steering Ram 1500 2015 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: RAM, Model Year: 2015, Model line: 1500, Model: Ram 1500 2015Pages: 871, PDF Size: 24.83 MB
Page 584 of 871

with a separate computer to modulate hydraulic pressure
to prevent wheel lockup and help avoid skidding on
slippery surfaces.
The system’s pump motor runs during an ABS stop to
provide regulated hydraulic pressure. The pump motor
makes a low humming noise during operation. This is
normal.
The ABS conducts a low-speed selftest at about 10 mph
(16 km/h). If you have your foot lightly on the brake
while this test is occurring, you may feel slight pedal
movement. The movement can be more apparent on ice
and snow. This is normal.
When you are in a severe braking condition involving
use of the ABS, you will experience some pedal drop as
the vehicle comes to a complete stop. This is the result of
the system reverting to the base brake system and is
normal.
Engagement of the ABS may be accompanied by a
pulsing sensation. You may also hear a clicking noise.
These occurrences are normal, and indicate that the
system is functioning.
WARNING!
•Pumping of the anti-lock brakes will diminish
their effectiveness and may lead to a collision.
Pumping makes the stopping distance longer. Just
press firmly on your brake pedal when you need to
slow down or stop.
•The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) cannot prevent
the natural laws of physics from acting on the
vehicle, nor can it increase braking or steering
efficiency beyond that afforded by the condition of
the vehicle brakes and tires or the traction afforded.
(Continued)
582 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 589 of 871

WARNING!(Continued)
•HSA is not a parking brake. If you stop the vehicle
on a hill without putting the transmission in PARK
or using the parking brake, it will roll down the
incline and could collide with another vehicle,
object or person, and cause serious or fatal injury.
Always remember to use the parking brake while
parking on a hill and that the driver is responsible
for braking the vehicle.
HSA Off
HSA is a Customer Programmable Feature in the EVIC/
DID. If you wish to turn off the HSA feature, refer to
“Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)/Driver
Information Display (DID)” in “Understanding Your
Instrument Panel” for further information.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
The ESC system enhances directional control and stabil-
ity of the vehicle under various driving conditions. ESC
corrects for oversteering or understeering of the vehicle
by applying the brake of the appropriate wheel to assist
in counteracting the oversteer or understeer condition.
Engine power may also be reduced to help the vehicle
maintain the desired path.
ESC uses sensors in the vehicle to determine the vehicle
path intended by the driver and compares it to the actual
path of the vehicle. When the actual path does not match
the intended path, ESC applies the brake of the appro-
priate wheel to assist in counteracting the oversteer or
understeer condition.
•Oversteer - when the vehicle is turning more than
appropriate for the steering wheel position.
•Understeer - when the vehicle is turning less than
appropriate for the steering wheel position.
5
STARTING AND OPERATING 587
Page 596 of 871

Activating HDC
Once HDC is enabled it will activate automatically if
driven down a grade of sufficient magnitude (greater
than approximately 8%). The set speed for HDC is
selectable by the driver, and can be adjusted by using the
Electronic range switches located on steering column
shifter. The following summarizes the HDC set speed:
GearApproximate HDC Set Speed
PNo set speed. HDC may be en-
abled but will not activate
R0.6 mph (1 km/h)
N1.2 mph (2 km/h)
1st0.6 mph (1 km/h)
2nd1.2 mph (2 km/h)
GearApproximate HDC Set Speed
3rd1.8 mph (3 km/h)
4th2.5 mph (4 km/h)
5th3.1 mph (5 km/h)
6th3.7 mph (6 km/h)
7th4.3 mph (7 km/h)
8th5.0 mph (8 km/h)
9th5.6 mph (9 km/h)
NOTE:During HDC the ERS +/- shifter input is used for
HDC target speed selection but will not affect the gear
chosen by the transmission. During HDC the transmis-
sion will shift appropriately for the driver-selected set
speed and corresponding driving conditions.
594 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 610 of 871

