wheel SSANGYONG RODIUS 2007 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2007, Model line: RODIUS, Model: SSANGYONG RODIUS 2007Pages: 465, PDF Size: 56.32 MB
Page 328 of 465
0-8
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
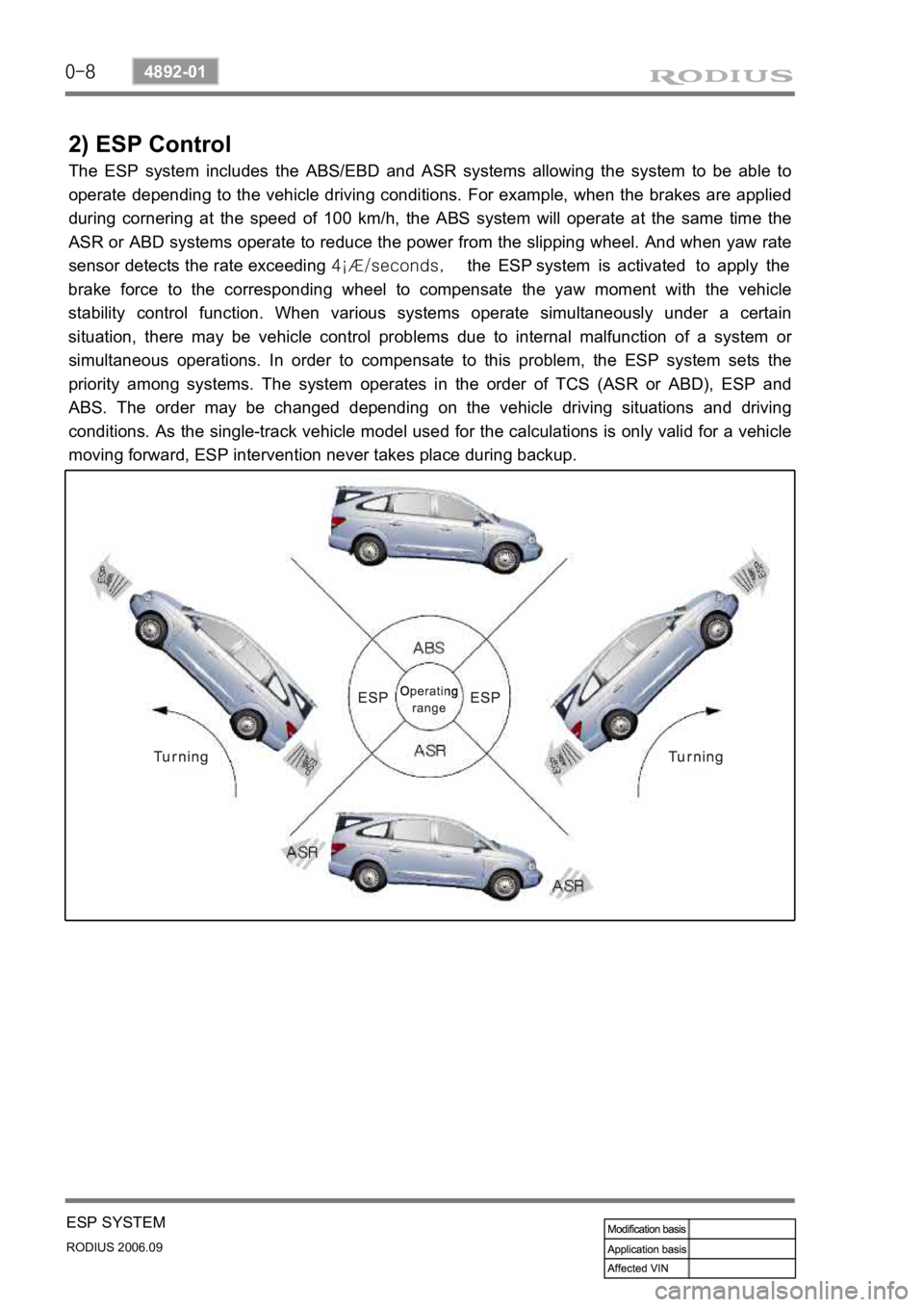
2) ESP Control
The ESP system includes the ABS/EBD and ASR systems allowing the system to be able to
operate depending to the vehicle driving conditions. For example, when the brakes are applied
during cornering at the speed of 100 km/h, the ABS system will operate at the same time the
ASR or ABD systems operate to reduce the power from the slipping wheel. And when yaw rate
sensor detects the rate exceeding 4¡Æ/seconds, the ESP system is activated to apply the
brake force to the corresponding wheel to compensate the yaw moment with the vehicle
stability control function. When various systems operate simultaneously under a certain
situation, there may be vehicle control problems due to internal malfunction of a system o
r
simultaneous operations. In order to compensate to this problem, the ESP system sets the
priority among systems. The system operates in the order of TCS (ASR or ABD), ESP and
ABS. The order may be changed depending on the vehicle driving situations and driving
conditions. As the single-track vehicle model used for the calculations is only valid for a vehicle
moving forward, ESP intervention never takes place during backup.
