Fuel filter SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: NEW ACTYON SPORTS, Model: SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013Pages: 751, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 97 of 751

03-20
(2) Di engine and its expected problems and remedies can be caused by
water in fuel
System supplement against paraffin separation ▶
In case of Diesel fuel, paraffin, one of the elements, can be separated from fuel during winter and then
can stick on the fuel filter blocking fuel flow and causing difficult starting finally. Oil companies supply
summer fuel and winter fuel by differentiating mixing ratio of kerosene and other elements by region and
season. However, above phenomenon can be happened if stations have poor facilities or sell improper
fuel for the season. In case of DI engine, purity of fuel is very important factor to keep internal
preciseness of HP pump and injector.
Accordingly, more dense mesh than conventional fuel filter is used. To prevent fuel filter internal clogging
due to paraffin separation, SYMC is using fuel line that high pressure and temperature fuel injected by
injector returns through fuel filter to have an effect of built-in heater (see fuel system).
System supplement and remedy against water in fuel ▶
As mentioned above, some gas stations supply fuel with excessive than specified water. In the
conventional IDI engine, excessive water in the fuel only causes dropping engine power or engine
hunting. However, fuel system in the DI engine consists of precise components so water in the fuel can
cause malfunctions of HP pump due to poor lubrication of pump caused by poor coating film during high