WARNING!
Overloading of your tires is dangerous. Overloading
can cause tire failure, affect vehicle handling, and
increase your stopping distance. Use tires of the
recommended load capacity for your vehicle. Never
overload them.
TIRES — GENERAL INFORMATION
Tire Pressure
Proper tire inflation pressure is essential to the safe and
satisfactory operation of your vehicle. Four primary areas
are affected by improper tire pressure:
•Safety and Vehicle Stability
•Economy
•Tread Wear
•Ride Comfort
Safety
WARNING!
•Improperly inflated tires are dangerous and can
cause collisions.
•Under-inflation increases tire flexing and can re-
sult in overheating and tire failure.
•Over-inflation reduces a tire’s ability to cushion
shock. Objects on the road and chuckholes can
cause damage that result in tire failure.
•Overinflated or under-inflated tires can affect ve-
hicle handling and can fail suddenly, resulting in
loss of vehicle control.
•Unequal tire pressures can cause steering prob-
lems. You could lose control of your vehicle.
(Continued)
608 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 611 of 871

WARNING!(Continued)
•Unequal tire pressures from one side of the vehicle
to the other can cause the vehicle to drift to the
right or left.
•Always drive with each tire inflated to the recom-
mended cold tire inflation pressure.
Both under-inflation and over-inflation affect the stability
of the vehicle and can produce a feeling of sluggish
response or over responsiveness in the steering.
NOTE:
•Unequal tire pressures from side to side may cause
erratic and unpredictable steering response.
•Unequal tire pressure from side to side may cause the
vehicle to drift left or right.
Economy
Underinflated tires will increase tire rolling resistance
resulting in higher fuel consumption.
Tread Wear
Improper cold tire inflation pressures can cause abnor-
mal wear patterns and reduced tread life, resulting in the
need for earlier tire replacement.
Ride Comfort And Vehicle Stability
Proper tire inflation contributes to a comfortable ride.
Over-inflation produces a jarring and uncomfortable
ride.
5
STARTING AND OPERATING 609
Page 622 of 871

