lock SKODA CITIGO 2012 1.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2012, Model line: CITIGO, Model: SKODA CITIGO 2012 1.GPages: 157, PDF Size: 3.9 MB
Page 77 of 157
What influences the driving safety?
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 74.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and his occupants. If your driving safety
is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at risk.
The following guidelines must therefore be observed. › Do not get distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, e.g. by your
passengers or mobile phone calls.
› Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, e.g. through medication, alco-
hol, drugs.
› Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
› Always adjust the driving speed to the road, traffic and weather conditions.
› Take regular breaks on long journeys – at least every two hours. ÐCorrect seated position
ä
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Correct seated position for the driver 76
Correct seated position for the front passenger 76
Correct seated position for the occupants on the rear seats 76
Examples of an incorrect seated position 76
WARNING
■ The front seats and rear head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size, in order to offer an optimal protection for you and your occu-
pants.
■ Always assume the correct seated position before setting off and do not
change this position while driving. Also advise your passengers to adopt the
correct seated position and not to change this position while the car is mov-
ing.
■ If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to life-
threatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
ä WARNING (Continued)
■ If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury is
increased due to incorrect routing of the seat belt.
■ The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering wheel.
The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash
panel. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag sys-
tem will not be able to properly protect you – hazard!
■ When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer
edge in the 9
o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering wheel in
the 12 o'clock position or in any other way (e.g. in the middle or inner edge of
the steering wheel). In such cases, you could severely injure the arms, hands
and head when the driver airbag is deployed.
■ The seat backrests must not be angled too far back when driving otherwise
this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of the airbag system –
risk of injury!
■ Ensure that there are no objects in the driver's footwell as they may get
caught behind the pedals when driving or applying the braking. You would
then no longer be able to operate the clutch, brake or accelerate.
■ Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven – never
place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the surfaces
of the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes nec-
essary to apply the brake or in the event of an accident. If an airbag is de-
ployed, you may suffer fatal injuries when adopting an incorrect seated posi-
tion! Ð
75
Passive Safety
Page 80 of 157
Seat belts
Seat belts
ä
Introduction Fig. 79
Driver wearing seat belt
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
The physical principle of a frontal collision 79
Fastening and unfastening seat belts 80
Belt tensioners 80
Seat belts that are fastened correctly offer good protection in the event of an ac-
cident. They reduce the risk of an injury and increase the chance of survival in the
event of a major accident.
Correctly fastened seat belts hold occupants of the car in the correct seated posi-
tion » Fig. 80 on page 79.
The seat belts reduce the kinetic energy (energy of motion) to a considerable ex-
tent. They also prevent uncontrolled movements which, in turn, may well result in
severe injuries.
The occupants of a vehicle who have fastened and correctly adjusted their seat
belt, profit to a major extent from the fact that the kinetic energy is optimally ab-
sorbed by the belts. The structure of the front end of the vehicle and other pas-
sive safety measures, such as the airbag system, also contribute to reducing the
kinetic energy. The energy produced is thus absorbed and there is less risk of in-
jury.
Particular safety aspects must be observed when transporting children in the ve-
hicle » page 87, Transporting children safely . WARNING
■ Fasten your seat belt before each journey – even when driving in town! This
also applies to the people seated at the rear – risk of injury!
■ Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of
ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child » page 80.
■ Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in
minor accidents. ■ The maximum protection which seat belts can offer is only achieved if you
are correctly seated » page 75, Correct seated position .
■ The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
■ The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twisted,
or chafe against any sharp edges.
■ A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then sud-
denly held firm by the belt.
■ The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. specta-
cles, ball-point pens, keys etc.) as this may be a cause of injuries.
■ No two persons (also not children) should ever use a single seat belt togeth-
er.
■ The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to pro-
tect and the risk of injury increases.
■ The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked by paper or similar objects
otherwise the belt tongue will not lock in place properly.
■ Many layers of clothing and loose clothing (e. g. a winter coat over a jacket)
do not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of the
seat belts. ■ It is prohibited to use clamps or other objects to adjust seat belts (e. g. for
shortening the belts for smaller persons).
■ The seat belts for the rear seats can only fulfil their function reliably when
the seat backrests are correctly locked into position » page 40, Folding the
rear seat backrest forwards. ■ The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may im-
pair proper operation of the inertia reel » page 103, Seat belts.
■ The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not attempt
to repair the seat belts yourself. £
78 Safety
Page 81 of 157

WARNING (Continued)
■ Check the condition of all the seat belts on a regular basis. If any damage to
the seat belts, seat belt connections, inertia reel or the lock is detected, the
relevant seat belt must be replaced by a specialist garage.
■ Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident and
were therefore stretched, must be replaced – this is best done by a specialist
garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The an-
chorage points for the belts should also be checked. Note
The national legal requirements must be observed when using seat belts. ÐThe physical principle of a frontal collision
Fig. 80
Driver without a fastened seat belt/rear seat passenger without a
fastened seat belt
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 78.
The physical principle of a frontal collision can be explained quite simply.
As soon as the vehicle is moving, so-called kinetic energy (the energy of motion)
is produced both in terms of the car as well as in terms of the occupants. The
magnitude of this kinetic energy depends essentially on the speed at which the
vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the vehicle including the occupants. The
greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the amount of energy which
has to be absorbed in the event of an accident. ä The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy
four times.
The common opinion that it is possible to support your body in a minor accident
with your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces
acting on the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed of 30 km/h to 50 km/h, the forces that your body
is exposed to in the event of an accident can exceed a tonne (1 000 kg).
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt, are
thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolled way parts of the interior of the car,
such as steering wheel, dash panel or windscreen » Fig. 80 – . In certain circum-
stances you could even be thrown out of the vehicle, which could cause life
threatening or even fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat occupants fasten their seat belts as they will
otherwise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the event
of an accident A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the seat belt is a dan-
ger not only to himself but also for those seated at the front » Fig. 80 – . Ð
79
Seat belts
Page 82 of 157
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
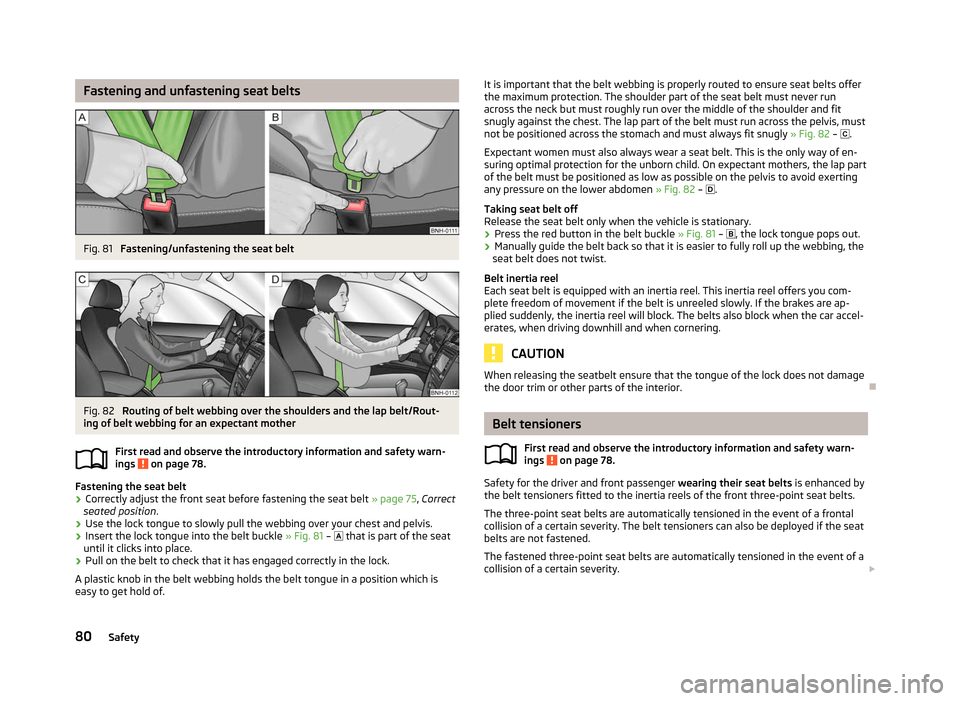
Fig. 81
Fastening/unfastening the seat belt Fig. 82
Routing of belt webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt/Rout-
ing of belt webbing for an expectant mother
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 78.
Fastening the seat belt
› Correctly adjust the front seat before fastening the seat belt
» page 75, Correct
seated position .
› Use the lock tongue to slowly pull the webbing over your chest and pelvis.
› Insert the lock tongue into the belt buckle
» Fig. 81 – that is part of the seat
until it clicks into place.
› Pull on the belt to check that it has engaged correctly in the lock.
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is
easy to get hold of.
