flat tire SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1998, Model line: MUSSO, Model: SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998Pages: 1463, PDF Size: 19.88 MB
Page 15 of 1463
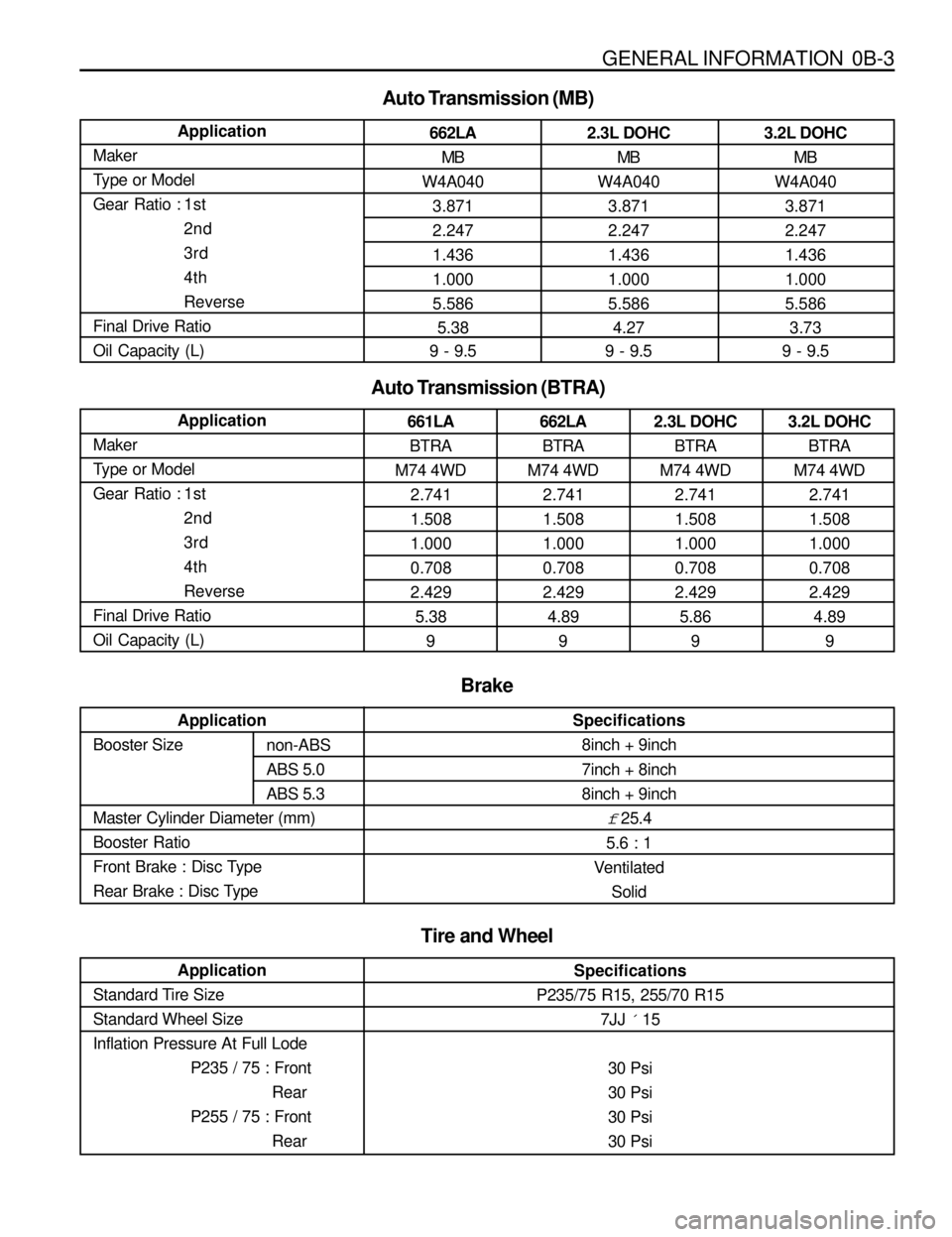
GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-3
662LA
MB
W4A040
3.871
2.247
1.436
1.000
5.586
5.38
9 - 9.5
Auto Transmission (MB)
Application
Maker
Type or Model
Gear Ratio : 1st
2nd
3rd
4th
Reverse
Final Drive Ratio
Oil Capacity (L)2.3L DOHC
MB
W4A040
3.871
2.247
1.436
1.000
5.586
4.27
9 - 9.53.2L DOHC
MB
W4A040
3.871
2.247
1.436
1.000
5.586
3.73
9 - 9.5
661LA
BTRA
M74 4WD
2.741
1.508
1.000
0.708
2.429
5.38
9
Auto Transmission (BTRA)
Application
Maker
Type or Model
Gear Ratio : 1st
2nd
3rd
4th
Reverse
Final Drive Ratio
Oil Capacity (L)662LA
BTRA
M74 4WD
2.741
1.508
1.000
0.708
2.429
4.89
92.3L DOHC
BTRA
M74 4WD
2.741
1.508
1.000
0.708
2.429
5.86
93.2L DOHC
BTRA
M74 4WD
2.741
1.508
1.000
0.708
2.429
4.89
9
Tire and Wheel
Specifications
P235/75 R15, 255/70 R15
7JJ ´ 15
30 Psi
30 Psi
30 Psi
30 Psi Application
Standard Tire Size
Standard Wheel Size
Inflation Pressure At Full Lode
P235 / 75 : Front
Rear
P255 / 75 : Front
Rear Application
Booster Size
Master Cylinder Diameter (mm)
Booster Ratio
Front Brake : Disc Type
Rear Brake : Disc Type
Specifications
8inch + 9inch
7inch + 8inch
8inch + 9inch
f 25.4
5.6 : 1
Ventilated
Solid
Brake
non-ABS
ABS 5.0
ABS 5.3
Page 19 of 1463
GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-7
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
Fuel Filter Replacement
Replace the engine fuel filter every.
lGasoline Engine : 60,000km (36,000 miles)
lDiesel Engine : 45,000km (24,000 miles)
Spark Plug Replacement
Replace spark plugs with same type.
lType : BOSCH : F8DC4
BERU : 14F-8DU4
Champion : C11YCC
lGap : 0.8 ± 0.1 mm
Spark Plug Wire Replacement
Clean wires and inspect them for burns, cracks or other
damage. Check the wire boot fit at the Distributor and at
the spark plugs. Replace the wires as needed.
Brake System Service
