weight SKODA SUPERB 2003 1.G / (B5/3U) Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2003, Model line: SUPERB, Model: SKODA SUPERB 2003 1.G / (B5/3U)Pages: 259
Page 80 of 259
Seats and Stowage79
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Note
•You have to adjust the inflation pressure of the tyres to the load of the
car - refer to tyre inflation pressure sticker on the inside of the fuel filler
flap.
•The backrest of the rear seats is a fixed element and can therefore not
be folded forward to increase the size of the luggage compartment!
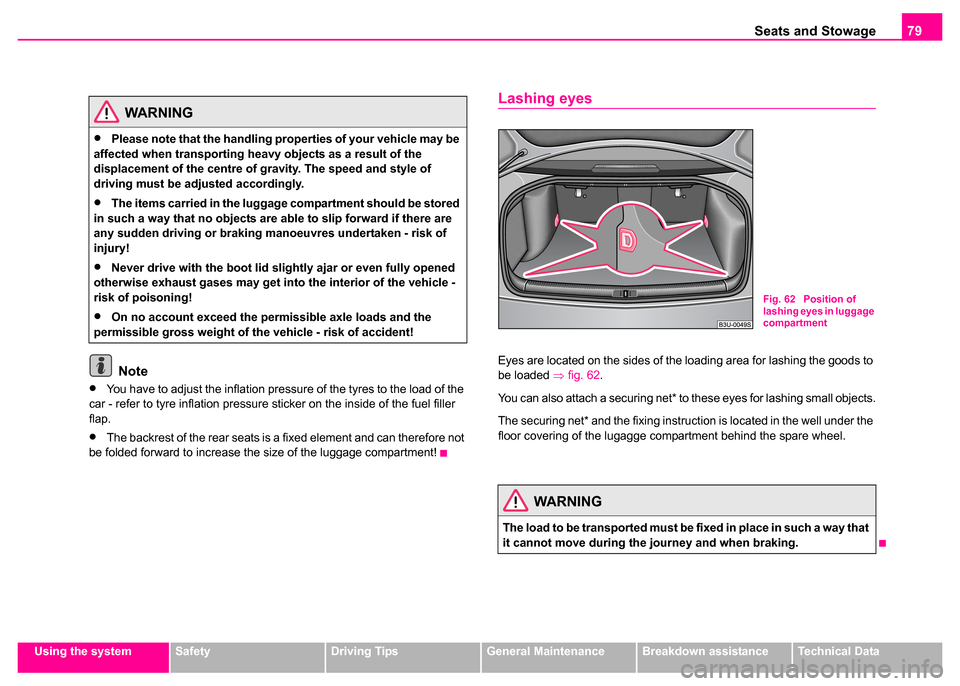
Lashing eyes
Eyes are located on the sides of the loading area for lashing the goods to
be loaded ⇒fig. 62 .
You can also attach a securing net* to these eyes for lashing small objects.
The securing net* and the fixing instruction is located in the well under the
floor covering of the lugagge compartment behind the spare wheel.
WARNING
•Please note that the handling properties of your vehicle may be
affected when transporting heavy objects as a result of the
displacement of the centre of gravity. The speed and style of
driving must be adjusted accordingly.
•The items carried in the luggage compartment should be stored
in such a way that no objects are able to slip forward if there are
any sudden driving or braking manoeuvres undertaken - risk of
injury!
•Never drive with the boot lid slightly ajar or even fully opened
otherwise exhaust gases may get into the interior of the vehicle -
risk of poisoning!
•On no account exceed the permissible axle loads and the
permissible gross weight of th e vehicle - risk of accident!
WARNING
The load to be transported must be fixed in place in such a way that
it cannot move during the journey and when braking.
Fig. 62 Position of
lashing eyes in luggage
compartment
Page 88 of 259

Seats and Stowage87
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
– Press on the bottom part of the handle and open the
compartments in the direction of arrow 3. The compartment
wall must be heard to engage in the slot in the bottom part of
the box.
Moving folding box into secured middle position
– Press on the button marked “PUSH” ⇒page 86, fig. 74
and carefully push the folding box into the secured middle
position. If correctly locked, the button marked “PUSH” is
moved back into its initial position. You can now use the space
which has become available for stowing further items of
luggage.
Caution
•The parts of the folding box can be damaged if handled roughly or in
an unprofessional way.
•The maximum weight of goods to be loaded should not exceed 25
kg.
