brake SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013 Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013Pages: 1336, PDF Size: 92.18 MB
Page 1111 of 1336
4890-00
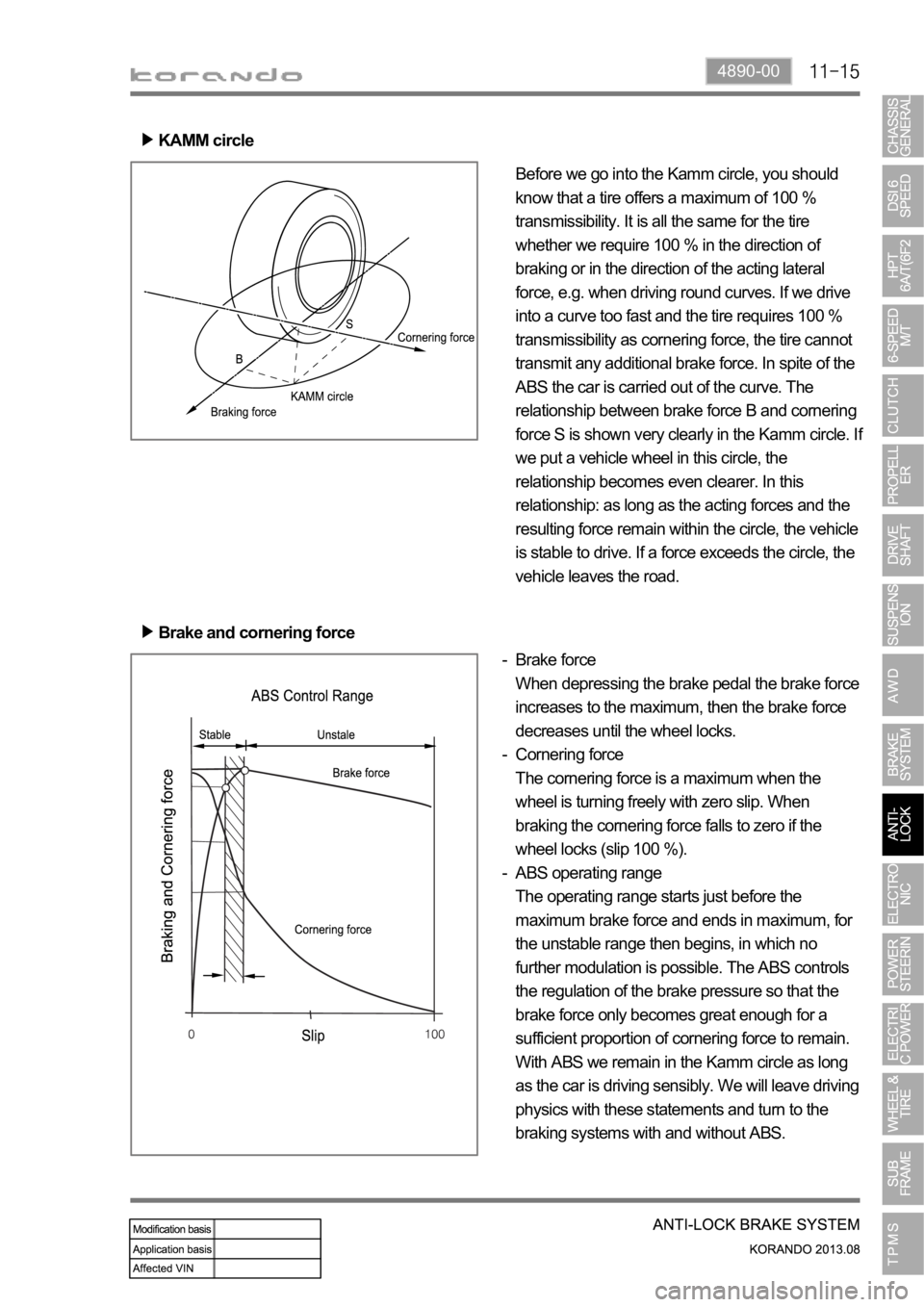
KAMM circle
Before we go into the Kamm circle, you should
know that a tire offers a maximum of 100 %
transmissibility. It is all the same for the tire
whether we require 100 % in the direction of
braking or in the direction of the acting lateral
force, e.g. when driving round curves. If we drive
into a curve too fast and the tire requires 100 %
transmissibility as cornering force, the tire cannot
transmit any additional brake force. In spite of the
ABS the car is carried out of the curve. The
relationship between brake force B and cornering
force S is shown very clearly in the Kamm circle. I
f
we put a vehicle wheel in this circle, the
relationship becomes even clearer. In this
relationship: as long as the acting forces and the
resulting force remain within the circle, the vehicle
is stable to drive. If a force exceeds the circle, the
vehicle leaves the road.