Page 330 of 465
0-10
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
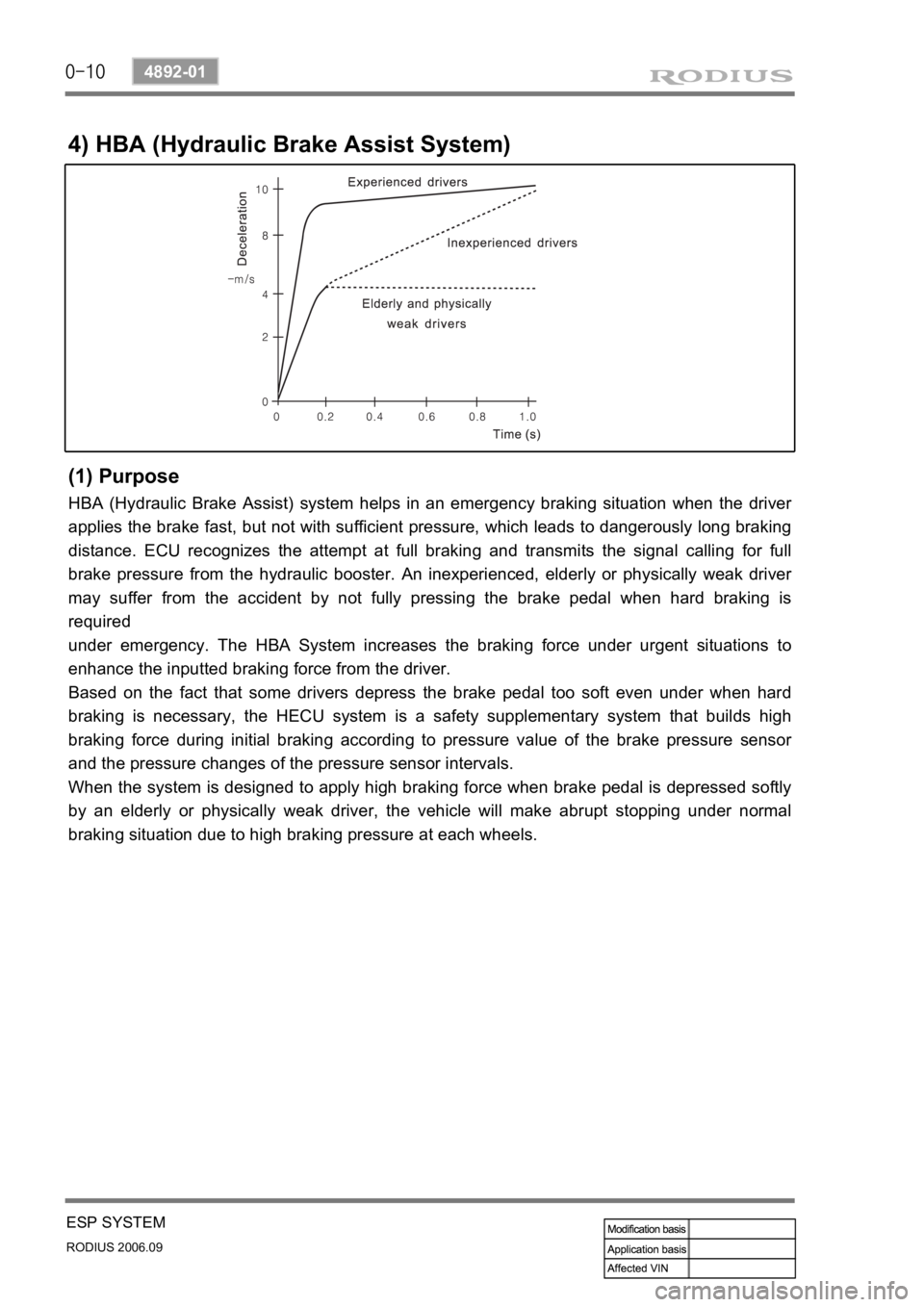
4) HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist System)
(1) Purpose
HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist) system helps in an emergency braking situation when the driver
applies the brake fast, but not with sufficient pressure, which leads to dangerously long braking
distance. ECU recognizes the attempt at full braking and transmits the signal calling for full
brake pressure from the hydraulic booster. An inexperienced, elderly or physically weak drive
r
may suffer from the accident by not fully pressing the brake pedal when hard braking is
required
under emergency. The HBA System increases the braking force under urgent situations to
enhance the inputted braking force from the driver.
Based on the fact that some drivers depress the brake pedal too soft even under when hard
braking is necessary, the HECU system is a safety supplementary system that builds high
braking force during initial braking according to pressure value of the brake pressure senso
r
and the pressure changes of the pressure sensor intervals.
When the system is designed to apply high braking force when brake pedal is depressed softly
by an elderly or physically weak driver, the vehicle will make abrupt stopping under normal
braking situation due to high braking pressure at each wheels.
