wiring SSANGYONG NEW REXTON 2012 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: NEW REXTON, Model: SSANGYONG NEW REXTON 2012Pages: 600, PDF Size: 73.29 MB
Page 166 of 600

8. ELECTRIC COMPONENTS AND LAYOUT
1) Wiring Harness Arrangement
Page 268 of 600

Name SizeNumbers of
fastenerTightening
torque (Nm)Note (total
tightening
torque)
Idler pulley/tensioner
pulley1
-
Glow plug M5 4
-
Vacuum pump
3 -
Timing gear case cover
7 -
1 -
3 -
Cylinder head cover
21 -
Oil dipstick gauge cover
1 -
Oil filter cap 1
-
Fuel rail
2 -
Injector clamp bolt
2 -
High pressure pipe
(between high pressure
pump and fuel rail
assembly)M17 1
-
High pressure pipe
(between fuel rail
assembly and injector)M17 4
-
Crankshaft position
sensor
1 -
Main wiring
5 -
Intake duct
3 -
Power steering pump
3 -
Cylinder head front cover
5 -
Page 273 of 600

Component SizeBolt
QuantitySpecified torque
(Nm)Remark
(Total torque)
Glow plug M5 4
-
Vacuum pump
3 -
Timing gear case cover
3 -
7 -
1 -
3 -
Cylinder head cover
21 -
Oil gauge tube
1 -
Oil filter cap 1
-
Fuel rail
2 -
Injector clamp bolt
2 -
High pressure pipe
(between HP pump and
fuel rail)M17 1
-
High pressure pipe
(between fuel rail and
injector)M17 4
-
Crank position sensor
1 -
Main wiring
5 -
Intake duct M8x25 4
-
Power steering pump
3 -
Cylinder head front cover
5 -
Ladder frame
5 -
Oil pump
3 -
Page 274 of 600

0000-00
3. CHECK AND INSPECTION
1) Cylinder
(1) Compression pressure test
Specified value
Compression ratio16.5 : 1
Test condition
Compression pressureStandard32 bar
Minimum18 bar
Differential limit between cylindersMaximum 3 bar
The compression pressure test is to check the conditions of internal components (piston, piston ring,
intake and exhaust vale, cylinder head gasket). This test provides current engine operating status.
Before cranking the engine, make sure that the test wiring, tools and persons are keeping away
from moving components of engine (e.g., belt and cooling fan).
Park the vehicle on the level ground and apply the parking brake.
Do not allow anybody to be in front of the vehicle. -
-
-
Measurement
Disconnect the fuel rail pressure sensor connector to cut off the fuel injection.
Remove the air cleaner duct and glow plugs. -
-
-
Place the diagram sheet to compression
pressure tester and install it into the plug hole. 1.
Page 324 of 600

(3) DI Engine Fuel System Check Procedure
If several DTCs are output simultaneously, check the electric wiring for open or short circuit.
Check the low pressure fuel system and fuel filter and confirm that there are no abnormalities. Carry
out the high pressure fuel system check.
Page 328 of 600