Brake force
When depressing the brake pedal the brake force
increases to the maximum, then the brake force
decreases until the wheel locks.
Cornering force
The cornering force is a maximum when the
wheel is turning freely with zero slip. When
braking the cornering force falls to zero if the
wheel locks (slip 100 %).
ABS operating range
The operating range starts just before the
maximum brake force and ends in maximum, for
the unstable range then begins, in which no
further modulation is possible. The ABS controls
the regulation of the brake pressure so that the
brake force only becomes great enough for a
sufficient proportion of cornering force to remain.
With ABS we remain in the Kamm circle as long
as the car is driving sensibly. We will leave driving
physics with these statements and turn to the
braking systems with and without ABS. -
-
- Brake and cornering force
Page 1112 of 1336

3) Basic ABS Control
Operation of ABS control unit
Applications of the ABS control unit The signals
produced by the wheel sensors are evaluated in
the electronic control unit. From the information
received, the control unit must first compute the
following variables:
Wheel speed
Reference speed
Deceleration
Slip -
-
-
-
Reference speed
The reference speed is the mean, I.e. average speed of all wheel speeds determined by simple
approximation.
Simplified ABS control
If, during braking, one wheel speed deviates from the reference speed, the ABS control unit attempts to
correct that wheel speed by modulating the brake pressure until it again matches the reference speed.
When all four wheels tend to lock, all four wheels speeds suddenly deviate from the previously
determined reference speed. In that case, the control cycle is initiated again in order to again correct the
wheel speed by modulating the brake pressure.
Page 1113 of 1336
4890-00
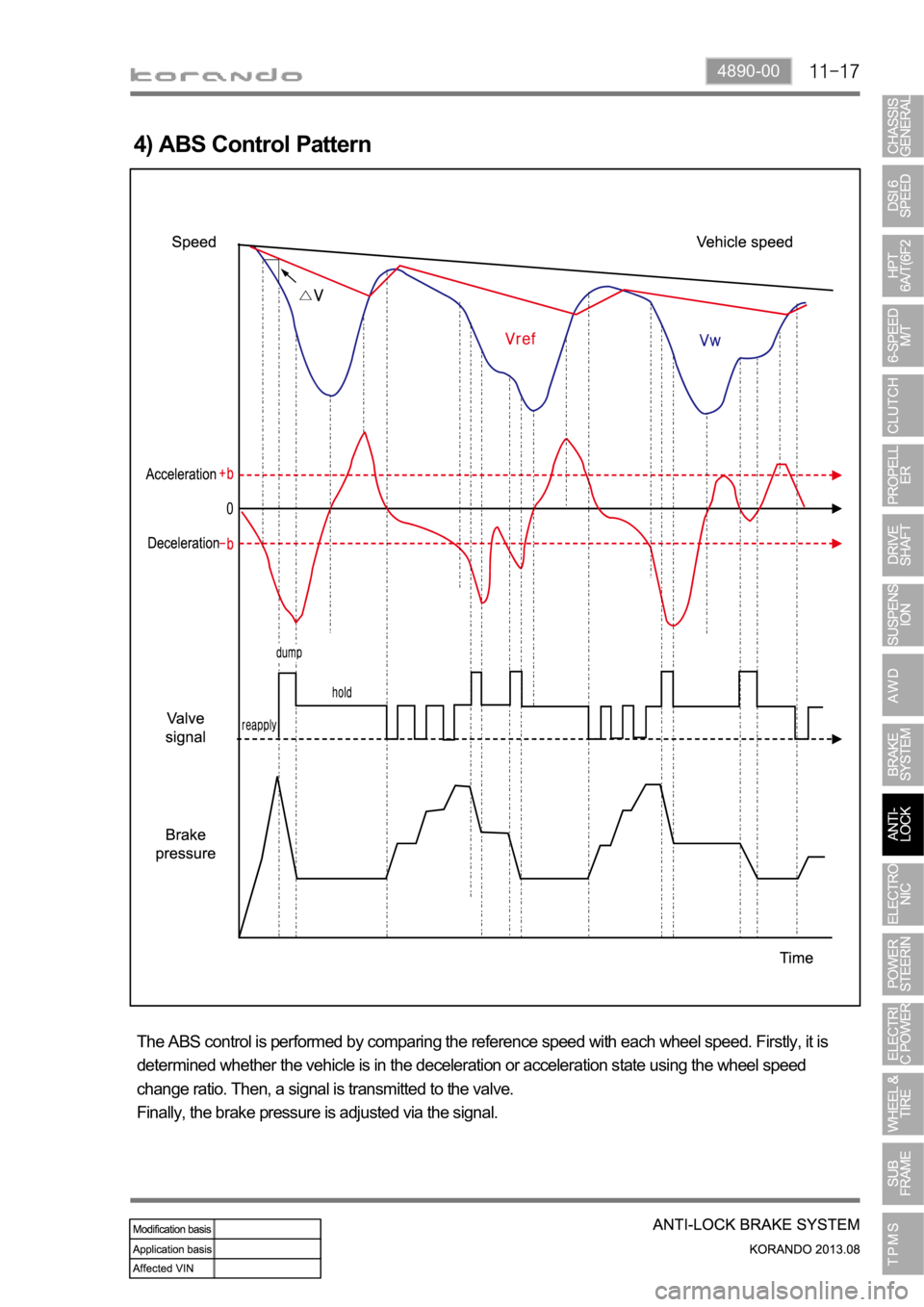
4) ABS Control Pattern
The ABS control is performed by comparing the reference speed with each wheel speed. Firstly, it is
