engine electri SSANGYONG KYRON 2008 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2008, Model line: KYRON, Model: SSANGYONG KYRON 2008Pages: 650, PDF Size: 73.24 MB
Page 190 of 650

ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM
undefined
1881-01
1881-01ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM
GENERAL
1. CAUTIONS FOR DI ENGINE
This chapter describes the cautions for DI engine equipped vehicle. This includes the water
separation from engine, warning lights, symptoms when engine malfunctioning, causes and
actions.
1) DI Engine
Comparatively conventional diesel engines, DI engine controls the fuel injection and timing
electrically, delivers high power and reduces less emission.
2) System Safety Mode
When a severe failure has been occurred in a vehicle, the system safety mode is activated to
protect the system. It reduces the driving force, restricts the engine speed (rpm) and stops
engine operation. Refer to "Diagnosis" section in this manual.
3) Water Separator Warning Light
When the water level inside water separator
in fuel filter exceeds a certain level (approx.
39 cc), this warning light comes on and
buzzer sounds.
Also, the driving force of the vehicle
decreases (torque reduction). If these
conditions occur, immediately drain the
water from fuel filter.
For the draining procedures, please refer to
"How to drain the water from fuel filter"
section.
4) Priming Pump
The priming pump installed in fuel pump is the device to fill the fuel into the fuel filter. When the
vehicle is under the conditions as below, press the priming pump until it becomes rigid before
starting the engine.
5) Conditions for Using Priming Pump
After run out of fuel
After draining the water from fuel separator
After replacing the fuel filter -
-
-
Page 193 of 650

undefined
1881-01
ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM
OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS
1. ELECTRONIC CONTROL OF FUEL SYSTEM
According to input signals from various sensors, engine ECU calculates driver's demand
(position of the accelerator pedal) and then controls overall operating performance of engine
and vehicle on that time.
ECU receives signals from sensors via data line and then performs effective engine air-fuel
ratio controls based on those signals. Engine speed is measured by crankshaft speed (position)
sensor and camshaft speed (position) sensor determines injection order and ECU detects