WARNING!
•Do not use a tire, wheel size or rating other than
that specified for your vehicle. Some combinations
of unapproved tires and wheels may change sus-
pension dimensions and performance characteris-
tics, resulting in changes to steering, handling, and
braking of your vehicle. This can cause unpredict-
able handling and stress to steering and suspen-
sion components. You could lose control and have
a collision resulting in serious injury or death. Use
only the tire and wheel sizes with load ratings
approved for your vehicle.
•Never use a tire with a smaller load index or
capacity, other than what was originally equipped
on your vehicle. Using a tire with a smaller load
index could result in tire overloading and failure.
You could lose control and have a collision.
(Continued)
WARNING!(Continued)
•Failure to equip your vehicle with tires having
adequate speed capability can result in sudden tire
failure and loss of vehicle control.
CAUTION!
Replacing original tires with tires of a different size
may result in false speedometer and odometer read-
ings.
SUPPLEMENTAL TIRE PRESSURE INFORMATION —
IF EQUIPPED
A light load vehicle condition is defined as two passen-
gers [150 lbs (68 kg) each] plus 200 lbs (91 kg) of cargo.
Cold tire inflation pressures for a lightly loaded vehicle
will be found on the face of the driver’s door.
620 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 625 of 871
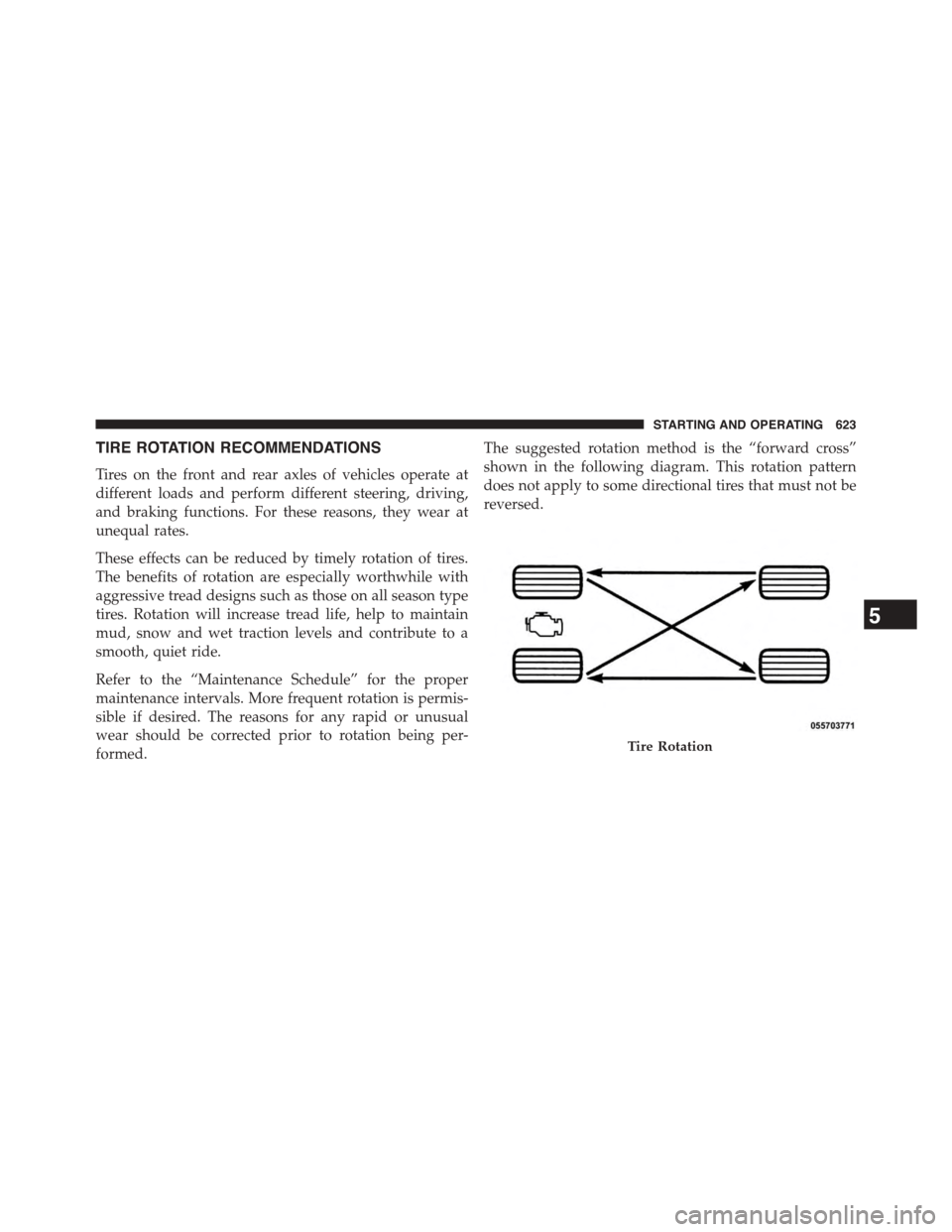
TIRE ROTATION RECOMMENDATIONS
Tires on the front and rear axles of vehicles operate at
different loads and perform different steering, driving,
and braking functions. For these reasons, they wear at
unequal rates.
These effects can be reduced by timely rotation of tires.
The benefits of rotation are especially worthwhile with
aggressive tread designs such as those on all season type
tires. Rotation will increase tread life, help to maintain
mud, snow and wet traction levels and contribute to a
smooth, quiet ride.
Refer to the “Maintenance Schedule” for the proper
maintenance intervals. More frequent rotation is permis-
sible if desired. The reasons for any rapid or unusual
wear should be corrected prior to rotation being per-
formed.
The suggested rotation method is the “forward cross”
shown in the following diagram. This rotation pattern
does not apply to some directional tires that must not be
reversed.
Tire Rotation
5
STARTING AND OPERATING 623
Page 652 of 871