determined whether the vehicle is in the deceleration or acceleration state using the wheel speed
change ratio. Then, a signal is transmitted to the valve.
Finally, the brake pressure is adjusted via the signal.
Page 1114 of 1336
5) EBD (Electronic Brake Force Distribution) System
System description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD works in a range in which the intervention
thresholds for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip is
detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically reproducing
a pressure-reduction function at the rear-wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes control of the brake force distribution between the
front and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system but for a fully loaded vehicle the efficiency of the
EBD system is higher due to the better use of rear axle braking capability.
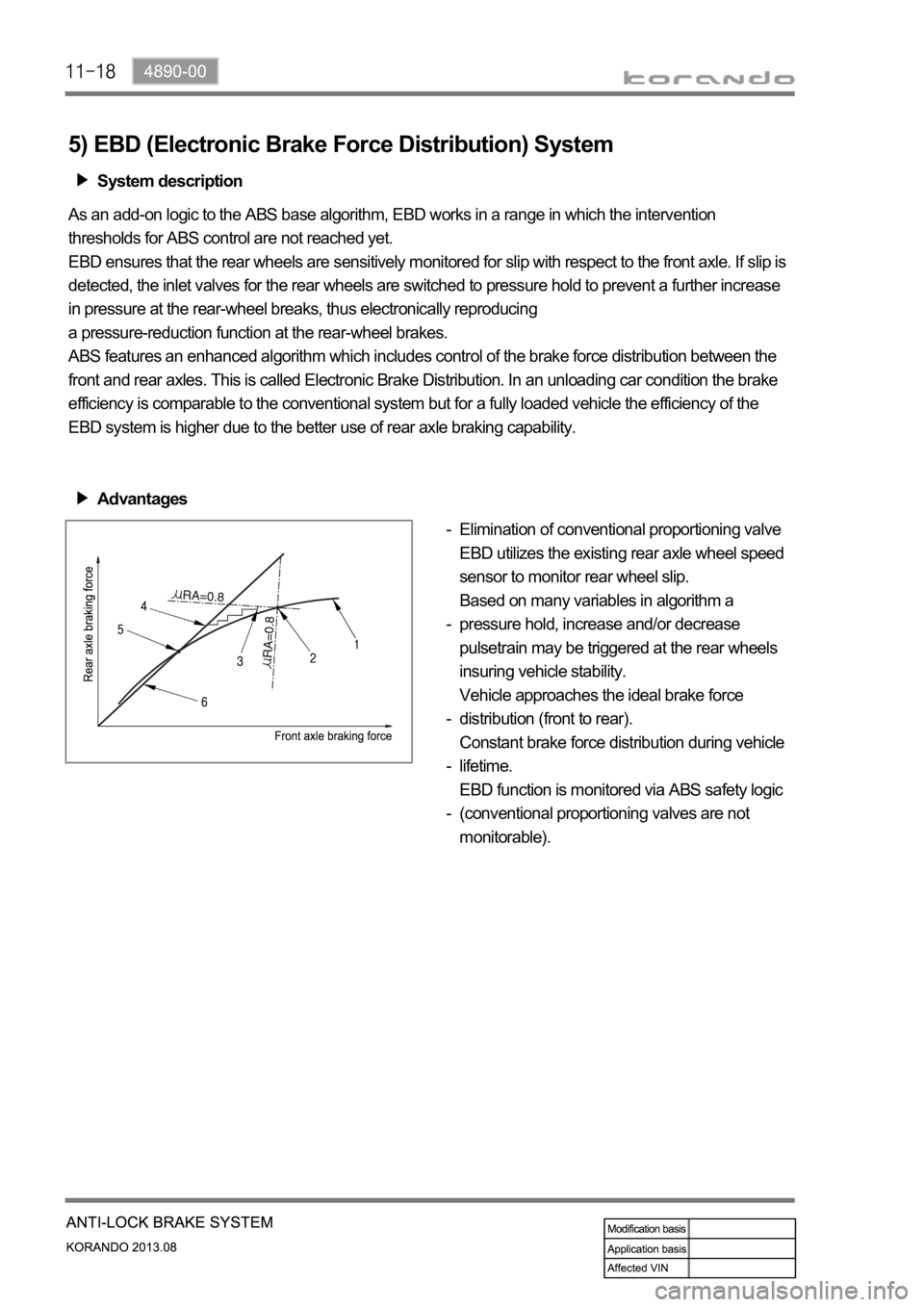
Advantages