Page 331 of 465
0-11
ESP SYSTEM
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
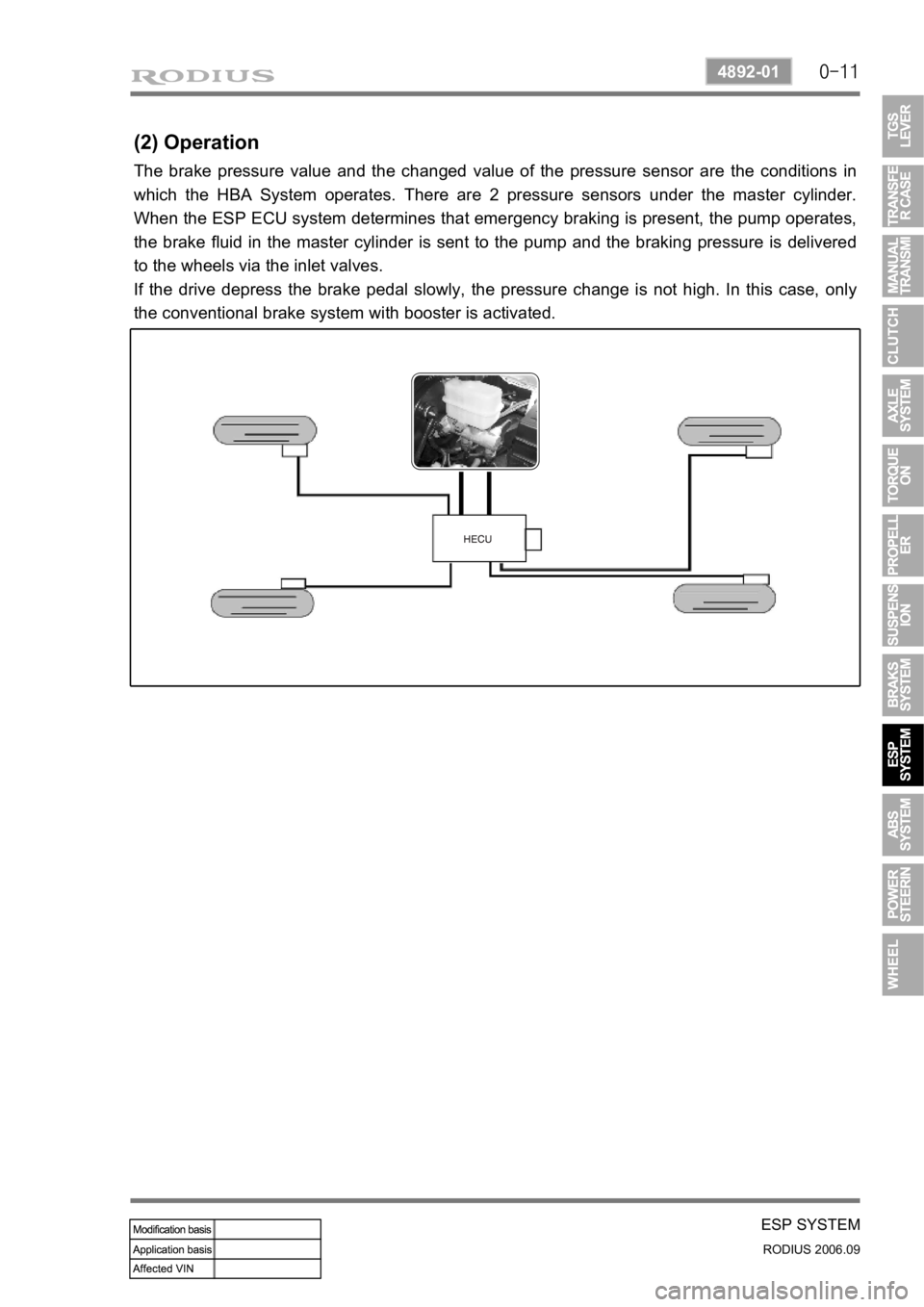
(2) Operation
The brake pressure value and the changed value of the pressure sensor are the conditions in
which the HBA System operates. There are 2 pressure sensors under the master cylinder.
When the ESP ECU system determines that emergency braking is present, the pump operates,
the brake fluid in the master cylinder is sent to the pump and the braking pressure is delivered
to the wheels via the inlet valves.
If the drive depress the brake pedal slowly, the pressure change is not high. In this case, only
the conventional brake system with booster is activated.
Page 334 of 465

0-14
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
(1) System Overview
When equipped with ABS, the braking force at each wheel will be controlled with 3-channel 4-
sensor method. And when equipped with ESP, 4 wheels will be controlled independently with 4-
channel method. (When controlling ABS system only, it will be operated with 3-channel
method.) When compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic
circuit has a normally-open separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in
secondary circuit. When the vehicle brakes are not applied during engine running or when
applying the non-ABS operating brakes, the normally-open separation valve and the inlet valve
are open, whereas the normally-closed shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed. When the
ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be closed by the solenoid
valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve. Then, the inlet
and outlet valves will be
closed or open depending on the braking pressure increase, decrease or unchanged
conditions.
