emergency brake SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013Pages: 1336, PDF Size: 92.18 MB
Page 771 of 1336
8712-03
7. SMART KEY VERIFICATION TIME CONTROL
The smart key verification time control consists of pre-verification timer and immobilizer verification timer,
and no verification process is required for 30 seconds after the each verification process has been
completed.
Pre-verification timer: Time for performing start & power mode function that controls the vehicle
power.
Immobilizer verification timer: Time for which the start with a smart key is possible after the SKM and
EMS (ECU) verify the immobilizer. -
-
Item Pre-verification timer Immobilizer verification timer
Operating power
Power OFF, ACC, IGN ON IGN ON after pre-verification (ACC)
FunctionTime for which the power control can be
carried out under the verified conditions
(30 seconds after the verification)Time for which the start request can be
carried out without a smart key under the
verified conditions
(30 seconds after the verification)
Input conditions
Verification
conditionsSmart key searching completed after the
following conditions are met:
Close signal input after any door
opened
Brake switch signal input
START/STOP switch signal input
After emergency slot inserted
After IGN OFF 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.Power changed to IGN ON after
valid pre-verification
Power changed to IGN ON by
smart key verification after pre-
verification timer completed
Smart key verification succeeded
by brake switch input after
immobilizer verification timer
completed with IGN ON
Smart key verification succeeded
after immobilizer verification timer
completed with IGN ON,
immobilizer verification and brake
switch input 1.
2.
3.
4. All doors closed
(including tailgate)
START/STOP switch input
Brake switch signal input
Smart key inserted into emergency
slot
Smart key searching completed
Engine start ON to OFF 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.Brake switch signal input
START/STOP switch input 1.
2.
Page 1101 of 1336

4890-00
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1) What is ABS?
When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels
are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability or rotate resulting in an
accident. ABS helps to maintain directional stability and control of the vehicle. ABS is designed to
secure more safety and increase the control of steering wheel during emergency braking situation. But,
ABS does not guarantee perfect safety beyond its physical limit. ABS in this vehicle contains EBD
