steering wheel SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: NEW ACTYON SPORTS, Model: SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013Pages: 751, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 613 of 751

11-114890-10
2) Component Overview By System
3) Part Overview By System
Part Vehicle with ABS Vehicle with ESP
HECU
Yes Yes Front wheel speed sensor
Rear wheel speed sensor
ABS warning lamp
EBD indicator lamp
G sensor (integrated in HECU) 4WD: Yes, 2WD: No No
Sensor cluster (Yaw rate sensor +
lateral sensor+ G sensor)
No Yes ESP operation indicator lamp and
warning lamp
ESP OFF switch and indicator
Steering wheel angle sensor
Function Vehicle with ABS Vehicle with ESP
ABS Yes
Yes EBD Yes
HBA
No
ARP
Page 618 of 751
11-16
2) Operation of ESP System
The ESP (Electronic Stability Program) has been developed to help a driver avoid danger of losing
control of the vehicle stability due to understeer or oversteer during cornering. The yaw rate sensor,
lateral sensor and longitudinal sensor in the sensor cluster and the steering wheel angle sensor under
the steering column detect the vehicle conditions when the inner or outer wheels are spinning during
oversteer, understeer or cornering. The ESP ECU controls against oversteer or understeer during
cornering by controlling the vehicle stability using input values from these sensors and applying the
braking force to the corresponding wheels independently. The system also controls the engine power
right before the wheel spin synchronized with the ASR function to decelerate the vehicle automatically in
order to maintain the vehicle stable during cornering.
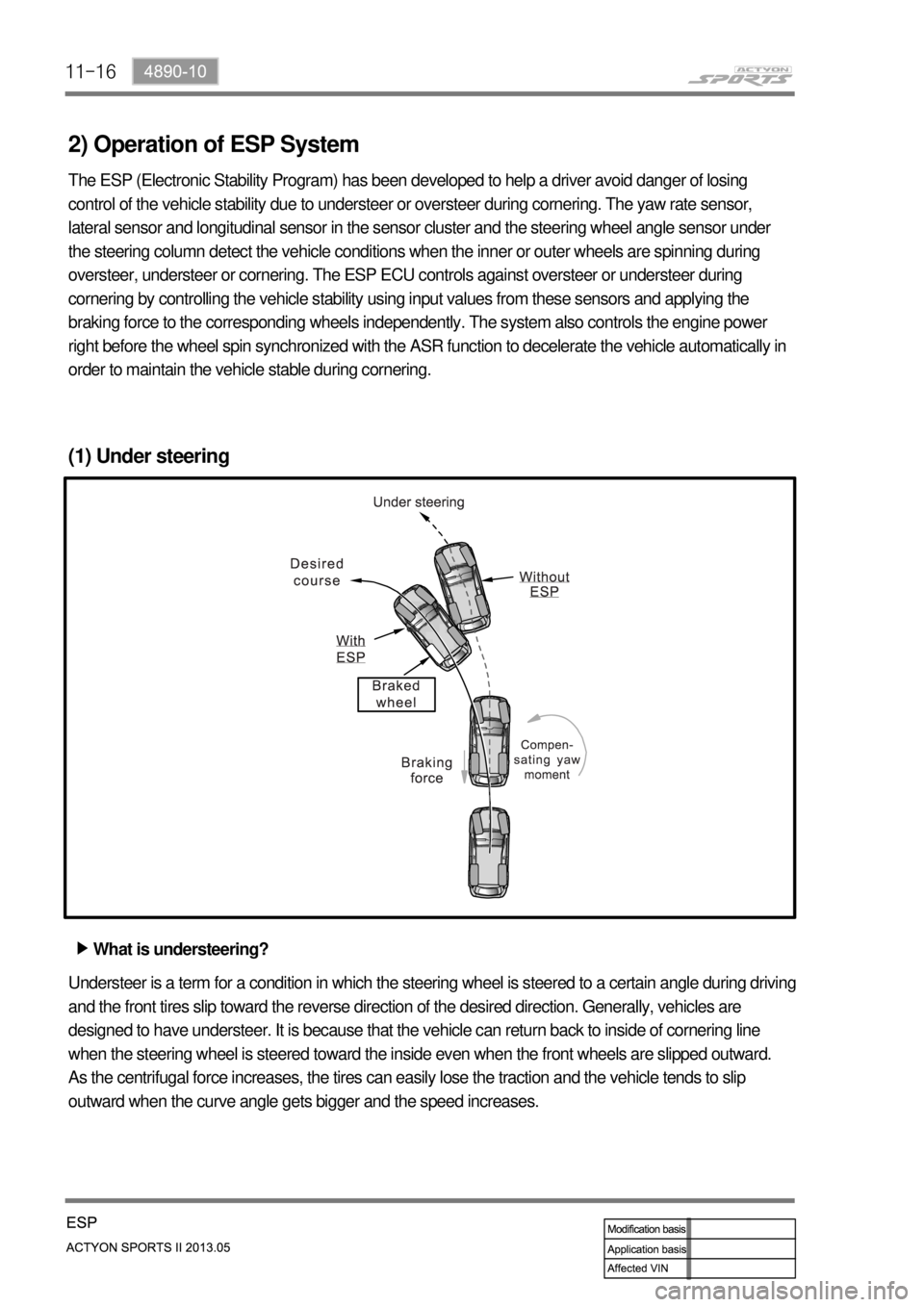
(1) Under steering
What is understeering? ▶
Understeer is a term for a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle during driving
and the front tires slip toward the reverse direction of the desired direction. Generally, vehicles are
designed to have understeer. It is because that the vehicle can return back to inside of cornering line
when the steering wheel is steered toward the inside even when the front wheels are slipped outward.
