fuel SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: RODIUS, Model: SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012Pages: 715, PDF Size: 79.36 MB
Page 347 of 715

15-22
(7) Knocking Control
A. Resetting the pilot injection
The knocking control is used to reset the pilot injection flow in closed loop for each injector. This method
allows the correction of any injector deviations over a period of time. The principle of use of the knocking
control is based on the detection of the combustion noises.
The sensor is positioned in such a way as to receive the maximum signal for all the cylinders. The raw
signals from the knock sensor are processed to obtain a variable which quantifies the intensity of the
combustion. This variable, known as the ratio, consists of the ratio between the intensity of the
background noise and the combustion noise.
A first window is used to establish the background noise level of the knocking control signal for each
cylinder. This window must therefore be positioned at a moment when there cannot be any
combustion.
The second window is used to measure the intensity of the pilot combustion. Its position is such that
only the combustion noises produced by the pilot injection are measured . It is therefore placed just
before the main injection. 1.
2.
The knock sensor does not allow any evaluation of the quantity injected. However, the pulse value will
be measured when the injector starts injection and this pulse value is called the MDP (Minimum Drive
Pulse). On the basis of this information, it is possible to efficiently correct the pilot flows. The pilot
injection resetting principle therefore consists of determining the MDP, in other words the pulse
corresponding to the start of the increase in value of the ratio (increase of vibration due to fuel
combustion).
Page 348 of 715

15-230000-00
This is done periodically under certain operating conditions. When the resetting is finished, the new
minimum pulse value replaces the value obtained during the previous resetting. The first MDP value is
provided by the C3I. Each resetting then allows the closed loop of the MDP to be updated according to
the deviation of the injector.
B. Detection of leaks in the cylinders
The accelerometer is also used to detect any injector which may have stuck open. The detection
principle is based on monitoring the ratio. If there is a leak in the cylinder, the accumulated fuel self-
ignites as soon as the temperature and pressure conditions are favorable (high engine speed, high load
and small leak).
This combustion is set off at about 20 degrees before TDC and before main injection.
The ratio therefore increases considerably in the detection window. It is this increase which allows the
leaks to be detected. The threshold beyond which a fault is signaled is a percentage of the maximum
possible value of the ratio.
Because of the severity of the recovery process (engine shut-down), the etection must be extremely
robust.
An increase in the ratio can be the consequence of various causes:
Pilot injection too much
Main combustion offset
Fuel leak in the cylinder -
-
-
If the ratio becomes too high, the strategy initially restricts the pilot injection flow and retards the main
injection. If the ratio remains high despite these interventions, this shows that a real leak is present, a
fault is signaled and the engine is shut down.
C. Detection of an accelerometer fault
This strategy permits the detection of a fault in the sensor or in the wiring loom connecting the sensor to
the ECU.
It is based on detection of the combustion. When the engine is idling, the detection window is set too low
for the combustion caused by the main injection. If the ratio increases, this shows that the knock sensor
is working properly, but otherwise a fault is signaled to indicate a sensor failure. The recovery modes
associated with this fault consist of inhibition of the pilot injection and discharge through the injectors.