Lowering folding boxAC
AD
AD
Fig. 75 Lowering
folding box
Fig. 76 Securing
folding box
Page 90 of 259

Seats and Stowage89
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Attachment points
Installing
When fitting on the feet of the roof bars, ensure that they are positioned
exactly between the arrow markings in the sealing strip on the roof
⇒fig. 77 . The markings are visible only when the doors are open.
Roof load
Distribute weight evenly over the roof luggage rack system. The maximum
permissible roof load (including roof rack system) of 100 kg and the
maximum permissible total weight of the vehicle should not be exceeded.
You cannot make full use of the permissible roof load if you use a roof
luggage rack system with a lower load carrying capacity. The load trans-
ported on the roof luggage rack system must not exceed the weight limit
which is stated in the fitting instructions.
Fig. 77 Attachment
points for roof bars
WARNING
•The items which you transport on the roof bar system must be
reliably attached - risk of accident!
•You must on no account exceed the permissible roof load, the
permissible axle loads and the permissible gross weight of your
vehicle - risk of accident!
•Please note that the handling properties of your vehicle change
when you transport heavy or bulky items on the roof bar system as
a result of the displacement of the centre of gravity and the
increased wind attack area - risk of accident! You must absolutely
adapt your style of driving and the speed of the vehicle to the
specific circumstances.
Page 121 of 259
Starting-off and Driving
120
Note
•The parking aid does not operate if you are towing a trailer (applies to
models which feature a factory-fitted towing device*).
•A system fault is indicated if a warning signal sounds for about 5
seconds after switching the ignition on and engaging reverse gear and
there is no obstacle close to your vehicle. Have the fault rectified by a
Škoda dealer.
•The sensors must be kept clean and free of ice to enable the parking
aid to operate properly.
Cruise control system (CCS)*
Introduction
The cruise control system makes it possible for the driver to maintain a
constant speed of his choosing from a speed of 30 km/h (20 mph) or
higher. This, of course, is only possible within the range which is permitted
by the power output and braking power of the engine. Using the cruise
control system - particularly on long journeys - makes it possible for you
to rest your “accelerator foot”.
Caution
Models fitted with a manual gearbox: Always depress the clutch pedal if
you switch on the cruise control system when the gearbox is in Neutral.
The engine will rev up and may even be damaged under certain circum-
stances.
Note
•The cruise control system is not able to maintain a constant speed
when driving on steep downhill sections. The weight of the vehicle
increases the speed at which it travels. One should shift down in good time
to a lower gear or slow the vehicle down by applying the foot brake.
•It is not possible on vehicles fitted with an automatic gearbox to switch
on the cruise control system if the selector lever is in the position P, N , R
or 2.
WARNING (continued)
•You should therefore satisfy yourself, before reversing, that
there is no small obstacle, such as a rock, thin post, trailer drawbar
etc., behind your vehicle. Such an obstacle might not be within the
range detected by the sensors.WARNING
For safety reasons the cruise control system must not be used in
dense traffic or on difficult road surfaces (such as road chips, or
slippery roads) - risk of accident!
Page 140 of 259

Seat belts139
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
The physical principle of a frontal
collision
The physical principle of a frontal accident can be explained quite simply: As soon as the vehicle is moving, so-called kinetic energy (the energy of
motion) is produced both in terms of the car as well as in terms of the
occupants. The magnitude of this kinetic energy depends essentially on
the speed at which the vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the vehicle
and the occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the
greater the amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an
accident.
The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor.
Doubling the speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour
increases the kinetic energy four times.
The common opinion that it is possible to support your body in a minor
accident with your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low
speed, the forces acting on the body are such that it is no longer possible
to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed within the range from 30 km/hour to 50
km/hour, the forces which are produced on your body in the event of an
accident can easily exceed 10,000 N (Newton). This equals a weight of
one tonne (1 000 kg).
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat
belt, are thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolled way parts of the inte-
rior of the car, such as steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen,
⇒fig. 121 .
The occupants of a vehicle who have not fastened their seat belts may
even be thrown out of the vehicle. This can result in fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat passengers fasten their seat belts as they
will otherwise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in
the event of an accident A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the
seat belt is a danger not only to himself but also for those seated at the
front ⇒fig. 122 .
Fig. 121 The driver is
thrown forward if not
wearing a belt
Fig. 122 The rear seat
occupant is thrown
forward if not wearing a
belt
Page 158 of 259

Transporting children safely 157
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Transporting children safely
What you should know about
transporting children!