ä It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed to ensure seat belts offer
the maximum protection. The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run
across the neck but must roughly run over the middle of the shoulder and fit
snugly against the chest. The lap part of the belt must run across the pelvis, must
not be positioned across the stomach and must always fit snugly
» Fig. 82 – .
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of en-
suring optimal protection for the unborn child. On expectant mothers, the lap part
of the belt must be positioned as low as possible on the pelvis to avoid exerting
any pressure on the lower abdomen » Fig. 82 – .
Taking seat belt off
Release the seat belt only when the vehicle is stationary.
› Press the red button in the belt buckle
» Fig. 81 – , the lock tongue pops out.
› Manually guide the belt back so that it is easier to fully roll up the webbing, the
seat belt does not twist.
Belt inertia reel
Each seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel. This inertia reel offers you com-
plete freedom of movement if the belt is unreeled slowly. If the brakes are ap-
plied suddenly, the inertia reel will block. The belts also block when the car accel-
erates, when driving downhill and when cornering. CAUTION
When releasing the seatbelt ensure that the tongue of the lock does not damage
the door trim or other parts of the interior. Ð Belt tensioners
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 78.
Safety for the driver and front passenger
wearing their seat belts is enhanced by
the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front three-point seat belts.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal
collision of a certain severity. The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the seat
belts are not fastened.
The fastened three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a
collision of a certain severity. £
ä
80 Safety
Page 85 of 157
Deployment factors
It is not possible to generally determine which deployment conditions apply to
the airbag system in every situation. An important role is played by factors such
as the type of object that the vehicle hits (hard, soft), the impact angle, vehicle
speed, etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which oc-
curs. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates the rele-
vant restraint system. If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is measured
during the collision remains below the prescribed reference values specified in
the control unit, the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well suf-
fer severe damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The following will be deployed in the event of a severe frontal collision:
› driver’s front airbag;
› passenger’s front airbag.
The following will be deployed in the event of a severe side collision: › Side airbags on the side of the accident.
In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed:
› the interior lighting comes on (if the switch for the interior light is in the door
contact position),
› the hazard warning light is switched on;
› all the doors are unlocked;
› the fuel supply to the engine is interrupted. Note
A grey white or red, non-harmful gas is released when the airbag is inflated. This
is perfectly normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle. Ð Front airbags
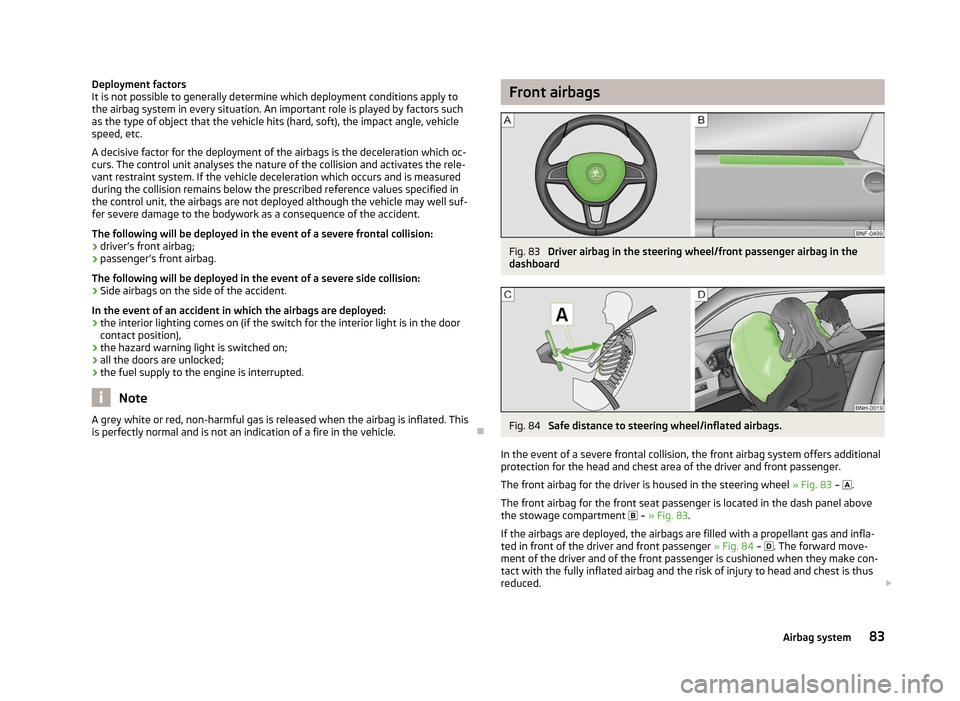
Fig. 83
Driver airbag in the steering wheel/front passenger airbag in the
dashboard Fig. 84
Safe distance to steering wheel/inflated airbags.