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve
EBD utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed
sensor to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a
pressure hold, increase and/or decrease
pulsetrain may be triggered at the rear wheels
insuring vehicle stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle
lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic
(conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable). -
-
-
-
-
Page 1115 of 1336
4890-00
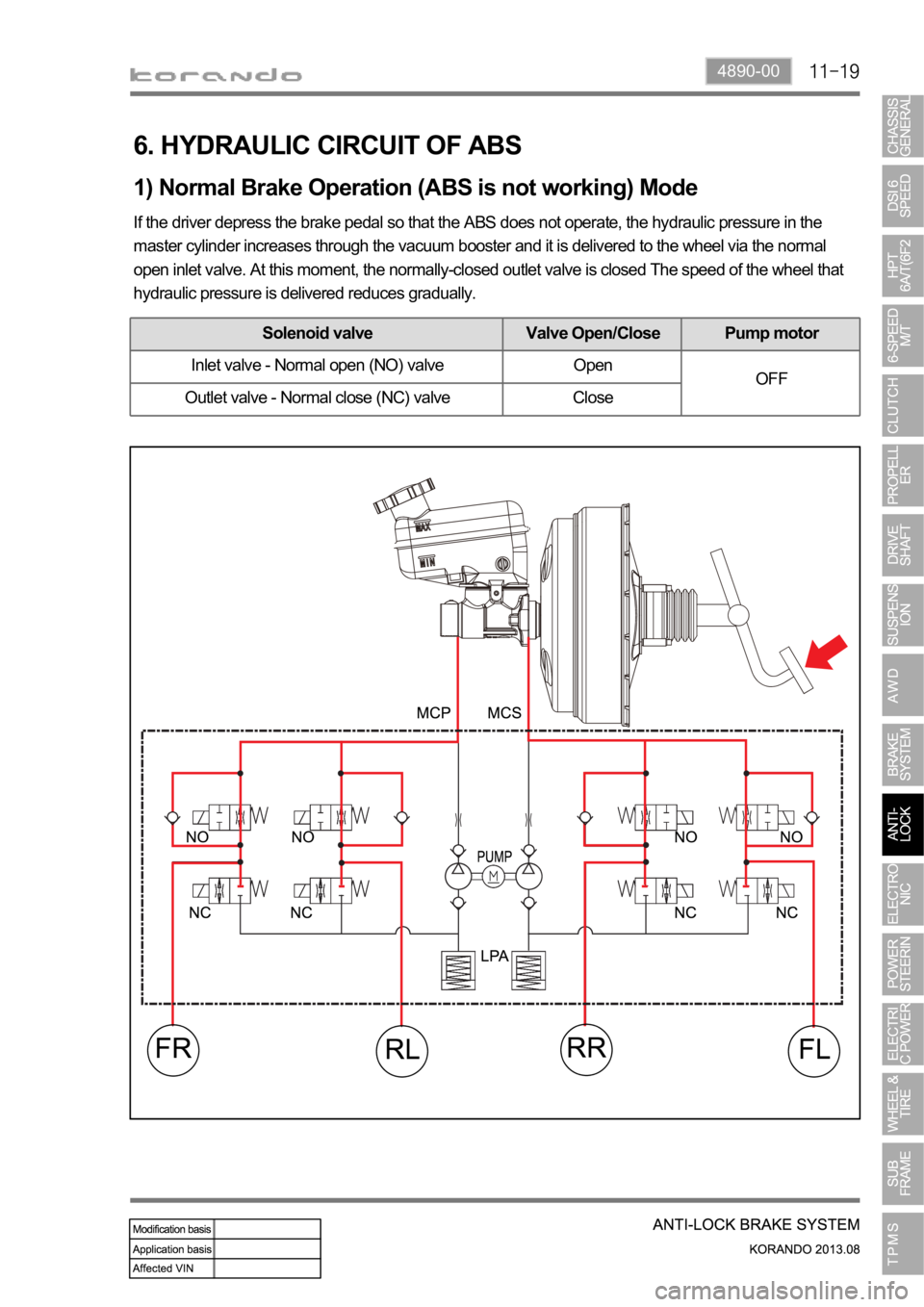
6. HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT OF ABS
1) Normal Brake Operation (ABS is not working) Mode
If the driver depress the brake pedal so that the ABS does not operate, the hydraulic pressure in the
master cylinder increases through the vacuum booster and it is delivered to the wheel via the normal
open inlet valve. At this moment, the normally-closed outlet valve is closed The speed of the wheel that
hydraulic pressure is delivered reduces gradually.