An introduction to the subject
Accident statistics have revealed that children are gener-
ally more safely transported on the rear seats than on the
front passenger seat.
Children younger than 12 years of age should normally travel on the rear
seat of the vehicle (take note of any national legal provisions which differ
from this). They should be secured there by means of a child restraint
system or by using the existing seat belts depending on their age, body
size and weight. The child seat should be mounted behind the front
passenger seat for safety reasons.
The physical principle of an accident does, of course, also apply to chil-
dren ⇒page 139. They differ from adults in that their muscles and bone
structure of children are not yet fully developed. Thus children are
exposed to increased risk of injury.
Children should be transported by using special child safety seats in order
to reduce this risk of injury.
Use only child safety seats which are officially approved and are suitable
for children and which comply with the ECE-R 44 Standard, which classi-
fies child safety seats into 5 groups ⇒page 161, “Classification of child
seats into groups”. Child restraint systems which have been tested for
conformity with ECE-R 44 have a non-detachable test seal (a large E
within a circle and below this the test number) attached to the seat. We recommend that you use child safety seats from the Škoda range of
genuine accessories. These child seats were developed and also tested
for use in Skoda vehicles. They fulfil the standard ECE-R 44.
Note
Any varying national legal regulations take priority over the information
provided in these instructions for use, or stated in this chapter.
Important safety informat
ion on using child safety
seats
Correct use of child safety seats considerably reduces the
risk of injury!
WARNING
Always comply with legal provis ions and instructions from the
relevant child safety seat manufacturer when installing and using
the child seat ⇒ in “Important safety information on using child
safety seats”.
WARNING
•All the occupants of the car - in particular children - must wear
a seat belt when the car is moving.
Page 162 of 259
Transporting children safely 161
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Child seat
Classification of child seats into groups
Only child safety seats which have an official approval and
are suitable for the child, may be used.
ECE-R 44 standard applies to child safety seats. ECE-R means:
Economic Commission of Europe - Regulation.
Child restraint systems which have been tested for conformity with ECE-
R 44 have a non-detachable test seal (a large E within a circle and below
this the test number) attached to the seat.
Child safety seats are classified in 5 groups: Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the
vehicle without a seat bolster.
Use of child seats
An overview of the usefulness of child seats on each of the seats:
U - universal category - seat is suitable for all approved types of child
safety seats.
WARNING (continued)
•Children must never be seated with their head in the deploy-
ment area of the side airbag. Risk of injury!
•Do not place any objects within the deployment area of the side
airbag. Risk of injury!
GroupWeight
00 -10 kg⇒ page 162
0+up to 13 kg⇒page 162
19 -18 kg⇒page 162
215 -25 kg⇒page 163
322 -36 kg⇒page 164
Child seat
according to
groupFront passenger seatRear seat
on the sideRear seat middle
0UUU
0+UUU
1UUU
2 and 3UUU
Page 164 of 259

Transporting children safely 163
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Child seats in Group 1 are for babies and small children up to 4 years of
age with a weight of between 9 and 18 kilograms. It is best for children in
the lower range of this group, to use a child seat which allows the child to
sit with its back to the direction of travel. It is best for children in the upper
range of the Group 0+, to use a child seat which allows the child to sit
⇒
fig. 140 in the direction of travel.
Child safety seats in which the child is seated with its back facing the
direction of travel, must not be used on the front passenger seat
⇒ page 158, “Use of child safety seats on the front passenger seat”.
Child safety seats in Group 2
For children up to about 7 years of age weighing between 15 and 25 kg
the optimal solution is a child safety seat in combination with the three-
point seat belt ⇒fig. 141 .
WARNING
•It is essential to always switch off the front passenger airbag
(airbags) when attaching in exceptional circumstances a child
safety seat on the front passenger seat where the child is seated
with its back facing in direction of travel (in some countries also
when the child is facing the direction of travel).
−by allowing a Skoda dealer to do this
− or by using the switch for the front passenger airbag*
⇒ page 155.
•The national legal provisions in certain countries require that
both the front, side and head airbags be deactivated. Please
comply with any differing national legal regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
•If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat
may suffer severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger
airbag or airbags are deployed.
•You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reacti-
vated by your Škoda dealer just as soon as you no longer use a
child safety seat on the front passenger seat.