Check the disc brake pads or the drum brake linings.
Check the pad and the lining thickness carefully.
Tire and Wheel Inspection and Rotation
Check the tires for abnormal wear or damage. To
equalize wear and obtain maximum tire life, rotate the
tires. If irregular or premature wear exists, check the
wheel alignment and check for damaged wheels. While
the tires and wheels are removed, inspect the brakes.
NORMAL VEHICLE USE
The maintenance instructions contained in the
maintenance schedule are based on the assumption
that the vehicle will be used for the following reasons:
lTo carry passengers and cargo within the limitation
of the tire inflation prassure. Refer to “Tire and Wheel”
in section 2E.
lTo be driven on reasonable road surfaces and within
legal operating limits.
EXPLANATION OF SCHEDULED
MAINTENANCE SERVICES
The services listed in the maintenance schedule are
further explained below. When the following maintenance
services are performed, make sure all the parts are
replaced and all the necessary repairs are done before
driving the vehicle. Always use the proper fluid and
lubricants.
Engine Oil and Oil Filter Change
Always use above the API SH grade or recommended
engine oil.
Engine Oil Viscosity
Engine oil viscosity (thickness) has an effect on fuel
economy and cold weather operation. Lower viscosity
engine oils can provide better fuel economy and cold
weather performance; however, higher temperature
weather conditions require higher viscosity engine oils
for satisfactory lubrication. Using oils of any viscosity
other than those viscosities recommended could result
in engine damage.
Cooling System Service
Drain, flush and refill the system with new coolant. Refer
to “Recommended Fluids And Lubricants” in this section.
Air Cleaner Element Replacement
Clean the air cleaner element every.
lGasoline Engine : 15,000km (10,000 miles)
lDiesel Engine : 10,000km (6,000 miles)
Replace the air cleaner element every .
lGasoline Engine : 60,000km (36,000 miles)
lDiesel Engine : 30,000km (18,000 miles)
Replace the air cleaner more often under dusty
conditions.
