SKODA CITIGO 2012 1.G Owner's Manual
Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2012, Model line: CITIGO, Model: SKODA CITIGO 2012 1.GPages: 157, PDF Size: 3.9 MB
Page 101 of 157
CAUTION
The temperature of the water used for cleaning must not exceed 60 °C – risk of
damaging the vehicle. ÐPreserving and polishing the vehicle paintwork
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Preserving the vehicle paintwork
Good wax treatment is an effective way of protecting the paintwork from harmful
environmental influences.
The vehicle must be treated with a high-quality hard wax polish at the latest,
when no more drops form on the clean paintwork.
A new layer of a high-quality hard wax polish can be applied to the clean body-
work after it has dried thoroughly. Even if you use a wax preserver regularly we
still recommend that you treat the paintwork of the vehicle at least twice a year
with hard wax.
Polishing
Polishing is necessary if the vehicle's paintwork has become unattractive and if it
is no longer possible to achieve a gloss with wax preservatives.
If the polish does not contain any preserving elements, the paint must be treated
with a preservative afterwards. CAUTION
■ Never apply wax to the windows.
■ Mat painted or plastic parts must not be treated with polishing products or hard
waxes. ■ Do not polish the paintwork of the vehicle in a dusty environment, otherwise
the paintwork can be scratched. ÐChrome parts
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.ä
ä First clean the chrome parts with a damp cloth and then polish them with a soft,
dry cloth. If this method does not completely clean chrome parts, use a specific
chrome care product. CAUTION
Do not polish the chrome parts in a dusty environment, otherwise they can be
scratched. Ð Paint damage
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Slight damage to paintwork such as scratches, scuffs or traces of chip damage
must be treated immediately.
The ŠKODA Service Partners have a range of matching
touch-up pens or spray
cans available in the colour of your vehicle. Note
We recommend that any repairs to damaged paintwork are carried out by a
ŠKODA Service Partner. Ð Plastic parts
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Plastic parts can be cleaned using a damp cloth. If this does not prove to be ade-
quate, the parts can be treated with special solvent-free plastic cleaning prod-
ucts.
Paint care products are not suitable for plastic parts. Ð
ä
ä
99
Taking care of and cleaning the vehicle
Page 102 of 157

De-icing windows and exterior mirrors
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Use a plastic ice scraper for removing snow and ice from the windows and mir-
rors. The ice scraper should not be moved forward and backward but in one direc-
tion to avoid any damage to the surface of the glass.
Clean the windows from the inside on a regular basis.
Dry the glass surfaces with a clean chamois leather or a cloth intended for this
purpose.
When drying the windows after washing the vehicle, do not use window leathers
that have been used to polish the bodywork. Residues of preservatives in the
window leather can dirty the window and reduce visibility. CAUTION
■ Never remove snow or ice from glass parts using warm or hot water – risk of
formation of cracks in the glass!
■ When removing snow or ice from windows and mirror lenses ensure that the
paintwork of the vehicle is not to damage.
■ Snow or ice that is contaminated with coarse dirt such as fine gravel, sand, and
salt must not be removed from the window glass and mirrors – risk of damage to
the surface of the windows and mirrors. ÐRadio reception
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Car parks, tunnels, tall buildings or mountains can disrupt the radio signal even
causing it to fail completely. ÐHeadlight lenses
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Use soap and clean water to clean the plastic headlight lenses.ä
ä
ä CAUTION
■ Never wipe the headlights dry and do not use any sharp objects to clean the
plastic lenses, this may damage the protective paintwork and consequently cause
the formation of cracks on the headlight lenses.
■ Do not use any aggressive cleaning or chemical solvent products to clean the
headlights – risk of damaging the headlight lenses. Ð Rubber seals
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
The rubber seals on doors, the sliding roof and other windows remain smoother
and last longer if the seals are treated regularly with a suitable rubber care prod-
uct. This helps to prevent leakages and premature wear of the seals. Rubber
seals which are well cared for also do not stick together in cold winter weather.
Ð Door lock cylinders
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Specific products must be used for de-icing door lock cylinders.
Note
■ When washing your vehicle, ensure as little water as possible gets into the lock-
ing cylinders. ■ We recommend that suitable materials from ŠKODA Original Accessories are
used for maintaining the door lock cylinders. Ð
ä
ä
100 General Maintenance
Page 103 of 157

Wheels
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Wheel rims
Also thoroughly wash the wheel rims when washing the vehicle on a regular ba-
sis. Regularly remove salt and brake abrasion from the wheel rims otherwise the
material will be affected. Damage to the paint layer on the wheel rims must be
touched up immediately.