speed pumping and bacterization (under long period parking). To prevent problems can be caused by
excessive water in fuel, water separator is installed inside of fuel filter. When fuel is passing filter, water
that has relatively bigger specific gravity is accumulated on the bottom of the filter.
Water drain from water separator ▶
If water in the separator on the fuel filter exceeds a certain level, it will be supplied to HP pump with fuel,
so the engine ECU turns on warning lamp on the meter cluster and buzzer if water level is higher than a
certain level.
Due to engine layout, a customer cannot easily drain water from fuel filter directly, so if a customer
checks in to change engine oil, be sure to perform water drain from fuel filter.
Water
separator
To separate the water from the fuel filter,
remove the fuel filter assembly first.
Page 100 of 751
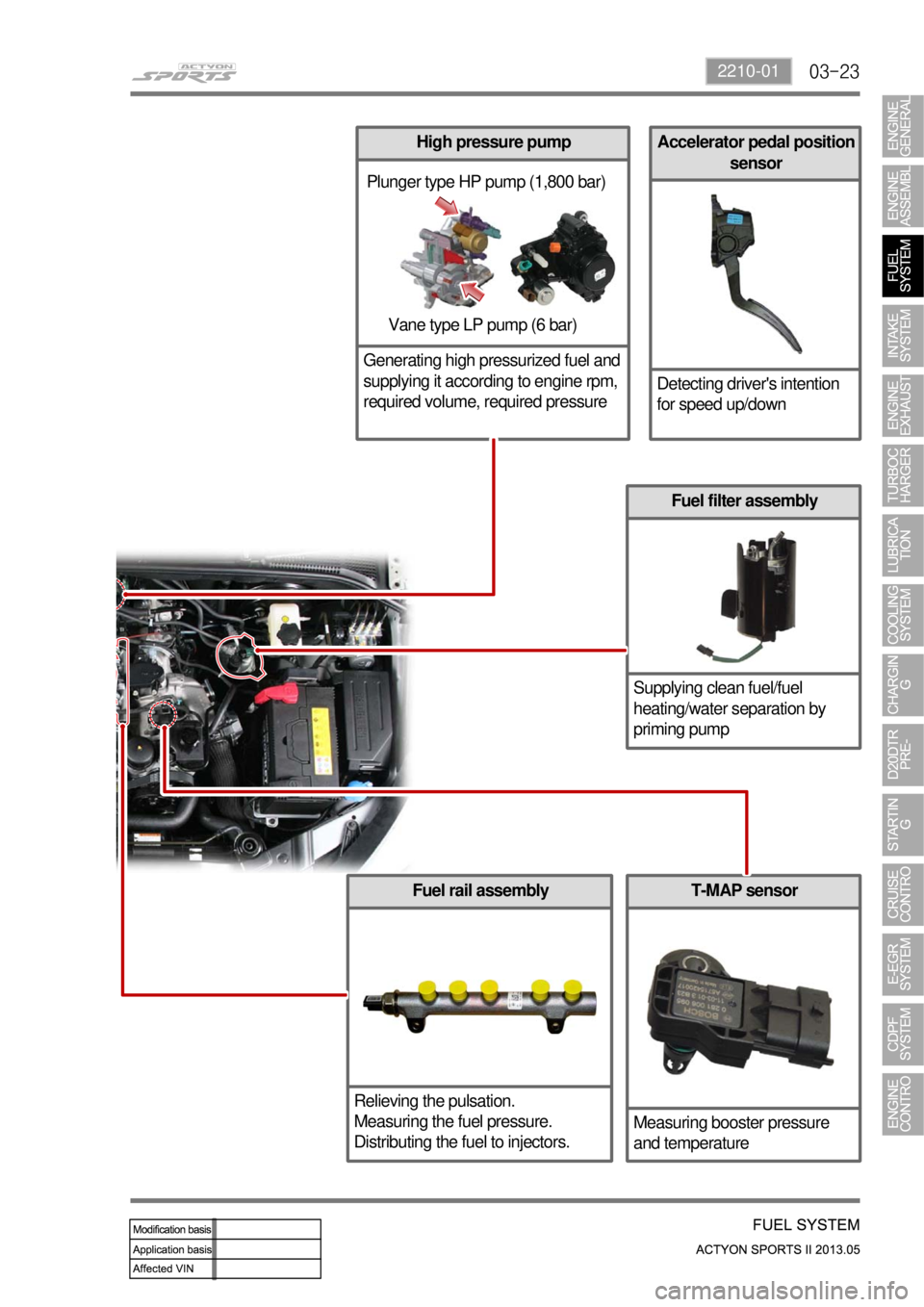
03-232210-01
Accelerator pedal position
sensor
Detecting driver's intention
for speed up/down
Fuel rail assembly
Relieving the pulsation.
Measuring the fuel pressure.
Distributing the fuel to injectors.
Fuel filter assembly
Supplying clean fuel/fuel
heating/water separation by
priming pump
Plunger type HP pump (1,800 bar)
Vane type LP pump (6 bar)
T-MAP sensor
Measuring booster pressure
and temperature
High pressure pump
Generating high pressurized fuel and
supplying it according to engine rpm,
required volume, required pressure
Page 101 of 751
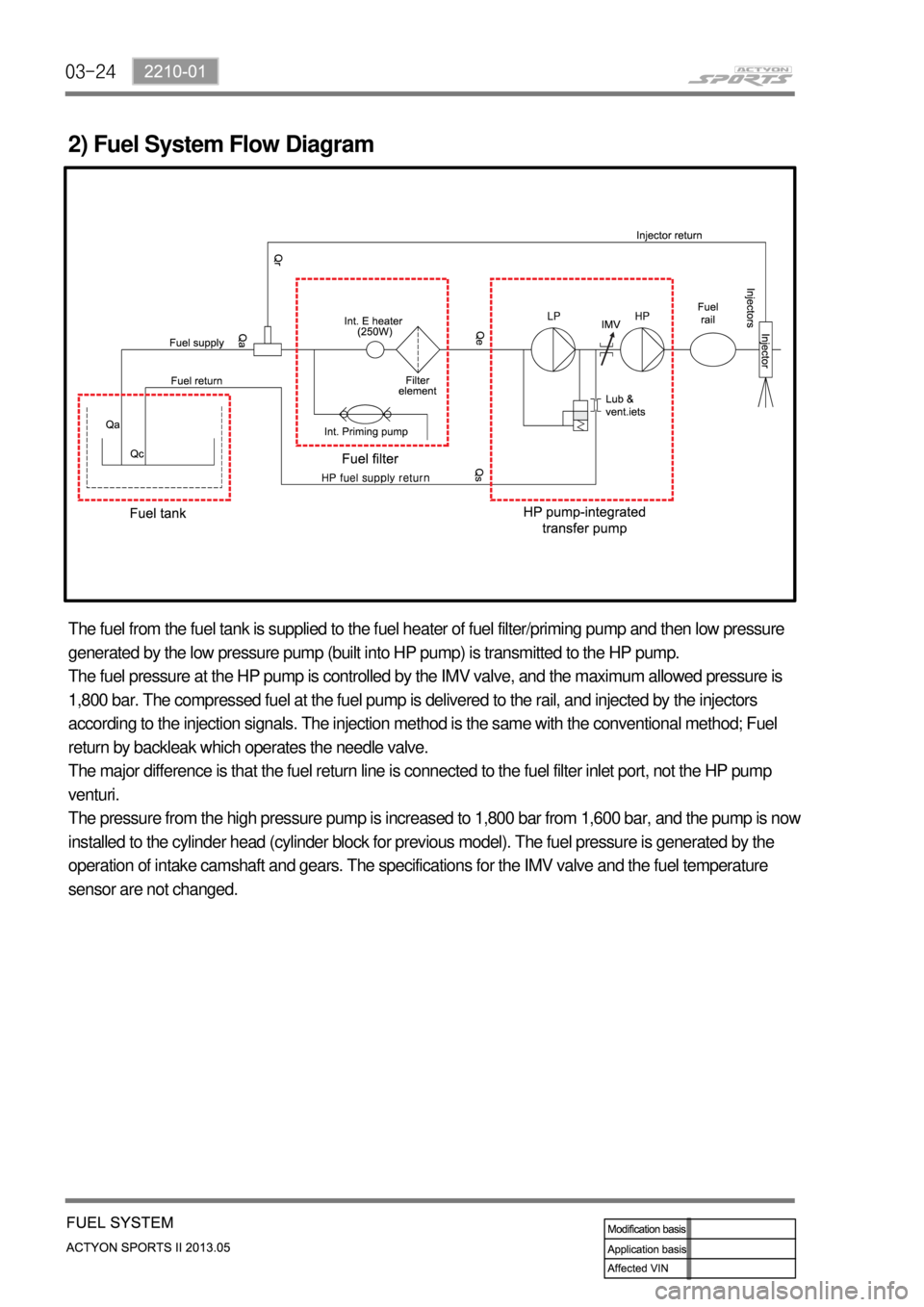
03-24
2) Fuel System Flow Diagram
The fuel from the fuel tank is supplied to the fuel heater of fuel filter/priming pump and then low pressure