(6) Low Pressure System Pressure Test
Inspection procedure
All wirings/connectors and fuel lines should be
connected and the engine should work
properly.
Prepare a special tool for low pressure test
and clean it thoroughly to prevent foreign
materials from entering. 1.
2.
Disconnect the key connector for fuel filter connection, and connect both connectors to the fuel filter
and hose. 3.
Start the engine and check visually for clogged low pressure fuel system, excessive air or air entry.
If the fuel flow is not sufficient or air is in the fuel, repair the leak area. 4.
5.
Page 379 of 600
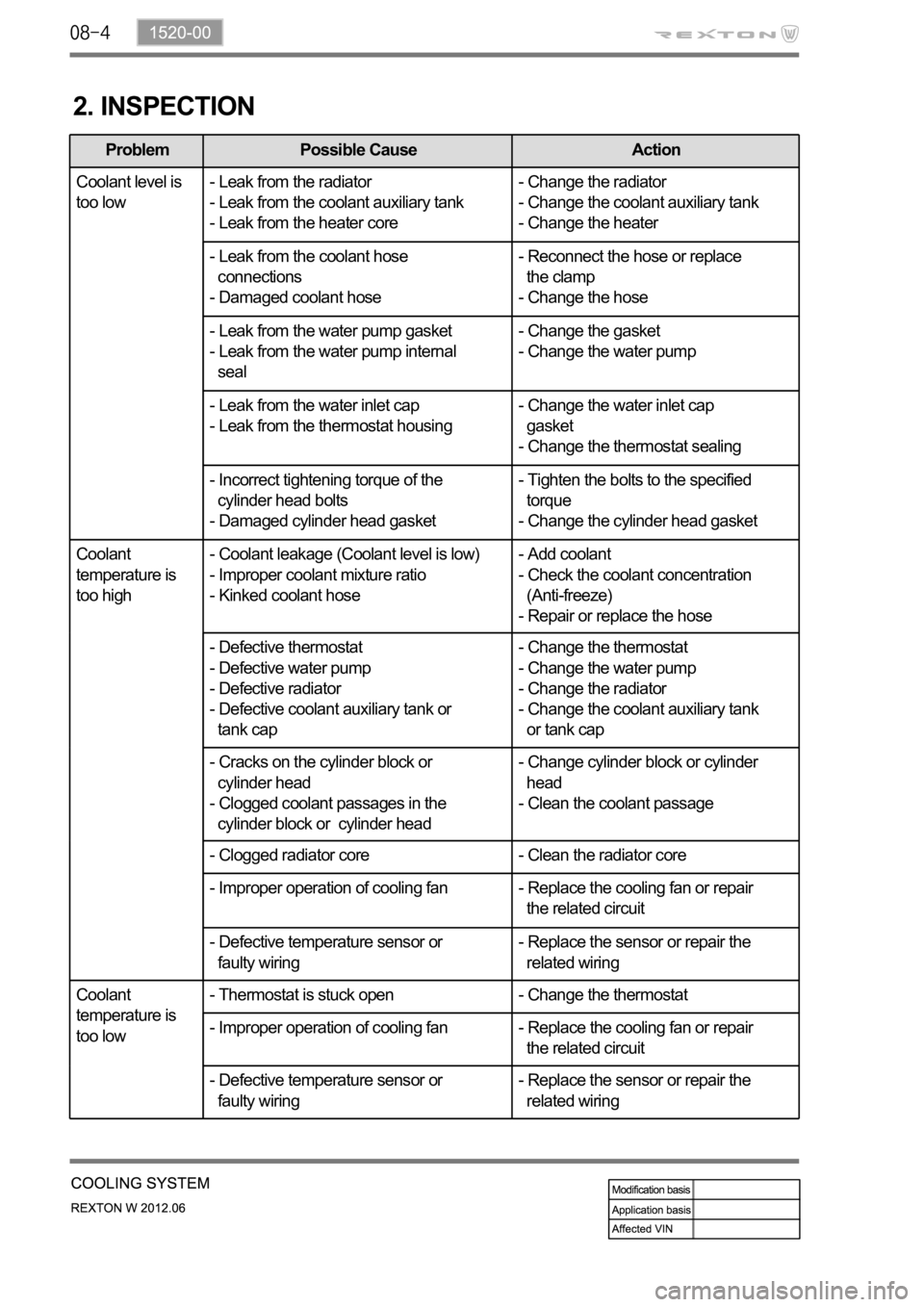
2. INSPECTION
Problem Possible Cause Action
Coolant level is
too low- Leak from the radiator
- Leak from the coolant auxiliary tank
- Leak from the heater core- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
- Change the heater
- Leak from the coolant hose
connections
- Damaged coolant hose- Reconnect the hose or replace
the clamp
- Change the hose
- Leak from the water pump gasket
- Leak from the water pump internal
seal- Change the gasket
- Change the water pump
- Leak from the water inlet cap
- Leak from the thermostat housing- Change the water inlet cap
gasket
- Change the thermostat sealing
- Incorrect tightening torque of the
cylinder head bolts
- Damaged cylinder head gasket- Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque
- Change the cylinder head gasket
Coolant
temperature is
too high- Coolant leakage (Coolant level is low)
- Improper coolant mixture ratio
- Kinked coolant hose- Add coolant
- Check the coolant concentration
(Anti-freeze)
- Repair or replace the hose
- Defective thermostat
- Defective water pump
- Defective radiator
- Defective coolant auxiliary tank or
tank cap- Change the thermostat
- Change the water pump
- Change the radiator
- Change the coolant auxiliary tank
or tank cap
- Cracks on the cylinder block or
cylinder head
- Clogged coolant passages in the
cylinder block or cylinder head- Change cylinder block or cylinder
head
- Clean the coolant passage
- Clogged radiator core - Clean the radiator core
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or
faulty wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Coolant
temperature is
too low- Thermostat is stuck open - Change the thermostat
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or
faulty wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Page 386 of 600