In the event of a severe frontal collision, the front airbag system offers additional
protection for the head and chest area of the driver and front passenger.
The front airbag for the driver is housed in the steering wheel » Fig. 83 – .
The front airbag for the front seat passenger is located in the dash panel above
the stowage compartment
– » Fig. 83.
If the airbags are deployed, the airbags are filled with a propellant gas and infla-
ted in front of the driver and front passenger » Fig. 84 – . The forward move-
ment of the driver and of the front passenger is cushioned when they make con-
tact with the fully inflated airbag and the risk of injury to head and chest is thus
reduced. £
83
Airbag system
Page 91 of 157
Group
Weight of the child Approximate age
1 9-18 kg up to 4 years
2 15-25 kg up to 7 years
3 22-36 kg over 7 years Ð
Suitability of child seats
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 87.
Overview of the suitability of child seats according to the standard ECE-R
44
Seat Child seat
type
Front passenger seat U
Car seat U
+
T
Universal category – a child seat with the word UNIVERSAL, which is de-
signed for fastening on the seat with the seat belt.
ISOFIX
– a child seat which is designed for fastening on the seat with eyelets
for the ISOFIX system is provided » page 89, Child seats with the ISOFIX
system.
TOP TETHER – a child seat which is designed for fastening on the seat with
an eyelet for the TOP TETHER system is provided » page 90, Child seat with
the TOP TETHER system. Ð
ä U
+
T Child seats with the ISOFIX system
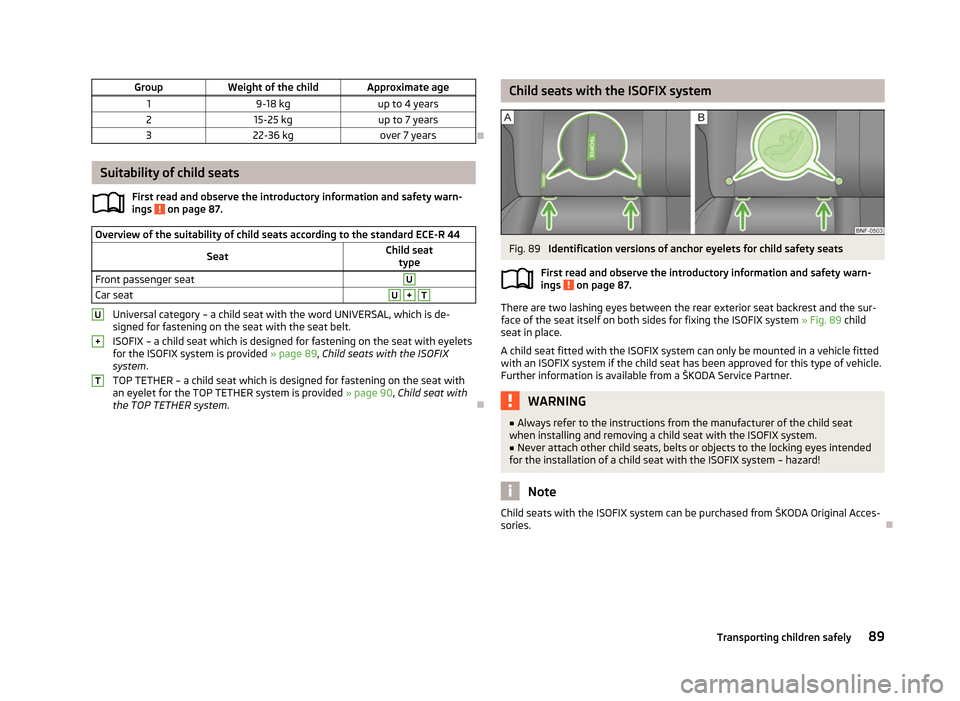
Fig. 89
Identification versions of anchor eyelets for child safety seats
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 87.
There are two lashing eyes between the rear exterior seat backrest and the sur-
face of the seat itself on both sides for fixing the ISOFIX system » Fig. 89 child
seat in place.
A child seat fitted with the ISOFIX system can only be mounted in a vehicle fitted
with an ISOFIX system if the child seat has been approved for this type of vehicle.
Further information is available from a ŠKODA Service Partner. WARNING
■ Always refer to the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat
when installing and removing a child seat with the
ISOFIX system.