function. In normal driving conditions, the brake system operates without ABS function.
2) What is EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution)?
EBD is an automobile brake technology that automatically varies the amount of force applied to each of a
vehicle's brakes, based on road conditions, speed, loading, etc. Always coupled with anti-lock braking
systems, EBD can apply more or less braking pressure to each wheel in order to maximize stopping
power whilst maintaining vehicular control. EBD does not operate when ABS is working. ABS effect according to braking conditions
Braking on split road Maneuvering while braking
Page 1131 of 1336
4) HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist System)
(1) Purpose
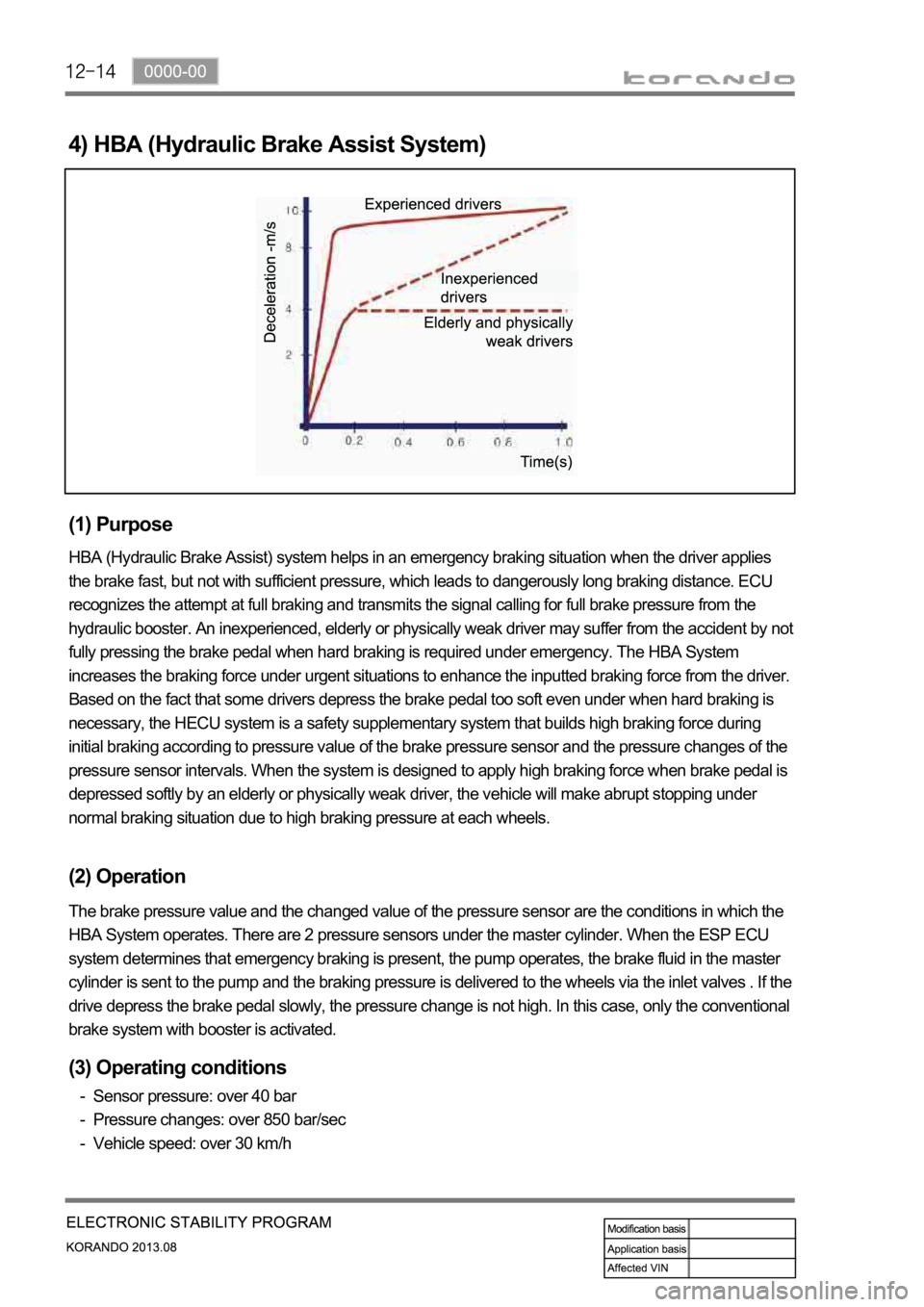
HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist) system helps in an emergency braking situation when the driver applies
the brake fast, but not with sufficient pressure, which leads to dangerously long braking distance. ECU
recognizes the attempt at full braking and transmits the signal calling for full brake pressure from the
hydraulic booster. An inexperienced, elderly or physically weak driver may suffer from the accident by not
fully pressing the brake pedal when hard braking is required under emergency. The HBA System
increases the braking force under urgent situations to enhance the inputted braking force from the driver.
Based on the fact that some drivers depress the brake pedal too soft even under when hard braking is
necessary, the HECU system is a safety supplementary system that builds high braking force during
initial braking according to pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and the pressure changes of the
pressure sensor intervals. When the system is designed to apply high braking force when brake pedal is
depressed softly by an elderly or physically weak driver, the vehicle will make abrupt stopping under
normal braking situation due to high braking pressure at each wheels.
(2) Operation
The brake pressure value and the changed value of the pressure sensor are the conditions in which the
HBA System operates. There are 2 pressure sensors under the master cylinder. When the ESP ECU
system determines that emergency braking is present, the pump operates, the brake fluid in the master
cylinder is sent to the pump and the braking pressure is delivered to the wheels via the inlet valves . If the
drive depress the brake pedal slowly, the pressure change is not high. In this case, only the conventional
brake system with booster is activated.