<0d96007b008f008c0047009e00880099009500900095008e004700930088009400970047008a00960094008c009a004700960095004700880095008b0047009e00880099009500900095008e00470089008c008c00970047009a0096009c0095008b009a00
47009e008f008c00950047009b008f008c0047006c007a0077> is operating
▶Driving feeling when the ESP is operating
<0d96007500960090009a008c004700880095008b0047009d0090008900990088009b0090009600950047009b008f0088009b0047008b00990090009d008c00990047009a008c0095009a008c009a0047009e008f008c00950047009b008f008c0047006c00
7a007700470090009a004700960097008c00990088009b0090>ng When the ESP operates during vehicle movement, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument
panel flickers and beep comes on every 0.1 seconds. The ESP operation shows that the
vehicle stability is extremely unstable and it is used to warn the driver. The ESP system is just a
supplementary system for the vehicle motion and it cannot control the vehicle when it exceeds
the physical limits. Do not solely rely on the system but be advised to drive the vehicle safely.
When the ESP system activates, the driving feeling can be different depending on vehicle
driving conditions. For example, you will feel differently when the ESP system is activated
during when ABS is operating with the brakes applied and when brakes are not applied on a
curve. Thus, the ESP system would make the driver feel more abruptly when the brakes are
applied during the ESP system activation.
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to the driver due to the pressure changes
caused by the motor and valve operations in a very short period of time. Extreme cornering will
trigger the ESP operation and this will make the driver feel noise and vibration due to sudden
brake application. Also, the ESP system controls the engine output. So, the driver may notice
the engine output decrease even when the accelerator pedal is being applied.
Page 335 of 465
0-15
ESP SYSTEM
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
<0d96006c007a00770047006f00a0008b00990088009c00930090008a0047009c00950090009b00470090009500470090008b009300900095008e004700880095008b00470095009600990094008800930047008900990088009200900095008e0047009700
96009a0090009b009000960095>
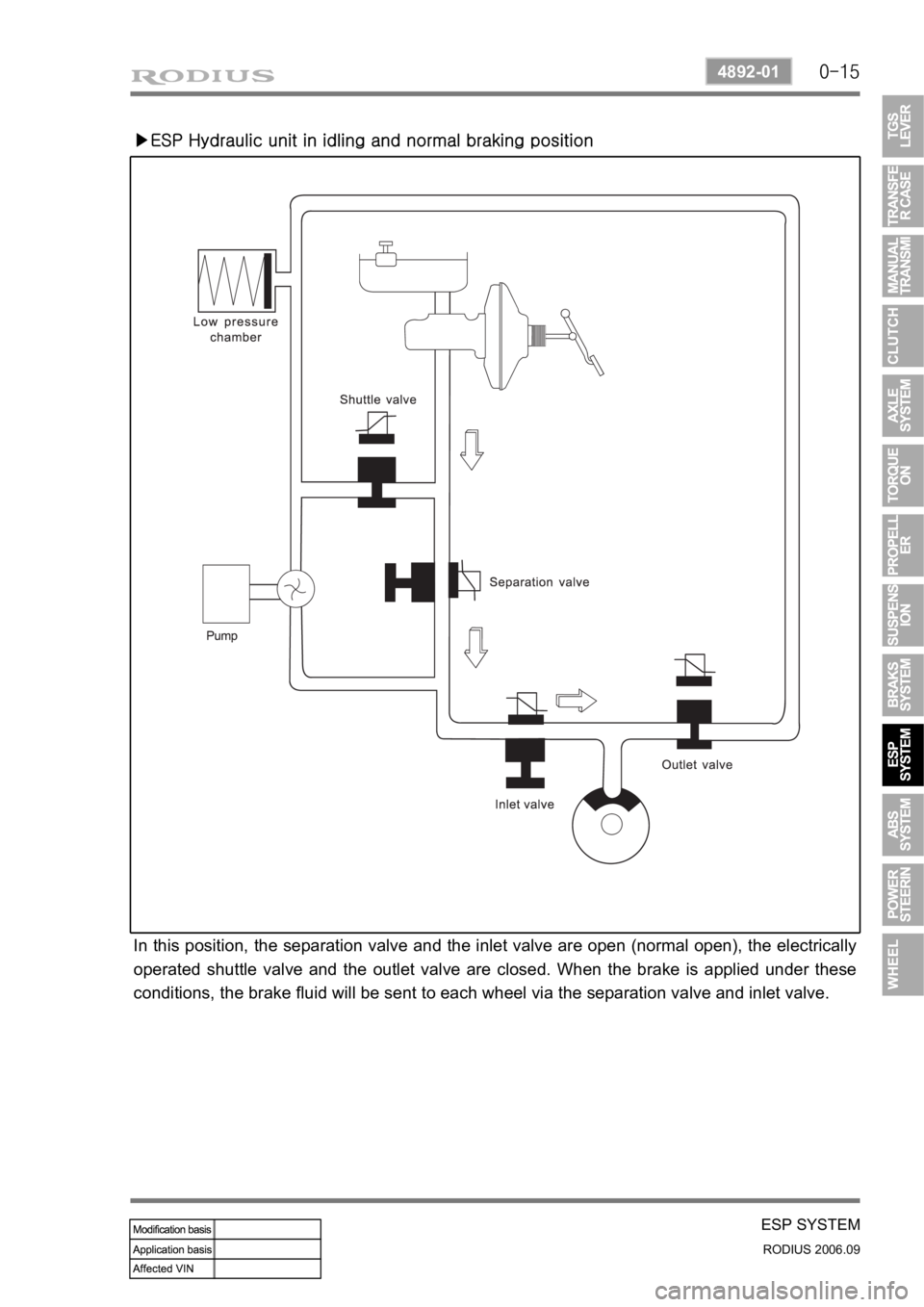
In this position, the separation valve and the inlet valve are open (normal open), the electrically
operated shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed. When the brake is applied under these
conditions, the brake fluid will be sent to each wheel via the separation valve and inlet valve.
