all the rust or dirt
off. See “Changing a Flat
Tire”
in the Index.
5-55
Page 281 of 354
Treadwear Temperature - A, B, C
The
treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on
the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified government test course.
For example, a tire graded
150 would wear one and
a half
(1.5) times as well on the government course as
a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires
depends upon the actual conditions of their use,
however, and may depart significantly from the norm
due
to variations in driving habits, service practices and
differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction - AA, A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are AA, A,
B, and C. Those grades represent the tire’s ability
to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete.
A tire marked C may have poor
traction performance. Warning: The traction grade
assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking
traction tests, and does not include acceleration,
cornering, hydroplaning, or peak traction characteristics. The
temperature grades are
A (the highest), B, and C,
representing the tire’s resistance to the generation
of heat and its ability
to dissipate heat when tested
under controlled conditions on a specified indoor
laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can
cause the material of the tire
to degenerate and
reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade
C corresponds to a
level of performance which all passenger car tires must
meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of
performance
on the laboratory test wheel than the
minimum required by law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination,
can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
5-58
Page 282 of 354

Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
The wheels on your vehicle were aligned and balanced
carefully at the factory
to give you the longest tire life
and best overall performance.
Scheduled wheel alignment and wheel balancing are
not needed. However,
if you notice unusual tire wear or
your vehicle pulling one way or the other, the alignment
may need to be reset.
If you notice your vehicle
vibrating when driving on a smooth road, your wheels
may need to be rebalanced.
Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked or badly rusted
or corroded. If wheel nuts keep coming loose, the
wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts should be replaced.
If the wheel leaks air, replace it (except some
aluminum wheels, which can sometimes be repaired).
See your dealer
if any of these conditions exist.
Your dealer will know the kind of wheel you need.
Each new ~hppl shnulc! hae the qqme inauj-carryin~
capacity, diameter, width, offset and be mounted
the same way as the one it replaces.
If you need to replace any of your wheels, wheel bolts
or wheel nuts, replace them only with new
GM
original equipment parts. This way, you will be sure to
have the right wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts
for your vehicle. Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel
bolts or wheel nuts on your vehicle can be
dangerous.
It could affect the braking and
handling
of your vehicle, make your tires lose
air and make you lose control. You could have a collision in which you or others could be
injured. Always use the correct wheel, wheel
bolts and wheel nuts for replacement.
Notice: The wrong wheel can also cause problems
with bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper height,
vehicle ground clearance and tire or tire chain
clearance to the body and chassis.
See
Changing a flat Tire on page 5-62 for more
information.
5-59