Solenoid valve Valve Open/Close Pump motor
Inlet valve - Normal open (NO) valve Open
OFF
Outlet valve - Normal close (NC) valve Close
Page 1116 of 1336
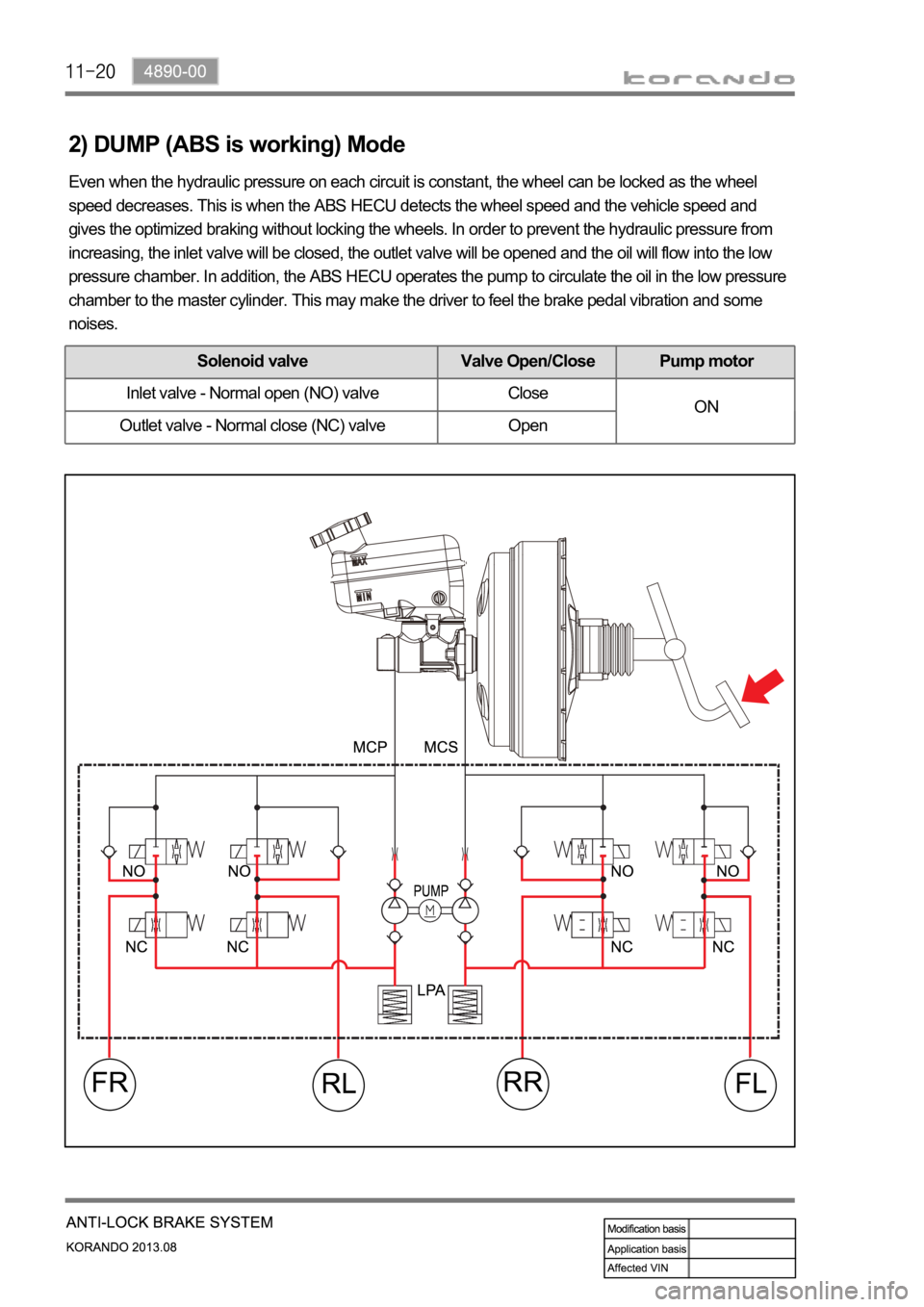
2) DUMP (ABS is working) Mode
Even when the hydraulic pressure on each circuit is constant, the wheel can be locked as the wheel
speed decreases. This is when the ABS HECU detects the wheel speed and the vehicle speed and
gives the optimized braking without locking the wheels. In order to prevent the hydraulic pressure from
increasing, the inlet valve will be closed, the outlet valve will be opened and the oil will flow into the low
pressure chamber. In addition, the ABS HECU operates the pump to circulate the oil in the low pressure
chamber to the master cylinder. This may make the driver to feel the brake pedal vibration and some
noises.