Frontal Area
The frontal area is the maximum height multiplied by the
maximum width of the front of a trailer.
Trailer Sway Control
The trailer sway control can be a mechanical telescoping
link that can be installed between the hitch receiver and
the trailer tongue that typically provides adjustable fric-
tion associated with the telescoping motion to dampen
any unwanted trailer swaying motions while traveling.
If equipped, the electronic Trailer Sway Control (TSC)
recognizes a swaying trailer and automatically applies
individual wheel brakes and/or reduces engine power to
attempt to eliminate the trailer sway.
Weight-Carrying Hitch
A weight-carrying hitch supports the trailer tongue weight,
just as if it were luggage located at a hitch ball or some other
connecting point of the vehicle. These kinds of hitches are
the most popular on the market today and they are com-
monly used to tow small and medium sized trailers.
Weight-Distributing Hitch
A weight-distributing system works by applying lever-
age through spring (load) bars. They are typically used
for heavier loads to distribute trailer tongue weight to the
tow vehicle’s front axle and the trailer axle(s). When used
in accordance with the manufacturer’s directions, it pro-
vides for a more level ride, offering more consistent
steering and brake control, thereby enhancing towing
safety. The addition of a friction/hydraulic sway control
also dampens sway caused by traffic and crosswinds and
contributes positively to tow vehicle and trailer stability.
Trailer sway control and a weight distributing (load
equalizing) hitch are recommended for heavier Tongue
Weights (TW) and may be required depending on vehicle
and trailer configuration/loading to comply with GAWR
requirements.
650 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 661 of 871
WARNING!(Continued)
•When hauling cargo or towing a trailer, do not
overload your vehicle or trailer. Overloading can
cause a loss of control, poor performance or dam-
age to brakes, axle, engine, transmission, steering,
suspension, chassis structure or tires.
•Safety chains must always be used between your
vehicle and trailer. Always connect the chains to
the hook retainers of the vehicle hitch. Cross the
chains under the trailer tongue and allow enough
slack for turning corners.
•Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a
grade. When parking, apply the parking brake on
the tow vehicle. Put the tow vehicle transmission in
PARK. For four-wheel drive vehicles, make sure
the transfer case is not in NEUTRAL. Always,
block or%chock%the trailer wheels.
(Continued)
WARNING!(Continued)
•GCWR must not be exceeded.
•Total weight must be distributed between the tow
vehicle and the trailer such that the following four
ratings are not exceeded:
1. GVWR
2. GTW
3. GAWR
4. Tongue weight rating for the trailer hitch uti-
lized.
5
STARTING AND OPERATING 659
Page 665 of 871

sliding the manual brake control lever will display the
GAIN setting for 10 seconds and the “Trailer Brake Status
Indicator Light” will not be displayed.
If a fault is detected in the trailer wiring or the Integrated
Trailer Brake Module (ITBM), the “Trailer Brake Status
Indicator Light” will flash.
GAIN Adjustment Buttons (+/-)
Pressing these buttons will adjust the brake control
power output to the trailer brakes in 0.5 increments. The
GAIN setting can be increased to a maximum of 10 or
decreased to a minimum of 0 (no trailer braking).
GAIN
The GAIN setting is used to set the trailer brake control
for the specific towing condition and should be changed
as towing conditions change. Changes to towing condi-
tions include trailer load, vehicle load, road conditions
and weather.
Adjusting GAIN
NOTE:This should only be performed in a traffic free
environment at speeds of approximately 20–25 mph
(30–40 km/h).
1. Make sure the trailer brakes are in good working
condition, functioning normally and properly ad-
justed. See your trailer dealer if necessary.
2.Hook up the trailer and make the electrical connections
according to the trailer manufacturer’s instructions.
3. When a trailer with electric/EOH brakes is plugged
in, the trailer connected message should appear in the
EVIC/DID (if the connection is not recognized by the
ITBM, braking functions will not be available), the
GAIN setting will illuminate and the correct type of
trailer must be selected from the EVIC/DID options.
4. Press the UP or DOWN button on the steering wheel
until “TRAILER TOW” appears on the screen.
5
STARTING AND OPERATING 663