driver's pedal position (driver's demand) through electrical signal that is generated by variable
resistance changes in accelerator pedal sensor. Air flow (hot film) sensor detects intake ai
r
volume and sends the signals to ECU. Especially, the engine ECU controls the air-fuel ratio by
recognizing instant air volume changes from air flow sensor to decrease the emissions (EGR
valve control). Furthermore, ECU uses signals from coolant temperature sensor and ai
r
temperature sensor, booster pressure sensor and atmospheric pressure sensor as
compensation signal to respond to injection starting, pilot injection set values, various
operations and variables.Components
High pressure fuel pump
Fuel injectors -
-Fuel rail
Electronic control unit(ECU) -
-Fuel pressure sensor
Various sensors and actuators -
-Supply line
Return line
ECU connecting line
Page 199 of 650
undefined
1881-01
ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM
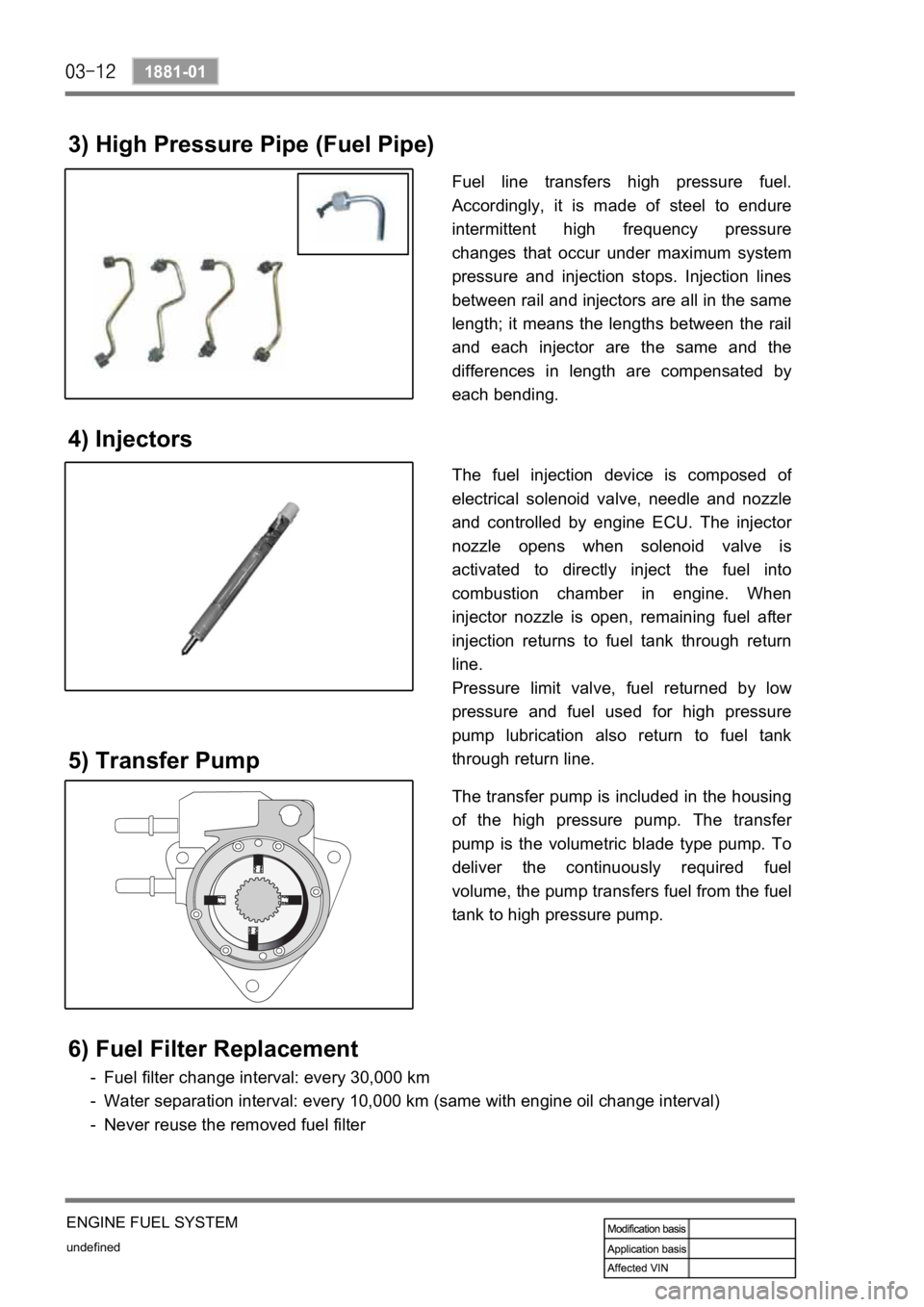
3) High Pressure Pipe (Fuel Pipe)
Fuel line transfers high pressure fuel.
Accordingly, it is made of steel to endure
intermittent high frequency pressure
changes that occur under maximum system
pressure and injection stops. Injection lines
between rail and injectors are all in the same
length; it means the lengths between the rail
and each injector are the same and the
differences in length are compensated by
each bending.
4) Injectors
The fuel injection device is composed of
electrical solenoid valve, needle and nozzle
and controlled by engine ECU. The injecto
r
nozzle opens when solenoid valve is
activated to directly inject the fuel into
combustion chamber in engine. When
injector nozzle is open, remaining fuel afte
r
injection returns to fuel tank through return
line.
Pressure limit valve, fuel returned by low
pressure and fuel used for high pressure
pump lubrication also return to fuel tank
through return line.
6) Fuel Filter Replacement
Fuel filter change interval: every 30,000 km
Water separation interval: every 10,000 km (same with engine oil change interval)
Never reuse the removed fuel filter -
-
-
The transfer pump is included in the housing
of the high pressure pump. The transfe
r
pump is the volumetric blade type pump. To
deliver the continuously required fuel
volume, the pump transfers fuel from the fuel
tank to high pressure pump.
5) Transfer Pump