Solenoid valve Valve Open/Close Pump motor
Inlet valve - Normal open (NO) valve Close
ON
Outlet valve - Normal close (NC) valve Open
Page 1118 of 1336
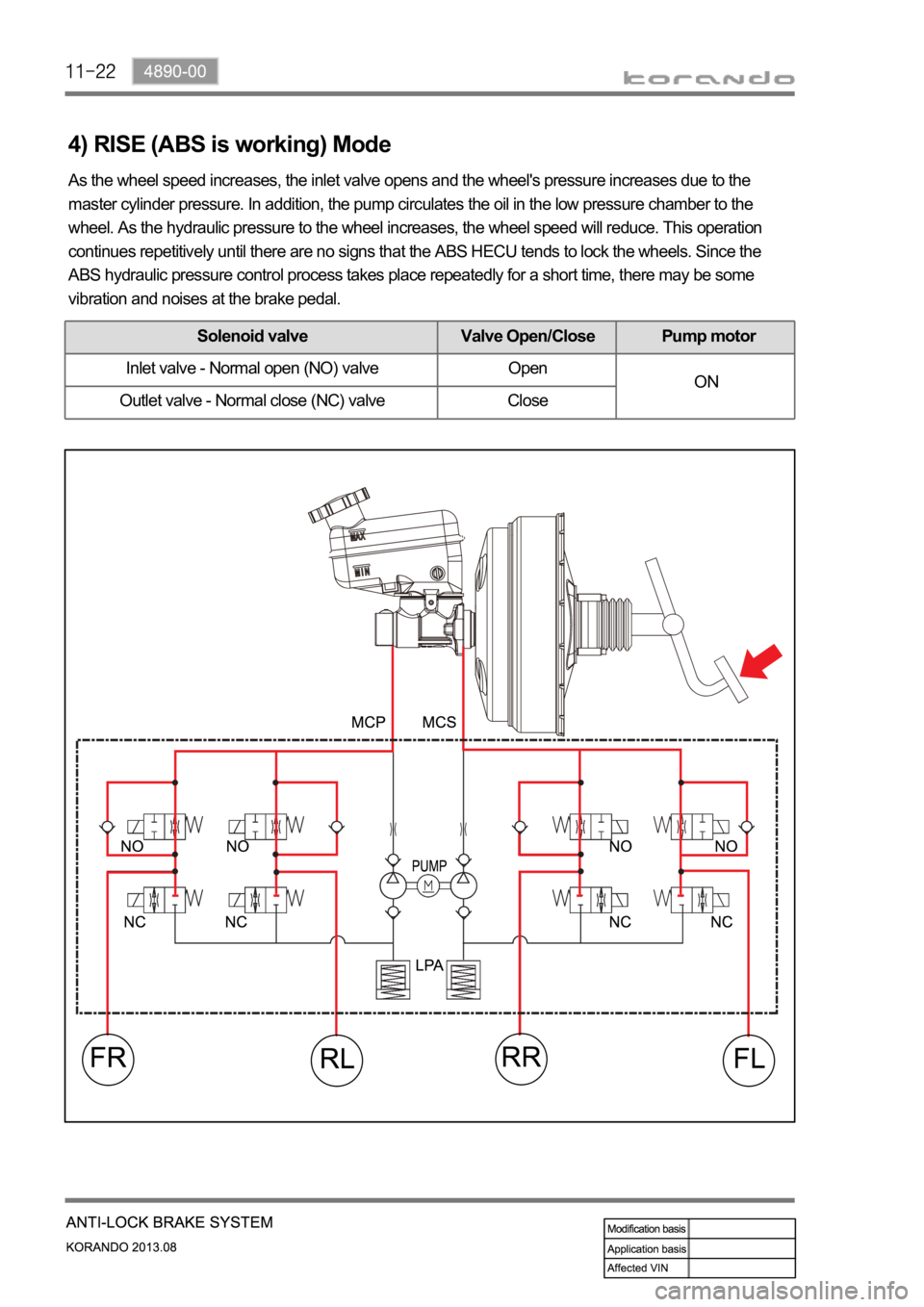
4) RISE (ABS is working) Mode
As the wheel speed increases, the inlet valve opens and the wheel's pressure increases due to the
master cylinder pressure. In addition, the pump circulates the oil in the low pressure chamber to the
wheel. As the hydraulic pressure to the wheel increases, the wheel speed will reduce. This operation
continues repetitively until there are no signs that the ABS HECU tends to lock the wheels. Since the
ABS hydraulic pressure control process takes place repeatedly for a short time, there may be some
vibration and noises at the brake pedal.