generated by the low pressure pump (built into HP pump) is transmitted to the HP pump.
The fuel pressure at the HP pump is controlled by the IMV valve, and the maximum allowed pressure is
1,800 bar. The compressed fuel at the fuel pump is delivered to the rail, and injected by the injectors
according to the injection signals. The injection method is the same with the conventional method; Fuel
return by backleak which operates the needle valve.
The major difference is that the fuel return line is connected to the fuel filter inlet port, not the HP pump
venturi.
The pressure from the high pressure pump is increased to 1,800 bar from 1,600 bar, and the pump is now
installed to the cylinder head (cylinder block for previous model). The fuel pressure is generated by the
operation of intake camshaft and gears. The specifications for the IMV valve and the fuel temperature
sensor are not changed.
Page 188 of 751

14-4
2. CAUTIONS
1) Standard pattern of soot accumulation
Abnormal Soot Accumulation ▶
Normal Soot Combustion ▶
Cautions to protect the catalyst filter ▶
Use the designated fuel only.
Observe the recommended service intervals of engine oil.
Check the engine oil level frequently and add if necessary.
Do not idle the vehicle unnecessarily.
Do not turn off the engine while the vehicle is running.
Do not shift the gear selector lever to neutral when going downhill.
Do not use improper engine oil or fuel additives.
Do not drive for a long time when the warning lamp is illuminated.
Make sure no flammable material, such as dry grass or tissue paper, contacts with the catalyst filter
while the vehicle is parked.