■ Never attach other child seats, belts or objects to the locking eyes intended
for the installation of a child seat with the
ISOFIX system – hazard! Note
Child seats with the ISOFIX system can be purchased from ŠKODA Original Acces-
sories. Ð
ä
89
Transporting children safely
Page 92 of 157

Child seat with the TOP TETHER system
Fig. 90
Rear seat: TOP TETHER
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 87.
There are fixing eyes on the rear side of the rear seat backrests for attaching the
fixing belt for a child seat with the TOP TETHER system » Fig. 90.WARNING
■ Always refer to the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat
when installing and removing a child seat with the
TOP TETHER system.
■ Only use child seats with the TOP TETHER system on the seats with the
locking eyes. ■ Only ever attach one belt from the child seat to a locking eye.
■ On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other an-
chorage points. Ð
ä
90 Safety
Page 99 of 157
General Maintenance
Taking care of and cleaning the vehicle
Taking care of your vehicle
ä
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Washing the vehicle 98
Automatic car wash systems 98
Washing by hand 98
Washing with a high-pressure cleaner 98
Preserving and polishing the vehicle paintwork 99
Chrome parts 99
Paint damage 99
Plastic parts 99
De-icing windows and exterior mirrors 100
Radio reception 100
Headlight lenses 100
Rubber seals 100
Door lock cylinders 100
Wheels 101
Underbody protection 101
Protection of hollow spaces 101
Artificial leather and materials 101
Fabric covers on electrically heated seats 102
Natural leather 102
Seat belts 103
Regular and proper care help to retain the efficiency and value of your vehicle. It
may also be one of the requirements for the acceptance of warranty claims relat-
ing to corrosion damage and paint defects on the bodywork.
We recommend using care products from
ŠKODA Original Accessories that are
available from ŠKODA Service Partners. The instructions for use on the package
must be observed. WARNING
■ Care products may be harmful to your health if not used according to the in-
structions.
■ Always store care products in a safe place, out of the reach of children – risk
of poisoning! ■ When washing your vehicle in the winter: Water and ice in the brake system
can affect the braking efficiency – risk of accident! ■ Only wash the vehicle when the ignition is switched off – risk of accident!
■ Protect your hands and arms from sharp-edged metal parts when cleaning
the underfloor, the inside of the wheel housings or the wheel trims – risk of
cuts!
■ Air fresheners and scents can be hazardous to heath when the temperature
inside the vehicle is high. CAUTION
■ Be sure to check clothing for colourfastness to avoid any damage or visible
stains on the material (leather), panels and textiles.
■ Cleaners containing solvents can damage the material being cleaned.
■ Do not wash your vehicle in bright sunlight – risk of paint damage.
■ If washing the vehicle in the winter using a hose or high-pressure cleaner, en-
sure that the jet of water is not aimed directly at the locking cylinders or the
door/panel joints – risk of freezing!
■ Do not use any insect sponges, rough kitchen sponges or similar cleaning prod-
ucts – risk of damaging the surface of paintwork. ■ Do not stick any stickers on the inside of the rear windows, in the vicinity of the
heating elements. These may get damaged.
■ Do not clean the inside of the rear window with sharp-edged objects or corro-
sive and acidic cleaning agents – risk of damaging the heating elements.
■ Do not attach scents and air fresheners to the dashboard – risk of damage to
the dashboard.
■ To avoid damaging the parking aid sensors while cleaning with high-pressure
cleaners or steam jets, the sensors must only be directly sprayed for short periods
while a minimum distance of 10
cm must be observed.
■ Do not clean the roof trim with a brush – risk of damage to the trim surface. For the sake of the environment
■ Used cans of vehicle care products represent a special type of hazardous waste.
These must be disposed of in accordance with national legal regulations. ■ Only wash the vehicle at washing bays intended for this purpose. £
97
Taking care of and cleaning the vehicle
Page 102 of 157

De-icing windows and exterior mirrors
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Use a plastic ice scraper for removing snow and ice from the windows and mir-
rors. The ice scraper should not be moved forward and backward but in one direc-
tion to avoid any damage to the surface of the glass.
Clean the windows from the inside on a regular basis.
Dry the glass surfaces with a clean chamois leather or a cloth intended for this
purpose.
When drying the windows after washing the vehicle, do not use window leathers
that have been used to polish the bodywork. Residues of preservatives in the
window leather can dirty the window and reduce visibility. CAUTION
■ Never remove snow or ice from glass parts using warm or hot water – risk of
formation of cracks in the glass!
