power steering SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012Pages: 1082, PDF Size: 96.1 MB
Page 831 of 1082

01-210000-00
ECU
The ECU controls the electric
power steering system
depending on the driving
conditions, based on the
signals from the torque and
angle sensor.
2) EPS (Electric Power Steering)
Fuse
The vehicle with EPS has
EPS fuse (80A) mounted to
the positive (+) terminal of the
battery, and this fuse supplies
power to the EPS unit
directly..
Steering gear box assembly
When the driver turns the steering wheel, a torque is generated and the torque sensor and the steering
angle sensor in the EPS system detect the rotation of the steering column to run the electric motor. At
this time, the worm gear connected to the motor drives the helical gear mounted to the steering column
to generate the assist torque for the steering column. This allows the driver to operate the steering
wheel easier.
ECU
Tie rod end
Tie rod end Gear boxSteering cylinder
Steering wheel assembly
BLAC motor
Lower
shaft Column
shaft
Colum shaft assembly
The column shaft assembly consists
of BLAC motor, ECU, torque and
angle sensors. The electric power
steering (EPS) system uses the
electric motor to assist the steering
force. It functions independently
regardless of whether the engine is
running or not, unlike the existing
hydraulic power steering.
The lower shafts functions in the
same way as the hydraulic type.
Page 834 of 1082

01-24
4) Basic Inspection
(1) Horn operation
Listen for the horn sound when pressing the horn pad on the steering wheel. -
(2) Brake operation
Check if there is any abnormal noise, unusually long braking distance, or uneven braking force. If the
brake warning lamp does not go out even after starting the engien or are flashing during driving,
have the brake system checked immediately.
Check the brake pipes and hoses for connection, oil leak, crack or interference after changing the
position of tires. When replacing the tires, check the brake disc for surface condition and wear.
Check the parking brake cable and brake operation. Shorten the checking interval if the parking
brake is used frequently. -
-
-
(3) Exhaust system
Be aware to any changes in sound or smell from the exhaust system. These may be caused by leak or
overheat. Have the exhaust system checked and repaired immediately.
Inspect the exhaust system including catalytic converter. Inspect all the components and body frame
near the exhaust system. -
-
(4) Tires
Unusual vibration of the steering wheel and seats or pulling to one side on the straight and level roads
may indicates the uneven tire inflation pressure or poor wheel balance. -
(5) Steering and suspension system
Inspect the front and rear suspension and the steering system for damage, looseness or missing
parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect the power steering line and the hoses for
connection, leak, crack and chafing. Inspect the drive axle boot and seals for damage, tear or leak.
Replace or repair the system if necessary. -
(6) Engine oil
Check the oil level when the engine is still warm and add the specified engine oil if necessary. -
(7) Coolant
Check the coolant level in the coolant reservoir, coolant conditions (contamination, foreign material),
and hoses for damage and leak. Replace or add the Ssangyong genuine coolant, if needed. -
(8) Engine drive belt
Check all drive belts on the engine for wear, crack and looseness. Retighten or replace the belt, if
needed. -
Page 936 of 1082

10-54890-00
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1) What is ABS?
When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels
are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability or rotate resulting in an
accident. ABS helps to maintain directional stability and control of the vehicle. ABS is designed to
secure more safety and increase the control of steering wheel during emergency braking situation. But,
ABS does not guarantee perfect safety beyond its physical limit. ABS in this vehicle contains EBD
function. In normal driving conditions, the brake system operates without ABS function.
2) What is EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution)?