For the vehicles used in urban traffic, driving on the expressways for more than 1 hour at least once
per week is needed so that the PM inside CDPF isn't collected to one side only. -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 199 of 751
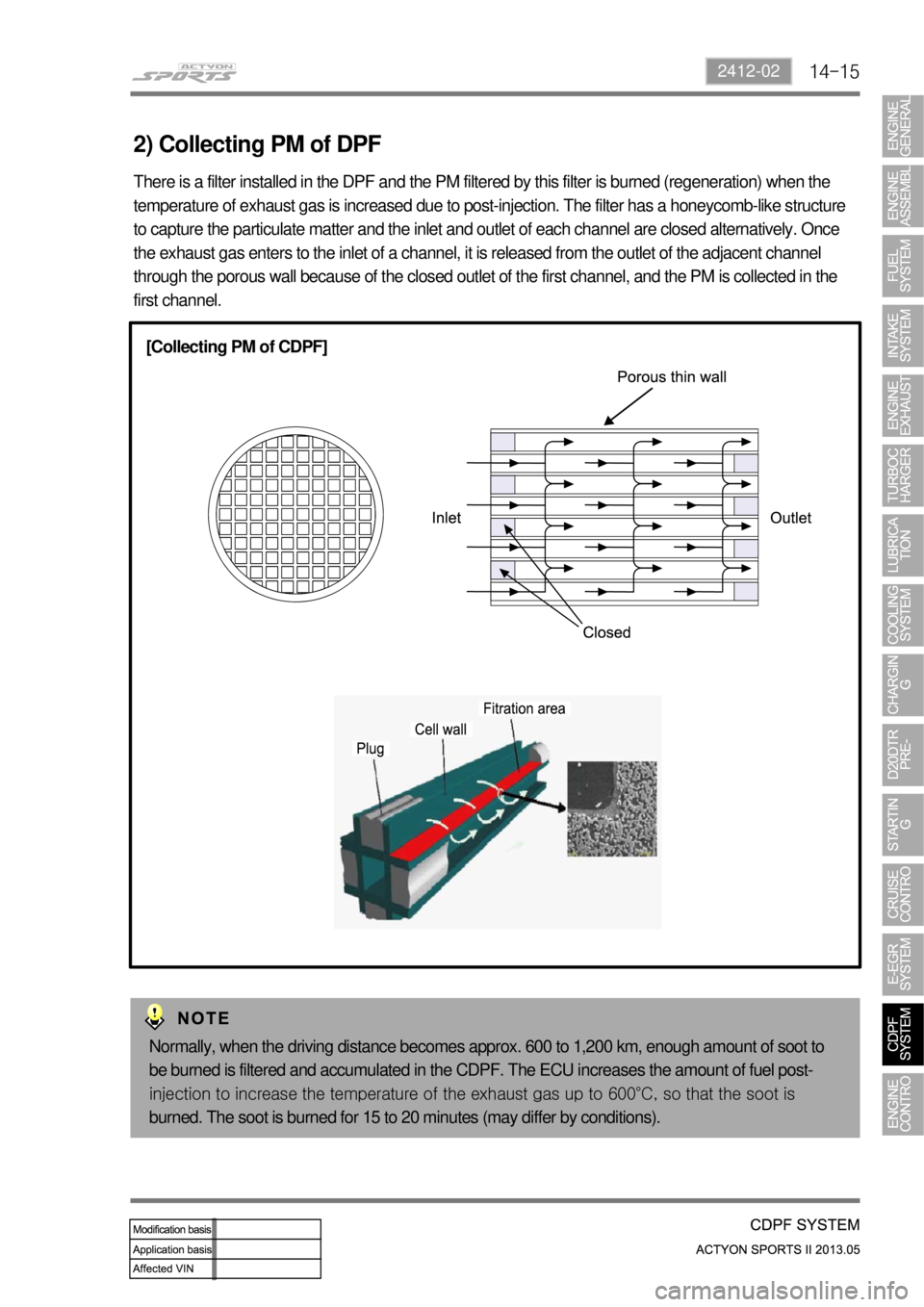
14-152412-02
2) Collecting PM of DPF
There is a filter installed in the DPF and the PM filtered by this filter is burned (regeneration) when the
temperature of exhaust gas is increased due to post-injection. The filter has a honeycomb-like structure
to capture the particulate matter and the inlet and outlet of each channel are closed alternatively. Once
the exhaust gas enters to the inlet of a channel, it is released from the outlet of the adjacent channel
through the porous wall because of the closed outlet of the first channel, and the PM is collected in the
first channel.
[Collecting PM of CDPF]
Normally, when the driving distance becomes approx. 600 to 1,200 km, enough amount of soot to
be burned is filtered and accumulated in the CDPF. The ECU increases the amount of fuel post-
<009000950091008c008a009b0090009600950047009b0096004700900095008a0099008c0088009a008c0047009b008f008c0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00470096008d0047009b008f008c0047008c009f008f0088009c00
9a009b0047008e0088009a0047009c00970047009b00960047>600°C, so that the soot is
burned. The soot is burned for 15 to 20 minutes (may differ by conditions).