2. INSPECTION
1) Alternator Output Test
Item How to check DTC set value / Action
Output
current
B terminal
current
Rotor
coil
resistance
L terminal
voltage
Disconnect the cable connected to the B
terminal on the alternator. Connect one end
of the ammeter to the B terminal and the
other end to the cable connected to the B
terminal.
Measure the maximum output value.
(Maintain the engine speed between 2,500
and 3,000 rpm.)
(Turn the headlamp and all the electrical
switches on.) 1.
2.Pass: If the measured current is 45
A or higher.
Fail: If the measured current is less
than 45 A.
Check the current of the B terminal. -
-
-
Move the gear selector lever to the neutral
position.
Maintain the engine speed at 2,500 rpm
with the vehicle unloaded.
(Turn all the electrical switches off.) 1.
2.Open circuit: If the measured
current is 5 A or higher. -
Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery.
Remove the B terminal and turn off the
ignition switch.
Measure the resistance between the L and
F terminals with an ohmmeter. 1.
2.
3.Pass: If the measured resistance is
Faulty rotor coil or slip ring: If the
measured resistance is less than
-
-
Connect the B terminal wiring.
Measure the voltage with the engine running. 1.
2.Specification: 12.5 V to 14.5 V
Faulty IC regulator or field coil: If
the measured voltage is 14.5 V or
higher. -
-
Disconnect the negative battery cable.
Connect the negative cable again after connecting the ammeter. -
-
Page 387 of 600

1451-01
2) Troubleshooting for Alternator
Item Cause Action
Overcharged batteryDefective alternator voltage regulator
Replace the alternator
Defective voltage detection wiring Repair or replace
Loose alternator drive belt Adjust the belt tension or replace
Discharged batteryPoor connection of related circuit or open
circuitRetighten the loose connection or
repair open circuit
Defective alternator voltage regulator
Replace the alternator
Defective alternator voltage regulator
Replace the alternator
Terminated battery Replace the battery
Defective ground Repair
Charge warning
lamp does not come
on when turning on
ignition switch with
engine stoppedDefective alternator voltage regulator
Replace the alternator
Open circuit in charge warning lamp, fuse
or wiringReplace or repair the charge warning
lamp or fuse
Defective ignition switch Replace the ignition switch
Defective ground of alternator circuit Repair
Charge warning
lamp is not turned
off after starting
engineDefective alternator voltage regulator
Replace the alternator
Corroded or worn battery cableRepair or replace the battery cable
Loose alternator drive belReplace the batteryAdjust the belt
tension or replace the belt
Defective wiring harness Repair or replace
Page 461 of 600

0000-00
This is done periodically under certain operating conditions. When the resetting is finished, the new
minimum pulse value replaces the value obtained during the previous resetting. The first MDP value is
provided by the C3I. Each resetting then allows the closed loop of the MDP to be updated according to
the deviation of the injector.
B. Detection of leaks in the cylinders
The accelerometer is also used to detect any injector which may have stuck open. The detection
principle is based on monitoring the ratio. If there is a leak in the cylinder, the accumulated fuel self-
ignites as soon as the temperature and pressure conditions are favorable (high engine speed, high load
and small leak).
This combustion is set off at about 20 degrees before TDC and before main injection.
The ratio therefore increases considerably in the detection window. It is this increase which allows the
leaks to be detected. The threshold beyond which a fault is signaled is a percentage of the maximum
possible value of the ratio.
Because of the severity of the recovery process (engine shut-down), the etection must be extremely
robust.
An increase in the ratio can be the consequence of various causes:
Pilot injection too much
Main combustion offset
Fuel leak in the cylinder -
-
-
If the ratio becomes too high, the strategy initially restricts the pilot injection flow and retards the main
injection. If the ratio remains high despite these interventions, this shows that a real leak is present, a
fault is signaled and the engine is shut down.
C. Detection of an accelerometer fault
This strategy permits the detection of a fault in the sensor or in the wiring loom connecting the sensor to
the ECU.
It is based on detection of the combustion. When the engine is idling, the detection window is set too low
for the combustion caused by the main injection. If the ratio increases, this shows that the knock sensor
is working properly, but otherwise a fault is signaled to indicate a sensor failure. The recovery modes
associated with this fault consist of inhibition of the pilot injection and discharge through the injectors.