Page 349 of 715
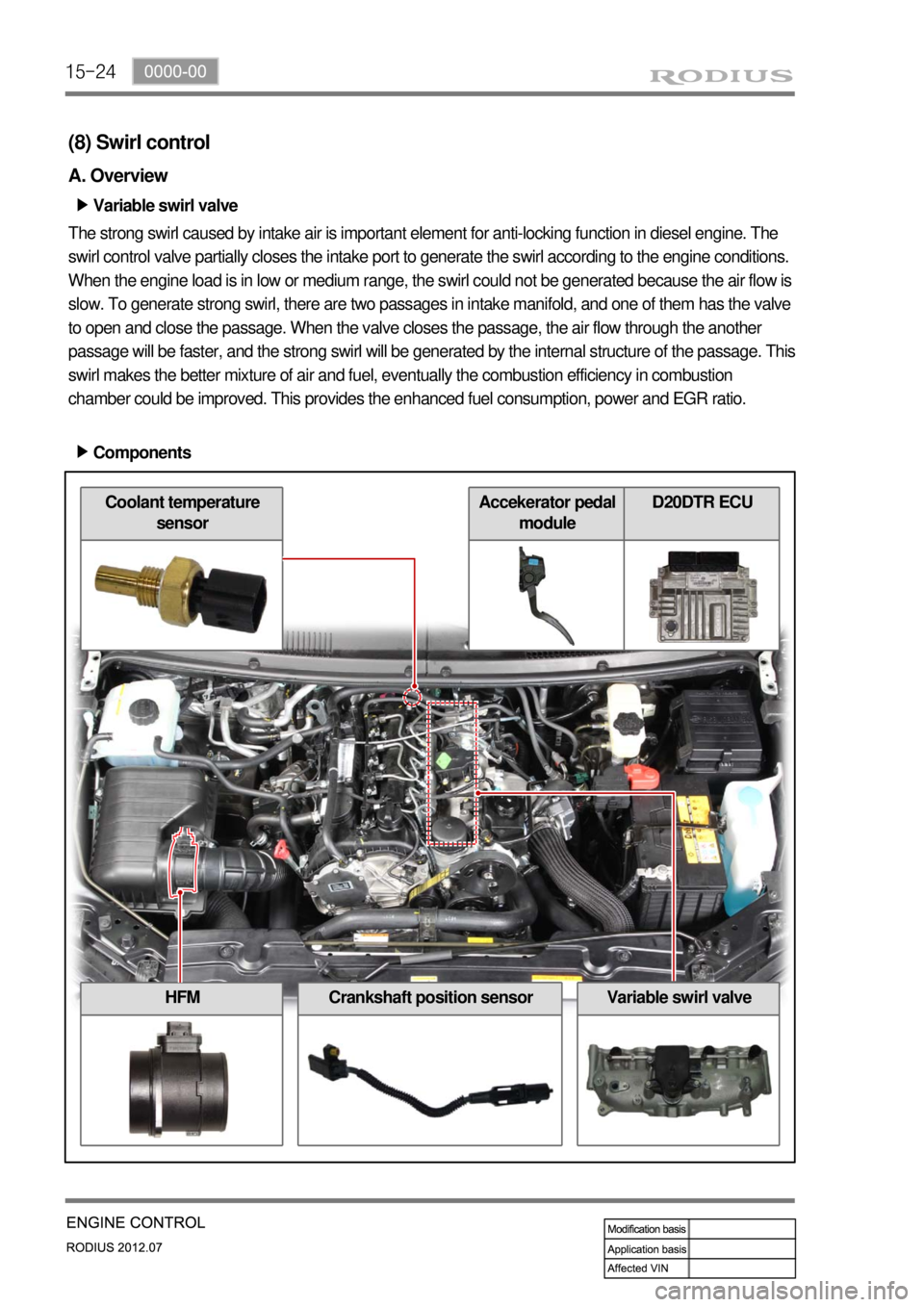
15-24
(8) Swirl control
A. Overview
Variable swirl valve ▶
The strong swirl caused by intake air is important element for anti-locking function in diesel engine. The
swirl control valve partially closes the intake port to generate the swirl according to the engine conditions.
When the engine load is in low or medium range, the swirl could not be generated because the air flow is
slow. To generate strong swirl, there are two passages in intake manifold, and one of them has the valve
to open and close the passage. When the valve closes the passage, the air flow through the another
passage will be faster, and the strong swirl will be generated by the internal structure of the passage. This
swirl makes the better mixture of air and fuel, eventually the combustion efficiency in combustion
chamber could be improved. This provides the enhanced fuel consumption, power and EGR ratio.
Components ▶
HFMCrankshaft position sensorVariable swirl valve
Coolant temperature
sensorAccekerator pedal
moduleD20DTR ECU
Page 351 of 715

15-26
C. Types of swirl
Swirl: One cylinder has two intake air ports, one is set horizontally and
the other one is set vertically. Swirl is the horizontal air flows in cylinder
due to the horizontal intake air ports.
