tyre SKODA FABIA 2004 1.G / 6Y Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2004, Model line: FABIA, Model: SKODA FABIA 2004 1.G / 6YPages: 247
Page 7 of 247

Contents
6
Driving Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intelligent Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic stability programme (ESP)* . . . . . .
Brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake booster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antilock brake system (ABS)* . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power steering* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Driving and the Environment. . . . . . . . . . . .
The first 1 500 kilometres and then afterwards
Catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Driving in an economical and environmentally
conscious manner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Environmental compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Motoring abroad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Avoiding damage to your vehicle . . . . . . . . . .
Towing a trailer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Towing a trailer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Detachable towing device* . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Maintenance . . . . . . . . . .
Care and cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Care of the exterior of vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . .
Care of the interior of vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Petrol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diesel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Refuelling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspecting and Replenishing. . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine compartment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cooling system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake fluid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . The battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Windscreen Wiper and Washer System . . . .
Wheels and Tyres . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessories, changes and replacement of
parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessories and replacement parts . . . . . . .
Technical changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Breakdown assistance . . . . . . . .
Breakdown assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
First-aid box* and warning triangle* . . . . . . . .
Fire extinguisher* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle tool kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Spray for repairing a tyre* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tyre repair kit* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Spare wheel* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Changing a wheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Jump-starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tow-starting and towing vehicle . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuses and light bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electric fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Identification data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
151
151
151
154
155
155
156
157
157
158
159
163
164
164
165
165
167
169
169
169
169
175
178
178
178
180
182
182
185
189
191 193
197
199
199
206
206
206
209
209
209
209
210
211
211
212
212
218
220
224
224
227
237
237
237
239
Page 74 of 247
Seats and Stowage73
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
– Attach the items of luggage to the lashing eyes or the safety
net* ⇒page 74.
In the event of an accident, there is such a high kinetic energy which is
produced by small and light objects that they can cause severe injuries.
The magnitude of the kinetic energy depends on the speed at which the
vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the object. The speed at which
the vehicle is travelling is in this case the more significant factor.
Example: In the event of a frontal collision at a speed of 50 km/h, an unse-
cured object with a weight of 4.5 kg produces an energy, which corre-
sponds to 20 times its own weight. This means that it results in a weight
of approx. 90 kg. You can imagine the injuries that can occur, if this “bullet”
is flying through the interior compartment and hits an occupant.
WARNING
•Store the objects in the luggage compartment and attach them
to the lashing eyes.
•Loose objects in the passenger compartment can be thrown
forward during a sudden manoeuvre or in case of an accident and
can injure the occupants or other oncoming traffic. This risk is still
increased, if the objects which are flying around are hit by a
deployed airbag. In this case, the objects which are thrown back
can injure the occupants - hazard.
•Please note that the handling properties of your vehicle may be
affected when transporting heavy objects as a result of the
displacement of the centre of gravity. The speed and style of
driving must be adjusted accordingly.
•The items carried in the luggage compartment should be stored
in such a way that no objects are able to slip forward if there are any
sudden driving or braking manoeuvres undertaken - risk of injury!
•Never drive with the boot lid slightly ajar or even fully opened
otherwise exhaust gases may get into the interior of the vehicle -
risk of poisoning!
•On no account exceed the permissible axle loads and the
permissible gross weight of the vehicle - risk of accident!
•Never transport occupants in the luggage compartment.
Caution
Please ensure that the heating elements of the rear window heater are not
damaged as a result of objects sliding in this area.
Note
•Tyre pressure must be adjusted to the load ⇒page 200, fig. 146 .
•The air circulation in the interior of the car helps to prevent the
windows from misting up. Stale air is diverted via the outlet nozzles into
the lateral trim panels of the luggage compartment. Check for yourself that
the outlet nozzles are not covered.
WARNING (continued)
Page 119 of 247

Passive Safety
118
should be observed when using the equipment and how you and the
people travelling with you can make full use of the existing safety equip-
ment. This Owner's Manual contains important warning notes, which you
and those travelling with you should pay attention to in order to reduce a
risk of injury.