Page 218 of 751
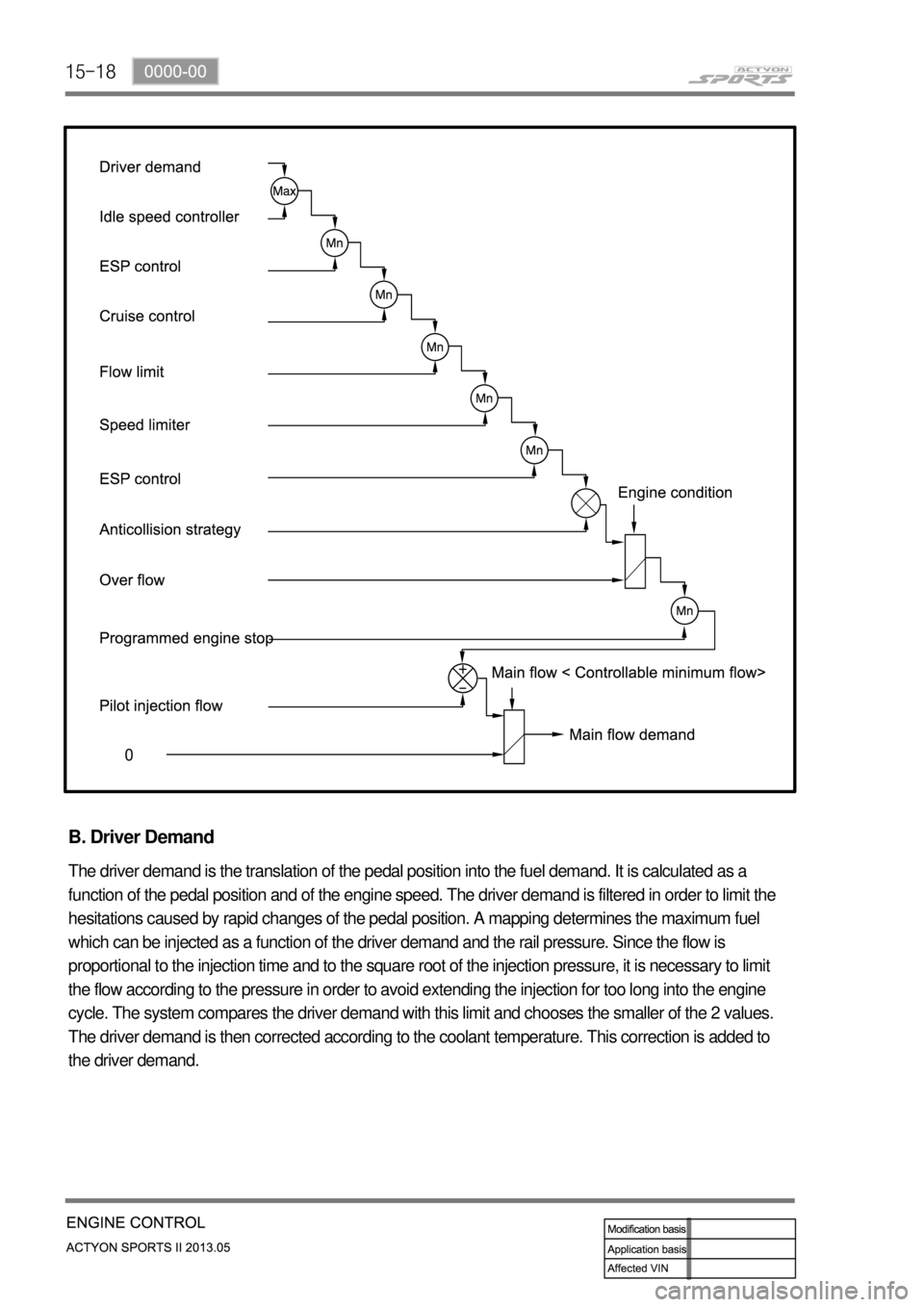
15-18
B. Driver Demand
The driver demand is the translation of the pedal position into the fuel demand. It is calculated as a
function of the pedal position and of the engine speed. The driver demand is filtered in order to limit the
hesitations caused by rapid changes of the pedal position. A mapping determines the maximum fuel
which can be injected as a function of the driver demand and the rail pressure. Since the flow is
proportional to the injection time and to the square root of the injection pressure, it is necessary to limit
the flow according to the pressure in order to avoid extending the injection for too long into the engine
cycle. The system compares the driver demand with this limit and chooses the smaller of the 2 values.