Tumble: Tumble is the vertical air flows in cylinder due to the vertical
intake air port
Squish is the air flow at end of compression process according to the
design of piston head. In this DI engine, the squish is generated to
bowl type.
D. Swirl control
In DI type diesel engine, the liquefied fuel is injected into the cylinder directly. If the fuel is evenly
distributed in short period, the combustion efficiency could be improved. To get this, there should be
good air flow in cylinder. In general, there are two intake ports, swirl port and tangential port, in each
cylinder. The swirl port generates the horizontal flow and the tangential port generates the longitudinal
flow. In low/mid load range, the tabgential port is closed to increase the horizontal flow. Fast flow
decreases the PM during combustion and increases the EGR ratio by better combustion efficiency.
Page 352 of 715

15-270000-00
Load Engine speedSwirl
valveAmount of
swirlRemarks
Low speed,
Low loadbelow 3,000 rpm Closed HeavyIncreased EGR ratio, better air-fuel
mixture (reduce exhaust gas))
High speed,
High loadover 3,000 rpm Open LightIncrease charge efficiency, higher
engine power
The variable swirl valve actuator operates when
turning the ignition switch ON/OFF position to
open/close the swirl valve. In this period, the soot
will be removed and the learning for swirl valve
position is performed.
Swirl: This is the twisted (radial) air flow along the cylinder wall during the intake stroke. This
stabilizes the combustion even in lean air-fuel mixture condition.
Swirl valve
E. Features
Swirl and air intake efficiency
To generate the swirl, the intake port should be serpentine design. This makes the resistance in air
flow. The resistance in air flow in engine high speed decreases the intake efficiency. Eventually, the
engine power is also decreased, Thus, the swirl operation is deactivated in high speed range to
increase the intake efficiency.
Relationship between swirl and EGR
To reduce Nox, it is essential to increase EGR ratio. However, if EGR ratio is too high, the PM also
could be very higher. And, the exhaust gas should be evenly mixed with newly aspired air. Otherwise,
PM and CO are dramatically increased in highly concentrated exhaust gas range and EGR ratio
could not be increased beyond a certain limit. If the swirl valve operates in this moment, the limit of
EGR ratio will be higher. -
-
F. Relationship between swirl and fuel injection pressur
The injector for DI engine uses the multi hole design. For this vehicle, there are 8 holes in injector. If the
swirl is too strong, the injection angles might be overlapped and may cause the increased PM and
insufficient engine power. Also, if the injection pressure is too high during strong swirl, the injection
angles might be overlapped. Therefore, the system may decreases the fuel injection pressure when the
swirl is too strong.
Page 360 of 715

15-350000-00
HFM (intake air
temperature)CDPF
Electric throttle
bodyCoolant
temperature
sensorOxygen sensor
Injector (C3I)
E-EGR valve
(11) Wide band oxygen sensor control
A. Overview
For diesel engine, combustion is not performed at the optimum (theoretically correct) air-fuel ratio and
the oxygen concentration is thin in most cases. So the wide-band oxygen sensor is used for this kind of
engine, and this sensor is a little different from the one that used for gasoline engine. The combustion in
diesel engine is controlled by fuel injection volume. Therefore, the wide band oxygen sensor should be
used in diesel engine. This sensor measures the air-fuel ratio in very wide range, and is also called full
range oxygen sensor.