Light alloy wheels
After washing thoroughly and treat the wheel rims with a protective product for
light alloy wheels. Products which cause abrasion must not be used to treat the
wheel rims. WARNING
Water, ice and grit in the brake system can affect the braking efficiency – risk
of accident! CAUTION
Severe layers of dirt on the wheels can also result in wheel imbalance. This may
show itself in the form of a wheel vibration which is transmitted to the steering
wheel which, in certain circumstances, can cause premature wear of the steering.
This means it is necessary to remove the dirt. Note
We recommend that any repairs to damaged paintwork are carried out by a
ŠKODA Service Partner. ÐUnderbody protection
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
The underside of your vehicle is protected for life against chemical and mechani-
cal influences.ä
ä As damage to the
protective layer when driving cannot be ruled out completely,
we recommend that you inspect the protective layer on the underside of your ve-
hicle and on the chassis at specific intervals – preferably at the beginning and end
of the winter.
ŠKODA Service Partners have suitable spray products and the necessary equip-
ment available, and are familiar with the instructions for use. We therefore rec-
ommend that touch-up work or additional corrosion protection measures are car-
ried out by a ŠKODA Service Partner. WARNING
Never use additional underbody protection or anti-corrosion agents for ex-
haust pipes, catalytic converters or heat shields. When the engine reaches its
operating temperature, these substances might ignite – risk of fire! Ð Protection of hollow spaces
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
All the cavities of your vehicle which are at risk from corrosion are protected for
life by a layer of protective wax applied in the factory.
This wax protection does not require to be inspected or re-treated. If any small
amount of wax flow out of the cavities at high temperatures, these must be re-
moved with a plastic scraper and the stains cleaned using a petroleum cleaner. WARNING
Safety regulations should be observed when using petroleum cleaner to re-
move wax – risk of fire! Ð Artificial leather and materials
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
The artificial leather can be cleaned using a damp cloth. If this does not prove to
be adequate, these parts can only be treated with special
solvent-free plastic
cleaning and care products . £
ä
ä
101
Taking care of and cleaning the vehicle
Page 104 of 157

Clean upholstery cover materials and cloth trims on doors, luggage compartment
cover, etc. using specific cleaning agents, e.g., dry foam. Use a soft sponge, brush,
or commercially available microfibre cloth. Use a cloth and a specific cleaning
agent to clean the roof trim.
Some clothing materials, such as dark denim, do, in part, not have sufficient col-
our fastness. This can cause damage or clearly visible discolouration to seat cov-
ers (fabric or leather) even when used correctly. This particularly applies to light
seat covers (fabric or leather). This is not a defect in the seat cover, but poor col-
our fastness of the clothing textiles. ÐFabric covers on electrically heated seats
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Do not clean the seat covers
using moisture as this can damage the seat heating
system.
Use a specific cleaning agent such as dry foam or similar to clean the covers. ÐNatural leather
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Depending on the amount of wear-and-tear, the leather should be cleaned on a
regular basis.
Normal cleaning
Clean soiled areas of the leather with slightly moistened cotton or woollen cloth.
Severe soiling
Ensure that the leather is not soaked through at any point and that no water gets
into the stitching of the seams.
Dry off the leather with a soft, dry cloth.
Removing stains
Remove fresh water-based stains (e.g., coffee, tea, juices, blood) with an absorb-
ent cloth or household cleaning paper. A specific cleaning agent is required for
dried-on stains.
ä
ä
Remove fresh
grease-based stains (e.g. butter, mayonnaise, chocolate, etc.) with
an absorbent cloth, household cleaning paper, or use a suitable cleaner if the
stain has not yet penetrated into the surface.
Use a grease solvent for grease stains which have dried in.
Remove specific stains (e.g. ball-point pens, marker pen, nail varnish, dispersion
paint, shoe polish, etc.) with a special stain remover suitable for leather.
Leather care
Treat the leather roughly every six months with a suitable leather care product.
Apply only a small amount of the cleaning and care product.
Dry off the leather with a soft, dry cloth. CAUTION
■ Avoid leaving the vehicle for lengthy periods in bright sunlight to avoid the
leather from bleaching. If the vehicle is parked in the open for lengthy periods,
protect the leather from direct sunlight by covering it.
■ Sharp-edged objects on items of clothing such as zip fasteners, rivets, sharp-
edged belts, jewellery and pendants may leave permanent scratches or signs of
rubbing on the surface.
■ The use of a mechanical steering wheel lock may damage the leather surface of
the steering wheel. Note
■ Use a care cream with light blocker and impregnation effect on a regular basis
and each time after cleaning. The cream nourishes the leather, allows it to
breathe and keeps it supple and also provides moisture. It also creates surface
protection. ■ Clean the leather every 2 to 3 months, remove any fresh stains as they occur.
■ Also look after the leather dye. Refresh any areas with a special coloured leath-
er cream as required.
■ The leather is a natural material with specific properties. During the use of the
vehicle, minor optical changes can occur on the leather parts of the covers (e. g
wrinkles or creases as a result of the stress of the covers). Ð
102 General Maintenance
Page 105 of 157

Seat belts
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Keep the seat belts clean!
Clean dirty seat belts using a mild soapy solution and remove coarse dirt with a
soft brush!
Check the condition of all the seat belts on a regular basis.
Belt webbing which has become severely soiled may prevent the inertia reel from
reeling up the belt properly. WARNING
■ The seat belts must not be removed for cleaning.
■ Never clean the seat belts chemically as chemical cleaning products could
destroy the fabric. The seat belts must also not be allowed to come into con-
tact with corrosive liquids (such as acids etc.).
■ Seat belts which have damage to the webbing, connections, inertia reel or
lock should be replaced by a ŠKODA specialist garage.
■ Inertia reel belts must be completely dried before being reeled up. Ðä
103
Taking care of and cleaning the vehicle
Page 106 of 157

Inspecting and replenishing
Fuel
ä
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Refuelling 104
Unleaded petrol 105
Vehicles running on CNG (compressed natural gas) » page 106.
The correct type of fuel for your vehicle and the tyre size and inflation pressure
are specified on the inside of the fuel filler flap » Fig. 95 on page 104
.WARNING
The national legal requirements must be observed if carrying a spare canister
in the vehicle. We do not recommend carrying any fuel canisters in your vehi-
cle for safety reasons. In the event of an accident, the canister might be dam-
aged and fuel may leak out – risk of fire! CAUTION
■ Never drive until the fuel tank is completely empty! The irregular supply of fuel
can cause misfiring, which can result in considerable damage to parts of the en-
gine and exhaust system. ■ Immediately remove any fuel that has spilled onto the vehicle's paintwork – risk
of paint damage! Ð Refuelling
Fig. 95
Filler flap with tank cap screwed
on
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 104.
Open fuel filler flap
›
Open the fuel filler flap with one hand
» Fig. 95.
› Hold the fuel filler cap on the fuel filler tube with one hand and unlock it by
moving it to the left with the vehicle key.
› Unscrew the filler cap by turning it to the left and place the cap onto the top of
the fuel filler flap » Fig. 95.
Closing the filler cap
› Turn the filler cap to the right until it clicks into place.
› Hold the fuel filler cap on the fuel filler tube with one hand and lock it by turn-
ing the vehicle key to the right and remove the key.
› Close the filler cap. CAUTION
The fuel tank is full just as soon as the pump nozzle switches off for the first
time, provided the nozzle has been operated properly. Do not continue filling the
fuel tank otherwise the expansion volume is filled up. Note
The fuel tank has a capacity of about 35 litres, containing a reserve of approx.
4 litres. Ð
ä
104 General Maintenance
Page 107 of 157

Unleaded petrol
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 104.
Your vehicle can only be operated with
unleaded fuel that complies with the
standard EN 228 (in Germany: standard DIN 51626-1 or E10 for unleaded fuel with
an octane rating of 95 RON and 91 RON or DIN 51626-2 or E5 for unleaded fuel
with the octane rating 95 RON and 98 RON).
Prescribed fuel – unleaded fuel 95/91 RON
Use unleaded fuel with the octane rating 95 RON. Unleaded petrol 91 RON can al-
so be used but results in a slight loss in performance.
If, in an emergency, the vehicle has to be refuelled with petrol of a lower octane
number than the one prescribed, the journey must only be continued at medium
engine speeds and a low engine load. Driving at high engine revs or a high engine
load can severely damage the engine! Refuel using petrol of the prescribed oc-
tane number as soon as possible.