Safety concerns everybody!
Before setting off
The driver is always fully responsible for his occupants
and for the operating safety of the vehicle.
For your own safety and the safety of the people travelling with you,
please pay attention to the following points before setting off.
•Ensure that the lighting and the turn signal system are functioning
properly.
•Inspect the tyre inflation pressure.
•Ensure that all the windows offer a good visibility to the outside.
•Safely attach the items of luggage ⇒page 72, “Loading the luggage
compartment”.
•Ensure that no objects can obstruct the pedal.
•Adjust the mirror, the front seat and the head restraint to match your
body size.
•Point out to your occupants that the head restraints must be adjusted
to match their body size.
•Protect the children in suitable child seats with correctly fastened seat
belts ⇒page 140, “Transporting children safely”.
•Adopt the correct seated position. Also inform your occupants to adopt
the correct seated position.
•Fasten the seat belt correctly. Also inform your occupants to properly
fasten the seat belts ⇒page 126, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
What influences the driving safety?
The driving safety is primarily determined by the style of
driving and the personal behaviour of all the occupants.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and his occupants. If your driving
safety is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at risk.
Please refer to the following guidelines.
•Do not get distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, e.g. by
your occupants or mobile phone calls.
•Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, e.g. through medica-
tion, alcohol, drugs.
•Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
•Adjust the driving speed at all times to the road condition as well as to
the traffic and weather conditions.
•Take regular breaks on long journeys - at the latest every two hours.
Page 153 of 247
Intelligent Technology
152
The ESP warning light ⇒page 34 lights up in the instrument cluster when
there is a fault on the ESP.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the
button ⇒page 151, fig. 126 . The ESP warning light ⇒ page 34 lights up
in the instrument cluster when the ESP is switched off.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice
in certain exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip,
to switch off the system.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck
then you should switch on the ESP again.
WARNING
It is also not possible for the E SP to overcome the physical limits
of the vehicle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still
always adapt your style of driving to the condition of the road
surface and the traffic situation. This particularly applies when
driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety offered
must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an
accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve
problem-free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the
tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP
⇒ page 206.
Traction control system (TCS)*
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels
from spinning when accelerating.
General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off,
accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface
are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when the engine is started and then
conducts a self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels
with the aid of the ABS sensors. If the wheels are spinning, the force trans-
Fig. 127 TCS switch
Page 154 of 247

Intelligent Technology153
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
mitted to the road surface is automatically adapted by reducing the engine
speed. This occurs at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS
⇒page 155, “Antilock
brake system (ABS)*”. The TCS will not f unction if a fault exists in the ABS
system.
The TCS warning light ⇒page 33 lights up in the instrument cluster when
there is a fault on the TCS.
Switching off
You can switch the TCS off and on again as you wish by pressing the
button ⇒page 152, fig. 127 . The TCS warning light ⇒page 33 lights up
in the instrument cluster when the TCS is switched off.
The TCS should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice
in certain exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip,
to switch off the system.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck
then you should switch on the TCS again.
WARNING
You should always adjust your style of driving to the conditions of
the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety
offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise -
risk of an accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve
problem-free operation of the TCS. Differing rolling circumferences of the
tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the TCS
⇒ page 206, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)*
The electronic differential lock prevents an individual
wheel from slipping.
Models fitted with ESP are equipped with electronic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off,
accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface
are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part
of the driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the
ABS sensors. Should only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery
surface there will be an appreciable difference in the speed of the driven
wheels. The EDL function brakes the slipping wheel and the differential
transmits a greater driving force to the other driven wheel. This control
process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in
order to avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel
Page 155 of 247

Intelligent Technology
154
which is being braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the
same characteristics as a vehicle not fitted with EDL.
The EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled
down.
WARNING
•Depress the accelerator carefully when accelerating on
uniformly slippery road surfaces, such as ice and snow. The driven
wheels might still spin despite the EDL and affect the stability of the
vehicle - risk of an accident!