WARNING
•When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please
comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the use
of child safety seats. If required, the airbag has to be deactivated,
−by allowing a Skoda dealer to do this
− or by using the switch for the front passenger airbag*
⇒ page 155.
Fig. 141 Child seat in
Group 2 installed on
the rear seat facing the
direction of travel
Page 183 of 259
Driving and the Environment
182
Avoid driving short distances
Short distances result in an above-average high fuel
consumption.
– Avoid driving a distance of no more than 4 km if the engine is
cold.
The engine and catalytic converter must first have reached their optimal
operating temperature in order to effectively reduce fuel consumption
and pollutant emissions.
The cold engine of a mid-range vehicle consumes 30 - 40 litres/100 km.
of fuel immediately after starting. Fuel consumption drops to 20 litres/100
km. after just 1 kilometre. The engine reaches its operating temperature
only after about four kilometres and the fuel consumption then stabilizes.
You should therefore avoid driving short distances whenever possible.
An important factor in this connection is also the ambient temperature.
The ⇒fig. 149 shows the different fuel consumptions for the same distance, on the one hand at +20°C and on the other hand at -10°C. Your
vehicle has a higher fuel consumption in winter than in summer.
Checking tyre inflation pressures
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.
Always ensure that your tyres are inflated to the correct pressure at all
times. The rolling resistance will be increased if the tyre filling pressure is
too low. This will not only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear
and the driving behaviour will worsen.
Always check the inflation pressure of the tyres when
cold.
Do not drive with winter tyres all year round for this costs about 10 %
more fuel. Winter tyres are also louder.
No unnecessary ballast
Transporting ballast costs fuel.
The fact that every kilogram of extra weight increases your fuel consump-
tion means that it is worth taking a look in the luggage compartment to
avoid transporting any unnecessary ballast.
It is particularly in town trafffic, when one is accelerating quite often, that
the vehicle weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption.
A rule of thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will
cause an increase in fuel consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
You may frequently also leave a roof rack fitted on just out of conven-
ience, although you no longer need it. The increased aerodynamic drag of
your vehicle causes it to use about 1 litre more fuel than normal at a speed
of 100 - 120 km/h, even when you are not carrying a load on the roof.
Fig. 149 Fuel
consumption in
litres/100 km at
different temperatures
Page 185 of 259

Towing a trailer
184
Towing a trailer
Towing a trailer
Technical requirements
The towing device must satisfy certain technical require-
ments.
Your vehicle is designed primarily for transporting persons and luggage.
It can, however, also be used for towing a trailer - provided certain tech-
nical equipment is fitted.
If your vehicle has already been supplied with a factory-fitted towing
device then everything that is necessary for towing a trailer in technical
terms, and in terms of the law, has already been taken into account.
Your vehicle is fitted with a 13-pin power socket for the electrical connec-
tion between the vehicle and trailer. If the trailer which you wish to tow has
a 7-pin connector , you can use a suitable adapter cable. You can obtain
such an adapter from a Škoda dealer.
This work must be carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's
specifications if a towing device is retrofitted.
Škoda dealers are familiar with details relating to retrofitting a towing
device and for any necessary modifications to the cooling system.
General Maintenance
There are a number of points to pay attention to when
towing a trailer.
Trailer load
The permissible trailer load must on no account be exceeded.
You can negotiate appropriately steeper inclines and descents if you do
not make full use of the permissible trailer load.
The trailer loads specified only apply for altitudes up to 1 000 metres
above mean sea level. The fact that the engine power output drops with
increasing height due to a lowering of air pressure and thus the ability to
climb, means that the towed weight must be reduced by 10% for every
further increase of 1 000 metres in height above sea level. The towed
weight is the weight of the (laden) vehicle and the (laden) trailer together.
One should take this into account before driving up to higher altitudes.
The trailer and drawbar load information on the type plate of the
towing device are merely test data for the towing device The data
relating to your vehicle, which is often less than this test data, can
be found in your vehicle registration documents or in the brochure -
Technical Data.
Distribution of the load
Distribute the load in the trailer in such a way that any heavy items are
located as close as possible to the axle. Secure the items to prevent them
slipping.
You can make full use of the permissible drawbar load indicated on the
ball head of the towing device, but you must not exceed this.
WARNING
We recommend that you have the towing device installed by a
Škoda dealer. He is familiar with all the relevant details relating to
retrofitting such equipment. There is a risk of an accident if the
towing device is not properly fitted.