EBD is an automobile brake technology that automatically varies the amount of force applied to each of a
vehicle's brakes, based on road conditions, speed, loading, etc. Always coupled with anti-lock braking
systems, EBD can apply more or less braking pressure to each wheel in order to maximize stopping
power whilst maintaining vehicular control. EBD does not operate when ABS is working.ABS effect according to braking conditions ▶
Braking on split road Maneuvering while braking
Page 937 of 1082
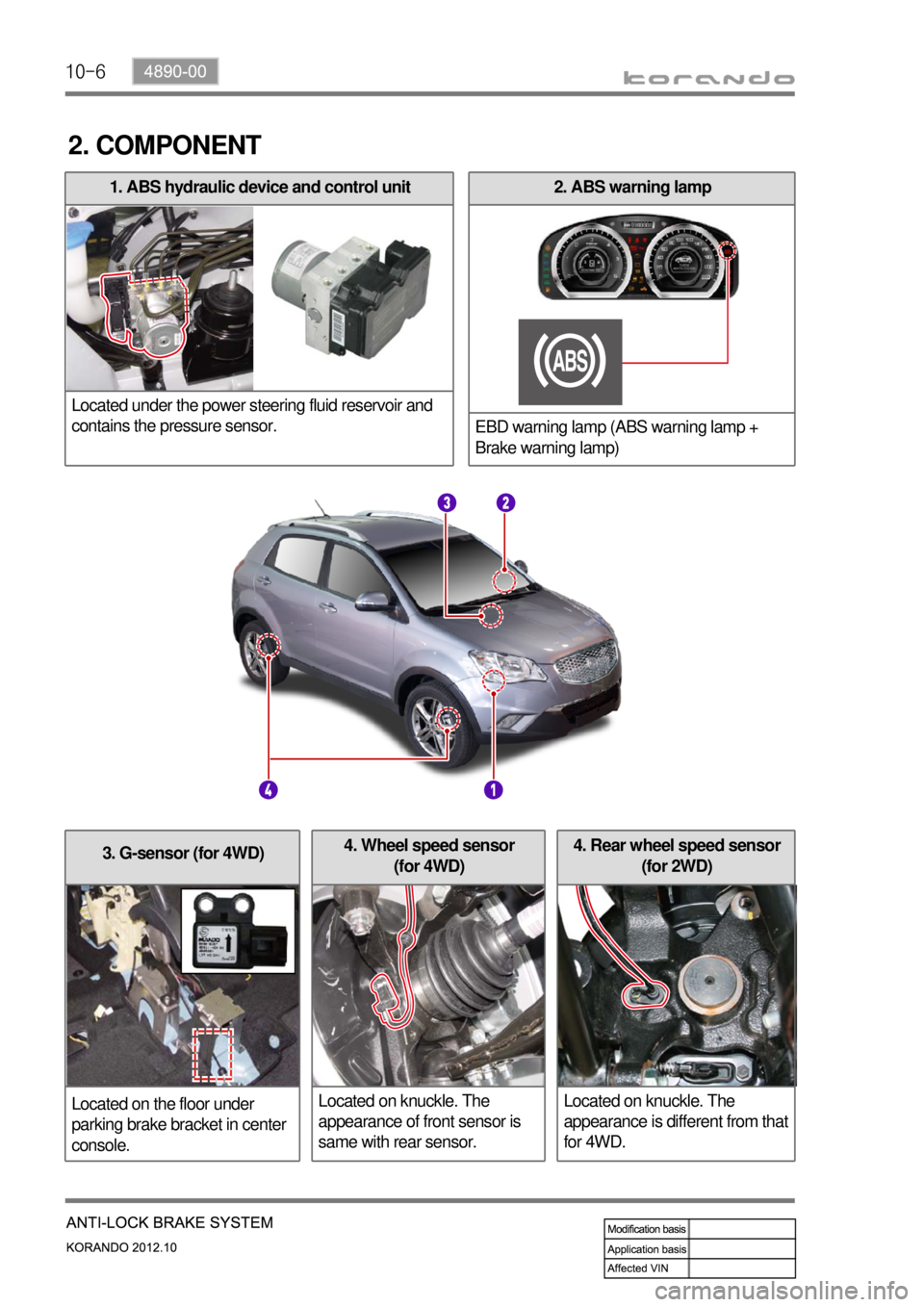
10-6
3. G-sensor (for 4WD)
Located on the floor under
parking brake bracket in center
console.4. Rear wheel speed sensor
(for 2WD)
Located on knuckle. The
appearance is different from that
for 4WD.4. Wheel speed sensor
(for 4WD)
Located on knuckle. The
appearance of front sensor is
same with rear sensor.