As the centrifugal force increases, the tires can easily lose the traction and the vehicle tends to slip
outward when the curve angle gets bigger and the speed increases.
Page 619 of 751

11-174890-10
ESP controls during understeer ▶
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses the
slipping route that occurs reversely against the vehicle cornering direction during understeer with the ya
w
rate sensor and lateral sensor. Then, the ESP system applies the braking force to the rear inner wheel to
compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its driving direction and the
driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
(2) Over steering
What is oversteering? ▶
Oversteer is a term of a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle during driving
and the rear tires slip outward losing traction.
Compared to understeering vehicles, it is hard to control the vehicle during cornering and the vehicle can
spin due to rear wheel moment when the rear tires lose traction and the vehicle speed increases.
ESP controls during oversteer ▶
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses the
slipping route that occurs towards the vehicle cornering direction during oversteer with the yaw rate
sensor and lateral sensor. Then the ESP system applies the braking force to the front outer wheel to
compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its driving direction and the
driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
Page 622 of 751
11-20
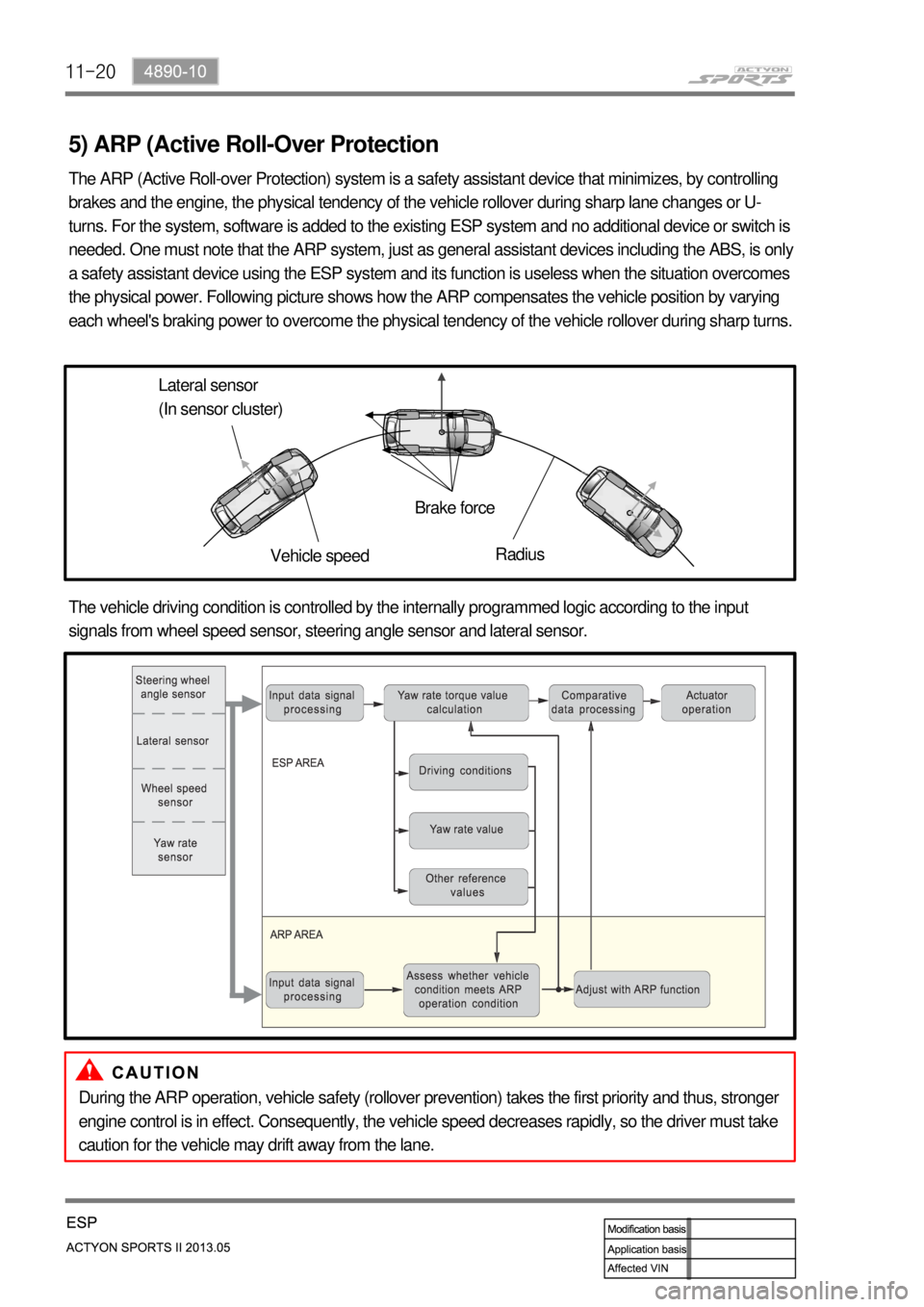
5) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch is
needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is only
a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation overcomes
the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle position by varying
each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp turns.
Lateral sensor
(In sensor cluster)
Vehicle speedBrake force
Radius
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus, stronger
engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver must take
caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Page 632 of 751

12-34610-01
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Description Specification
Steering wheel Type 4-spoke type
Gear box
(HPS)Type Rack and pinion type
Gear ratio 40.245
Steering angle Inner36.2˚
Outer32.4˚
Oil pump
(HPS)Type Vane type
Maximum pressure (kgf/cm2)90 ± 3
Pulley size (mm)Ø115
Operating temperature-40℃~150℃
Minimum turning radius (m) 5.8
Steering oil Type S-PSF-3
Capacity (L) Approx. 1.0
Service interval Daily check and add if necessary.
Steering column shaft Tilting angle-4.0/ 0° /+4.0° / +8.0°
This section describes the power steering pump and gear box based on the HPS (Hydraulic Power
Steering) system. For the information of the SSPS (Speed Sensing Power Steering) system, refer to
SSPS section under CHASSIS.
Page 636 of 751

12-74610-01
Steering Wheel Body & Heated Wire Controller
Heated pad and controller added to steering wheel body
Heated Steering Wheel Adopted ▶
HEATED STEERING WHEEL SWITCH
Heated steering wheel switch added to cluster fascia panel switch assembly
Heated pad (inside)
controller
Page 637 of 751

12-8
Change of Steering Wheel & Steering Column Shaft ▶
Appearance of steering wheel boss part changed
Steering wheel assembly boss part
Page 639 of 751

12-10
3. SYSTEM LAYOUT
1) Steering Wheel and Column
Body assembly - steering wheel
Damper - steering wheel
Screw
Lid
Bolt
Column & shaft assembly - tilt
Shaft assembly - lower
Nut (39.2~58.5 Nm) 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.Washer
Bolt (19.6 ~ 24.5 Nm)
Bolt (19.6 ~ 24.5 Nm)
Nut
Bolt - joint (17.6~24.5 Nm)
Washer
Blanking cover - cruise switch 9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Page 642 of 751
12-134610-01
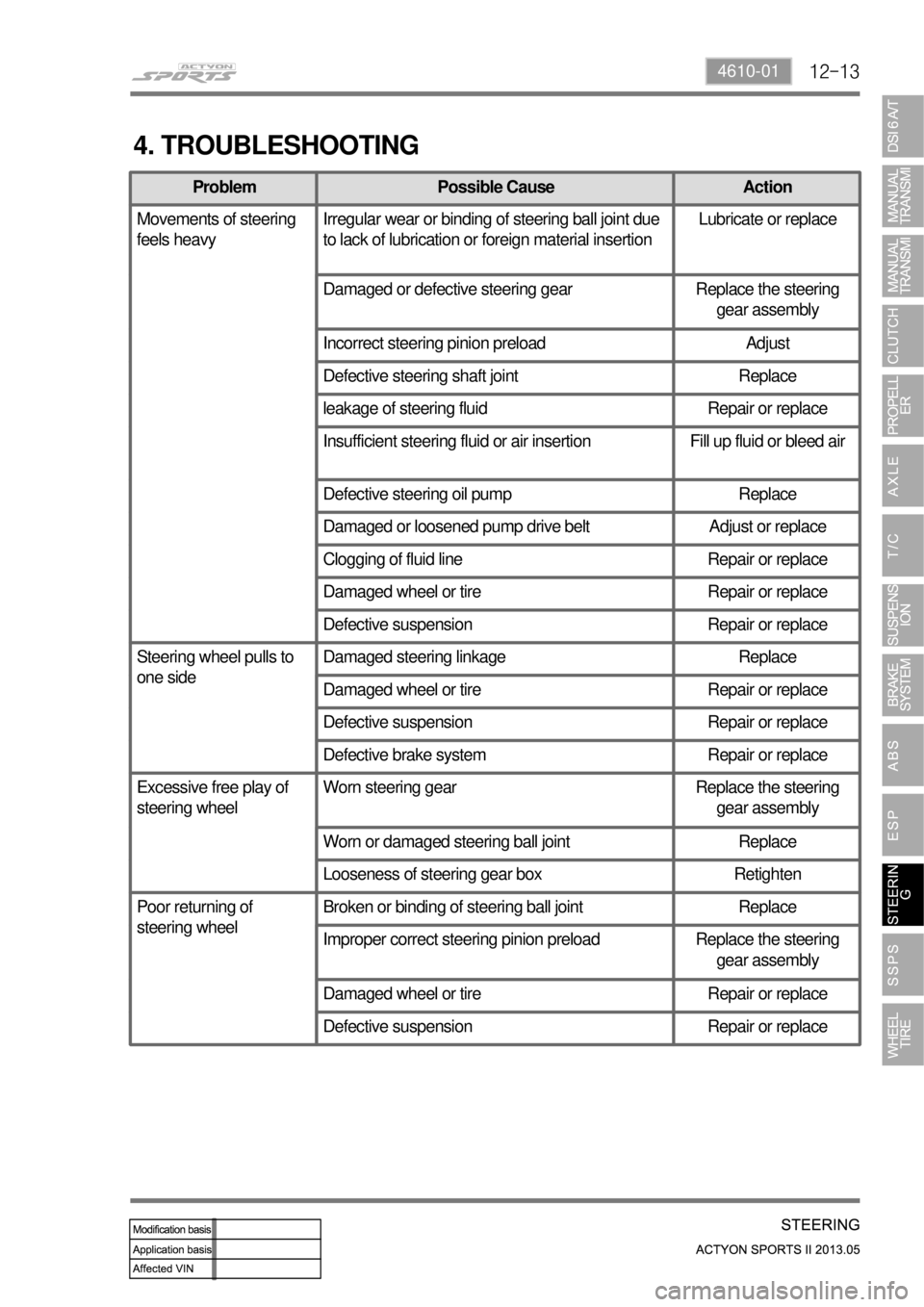
4. TROUBLESHOOTING
Problem Possible Cause Action
Movements of steering
feels heavyIrregular wear or binding of steering ball joint due
to lack of lubrication or foreign material insertionLubricate or replace
Damaged or defective steering gear Replace the steering
gear assembly
Incorrect steering pinion preload Adjust
Defective steering shaft joint Replace
leakage of steering fluid Repair or replace
Insufficient steering fluid or air insertion Fill up fluid or bleed air
Defective steering oil pump Replace
Damaged or loosened pump drive belt Adjust or replace
Clogging of fluid line Repair or replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Steering wheel pulls to