The wide band oxygen sensor measures the oxygen density in exhaust gas and sends it to ECU to
control the EGR more precisely. -
B. Components
D20DTR ECU
Page 373 of 715
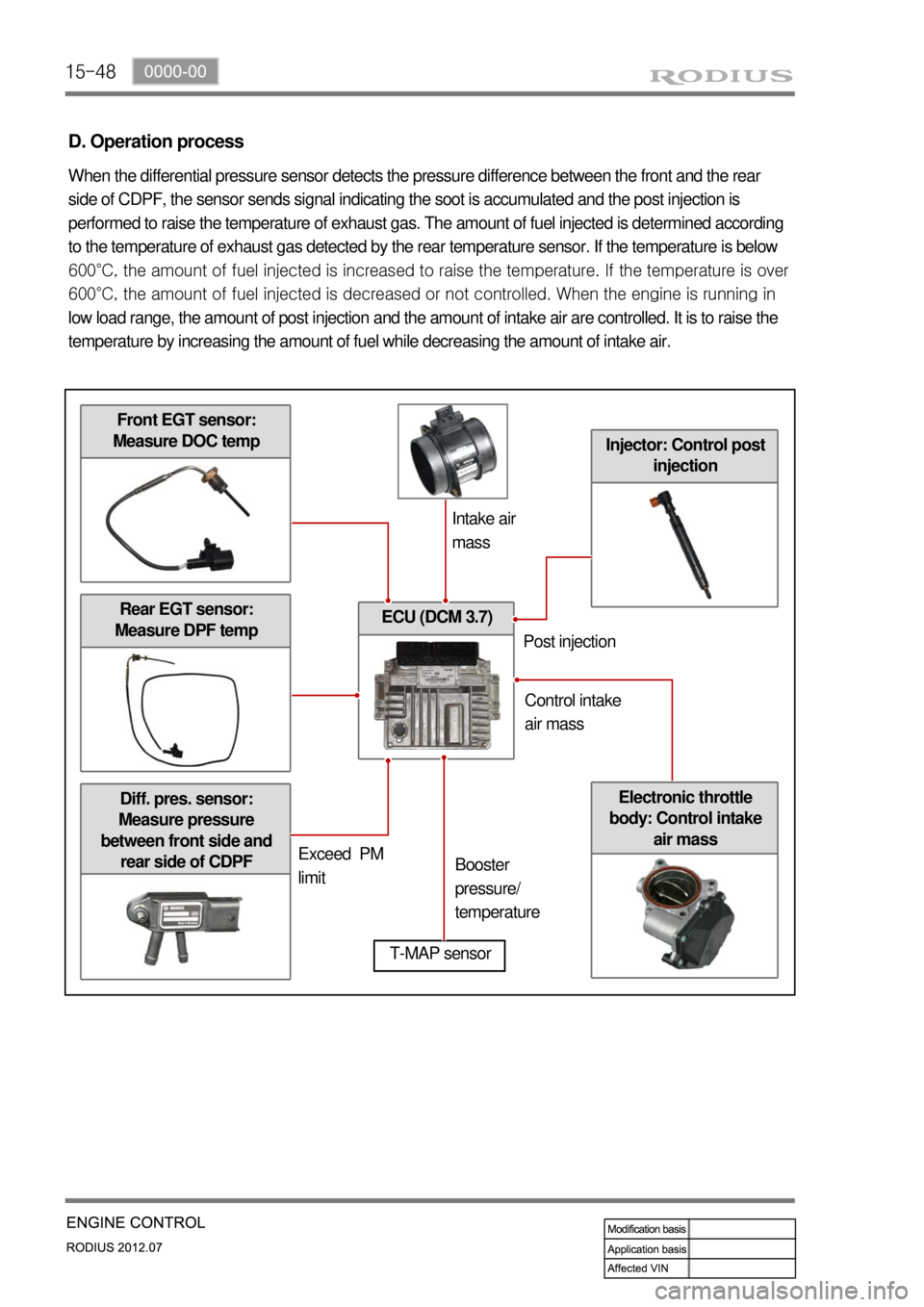
15-48
Rear EGT sensor:
Measure DPF temp
Diff. pres. sensor:
Measure pressure
between front side and
rear side of CDPFElectronic throttle
body: Control intake
air mass
ECU (DCM 3.7)
Injector: Control post
injection
D. Operation process
When the differential pressure sensor detects the pressure difference between the front and the rear
side of CDPF, the sensor sends signal indicating the soot is accumulated and the post injection is
performed to raise the temperature of exhaust gas. The amount of fuel injected is determined according
to the temperature of exhaust gas detected by the rear temperature sensor. If the temperature is below
600°C, the amount of fuel injected is increased to raise the tem
perature. If the temperature is over
600°C, the amount of fuel injected is decreased or not controlled. When the engine is running in
low load range, the amount of post injection and the amount of intake air are controlled. It is to raise the
temperature by increasing the amount of fuel while decreasing the amount of intake air.