Tire Rotation (Left - Hand Drive Type)
Page 21 of 1463

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-9
Chassis and Body
Months
MAINTENANCE
ITEMMAINTENANCE INTERVALKilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
120 105 90 75 60 45 30 15 1
96 84 72 60 48 36 24 12
- x1,000 km
Exhaust pipes & mountings
Brake/Clutch fluid(3)(4)
Parking brake/Brake pads F & R (5)
Brake line & connections (including booster)
Manual transmission oil (3)
Clutch & brake pedal free play
Front & Rear Differential Fluid (3)I
R
I
I
I
I
I-
-
-
I
I
-
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
R
I
RI
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
R
I
RI
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
I
Automatic transmission fluid (MB W4A040) (6)
Automatic transmission fluid (BTRA M74)
Chassis & underbody bolts & nuts tight/secure
Tire condition & inflation pressure
Wheel alignment (7)
Steering wheel & linkage
Power steering fluid & lines* (3)
Drive shaft boots
Seat belts, buckles & anchors
Lubricate locks, hinges & bonnet latchI
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
IR
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
IR
R
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Transfer case fluidRIII
Inspect & ADJUST when abnormal condition is noted
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Chart Symbols :
I - Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R - Replace or change.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
(4) Change the brake / clutch fluid every 15,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions:
- Driving in hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- Towing a trailer frequently
(5) More frequent maintenance is required if under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling, frequent low -
speed operation in stop-and-go traffic or driving in dusty condition.
(6) Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter every 75,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions.
- In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly reaches 32°C (90°F) or higher, or
- In hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- When doing frequent trailer towing, or
- Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
(7) If necessary, rotate and balance wheels.
Page 23 of 1463

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-11
Chassis and Body
Months
-
MAINTENANCE
ITEMMAINTENANCE INTERVAL
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 1
60 54 48 42 36 30 24 18 12 6 x1,000 km
Exhaust pipes & mountings
Brake/clutch fluid(3) (4)
Parking brake/Brake pads (F & R) (5)
Brake line & connections (including booster)
Manual transmission fluid (3)
Clutch & brake pedal free play
F & R Differential fluid (3)
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
R
I
RI
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
R
I
R
Automatic transmission fluid (BTRA M74) (6)
Chassis & underbody bolts & nuts tight/secure
Tire condition & inflation pressure
Wheel alignment (7)
Steering wheel & linkage
Power steering fluid & lines* (3)
Drive shaft boots
Seat belts, buckles & anchors
Lubricate locks, hinges & bonnet latchI
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Transfer case fluid (3)R
IR
I II
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Inspect & ADJUST when abnormal condition is noted
II
I
Chart Symbols :
I - Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R - Replace or change.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
(4) Change the brake / clutch fluid more regularly if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions :
- Driving in hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- Towing a trailer frequently
(5) More frequent maintenance is required if under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling, frequent low -
speed operation in stop-and-go traffic or driving in dusty condition.
(6) Change automatic transmission fluid every 70,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions.
- In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly reaches 32°C (90°F) or higher, or
- In hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- When doing frequent trailer towing, or
- Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
(7) If necessary, rotate and balance wheels.
Page 818 of 1463

SUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS 2A-3
DIAGNOSIS
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
Checks
Loosened Mountings
Damaged or Worn wheel Bearing
Damaged Shock Absorber
Damaged TireAction
Retightening
Replace
Replace
Replace
Abnormal Noises
Checks
Broken Stabilizer Bar
Faulty Shock AbsorberAction
Replace
Replace
Vehicle Rolling
Checks
Over Inflated Tire
Faulty Shock Absorber
Loosened wheel Nut
Bent or Broken Coil Spring
Damaged Tire
Worn BushingAction
Pressure Adjustment
Replace
Tighten as Specified
Replace
Replace
Replace
Poor Riding
Problems in the steering, the suspension, the tires, and
the wheels involve several systems. Consider all systems
when you diagnose a complaint. Some problems, such
as abnormal or excessive tire wear and scuffed tires,
may by the result of hard driving. Always road test thevehicle first. If possible, do this road test with the
customer.
Proceed with the following preliminary checks. Correct
any substandard conditions.
Checks
Incorrect Wheel Alignment
Excessive Resistance of Lower Arm Ball Joint
Insufficient Tire Pressure
Faulty Power Steering
Action
Repair
Replace
Adjust
Repair or Replace
Hard Steering
Checks
Deformed Arm Assembly
Worn Bushing
Bent or Broken Coil Spring
Difference Between L/H & R/H HeightsAction
Replace
Replace
Replace
Adjust
Vehicle Pulls to Right or Left
Page 830 of 1463

2B-2 WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DIAGNOSIS
TIRE DIAGNOSIS
Irregular and Premature Wear
Irregular and premature tire wear has many causes.
Some of them are incorrect inflation pressures, lack of
regular rotation, poor driving habits, or improper wheel
alignment.