2. ABS warning lamp
EBD warning lamp (ABS warning lamp +
Brake warning lamp)1. ABS hydraulic device and control unit
Located under the power steering fluid reservoir and
contains the pressure sensor.
2. COMPONENT
Page 958 of 1082

11-6
1. OVERVIEW
The ESP (Electronic Stability Program) has been developed to help a driver avoid danger of losing
control of the vehicle stability due to understeer or oversteer during cornering. The yaw rate sensor,
lateral sensor and longitudinal sensor in the sensor cluster and the steering wheel angle sensor under
the steering column detect the vehicle conditions when the inner or outer wheels are spinning during
oversteer, understeer or cornering. The ESP ECU controls against oversteer or understeer during
cornering by controlling the vehicle stability using input values from these sensors and applying the
braking force to the corresponding wheels independently. The system also controls the engine power
right before the wheel spin synchronized to decelerate the vehicle automatically in order to maintain the
vehicle stable during cornering.
Page 959 of 1082

11-70000-00
3. ESP OFF switch
Located on the left side of
instrument panel.2. Steering wheel angle
sensor
Located on column shaft with
contact coil.1. HECU assembly
Located under the power
steering fluid reservoir and
contains the pressure sensor.
2. COMPONENTS
4. Sensor cluster
Located on the floor under front
passenger seat.5. Wheel speed sensor
(4WD/2WD-front)
Located on knuckle. the
appearance of front sensor is
same with rear sensor.6. Rear wheel speed sensor
(2WD)
Located on knuckle. The
appearance is different from
that for 4WD.
Page 964 of 1082

11-12
2) Operation of ESP System
The ESP (Electronic Stability Program) has been developed to help a driver avoid danger of losing
control of the vehicle stability due to understeer or oversteer during cornering. The yaw rate sensor,
lateral sensor and longitudinal sensor in the sensor cluster and the steering wheel angle sensor under
the steering column detect the vehicle conditions when the inner or outer wheels are spinning during
oversteer, understeer or cornering. The ESP ECU controls against oversteer or understeer during
cornering by controlling the vehicle stability using input values from these sensors and applying the
braking force to the corresponding wheels independently. The system also controls the engine power
right before the wheel spin synchronized with the ASR function to decelerate the vehicle automatically in
order to maintain the vehicle stable during cornering.
(1) Under steering
What is understeering? ▶
Understeer is a term for a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle during driving