Prescribed fuel – unleaded petrol min. 95 RON
Use unleaded fuel with the octane rating 95 RON.
In case of necessity, you can refuel with petrol with the octane rating 91 RON if
petrol with the octane rating 95 RON is not available. The journey must only be
continued at medium engine speeds and a minimum engine load. Driving at high
engine revs or a high engine load can severely damage the engine! Refuel using
petrol of the prescribed octane number as soon as possible.
Even in the event of an emergency, petrol of a lower octane number than 91 RON
must not be used, otherwise the engine can be severely damaged!
Unleaded petrol with higher octane number
Unleaded petrol that has a higher octane number than that required by the en-
gine can be used without limitations.
On vehicles with prescribed unleaded petrol 95/91 RON, the use of petrol with a
higher octane number than 95 RON does not result in a noticeable power in-
crease or a lower fuel consumption.
On vehicles using prescribed unleaded petrol of min. 95 RON, the use of petrol
with a higher octane number than 95 RON can increase the power and reduce
fuel consumption. ä
Prescribed fuel – unleaded petrol 98/(95) RON
Use unleaded fuel with the octane rating
98 RON. Unleaded petrol 95 RON can
also be used but results in a slight loss in performance.
In case of necessity, you can refuel with petrol with the octane rating 91 RON of
unleaded fuel with octane rating 98 RON or 95 RON is not available. The journey
must only be continued at medium engine speeds and a minimum engine load.
Driving at high engine revs or a high engine load can severely damage the engine!
Refuel using petrol of the prescribed octane number as soon as possible.
Even in the event of an emergency, petrol of a lower octane number than 91 RON
must not be used, otherwise the engine can be severely damaged!
Fuel additives
Only use unleaded petrol, which complies with the standard EN
228 (in Germany:
standard DIN 51626-1 or E10 for unleaded fuel with an octane rating of 95 RON
and 91 RON or DIN 51626-2 or E5 for unleaded fuel with an octane rating of
95 RON and 98 RON), as these meet all of the requirements for fault-free engine
operation. We therefore recommend that no fuel additives are used. CAUTION
■ All
ŠKODA vehicles with petrol engines must only be operated with unleaded
petrol. Just filling the tank with leaded petrol once will damage the exhaust sys-
tem!
■ Engine parts can be damaged if petrol with a lower octane number than the one
prescribed is used.
■ In no case may fuel additives with metal components be used, especially not
with manganese and iron content.
LRP (lead replacement petrol) fuels with met-
allic components may not be used. There is a risk of causing considerable damage
to parts of the engine or exhaust system!
■ Fuels with metallic content may not be used. There is a risk of causing consider-
able damage to parts of the engine or exhaust system!
■ The use of unsuitable fuel additives can cause considerable damage to parts of
the engine or the exhaust system. Ð
105
Inspecting and replenishing
Page 108 of 157
Vehicle running on CNG (compressed natural gas)
ä
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Refuelling 106
Automatically switching over from CNG mode to petrol mode 107
Natural gas as fuel 107
Regular inspections of gas systems 108
Safe natural gas 108
Natural gas quality and consumption 108
WARNING
■ When operating a CNG-powered vehicle, the national legal requirements
must be observed.
■ If a fault occurs or a leak in the natural gas system is suspected or if you
smell gas, proceed as follows: ■Stop immediately and switch off the ignition (this will close the solenoid
valves on the natural gas tanks automatically);
■ Open the doors to ventilate the vehicle sufficiently;
■ Immediately extinguish cigarettes, and remove and switch off other spark-
or fire-causing objects from the vehicle immediately.
■ Seek help from a ŠKODA
specialist garage to correct the fault on the gas
system.
■ The following is considered faults on the gas system:
■ Gas leakage from any part of the gas system as well as an error on the
ventilation system.
■ Continuous gas venting through the safety valves.
■ Cracks or damage that could result in a gas leak.
■ Fault in the reduction device, the pressure regulator, gas mixer or in the
injection valves, the pressure gauge, the shut-off or check valves and tank
fixtures.
■ If gas flows into the gas mixer or into the injection valves though the en-
gine is stopped.
■ Exceeding the permissible limits for contaminants in the exhaust gas. WARNING (Continued)
■ A natural gas-powered vehicle must be shut down if no periodic testing of
pressure accumulators is performed or an approved component has been re-
placed by a non-approved component. The vehicle owner is responsible for
properly conducted tests.