Rotate the tires if :
lThe front tire wear is different from the rear.
lThe left and right front tire wear is unequal.
lThe left and right rear tire wear is unequal, Check
wheel alignment if :
lThe left and right front tire wear is unequal.
lThe wear is uneven across the tread of either front
tire.
lThe front tire treads are scuffed with “feather” edges
on the side of the tread ribs or blocks.
Tread Wear Indicators
The original equipment tires have built-in tread wear
indicators to show when the tires need replacement.
These indicators appear as bands when the tire tread
depth becomes shallow. Tire replacement is
recommended when the indicators appear in three or
more grooves at six locations.
Radial Tire Waddle
Waddle is side-to-side movement at the front or rear of
the vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being straight
within the tire, or by excessive lateral runout of the tire
or wheel.
The vehicle must be road tested to determine which end
of the vehicle has the faulty tire. The rear end of the
vehicle will shake from side to side or “waddle” if the
waddle tire is on the rear of the vehicle. From the driver’s
seat, it feels as though someone is pushing on the side
of the vehicle. If the faulty tire is on the front of the vehicle,
the waddle is more visual. The front sheet meld appears
to be moving back and forth, and the drivers seat feels
like the pivot point in the vehicle.
Waddle can be diagnosed using the method of
substituting known good tire and wheel assemblies on
the problem vehicle
1. Road test the vehicle to determine if the waddle is
coming from the front or the rear of the vehicle.
2. Install good tires and wheels from a similar vehicle in
place of those on the offending end of the problem
vehicle. If the source of the waddle is not obvious,
change the rear tires.
Page 833 of 1463

WHEEL ALIGNMENT 2B-5
VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
Wheel imbalance causes most highway speed vibration
problems. A vibration can remain after dynamic
balancing because:
lA tire is out of round.
lA rim is out of round.
lA tire stiffness variation exists.
Measuring tire and wheel free runout will uncover only
part of the problem, All three causes, known as loaded
radial runout, must be checked using method of
substituting known good tire and wheel assemblies on
the problem vehicle.
Preliminary Checks
Prior to performing any work, always road test the car
and perform a careful visual inspection for:
lObvious tire and wheel runout.
lObvious drive axle runout.
lImproper tire inflation.
lIncorrect trim height.
lBent or damaged wheels.
lDebris build-up on the tire or the wheel.
lIrregular or excessive tire wear.
lImproper tire bead seating on the rim,
lImperfections in the tires, including: tread
deformations, separations, or bulges from impact
damage. Slight sidewall indentations are normal and
will not affect ride quality.
Tire Balancing
Balance is the easiest procedure to perform and should
be done first if the vibration occurs at high speeds. Do
an off-vehicle, two-plane dynamic balance first to correct
any imbalance in the tire and wheel assembly.
An on-vehicle finish balance will correct any brake drum,
rotor, or wheel cover imbalance, If balancing does not
correct the high-speed vibration, or if the vibration occurs
at low speeds, runout is the probable cause.
Page 834 of 1463

2B-6 WHEEL ALIGNMENT
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON VEHICLE SERVICE
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Vehicle Height
1. Check the tire for proper inflation.
2. Measure ‘A’ from the center of the lower arm rear mounting
bolt end to the ground.
3. Measure ‘B’ from the center of the steering knuckle shaft to
the ground.
4. If the difference between ‘A’ and ‘B’ is not within specification,
adjust vehicle height using torsion bar height control bolt.
‘B’ - ‘A’
Notice
Before wheel alignment, adjust vehicle height first.
31 - 36mm
Toe-in
1. Measure toe-in.
Specification0 - 4mm
2. If toe-in is not within specification, loosen the tie rod nuts
and adjust it by turning the tie rod.