and the front tires slip toward the reverse direction of the desired direction. Generally, vehicles are
designed to have understeer. It is because that the vehicle can return back to inside of cornering line
when the steering wheel is steered toward the inside even when the front wheels are slipped outward.
As the centrifugal force increases, the tires can easily lose the traction and the vehicle tends to slip
outward when the curve angle gets bigger and the speed increases.
Page 968 of 1082
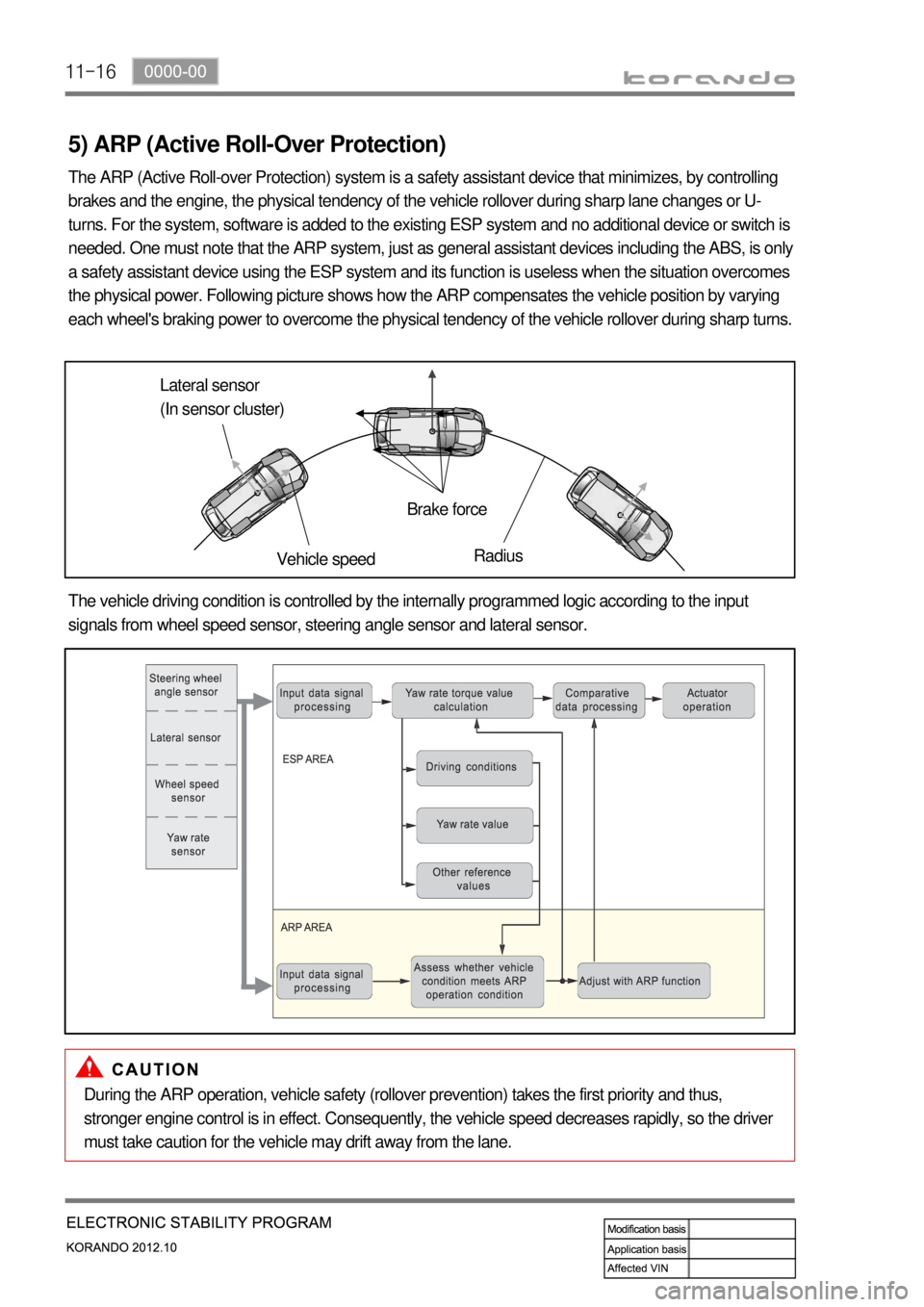
11-16
5) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection)
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch is
needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is only
a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation overcomes
the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle position by varying
each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp turns.
Lateral sensor
(In sensor cluster)
Vehicle speedBrake force
Radius
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus,
stronger engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver
must take caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Page 981 of 1082
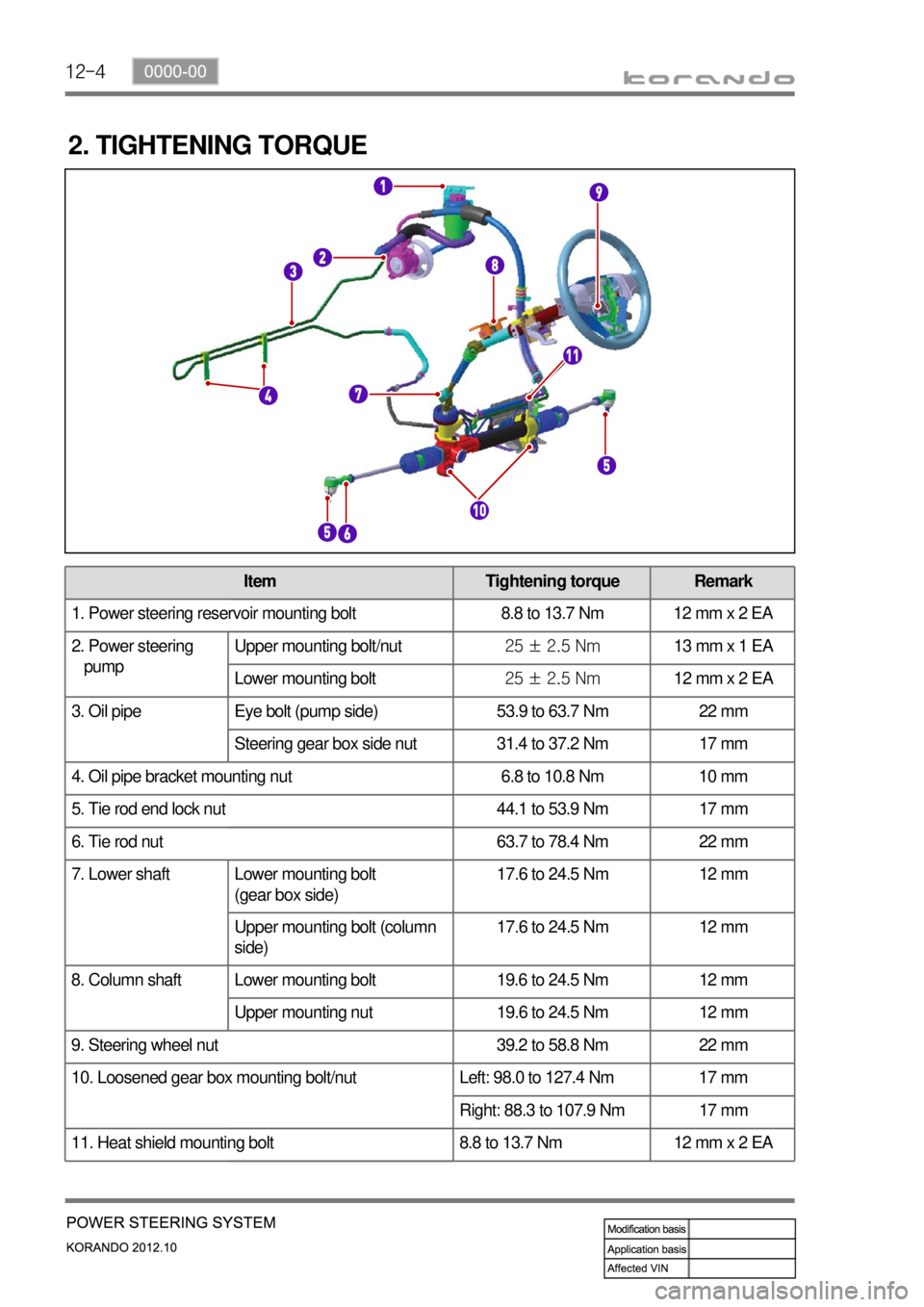
12-4
2. TIGHTENING TORQUE
Item Tightening torque Remark
1. Power steering reservoir mounting bolt 8.8 to 13.7 Nm 12 mm x 2 EA