The driver demand is then corrected according to the coolant temperature. This correction is added to
the driver demand.
Page 250 of 751

15-50
E. Cautions
Use only specified Engine Oil (approved by MB Sheet 229.51) for CDPF. -
Use only specified engine oil (Low Ash Oil) ▶
The vehicle equipped with CDPF should use specific engine oil to improve the engine performance
and fuel economy, and ensure the service life of CDPF. -
Issue with normal engine oil ▶
Sulfur, one of the contents of engine oil is burned and generates soot that is not regenerated by the
DPF. This remains on the filter as ashes and keeps accumulating. Eventually, this ashes will block
the filter. -
Benefit for specified engine oil ▶
Minimized the sulfur content of engine oil which reduces the service life.
Improved fuel economy and emission level of CO2 with high performance and low viscosity.
Increased service life of engine oil with high resistance to temperature. -
-
-
Problems when using unspecified engine oil ▶
The service life of filter may be reduced by 30% or more by the ashes accumulated on the filter.
The fuel economy may be reduced because of engine rolling resistance, frequent regeneration of
DPF. -
-
These problems are also caused by oil with high sulfur content, such as tax exemption oil and
heating oil, etc. *
Page 257 of 751
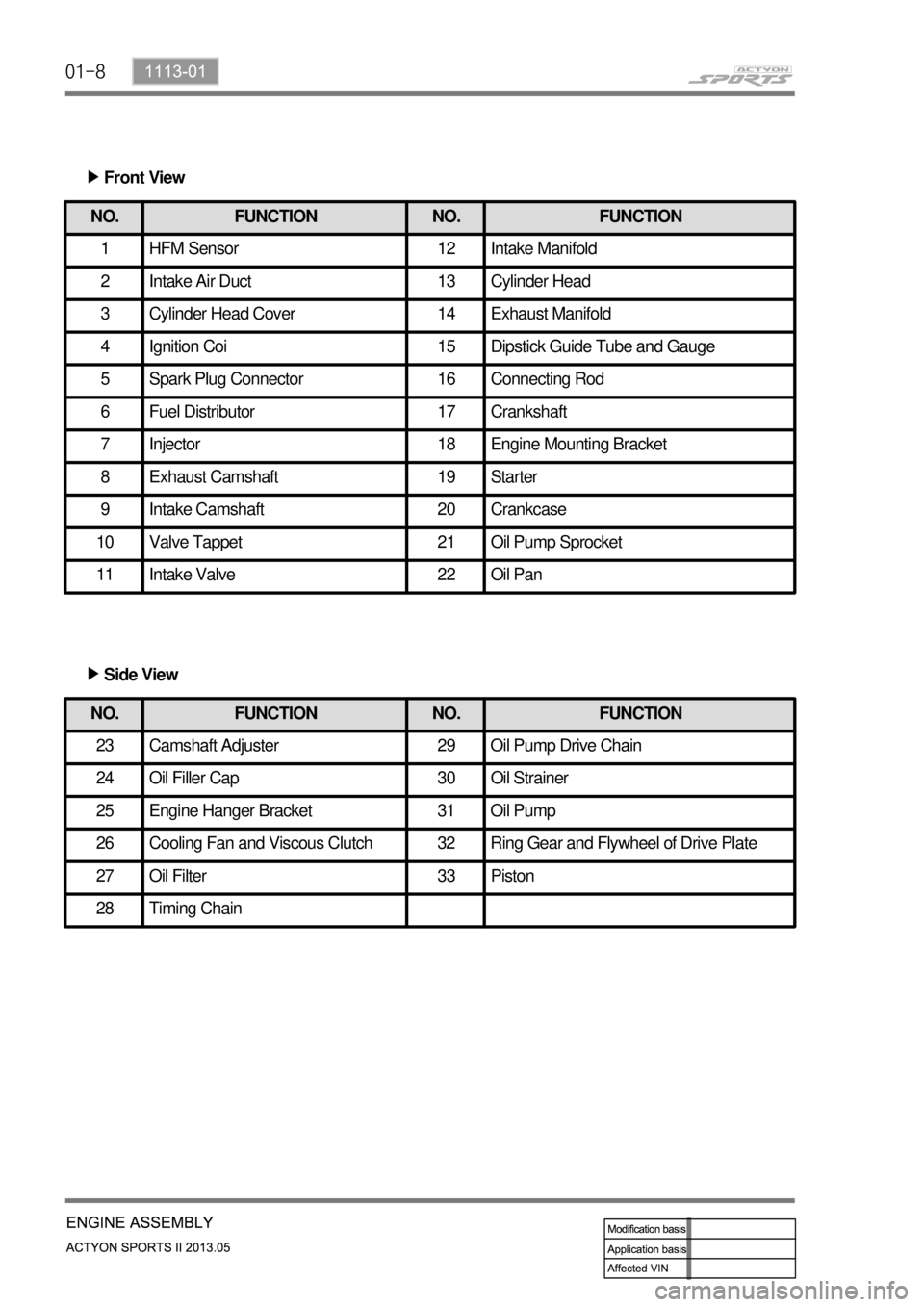
01-8
Front View ▶
NO. FUNCTION NO. FUNCTION
1 HFM Sensor 12 Intake Manifold
2 Intake Air Duct 13 Cylinder Head
3 Cylinder Head Cover 14 Exhaust Manifold
4 Ignition Coi 15 Dipstick Guide Tube and Gauge
5 Spark Plug Connector 16 Connecting Rod
6 Fuel Distributor 17 Crankshaft
7 Injector 18 Engine Mounting Bracket
8 Exhaust Camshaft 19 Starter
9 Intake Camshaft 20 Crankcase
10 Valve Tappet 21 Oil Pump Sprocket
11 Intake Valve 22 Oil Pan
NO. FUNCTION NO. FUNCTION
23 Camshaft Adjuster 29 Oil Pump Drive Chain
24 Oil Filler Cap 30 Oil Strainer
25 Engine Hanger Bracket 31 Oil Pump
26 Cooling Fan and Viscous Clutch 32 Ring Gear and Flywheel of Drive Plate
27 Oil Filter 33 Piston
28 Timing Chain
Side View ▶
Page 274 of 751

02-52211-06
1. FUEL SYSTEM
The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all