Front EGT sensor:
Measure DOC temp
T-MAP sensor
Intake air
mass
Exceed PM
limitBooster
pressure/
temperaturePost injection
Control intake
air mass
Page 374 of 715

15-490000-00
E. Cautions
Use only specified Engine Oil (approved by MB Sheet 229.51) for CDPF. -
Use only specified engine oil (Low Ash Oil) ▶
The vehicle equipped with CDPF should use specific engine oil to improve the engine performance
and fuel economy, and ensure the service life of CDPF. -
Issue with normal engine oil ▶
Sulfur, one of the contents of engine oil is burned and generates soot that is not regenerated by the
DPF. This remains on the filter as ashes and keeps accumulating. Eventually, this ashes will block
the filter. -
Benefit for specified engine oil ▶
Minimized the sulfur content of engine oil which reduces the service life.
Improved fuel economy and emission level of CO2 with high performance and low viscosity.
Increased service life of engine oil with high resistance to temperature. -
-
-
Problems when using unspecified engine oil ▶
The service life of filter may be reduced by 30% or more by the ashes accumulated on the filter.
The fuel economy may be reduced because of engine rolling resistance, frequent regeneration of
DPF. -
-
These problems are also caused by oil with high sulfur content, such as tax exemption oil and
heating oil, etc. *
Page 387 of 715

03-32211-22
1. FUEL SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
Use Only Unleaded Fuel Rated at 89 Octane or Higher ▶
Fuel quality and additives contained in fuel have a significant effect on power output, drivability,
and life of theengine. Fuel with too low an octane number can cause engine knock.
Do Not Use Methanol ▶
Fuels containing methanol (wood alcohol) should not be used in vehicle.
This type of fuel can reduce vehicle performance and damage components of the fuel system.
Vehicle Fueling from Drums or Storage Containers ▶
For safety reasons (particularly when using noncommercial fueling systems) fuel containers,
pumps and hoses must be properly earthed. Static electricity build up can occur under certain
atmospheric and fuel flow conditions if unearthed hoses, particularly plastic, are fitted to the fuel-
dispensing pump.
It is therefore recommended that earthed pumps with integrally earthed hoses be used, and that
storage containers be properly earthed during all noncommercial fueling operations.
Page 390 of 715

05-32420-01
1. OVERVIEW OF EXHAUST SYSTEM
When you are inspecting or replacing exhaust system components, make sure there is
adequate clearance from all points on the underbody to avoid possible overheating of the
floor panel and possible damage to the passenger compartment insulation and trim
materials.
Check the complete exhaust system and the nearby body areas and trunk lid for broken,
damaged, missing or mispositioned parts, open seams, holes, loose connections, or other
deterioration which could permit exhaust fumes to seep into the trunk may be an indication of
a problem in one of these areas. Any defects should be corrected immediately. -
2. OVERVIEW OF MUFFLER
Aside from the exhaust manifold connection, the exhaust system uses a flange and seal joint
design rather than a slip joint coupling design with clamp and U-bolts.
If hole, open seams, or any deterioration is discovered upon inspection of the front muffler and
pipe assembly, the complete assembly should be replace, the complete assembly should be
replaced.
The same procedure is applicable to the rear muffler assembly. Heat shields for the front and rear
muffler assembly and catalytic converter protect the vehicle and the environment from the high
temperatures that the exhaust system develops.
3. OVERVIEW OF CATALYTIC CONVERTER
When jacking or lifting the vehicle from the body side rails, be certain that the lift pads do not
contact the catalytic converter, as this could damage the catalytic converter. -
Use of anything other than unleaded fuel will damage the catalyst in the catalytic converter. -
The catalytic converter are emission-control devices added to the exhaust system to
reduce pollutants from the exhaust pipes.
The oxidation catalyst is coated with a catalytic material containing platinum and
palladium, which reduces levels of hydrocarbon (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) from
the exhaust gas. The three-way catalyst has coatings which contain platinum and
rhodium, which additionally lower the levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). ·
·