Page 336 of 465
0-16
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
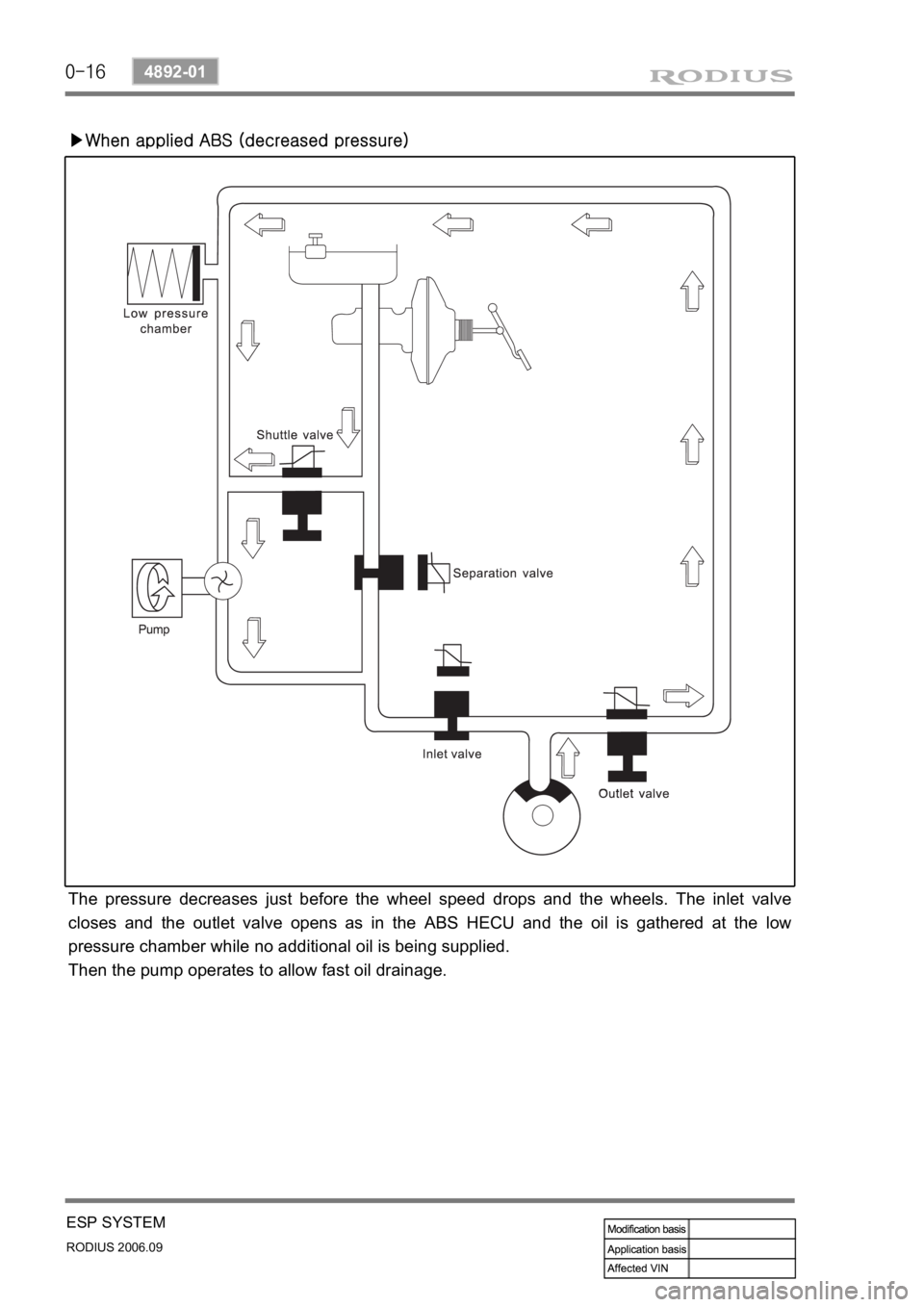
▶When applied ABS (decreased pressure)
The pressure decreases just before the wheel speed drops and the wheels. The inlet valve
closes and the outlet valve opens as in the ABS HECU and the oil is gathered at the low
pressure chamber while no additional oil is being supplied.