•You should always adapt your style of driving to the condition
of road surface and to the traffic situation even when your vehicle
is fitted with EDL. The increased safety offered must not tempt you
to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an accident!
Note
•If the ABS or TCS or ESP warning li ght comes on, this may also indi-
cate a fault in the EDL. Please have the vehicle inspected as soon as
possible by a Škoda dealer.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the EDL
⇒ page 206, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Brakes
What has a negative effect on braking efficiency?
Wear-and-tear
Wear-and-tear to the brake pads is greatly dependent on the operating
conditions of the vehicle and your style of driving. Particularly if you drive a great deal in towns and over short distances or if you adopt a sporty style
of driving, it may be necessary to have the thickness of the brake pads
inspected at a Škoda dealer between the service inspections.
Wet roads or road salt
There may be a certain delay before the brakes take full effect under
certain conditions such as when driving through water, during heavy rain
showers or after the vehicle has been washed in an automatic vehicle
wash, since the brake discs and brake pads may be moist or even have a
coating of ice on them in winter. You should dry the brakes as soon as
possible (by applying and releasing the brakes several times, if the road
conditions and the traffic situation allows it).
There also may be a certain delay before the full braking efficiency is avail-
able when driving on roads which have been treated with road salt if you
have not used the brakes for some considerable time beforehand. The
layer of salt on the brake discs and brake pads must first be rubbed off
when you apply the brakes.
Corrosion
Corrosion on the brake discs and dirt on the bake pads occur if the vehicle
has been parked for a long period and if you do not make much use of the
braking system.
We recommend cleaning the brake discs by firmly applying the brakes at
a fairly high speed if you do not make much use of the braking system or
if surface corrosion is present
⇒.
Faults in the brake surface
If you notice that the braking distance has suddenly become longer and
that the brake pedal can be depressed further, it is possible that a brake
circuit of the dual-circuit brake system has failed. Drive, in such cases, to
the nearest Škoda dealer without delay in order to have the problem recti-
fied. Drive at a reduced speed while on your way to the dealer and adapt
your style of driving to the higher brake pedal pressure required.
Page 157 of 247
Intelligent Technology
156
Operating principle
As soon as the vehicle speed has increased to about 20 km/hour an auto-
matic test procedure is conducted during which you will be able to hear a
pumping noise for about 1 second.
The brake pressure will be reduced on a wheel which is rotating at a speed
which is too low for the speed of the vehicle and tending to lock. This
control cycle is noticeable from a pulsating movement of the brake
pedal which is accompanied by noises. This is consciously intended to
provide the driver with the information that the wheels are tending to lock
(ABS control range). You must always keep the brake pedal depressed to
enable the ABS to optimally control the brake application in this braking
range. Never interrupt the application of the brakes!
WARNING
•The ABS can also not overcome the physical limits of your
vehicle. Please do not forget this, particularly when driving on icy
or wet road surfaces. If the ABS is operating within the control
range, adapt your speed immediately to the conditions of the road
surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety offered by
the ABS must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise -
risk of an accident!
•The normal braking system is still fully functional if there is an
ABS fault. Visit a Škoda dealer as quickly as possible and adjust
your style of driving to take account of the ABS fault in the mean-
time since you will not know how great the damage is.
Note
•A warning light comes on if a fault occurs in the ABS system
⇒ page 34.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ABS
⇒ page 206, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Power steering*
The power steering enables you to steer the vehicle with less physical
force.
The steering characteristics can be changed by a Škoda dealer.
You will place great stresses on the power steering system if the steering
is turned to full lock when the vehicle is stationary. Turning the steering to
full lock in such a situation will be accompanied by noises.
It is still possible to fully steer the vehicle if the power steering fails or if the
engine is not running (vehicle being towed in). The only difference is that
greater physical effort is required.
It is possible that the hydraulic pump of the power steering will not run due
to the low vehicle network voltage if the battery has gone flat and the
engine must started with the help off jump leads. This condition will be
indicated by lighting up of the warning light.