2. Power steering
pumpUpper mounting bolt/nut25 ± 2.5 Nm13 mm x 1 EA
Lower mounting bolt25 ± 2.5 Nm12 mm x 2 EA
3. Oil pipe Eye bolt (pump side) 53.9 to 63.7 Nm 22 mm
Steering gear box side nut 31.4 to 37.2 Nm 17 mm
4. Oil pipe bracket mounting nut 6.8 to 10.8 Nm 10 mm
5. Tie rod end lock nut 44.1 to 53.9 Nm 17 mm
6. Tie rod nut 63.7 to 78.4 Nm 22 mm
7. Lower shaft Lower mounting bolt
(gear box side)17.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
Upper mounting bolt (column
side)17.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
8. Column shaft Lower mounting bolt 19.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
Upper mounting nut 19.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
9. Steering wheel nut 39.2 to 58.8 Nm 22 mm
10. Loosened gear box mounting bolt/nut Left: 98.0 to 127.4 Nm 17 mm
Right: 88.3 to 107.9 Nm 17 mm
11. Heat shield mounting bolt 8.8 to 13.7 Nm 12 mm x 2 EA
Page 982 of 1082
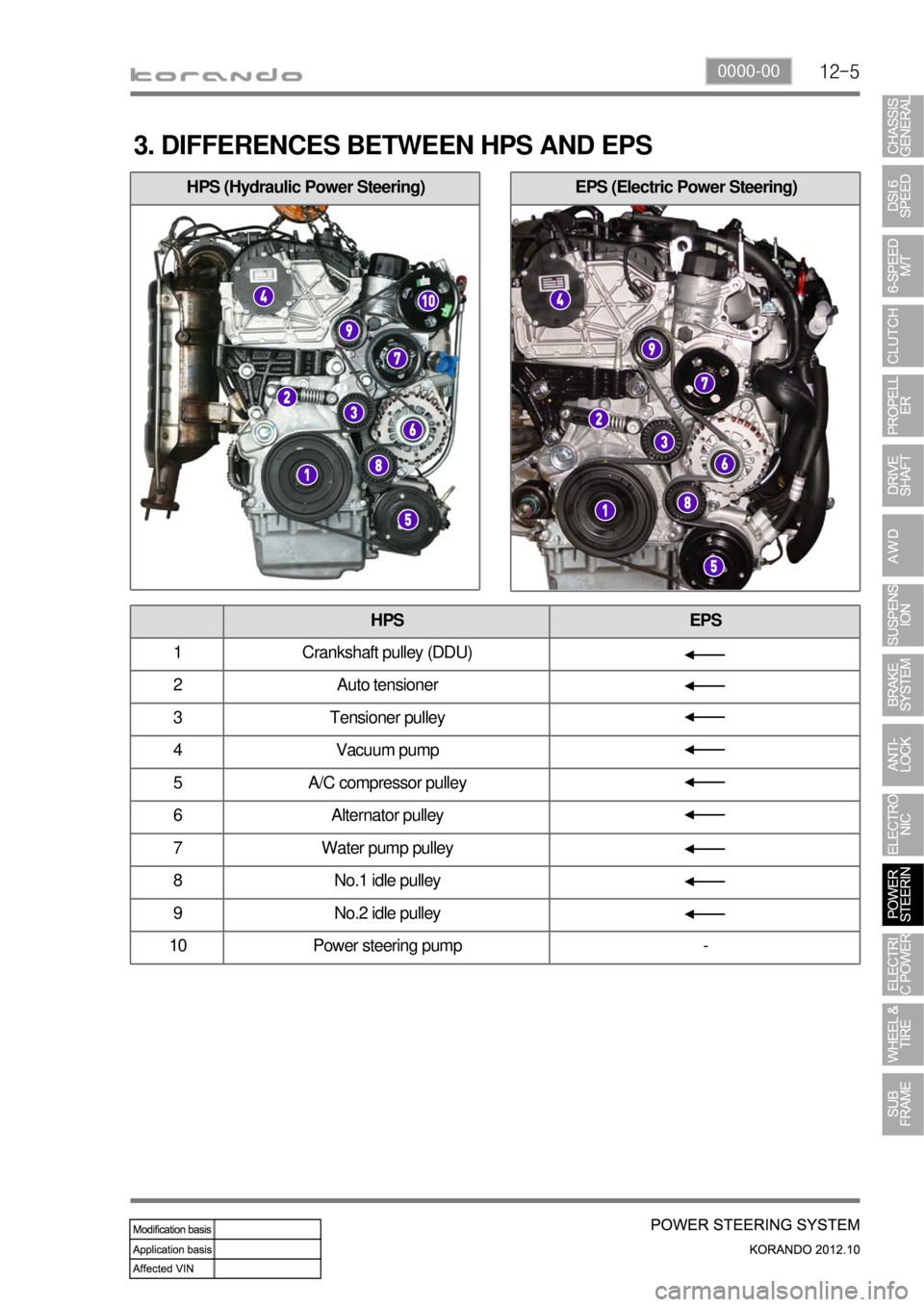
12-50000-00
3. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HPS AND EPS
HPS EPS
1 Crankshaft pulley (DDU)
2 Auto tensioner
3 Tensioner pulley
4 Vacuum pump
5 A/C compressor pulley
6 Alternator pulley
7 Water pump pulley
8 No.1 idle pulley
9 No.2 idle pulley
10 Power steering pump -
HPS (Hydraulic Power Steering)EPS (Electric Power Steering)