Then the pump operates to allow fast oil drainage.
Page 337 of 465
0-17
ESP SYSTEM
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
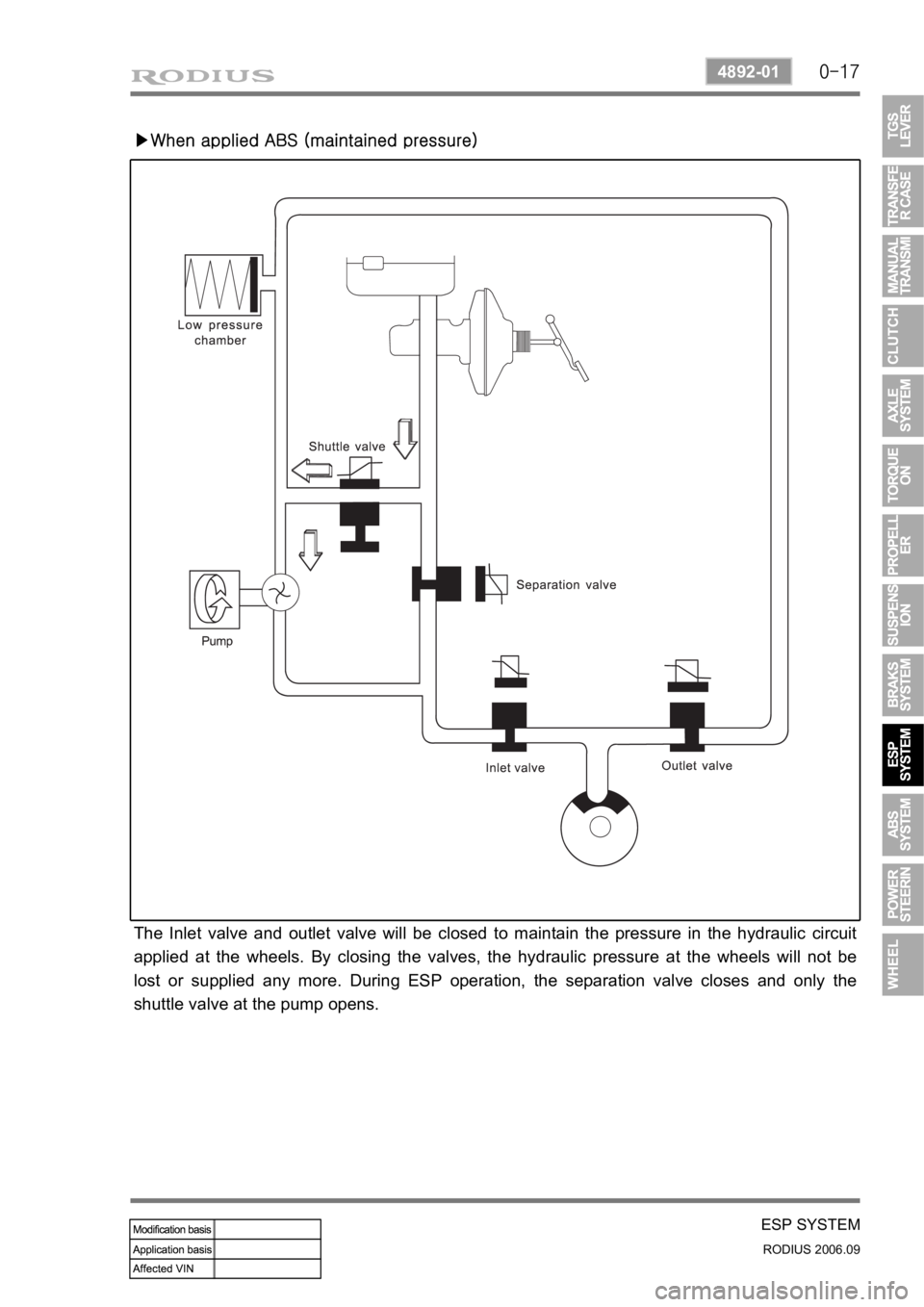
▶When applied ABS (maintained pressure)
The Inlet valve and outlet valve will be closed to maintain the pressure in the hydraulic circuit
applied at the wheels. By closing the valves, the hydraulic pressure at the wheels will not be
lost or supplied any more. During ESP operation, the separation valve closes and only the
shuttle valve at the pump opens.