The power steering operates again if the battery is charged to a specific
range when engine is running. It also operates again, if the engine can be
started with its own battery.
Caution
Do not leave the steering at full lock for more than 15 seconds when the
engine is running - risk of damaging the power steering!
Note
Have the steering inspected as soon as possible by a Škoda dealer if
there is a leak or fault in the system.
Page 158 of 247

Driving and the Environment157
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Driving and the Environment
The first 1 500 kilometres and then
afterwards
A new engine
The engine has to be run in during the first 1 500 kilome-
tres.
Up to 1 000 kilometres
– Do not drive faster than 3/4 of the mamimum speed of the gear
in use, that is 3/4 of the maximum permissible engine speed.
– Do not use full throttle.
– Avoid high engine revolutions.
– Do not tow a trailer.
From 1 000 up to 1 500 kilometres
– Increase the power output of the engine gradually up to the
full speed of the gear engaged, that is up to the maximum
permissible engine revolutions.
During the first operating hours the engine has higher internal friction than
later until all of the moving parts have harmonized. The driving style which
you adopt during the first approx.1 500 kilometres plays a decisive part in
the success of running in your car.
You should not drive at unnecessarily high engine revolutions even after
the running-in period is complete. The maximum permissible engine speed is marked by the beginning of the red zone on the scale of the revo-
lutions counter. Shift up into the next higher gear on a vehicle fitted with
manual gearbox before the red zone is reached.
Extremely high engine
revolutions are automatically governed, by the way.
For a vehicle fitted with a manual gearbox the converse situation also
applies: Do not drive at engine revolutions which are too low. Shift down
as soon as the engine is no longer running smoothly.
Caution
All the speed and engine revolution figures apply only when the engine is
at its normal operating temperature. Never rev up an engine which is cold,
neither when the vehicle is stationary nor when driving in individual gears.
For the sake of the environment
Not driving at unnecessarily high engine revolutions and shifting to a
higher gear as early as possible are ways to minimise fuel consumption
and operating noise levels and protects the environment.
New tyres
New tyres have to be “run in” since they do not offer optimal grip at first.
You should take account of this fact for the first 500 kilometres and drive
particularly carefully.
Page 160 of 247

Driving and the Environment159
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
For the sake of the environment
Even if the exhaust system is operating properly, a sulphur-like exhaust
odour may be produced under certain operating conditions of the engine.
This depends on the sulphur content of the fuel. It is often sufficient to
refuel with unleaded premium-grade petrol of a different brand or at a
different filling station.
Driving in an economical and
environmentally conscious manner
General
Your personal style of driving is a major factor.
Your fuel consumption, any pollution of the environmental and the wear-
and-tear to the engine, brakes and tyres, depend essentially on three
factors:
•your personal style of driving
•the conditions under which your vehicle is operated
•technical aspects
You can easily improve your fuel economy by 10 - 15 percent by driving in
an economical way with foresight. This section is intended to provide you
with a number of tips on how to protect the environment and at the same
time save money.
The fuel consumption can naturally also be influenced by factors which
are beyond the driver's control. It is, for example, normal for the fuel
consumption to increase in winter and under worsened conditions such as
poor road conditions, towing a trailer, etc. The technical requirements for low fuel usage and economic efficiency of
the vehicle have already been built into the vehicle at the works. Special
attention has been given to minimising negative effects on the environ-
ment. It is necessary to take note of the guidelines given in this chapter in
order to make best use of these characteristics and to maintain their
effectiveness.
Looking ahead when driving
A vehicle's highest fuel consumption occurs it accelerates.
Avoid accelerating and braking unnecessarily. If you drive with forsight
you will not need to brake so often and will also then not have to accel-
erate so much. Let your vehicle coast to a stop, for example, if this is
possible, when you see that the next set of traffic lights is at red.
Page 163 of 247
Driving and the Environment
162
Avoid driving short distances
Short distances result in an above-average high fuel
consumption.