■ The natural gas tanks must not be exposed to a heat source.
■ Always switch off the ignition in case of an accident or vehicle fire!
■ It is prohibited to drive into enclosed storage places, garages and similar
areas where it is specifically not allowed to enter with CNG-powered vehicles. Ð Refuelling
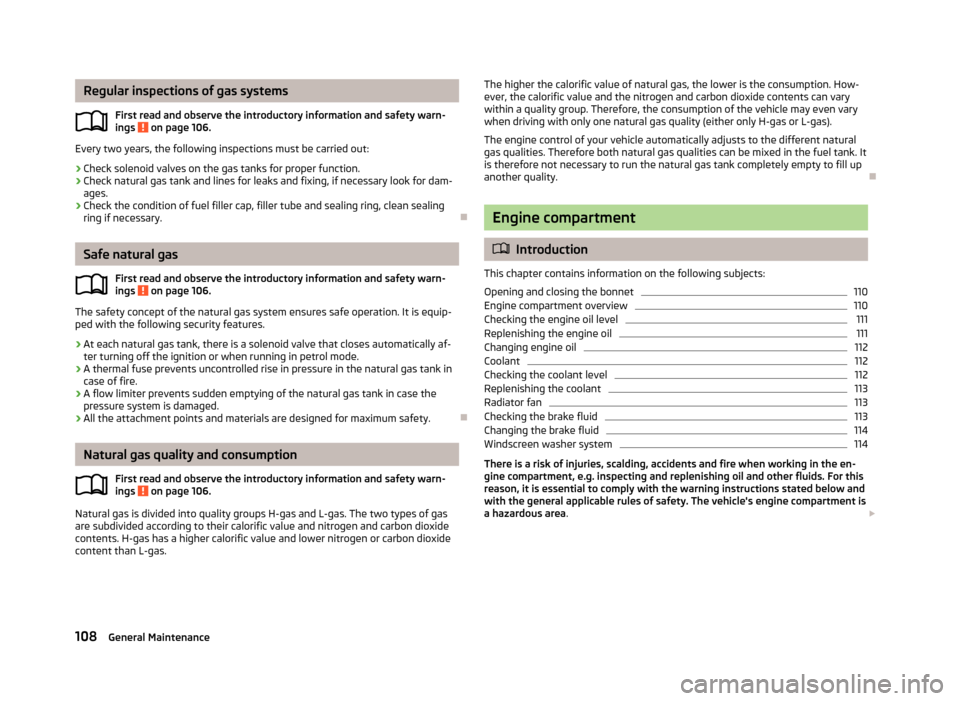
Fig. 96
Fuel filler
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 106.
The gas filler tube for refuelling with natural gas is located behind the fuel filler
flap next to the petrol filler tube.
The filling couplings of the natural gas refuelling systems may differ in handling.
When refuelling with natural gas at unfamiliar refuelling systems, you should
seek help from trained fuel station staff. If unsure, have the refuelling done by
trained fuel station staff.
The operating instructions of the refuelling system must always be followed.
Open fuel filler flap
›
Open the fuel filler flap with one hand.
› Remove the cap 1
» Fig. 96
from the gas filler tube 2
.
› Plug the filling coupling of the refuelling system on the gas filler tube 2
.
£
ä
106 General Maintenance
Page 109 of 157

The fuel tank is full when the compressor of the refuelling system automatically
switches off. To stop the refuelling operation prematurely, press the
“Stop ” but-
ton of the refuelling system.
Closing the filler cap
› Check that the sealing ring 3
» Fig. 96
has remained in the gas filler tube. If it
has slipped onto the filling coupling, reinsert it into the gas filler tube.
› Plug the cap 1
onto the gas filler tube.
› Close the filler cap.
In the following situation, it is possible that the tank cannot be fully filled with
natural gas.
› At very high ambient temperatures. The natural gas refuelling systems have
overheating protection. When the ambient temperature reaches a predefined
value, the refuelling system automatically switches off.
› If the refuelling system has been in operation for a longer period, the filling
pressure of the natural gas refuelling system slightly drops. WARNING
■ Stop the engine before refuelling.
■ Always switch off your mobile phone, do not smoke and do not use open
flames when refuelling with natural gas – risk of explosion!