Page 338 of 465
0-18
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
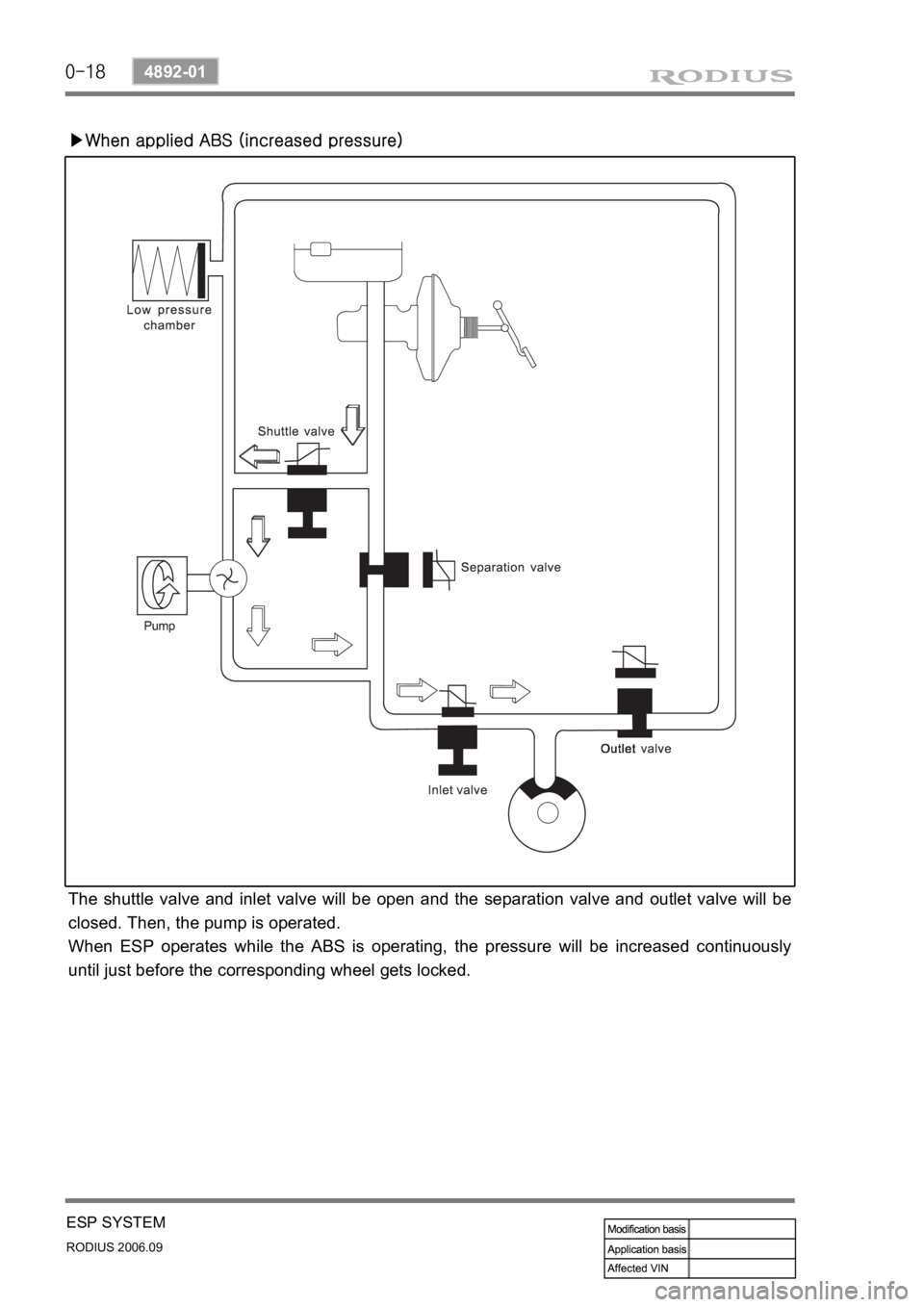
▶When applied ABS (increased pressure)
The shuttle valve and inlet valve will be open and the separation valve and outlet valve will be
closed. Then, the pump is operated.
When ESP operates while the ABS is operating, the pressure will be increased continuously
until just before the corresponding wheel gets locked.