(3) Operating conditions
Sensor pressure: over 40 bar
Pressure changes: over 850 bar/sec
Vehicle speed: over 30 km/h -
-
-
Page 1142 of 1336
0000-00
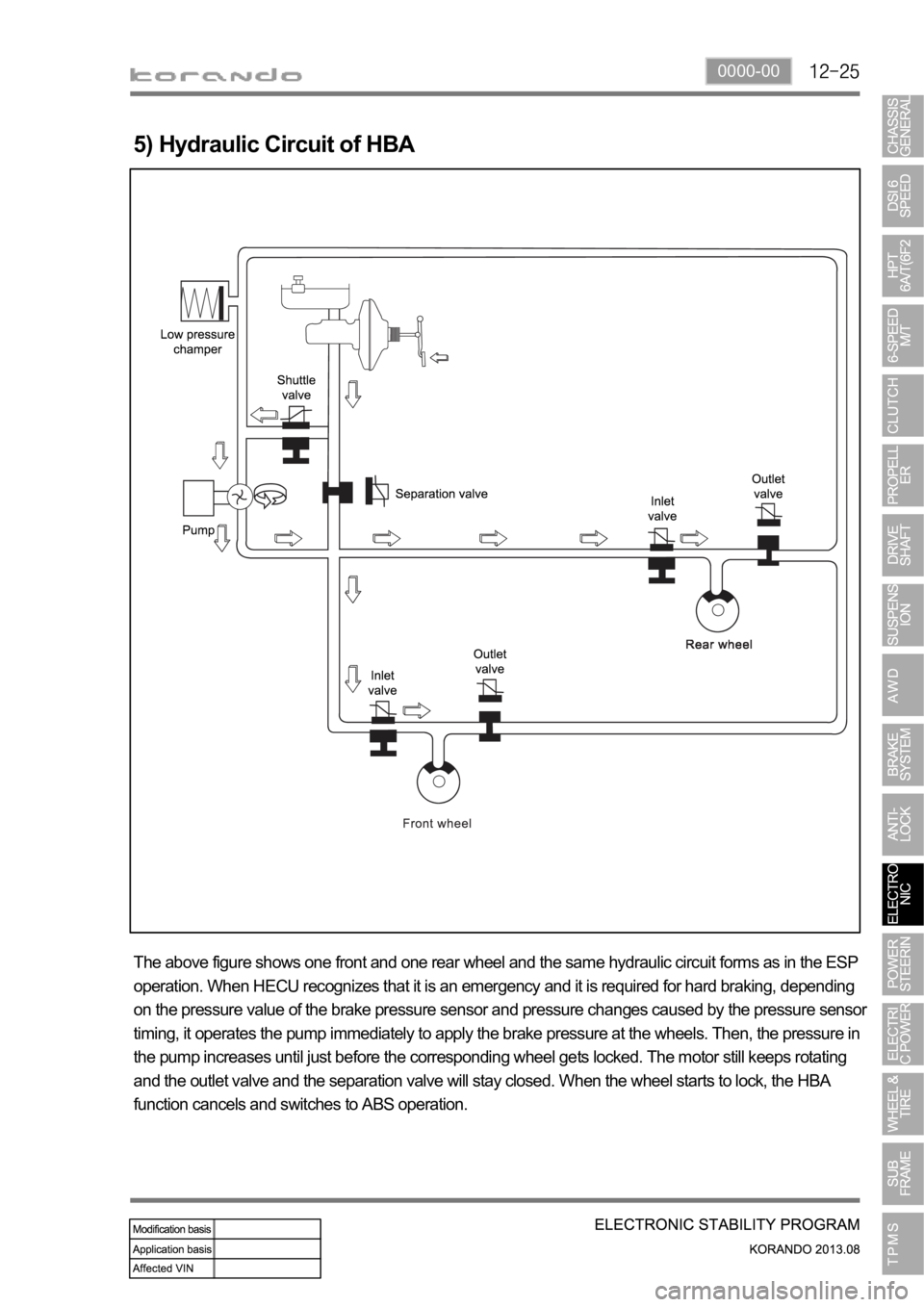
5) Hydraulic Circuit of HBA
The above figure shows one front and one rear wheel and the same hydraulic circuit forms as in the ESP
operation. When HECU recognizes that it is an emergency and it is required for hard braking, depending
on the pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and pressure changes caused by the pressure sensor
timing, it operates the pump immediately to apply the brake pressure at the wheels. Then, the pressure in
the pump increases until just before the corresponding wheel gets locked. The motor still keeps rotating
and the outlet valve and the separation valve will stay closed. When the wheel starts to lock, the HBA
function cancels and switches to ABS operation.
Page 1232 of 1336

8810-00
1. AIR BAG SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The air bag system is divided into front air bag system and side air bag system. The system protects the
occupant's body by deploying the air bags in the event of a collision. The system consists of 8 inflators
including the inflators of the seat belt pretensioners, air bag unit (SDM), and 4 impact sensors on the
front side and both sides of the vehicle. The air bag unit (SDM) determines the operation of each air bag
module and seat belt pretensioners using the crash signals from the front and side impact sensors in the
event of a collision. The front and side air bag systems are operated independently, and the body control
module (BCM) activates the auto door unlock function and various lamps including hazard warning lamp
and room lamps, when the crash signal from the SDM is received to notify others of emergency situation
and let the occupant escape easily. The SDM is equipped with self diagnosis function, and it performs
the diagnosis on the internal/external devices of the air bag system for a certain period of time after IGN
ON. And it monitors the air bag system regularly and turns on the air bag warning lamp on the
instrument cluster when a fault is found in the system, to notify the driver. The SDM has event data
recorder (EDR) function that stores the driving information data transmitted through CAN communication
from various units (vehicle speeds, engine rpm, brake application, etc.) in a crash or near crash event,
when the acceleration sensor in the air bag unit detects a sharp acceleration change, regardless of the
air bag deployment