– Avoid driving a distance of no more than 4 km if the engine is
cold.
The engine and catalytic converter must first have reached their optimal
operating temperature in order to effectively reduce fuel consumption
and pollutant emissions.
The cold engine vehicle consumes approx. 15 - 20 litres/100 km of fuel
immediately after starting. Fuel consumption drops to 10 litres/100 km
after just 1 kilometre. The engine reaches its operating temperature
(outside temperature and engine dependent) only after about 4 to 10 kilo-
metres and the fuel consumption then stabilizes. You should therefore
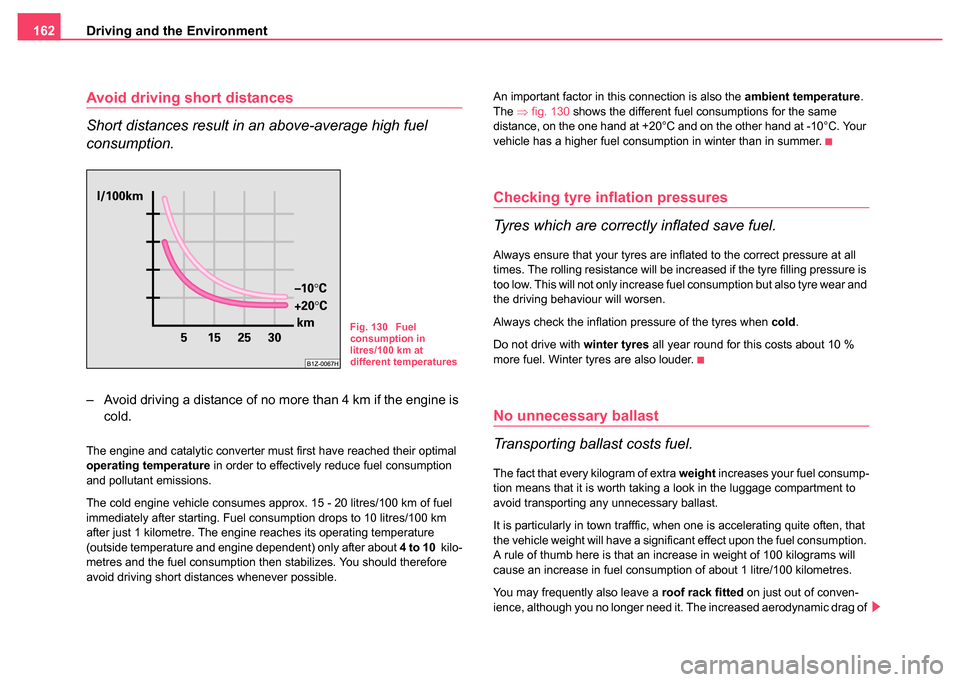
avoid driving short distances whenever possible. An important factor in this connection is also the
ambient temperature.
The ⇒fig. 130 shows the different fuel consumptions for the same
distance, on the one hand at +20°C and on the other hand at -10°C. Your
vehicle has a higher fuel consumption in winter than in summer.
Checking tyre inflation pressures
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.
Always ensure that your tyres are inflated to the correct pressure at all
times. The rolling resistance will be increased if the tyre filling pressure is
too low. This will not only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear and
the driving behaviour will worsen.
Always check the inflation pressure of the tyres when cold.
Do not drive with winter tyres all year round for this costs about 10 %
more fuel. Winter tyres are also louder.
No unnecessary ballast
Transporting ballast costs fuel.
The fact that every kilogram of extra weight increases your fuel consump-
tion means that it is worth taking a look in the luggage compartment to
avoid transporting any unnecessary ballast.
It is particularly in town trafffic, when one is accelerating quite often, that
the vehicle weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption.
A rule of thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will
cause an increase in fuel consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
You may frequently also leave a roof rack fitted on just out of conven-
ience, although you no longer need it. The increased aerodynamic drag of
Fig. 130 Fuel
consumption in
litres/100 km at
different temperatures