Solenoid valve Valve Open/Close Pump motor
Inlet valve - Normal open (NO) valve Open
ON
Outlet valve - Normal close (NC) valve Close
Page 1124 of 1336
0000-00
3. PRECAUTIONS
The warning lamp flashes and warning beep sounds when the ESP is operating
When the ESP operates during vehicle movement, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument panel
flashes and beep comes on every 0.1 second. The ESP system is only a supplementary device for
comfortable driving. When the vehicle exceeds its physical limits, it cannot be controlled.
Do not rely on the system. Keep on the safe driving.
Feeling when ESP is working
When the ESP system activates, the feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving conditions.
For example, you will feel differently when the ESP system is activated during the ABS is operating
with the brakes applied and when the brakes are not applied on a curve.
If the ESP system operates when the brake is applied, the brake pressure will be increased on the
corresponding wheel which already has braking pressure for the ESP controls.
ARP Operation
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus,
stronger engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver
must take caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Noise and vibration that driver feels when ESP system is operating
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to the driver due to the pressure changes caused
by the motor and valve operations in a very short period of time. And, keep in mind that the output
and vehicle speed could be decreased without rpm increase due to the ASR function that controls
the engine power.
Page 1125 of 1336

4. WARNING LAMPS
1) ABS
ABS warning lamp module indicates the self-diagnosis and malfunction.
ABS warning lamp ON: Warning Lamp
When turning the ignition switch to ON position, ABS warning lamp comes on for 3 seconds for self-
diagnosis and goes off if the system is OK (initialization mode).
When the system is defective, the warning lamp comes on.
When the self-diagnosis is performing, the warning lamp comes on.
When the HECU connector is disconnected, the warning lamp comes on.
ABS is not available during lamp ON. In this condition, Only normal brake system without ABS
function is available.
When the communication between warning lamp CAN module in meter cluster, the warning lamp
comes on. 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.ABS warning lamp
Brake warning lamp
ESP OFF indicator
ESP warning lamp/indicator
EBD warning lamp 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Page 1126 of 1336

0000-00
2) EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution) Warning Lamp (Brake
Warning Lamp)
EBD warning lamp when the system perform the self diagnosis and when it detects the malfunction of
EBD system. However, the brake warning lamp comes on regardless of EBD when the parking brake is
applied.
EBD warning lamp ON:
When turning the ignition switch to ON position, ABS warning lamp and the brake warning lamp
comes on for 3 seconds for self diagnosis and goes off if the system is OK (initialization mode).
When applying the parking brake, the brake warning lamp comes on.
When the brake fluid is not sufficient, the brake warning lamp comes on.
When the self-diagnosis is performing, the warning lamp comes on.
When the HECU connector is disconnected, the warning lamp comes on.
When the system is defective, ABS warning lamp and the brake warning lamp come on
simultaneously. 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
When the solenoid valve is defective
When one or more wheel sensors are defective
When ABS HECU is defective
When the voltage is abnormal
When valve relay is defective a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
When the communication between warning lamp CAN module in meter cluster, the warning lamp
comes on. 7.
3) ESP OFF Indicator
ESP OFF indicator ON:
When turning the ignition switch to ON position, ESP warning lamp comes on for 3 seconds for self
diagnosis and goes off if the system is OK (initialization mode).
When the ESP OFF switch is pressed to turn off ESP function, ESP OFF indicator comes on. 1.
2.
4) ESP Warning Lamp
ESP warning lamp ON:
When turning the ignition switch to ON position, ESP warning lamp comes on for 3 seconds for self
diagnosis and goes off if the system is OK (initialization mode).
When the system is defective, the warning lamp comes on.
When the ESP function is activated, ESP warning lamp blinks with the interval of 2 Hz.
When the communication between warning lamp CAN module in meter cluster, the warning lamp
comes on. 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
5) ESP OFF Switch
If ESP OFF switch is pressed, ESP function is deactivated and the ESP OFF indicator in the instrument
cluster comes on.
To resume the ESP function, press the switch again. At this time, ESP OFF indicator goes out.