operating conditions.
The fuel is delivered to the engine by the individual fuel injectors mounted into the intake manifold nea
r
each cylinder.
The main fuel control sensors are the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and the oxygen (O2) sensors.
The MAF sensor monitors the mass flow of the air being drawn into the engine. An electrically heated
element is mounted in the intake air stream, where it is cooled by the flow of incoming air. Engine Control
Module (ECM) modulates the flow of heating current to maintain the temperature differential between the
heated film and the intake air at a constant level. The amount of heating current required to maintain the
temperature thus provides an index for the mass air flow. This
concept automatically compensates for variations in air density, as this is one of the factors that
determines the amount of warmth that the surrounding air absorbs from the heated element. MAF
sensor is located between the air filter and the throttle valve.
Under high fuel demands, the MAF sensor reads a high mass flow condition, such as wide open throttle.
The ECM uses this information to enrich the mixture, thus increasing the fuel injector on-time, to provide
the correct amount of fuel. When decelerating, the mass flow decreases. This mass flow change is
sensed by the MAF sensor and read by the ECM, which then decreases the fuel injector on-time due to
the low fuel demand conditions.
The O2 sensors are located in the exhaust pipe before catalytic converter. The O2 sensors indicate to
the ECM the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, and the ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine
by controlling the fuel injectors. The best air/fuel ratio to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 to 1, which
allows the catalytic converter to operate most efficiently. Because
of the constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system is called a "closed
loop" system.
The ECM uses voltage inputs from several sensors to determine how much fuel to provide to the engine.
The fuel is delivered under one of several conditions, called "modes".