■ When refuelling, never get into the vehicle. If you have to get into your vehi-
cle in exceptional cases, close the door and touch a metal surface before you
touch the filling coupling again. This will avoid electrostatic discharges, which
may generate sparks. Sparks can cause a fire during refuelling. ■ Natural gas is highly explosive and flammable. Incorrect refuelling or improp-
er handling of natural gas can cause a fire, an explosion and injuries. Note
■ The natural gas system of your vehicle is suitable both for fuelling from small
compressors (slow fuelling) and for fuelling from natural gas stations with large
compressors (quick fuelling). ■ Noises that occur during refuelling represent no risk.
■ If the vehicle is parked for a longer period of time immediately after refuelling,
the situation may arise in which the pointer of the fuel tank gauge does not indi-
cate exactly the same level as was the case immediately after refuelling when the
engine is restarted. This is not due to any system leakages but a drop in pressure
in the natural gas fuel tank due to technical reasons after a cooling phase directly
after refuelling. ■
For frequent short-haul traffic, especially at low outside temperatures, the vehi-
cle is driven more frequently in petrol mode than in natural gas mode. This is why
the petrol tank runs empty faster than the natural gas tank.
■ The capacity of the natural gas tank is about 11 kg, of which about 1.5
kg are a
reserve.
■ The capacity of the petrol tank is about 10 l, of which about 5 l
are a reserve.Ð Automatically switching over from CNG mode to petrol mode
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 106.
The vehicle automatically switches over from CNG mode to petrol mode when the
following conditions are met:
› when starting the engine, if the coolant temperature is below 15 °C,
› when the natural gas tank is empty,
› after refuelling with natural gas. Ð Natural gas as fuel
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 106.
Natural gas is an alternative fuel for motor vehicles. Its main component is meth-
ane (CH 4). The rest is carbon dioxide and lower hydrocarbons.
The strict legal requirements for exhaust emissions of motor vehicles are decisive
for the current significance of natural gas. In direct comparison to all other fossil
fuels, natural gas is one of the fuels which cause the lowest emissions.
Natural gas is odourless and lighter than air. For safety reasons, it is saturated
with odorous substances, so that is perceived even in very small amounts. Ð
ä
ä
107
Inspecting and replenishing
Page 110 of 157
Regular inspections of gas systems
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 106.
Every two years, the following inspections must be carried out:
› Check solenoid valves on the gas tanks for proper function.
› Check natural gas tank and lines for leaks and fixing, if necessary look for dam-
ages.
› Check the condition of fuel filler cap, filler tube and sealing ring, clean sealing
ring if necessary. ÐSafe natural gas
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 106.
The safety concept of the natural gas system ensures safe operation. It is equip-
ped with the following security features.
› At each natural gas tank, there is a solenoid valve that closes automatically af-
ter turning off the ignition or when running in petrol mode.
› A thermal fuse prevents uncontrolled rise in pressure in the natural gas tank in
case of fire.
› A flow limiter prevents sudden emptying of the natural gas tank in case the
pressure system is damaged.
› All the attachment points and materials are designed for maximum safety. ÐNatural gas quality and consumption
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 106.
Natural gas is divided into quality groups H-gas and L-gas. The two types of gas
are subdivided according to their calorific value and nitrogen and carbon dioxide
contents. H-gas has a higher calorific value and lower nitrogen or carbon dioxide
content than L-gas.ä
ä
ä The higher the calorific value of natural gas, the lower is the consumption. How-
ever, the calorific value and the nitrogen and carbon dioxide contents can vary
within a quality group. Therefore, the consumption of the vehicle may even vary
when driving with only one natural gas quality (either only H-gas or L-gas).
The engine control of your vehicle automatically adjusts to the different natural
gas qualities. Therefore both natural gas qualities can be mixed in the fuel tank. It
is therefore not necessary to run the natural gas tank completely empty to fill up
another quality. Ð Engine compartment
ä
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Opening and closing the bonnet 110
Engine compartment overview 110
Checking the engine oil level 111
Replenishing the engine oil 111
Changing engine oil 112
Coolant 112
Checking the coolant level 112
Replenishing the coolant 113
Radiator fan 113
Checking the brake fluid 113
Changing the brake fluid 114
Windscreen washer system 114
There is a risk of injuries, scalding, accidents and fire when working in the en-
gine compartment, e.g. inspecting and replenishing oil and other fluids. For this
reason, it is essential to comply with the warning instructions stated below and
with the general applicable rules of safety. The vehicle's engine compartment is
a hazardous area . £
108 General Maintenance