Page 339 of 465
0-19
ESP SYSTEM
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
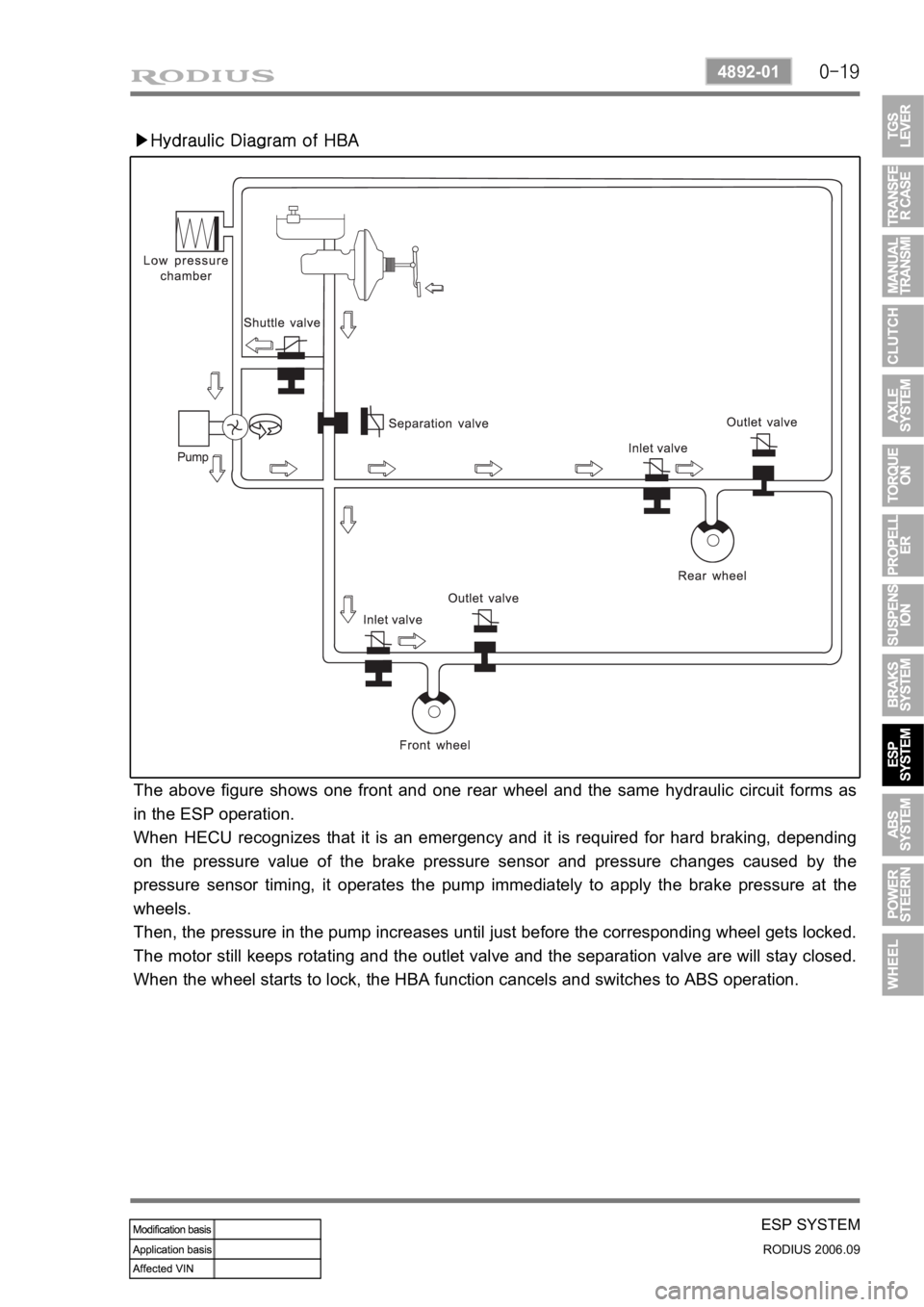
▶Hydraulic Diagram of HBA
The above figure shows one front and one rear wheel and the same hydraulic circuit forms as
in the ESP operation.
When HECU recognizes that it is an emergency and it is required for hard braking, depending
on the pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and pressure changes caused by the
pressure sensor timing, it operates the pump immediately to apply the brake pressure at the
wheels.
Then, the pressure in the pump increases until just before the corresponding wheel gets locked.
The motor still keeps rotating and the outlet valve and the separation valve are will stay closed.
When the wheel starts to lock, the HBA function cancels and switches to ABS operation.
Page 343 of 465

0-4
RODIUS 2006.09
4892-01
ABS SYSTEM
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
The aim of the ABS is to mmaintain steerability and driving stability and to take the burden off
the driver. If the stopping distance is shorter on some road surfaces (carriageway conditions),
this is a gift of physics and not a development aim.
ABS is a device which senses that one or more of the wheels are locking up during braking. It
monitors the rotational speeds of the wheels and reduces hydraulic pressure to any wheel it
senses locking up. It is controlled by both mechanical and electronic components. When you
apply the brakes, the ABS will regulate the flow of brake fluid being delivered to the brake
calipers. By the use of electronic computers, the brakes rapidly alternate (at a rate of 30 times
per second) from full pressure to full release.
1) DRIVING PHYSICS
To give you a better understanding of the tasks and functions of ABS, we will first look at the
physics principles.
(1) The Stopping Distance
The stopping distance depends on the vehicle weight and initial speed when braking starts.
This also applies for vehicle with ABS, where ABS always tries to set an optimum brake force
on each wheel. As great forces are exerted between the tires and the carriageway when
braking, even with ABS the wheels may scream and rubber is left on the road. With an
ABS
skid mark one may be able to clearly recognize the tire profile. The skid mark of an ABS vehicle
does not however leave any hint of the speed of the vehicle in the case of an accident, as it can
only be clearly drawn at the start of braking.
(2) Brake Force on a Wheel
The maximum possible brake force on a wheel depends on the wheel load and the adhesion
coefficient between tire and carriageway. With a low adhesion coefficient the brake force, which
can be obtained is very low. You are bound to know the result already from driving on winte
r
roads. With a high adhesion coefficient on a dry road, the brake force, which can be obtained,
is considerably higher. The brake force, which can be obtained, can be calculated from below
formula: