Seat Exeo 2012 Owner's Guide
Manufacturer: SEAT, Model Year: 2012, Model line: Exeo, Model: Seat Exeo 2012Pages: 317, PDF Size: 5.29 MB
Page 21 of 317

19
Seat belts
Why wear seat belts? Physical principles of frontal collisions
In the event of a frontal collision, a large amount of kinetic
energy must be absorbed.
Fig. 6 Vehicle about to
hit a wall: the occupants
are not wearing seat
belts
Fig. 7 The vehicle hits
the wall: the occupants
are not wearing seat
belts
It is easy to explain how the laws of physics work in the case of a head-on
collision: When a vehicle starts moving ⇒ Fig. 6, a certain amount of energy
known as kinetic energy is produced in the vehicle and its occupants.
The amount of kinetic energy depends on the speed of the vehicle and the
weight of the vehicle and its passengers. The higher the speed and the
greater the weight, the more energy there is to be released in an accident.
The most significant factor, however, is the speed of the vehicle. If the
speed doubles from 25 km/h to 50 km/h, for example, the kinetic energy is
multiplied by four.
Because the passengers in our example are not restrained by seat belts, in
the case of a head-on collision all of their kinetic energy has to be absorbed
at the point of impact ⇒ Fig. 7.
Even at speeds of 30 km/h to 50 km/h, the forces acting on bodies in a col-
lision can easily exceed one tonne (1000 kg). At greater speed these forces
are even higher.
Passengers not wearing seat belts are not “attached” to the vehicle. In a
head-on collision, they will move forward at the same speed their vehicle
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 22 of 317
20Seat belts
was travelling just before the impact. This example applies not only to
head-on collisions, but to all accidents and collisions.
The danger of not using the seat belt
The general belief that the passengers can protect them-
selves with their hands in a minor collision is false.
Fig. 8 A driver not wear-
ing a seat belt is thrown
forward violently.
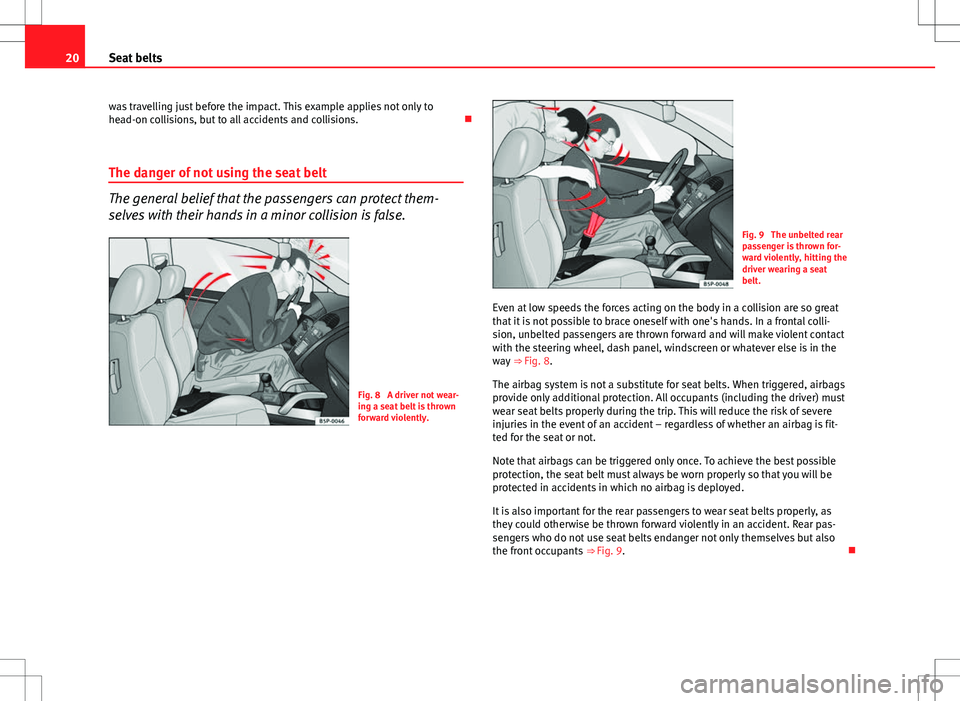
Fig. 9 The unbelted rear
passenger is thrown for-
ward violently, hitting the
driver wearing a seat
belt.
Even at low speeds the forces acting on the body in a collision are so great
that it is not possible to brace oneself with one's hands. In a frontal colli-
sion, unbelted passengers are thrown forward and will make violent contact
with the steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen or whatever else is in the
way ⇒ Fig. 8.
The airbag system is not a substitute for seat belts. When triggered, airbags
provide only additional protection. All occupants (including the driver) must
wear seat belts properly during the trip. This will reduce the risk of severe
injuries in the event of an accident – regardless of whether an airbag is fit-
ted for the seat or not.
Note that airbags can be triggered only once. To achieve the best possible
protection, the seat belt must always be worn properly so that you will be
protected in accidents in which no airbag is deployed.
It is also important for the rear passengers to wear seat belts properly, as
they could otherwise be thrown forward violently in an accident. Rear pas-
sengers who do not use seat belts endanger not only themselves but also
the front occupants ⇒ Fig. 9.
Page 23 of 317

21
Seat belts
Seat belt protection
Passengers not wearing seat belts risk severe injuries in the
event of an accident.
Fig. 10 A driver wearing
the seat belt properly is
secured by the belt in
sharp braking
Properly worn seat belts hold the vehicle occupants in the correct sitting po-
sitions and substantially reduce the kinetic energy in the event of an acci-
dent. Seat belts also help to prevent uncontrolled movements that could
lead to severe injuries. In addition, properly worn seat belts reduce the dan-
ger of being thrown from the vehicle.
Passengers wearing their seat belts correctly benefit greatly from the ability
of the belts to absorb kinetic energy. The front part of your vehicle and other
passive safety features (such as the airbag system) are also designed to ab-
sorb the kinetic energy released in a collision. Taken together, all these fea-
tures reduce the releasing kinetic energy and consequently, the risk of in-
jury.
Our examples describe frontal collisions. Of course, properly worn seat belts
substantially reduce the risk of injury in all other types of accidents. This is
why it is so important to fasten seat belts before every trip, even when "just
driving around the corner". Ensure that your passengers wear their seat belts as well. Accident statistics
have shown that wearing seat belts is an effective means of substantially
reducing the risk of injury and improving the chances of survival in a seri-
ous accident. Furthermore, properly worn seat belts improve the protection
provided by airbags in the event of an accident. For this reason, wearing a
seat belt is required by law in most countries.
Although your vehicle is equipped with airbags, the seat belts must be fas-
tened and worn. The front airbags, for example, are only triggered in some
frontal accidents. The front airbags will not be triggered during minor frontal
collisions, minor side collisions, rear collisions, overturns or accidents in
which the airbag trigger threshold value in the control unit is not exceeded.
Therefore, you should always wear your seat belt and ensure that your pas-
sengers have fastened their seat belts properly before you drive off!
Safety instructions on using seat belts
If seat belts are used correctly, they can reduce the risk of in-
jury in an accident.
– Always wear the seat belt as described in this section.
– Ensure that the seat belts can be fastened at all times and are
not damaged.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 24 of 317

22Seat belts
WARNING
● If the seat belts are worn incorrectly or not at all, the risk of severe
injuries increases. The optimal protection from seat belts can be ach-
ieved only if you use them properly.
● Fasten your seat belt before every trip - even when driving in town.
The other passengers must also wear the seat belts at all times, other-
wise they run the risk of being injured.
● The seat belt cannot offer its full protection if the seat belt is not
positioned correctly.
● Never allow two passengers (even children) to share the same seat
belt.
● Keep both feet in the footwell in front of your seat as long as the vehi-
cle is in motion.
● Never unbuckle a seat belt while the vehicle is in motion. Risk of fatal
injury.
● The seat belt must never be twisted while it is being worn.
● The seat belt should never lie on hard or fragile objects (such as
glasses or pens, etc.) because this can cause injuries.
● Do not allow the seat belt to be damaged or jammed, or to rub on any
sharp edges.
● Never wear the seat belt under the arm or in any other incorrect posi-
tion.
● Loose, bulky clothing (such as an overcoat over a jacket) impairs the
proper fit and function of the belts, reducing their capacity to protect.
● The slot in the seat belt buckle must not be blocked with paper or
other objects, as this can prevent the latch plate from engaging securely.
● Never use seat belt clips, retaining rings or similar instruments to al-
ter the position of the belt webbing.WARNING (Continued)
● Frayed or torn seat belts or damage to the connections, belt retrac-
tors or parts of the buckle could cause severe injuries in the event of an
accident. Therefore, you must check the condition of all seat belts at reg-
ular intervals.
● Seat belts which have been worn in an accident and stretched must
be replaced by a specialised workshop. Renewal may be necessary even
if there is no apparent damage. The belt anchorage should also be
checked.
● Do not attempt to repair a damaged seat belt yourself. The seat belts
must not be removed or modified in any way.
● The belts must be kept clean, otherwise the retractors may not work
properly ⇒ page 219.
Page 25 of 317

23
Seat belts
Seat belts
Seat belt adjustment
The seat belts for the front and rear occupants are locked in-
to position by a latch.
Fig. 11 Belt buckle and
latch plate of seat belt
The seat belt cannot offer its full protection if the seat belt is not
positioned correctly.
– Adjust the seat and head restraint correctly.
– To fasten the belt, take hold of the latch plate and pull it slowly
across your chest and lap.
– Insert the latch into the buckle for the appropriate seat and
push it down until it is securely locked with a click ⇒ Fig. 11.
– Pull the belt to ensure that the latch plate is securely engaged
in the buckle. The seat belts are equipped with an automatic retractor on the shoulder
strap. Full freedom of movement is permitted when the shoulder belt is
pulled slowly. However, during sudden braking, during travel in steep areas
or bends and during acceleration, the automatic retractor on the shoulder
belt is locked.
The automatic belt retractors on the front seats are fitted with seat belt ten-
sioners
⇒ page 27.
WARNING
● An incorrectly worn seat belt can cause severe injuries in the event of
an accident.
● The seat belts offer best protection only when the backrests are in an
upright position and the seat belts have been fastened properly.
● Never put the latch plate in the buckle of another seat. If you do this,
the seat belt will not protect you properly and the risk of injury is in-
creased.
● If an occupant is incorrectly belted in, the belt cannot protect him or
her properly. An incorrectly positioned seat belt can cause extremely se-
vere injuries.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 26 of 317

24Seat belts
Seat belt position
Seat belts offer their maximum protection only when they
are properly positioned.
Fig. 12 Correct seat belt
and head restraint posi-
tions, viewed from front
Fig. 13 Correct seat belt
and head restraint posi-
tions, viewed from side The following features are available to adjust the seat belt in the shoulder
region:
●
belt height adjustment for the front seats.
● front seat height adjustment*.
WARNING
● An incorrectly worn seat belt can cause severe injuries in the event of
an accident.
● The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie on the centre of the shoul-
der, never across the neck. The seat belt must lie flat and snugly on the
torso ⇒ Fig. 12.
● The lap part of the seat belt must lie across the pelvis, never across
the stomach. The seat belt must lie flat and snugly on the pelvis
⇒ Fig. 13. Pull the belt tight if necessary to take up any slack.
● Read and observe the warnings ⇒ page 21.
Page 27 of 317

25
Seat belts
Pregnant women must also fasten their seat belts properly
The best protection for the unborn child is for the mother to
wear the seat belt properly at all times during the pregnan-
cy.
Fig. 14 Positioning seat
belts during pregnancy
The seat belt provides maximum protection only when the seat belt
is properly positioned ⇒ page 24.
– Adjust the front seat and head restraint correctly ⇒ page 10.
– Holding the latch plate, pull the belt evenly across your chest
and as low as possible over the pelvis ⇒ Fig. 14.
– Insert the latch plate into the buckle for the appropriate seat
and push it down until it is securely locked with a click ⇒
.
– Pull the belt to ensure that the latch plate is securely engaged
in the buckle.
WARNING
● An incorrectly worn seat belt can cause severe injuries in the event of
an accident.
● For pregnant women, the lap part of the seat belt must lie as low as
possible over the pelvis, never across the stomach, and always lie flat so
that no pressure is exerted on the abdomen.
● Read and observe the warnings ⇒ page 21.
Seat belt release
The seat belt must not be unfastened until the vehicle has
come to a standstill.
Fig. 15 Removing latch
plate from buckle
– Press the red button on the belt buckle ⇒
Fig. 15. The latch
plate is released and springs out ⇒
.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 28 of 317

26Seat belts
–Guide the belt back by hand so that it rolls up easily and the
trim is not damaged
WARNING
Never unbuckle a seat belt while the vehicle is in motion. If you do, you
increase the risk of sustaining severe or fatal injuries.
Seat belt height adjustment
Seat belt height adjusters can be used to adjust the height
of the shoulder area of the seat belt.
Fig. 16 Belt height ad-
juster
The belt height adjuster can be lowered by keeping the button
pressed down at the same time.
– Press button ⇒
Fig. 16 1
to adjust the belt height. –
Take hold of the top guide fitting and slide it up or down so that
the shoulder part of the seat belt is positioned roughly midway
over the shoulder, although it must never rest against the neck
⇒ Fig. 16 2
⇒ in Seat belt position on page 24.
– After adjusting, pull the belt sharply to check that the catch on
the guide fitting is engaged securely.
Note
It is also possible to adjust the height of the front seats to obtain the best
position for the front seat belts.
Incorrectly fastened seat belts
Incorrectly worn seat belts can cause severe or even mortal
injuries. Seat belts can provide optimal protection only if the belt web is
properly worn. The seat belts must be fastened exactly in the order
described in this chapter. An incorrect sitting position impairs sub-
stantially the protection a seat belt offers and can lead to severe or
fatal injuries. The risk of severe or fatal injuries is especially in-
creased when a deploying airbag strikes an occupant who has as-
sumed an incorrect sitting position. As the driver, you are responsi-
ble for all vehicle occupants, especially children. Therefore:
– Never allow anyone to wear the seat belt incorrectly while the
vehicle is moving ⇒
.
Page 29 of 317

27
Seat belts
WARNING
● An incorrectly worn seat belt increases the risk of severe injuries.
● Before every trip, instruct your passengers to adjust their seat belts
properly and to wear them for the whole journey.
● Read and always observe information and warnings concerning the
use of seat belts ⇒ page 21.
Seat belt tensioners
Function of the seat belt tensioner
During a frontal collision, the seat belts on the front seats
are retracted automatically. The seat belts for the front occupants are equipped with belt tensioners.
Sensors will trigger the belt tensioners during severe head-on, lateral and
rear collisions only if the seat belt is being worn. This retracts and tightens
the seat belts, reducing the forward motion of the occupants.
The seat belt tensioner can be triggered only once.
The seat belt tensioners will not be triggered in the event of a light frontal,
side or rear collision, if the vehicle overturns or in situations where no large
forces act on the front, side or rear of the vehicle.
Note
● If the seat belt tensioners are triggered, a fine dust is produced. This is
normal and it is not an indication of fire in the vehicle.
● The relevant safety requirements must be observed when the vehicle or
components of the system are scrapped. Specialised workshops are famili-
ar with these regulations, which are also available to you. Service and disposal of belt tensioners
The belt tensioners are components of the seat belts that are installed in
the seats of your vehicle. If you work on the belt tensioners or remove and
install parts of the system when performing other repair work, the seat belt
may be damaged. The consequence may be that, in the event of an acci-
dent, the belt tensioners function incorrectly or not at all.
So that the effectiveness of the seat belt tensioner is not reduced and that
removed parts do not cause any injuries or environmental pollution, regula-
tions, which are known to the specialised workshops, must be observed.
WARNING
● Improper use or repairs not carried out by qualified mechanics in-
crease the risk of severe or fatal injuries. The belt tensioners may fail to
trigger or may trigger in the wrong circumstances.
● Never attempt to repair, adjust, remove or install parts of the belt ten-
sioners or seat belts.
● The seat belt tensioner, seat belt and automatic retractor cannot be
repaired.
● Any work on the belt tensioners and seat belts, including the removal
and refitting of system parts in conjunction with other repair work, must
be performed by a specialised workshop only.
● The belt tensioners will only provide protection for one accident and
must be changed if they have been activated.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 30 of 317

28Airbag system
Airbag system
Brief introduction Why wear a seat belt and assume the correct sitting
position?
For the inflating airbags to achieve the best protection, the
seat belt must always be worn properly and the correct sit-
ting position must be assumed.For your own safety and the safety of the passengers, please en-
sure the following before driving:
– Always wear the seat belt properly ⇒ page 18.
– Adjust the driver seat and the steering wheel correctly
⇒ page 10.
– Adjust the front passenger seat correctly ⇒ page 11.
– Adjust the head restraint correctly ⇒ page 13.
– Use the correct child restraint system to protect children in your
vehicle ⇒ page 46.
The airbag is deployed at high speed in fractions of a second. If you have an
incorrect seating position at the time the airbag is deployed, it could cause
you critical injuries. Therefore, it is essential that all passengers in the vehi-
cle assume a correct sitting position while travelling.
A sharp braking before an accident may cause a passenger not wearing a
seat belt to be thrown forward into the area of the deploying airbag. In this case, the inflating airbag may inflict critical or fatal injuries on the occupant.
This also applies to children.
Always maintain the greatest possible distance between yourself and the
front airbag. This way, the front airbags can completely deploy when trig-
gered, providing their maximum protection.
The most important factors that will trigger an airbag are: the type of acci-
dent, the angle of collision and the speed of the vehicle.
Whether the airbags are triggered depends primarily on the vehicle deceler-
ation rate resulting from the collision and detected by the control unit. If the
vehicle deceleration occurring during the collision and measured by the
control unit remains below the specified reference values, the front, side
and/or curtain airbag will not be triggered. Take into account that the visible
damage in a vehicle involved in an accident, no matter how serious, is not a
determining factor for the airbags to have been triggered.
WARNING
● Wearing the seat belt incorrectly or assuming an incorrect sitting po-
sition can lead to critical or fatal injuries.
● All occupants, including children, who are not properly belted can
sustain critical or fatal injuries if the airbag is triggered. Children up to
12 years old should always travel on the rear seat. Never transport chil-
dren in the vehicle if they are not restrained or the restraint system is not
appropriate for their age, size or weight.
● If you are not wearing a seat belt, if you lean forward or to the side
while travelling or assume an incorrect sitting position, there is a sub-
stantially increased risk of injury. This increased risk of injury will be fur-
ther increased if you are struck by an inflating airbag.