Page 406 of 751
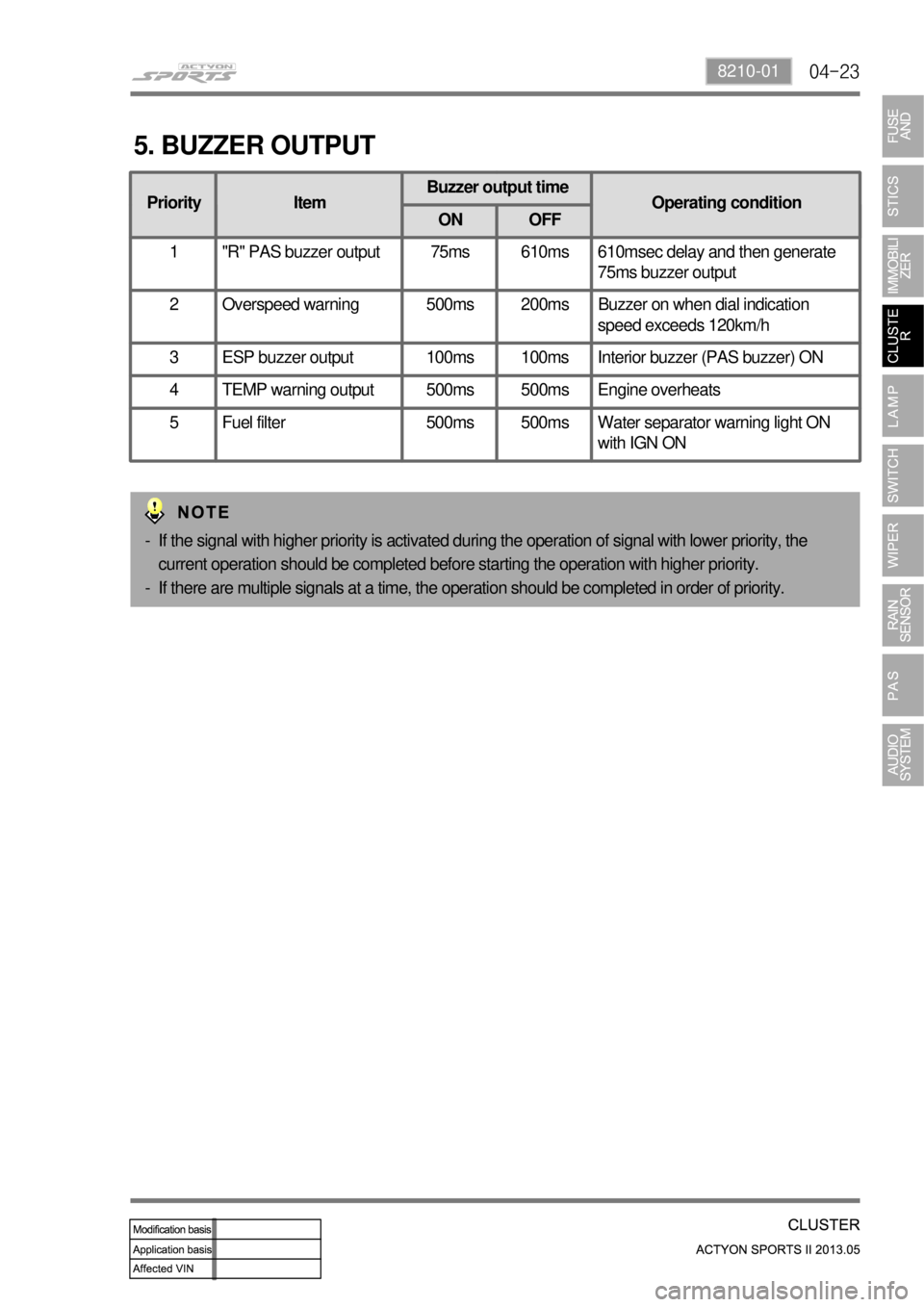
04-238210-01
5. BUZZER OUTPUT
Priority ItemBuzzer output time
Operating condition
ON OFF
1 "R" PAS buzzer output 75ms 610ms 610msec delay and then generate
75ms buzzer output
2 Overspeed warning 500ms 200ms Buzzer on when dial indication
speed exceeds 120km/h
3 ESP buzzer output 100ms 100ms Interior buzzer (PAS buzzer) ON
4 TEMP warning output 500ms 500ms Engine overheats
5 Fuel filter 500ms 500ms Water separator warning light ON
with IGN ON
If the signal with higher priority is activated during the operation of signal with lower priority, the
current operation should be completed before starting the operation with higher priority.
If there are multiple signals at a time, the operation should be completed in order of priority. -
-