one sideDamaged steering linkage Replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Defective brake system Repair or replace
Excessive free play of
steering wheelWorn steering gear Replace the steering
gear assembly
Worn or damaged steering ball joint Replace
Looseness of steering gear box Retighten
Poor returning of
steering wheelBroken or binding of steering ball joint Replace
Improper correct steering pinion preload Replace the steering
gear assembly
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Page 643 of 751
12-14
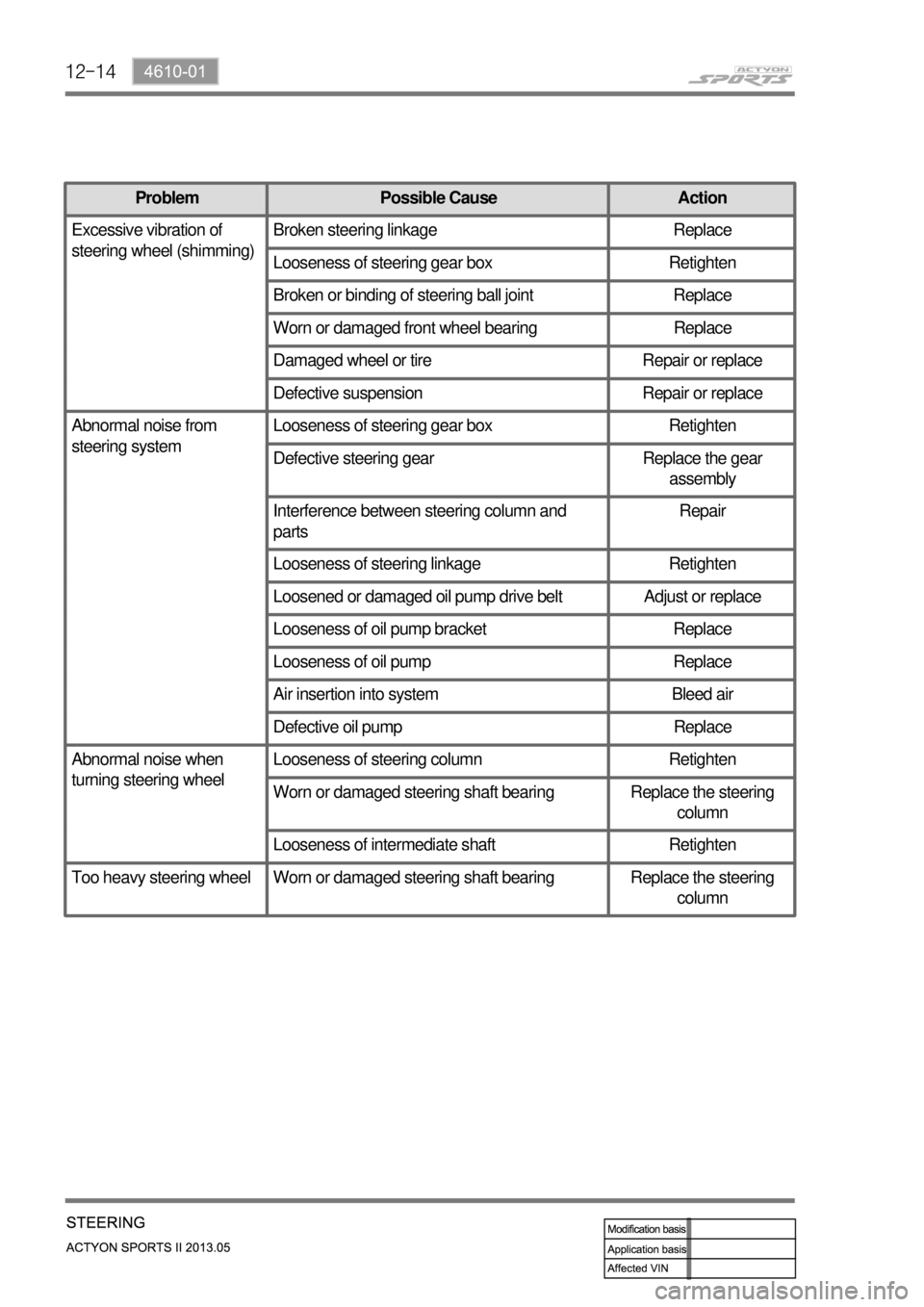
Problem Possible Cause Action
Excessive vibration of
steering wheel (shimming)Broken steering linkage Replace
Looseness of steering gear box Retighten
Broken or binding of steering ball joint Replace
Worn or damaged front wheel bearing Replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Abnormal noise from
steering systemLooseness of steering gear box Retighten
Defective steering gear Replace the gear
assembly
Interference between steering column and
partsRepair
Looseness of steering linkage Retighten
Loosened or damaged oil pump drive belt Adjust or replace
Looseness of oil pump bracket Replace
Looseness of oil pump Replace
Air insertion into system Bleed air
Defective oil pump Replace
Abnormal noise when
turning steering wheelLooseness of steering column Retighten
Worn or damaged steering shaft bearing Replace the steering
column
Looseness of intermediate shaft Retighten
Too heavy steering wheel Worn or damaged steering shaft bearing Replace the steering
column