Page 863 of 1463
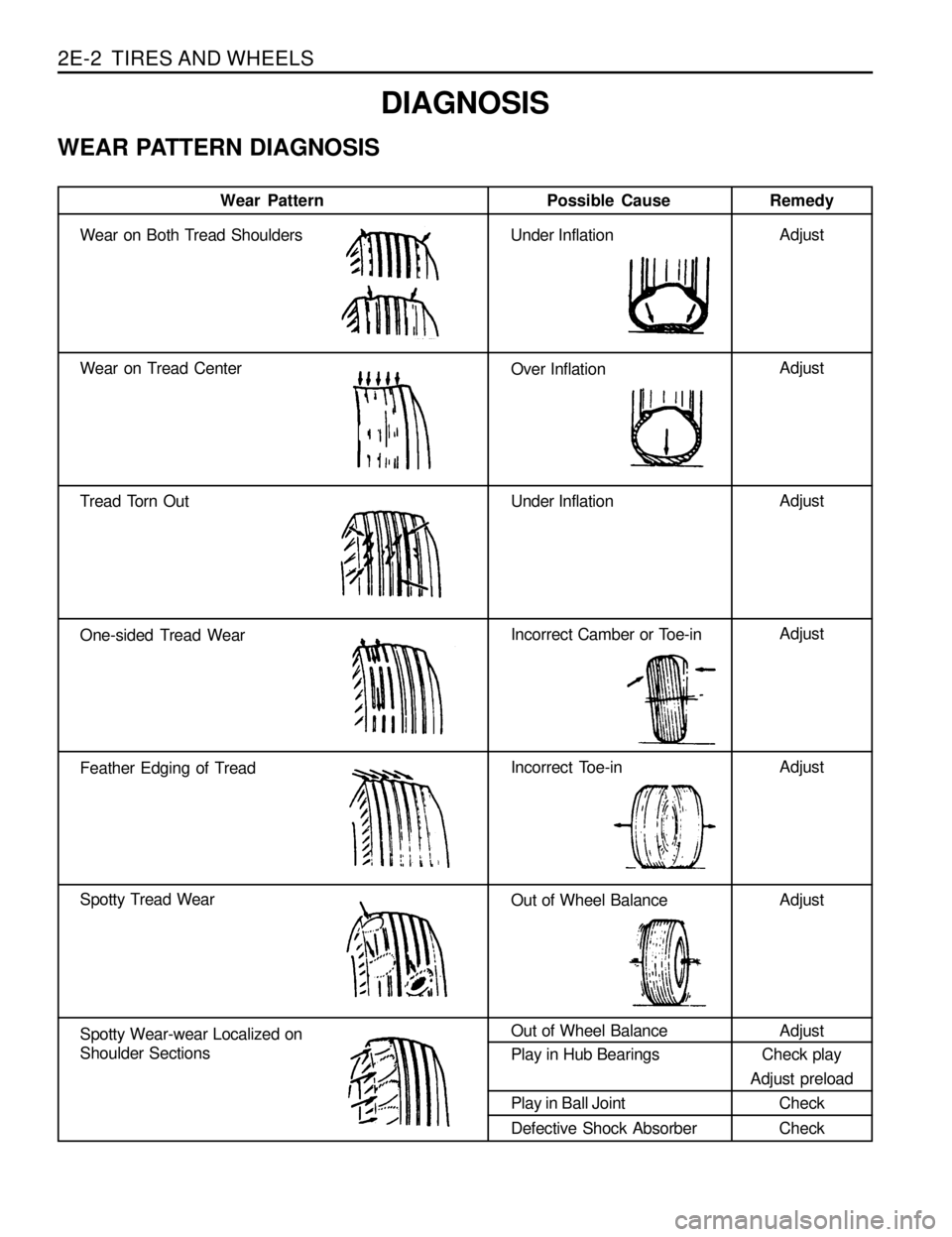
2E-2 TIRES AND WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS
WEAR PATTERN DIAGNOSIS
Wear Pattern Possible CauseRemedy
Wear on Both Tread Shoulders Under Inflation
Wear on Tread Center
Over Inflation
Tread Torn Out Under Inflation
One-sided Tread WearIncorrect Camber or Toe-in
Feather Edging of TreadIncorrect Toe-in
Spotty Tread Wear
Out of Wheel Balance
Spotty Wear-wear Localized on
Shoulder SectionsOut of Wheel Balance
Play in Hub Bearings
Play in Ball Joint
Defective Shock Absorber
Adjust
Adjust
Adjust
Adjust
Adjust
Adjust
Adjust
Check play
Adjust preload
Check
Check
Page 867 of 1463

2E-6 TIRES AND WHEELS
4. Tire pressure inspection.
lTire pressure.
lCheck tread contact with road.
Notice
lIf underinflated, tire may come away from the wheel
during rapid steering.
lAn overinflated tire will cause a hard riding and uneven
wear.
Front & Rear
(P235/75R15)2.1kg/cm (30PSI)2
5. Wheel balance.
lBalance weights should be on each side. When the wheel
is out of balance or a tire has been repaired, be sure to
balance the wheel again.
lIf total weight is over 150g, readjust the balance by
reinstalling the tire on the wheel.
lBalance weight should not protrude from the wheel rim
over 3mm.
lFor aluminum wheel, use aluminum wheel balance weight
only.