■ When removing snow or ice from windows and mirror lenses ensure that the
paintwork of the vehicle is not to damage.
■ Snow or ice that is contaminated with coarse dirt such as fine gravel, sand, and
salt must not be removed from the window glass and mirrors – risk of damage to
the surface of the windows and mirrors. ÐRadio reception
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Car parks, tunnels, tall buildings or mountains can disrupt the radio signal even
causing it to fail completely. ÐHeadlight lenses
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Use soap and clean water to clean the plastic headlight lenses.ä
ä
ä CAUTION
■ Never wipe the headlights dry and do not use any sharp objects to clean the
plastic lenses, this may damage the protective paintwork and consequently cause
the formation of cracks on the headlight lenses.
■ Do not use any aggressive cleaning or chemical solvent products to clean the
headlights – risk of damaging the headlight lenses. Ð Rubber seals
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
The rubber seals on doors, the sliding roof and other windows remain smoother
and last longer if the seals are treated regularly with a suitable rubber care prod-
uct. This helps to prevent leakages and premature wear of the seals. Rubber
seals which are well cared for also do not stick together in cold winter weather.
Ð Door lock cylinders
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Specific products must be used for de-icing door lock cylinders.
Note
■ When washing your vehicle, ensure as little water as possible gets into the lock-
ing cylinders. ■ We recommend that suitable materials from ŠKODA Original Accessories are
used for maintaining the door lock cylinders. Ð
ä
ä
100 General Maintenance
Page 104 of 157

Clean upholstery cover materials and cloth trims on doors, luggage compartment
cover, etc. using specific cleaning agents, e.g., dry foam. Use a soft sponge, brush,
or commercially available microfibre cloth. Use a cloth and a specific cleaning
agent to clean the roof trim.
Some clothing materials, such as dark denim, do, in part, not have sufficient col-
our fastness. This can cause damage or clearly visible discolouration to seat cov-
ers (fabric or leather) even when used correctly. This particularly applies to light
seat covers (fabric or leather). This is not a defect in the seat cover, but poor col-
our fastness of the clothing textiles. ÐFabric covers on electrically heated seats
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Do not clean the seat covers
using moisture as this can damage the seat heating
system.
Use a specific cleaning agent such as dry foam or similar to clean the covers. ÐNatural leather
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 97.
Depending on the amount of wear-and-tear, the leather should be cleaned on a
regular basis.
Normal cleaning
Clean soiled areas of the leather with slightly moistened cotton or woollen cloth.
Severe soiling
Ensure that the leather is not soaked through at any point and that no water gets
into the stitching of the seams.
Dry off the leather with a soft, dry cloth.
Removing stains
Remove fresh water-based stains (e.g., coffee, tea, juices, blood) with an absorb-
ent cloth or household cleaning paper. A specific cleaning agent is required for
dried-on stains.
ä
ä
Remove fresh
grease-based stains (e.g. butter, mayonnaise, chocolate, etc.) with
an absorbent cloth, household cleaning paper, or use a suitable cleaner if the
stain has not yet penetrated into the surface.
Use a grease solvent for grease stains which have dried in.
Remove specific stains (e.g. ball-point pens, marker pen, nail varnish, dispersion
paint, shoe polish, etc.) with a special stain remover suitable for leather.
Leather care
Treat the leather roughly every six months with a suitable leather care product.
Apply only a small amount of the cleaning and care product.
Dry off the leather with a soft, dry cloth. CAUTION
■ Avoid leaving the vehicle for lengthy periods in bright sunlight to avoid the
leather from bleaching. If the vehicle is parked in the open for lengthy periods,
protect the leather from direct sunlight by covering it.
■ Sharp-edged objects on items of clothing such as zip fasteners, rivets, sharp-
edged belts, jewellery and pendants may leave permanent scratches or signs of
rubbing on the surface.
■ The use of a mechanical steering wheel lock may damage the leather surface of
the steering wheel. Note
■ Use a care cream with light blocker and impregnation effect on a regular basis
and each time after cleaning. The cream nourishes the leather, allows it to
breathe and keeps it supple and also provides moisture. It also creates surface
protection. ■ Clean the leather every 2 to 3 months, remove any fresh stains as they occur.
■ Also look after the leather dye. Refresh any areas with a special coloured leath-
er cream as required.
■ The leather is a natural material with specific properties. During the use of the
vehicle, minor optical changes can occur on the leather parts of the covers (e. g
wrinkles or creases as a result of the stress of the covers). Ð
102 General Maintenance