brake sensor SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: RODIUS, Model: SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012Pages: 715, PDF Size: 79.36 MB
Page 164 of 715

02-70000-00
3. CHECK AND INSPECTION
1) Cylinder
(1) Compression pressure test
Specified value ▶
Compression ratio16.5 : 1
Test conditionat normal operating temperature (80˚C)
Compression pressur
eStandard32 bar
Minimum18 bar
Differential limit between cylindersMaximum 3 bar
The compression pressure test is to check the conditions of internal components (piston, piston
ring, intake and exhaust vale, cylinder head gasket). This test provides current engine operating
status.
Measurement ▶
<007e0088009900940047009b008f008c0047008c0095008e00900095008c0047009c00970047009b00960047009500960099009400880093004700960097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00
47004f005f005700b6006a00500055>
Disconnect the fuel rail pressure sensor connector to cut off the fuel injection.
Remove the air cleaner duct and glow plugs. -
-
-
Place the diagram sheet to compression
pressure tester and install it into the plug
hole. 1. Before cranking the engine, make sure that the test wiring, tools and persons are keeping
away from moving components of engine (e.g., belt and cooling fan).
Park the vehicle on the level ground and apply the parking brake.
Do not allow anybody to be in front of the vehicle. -
-
-
Page 328 of 715
15-30000-00
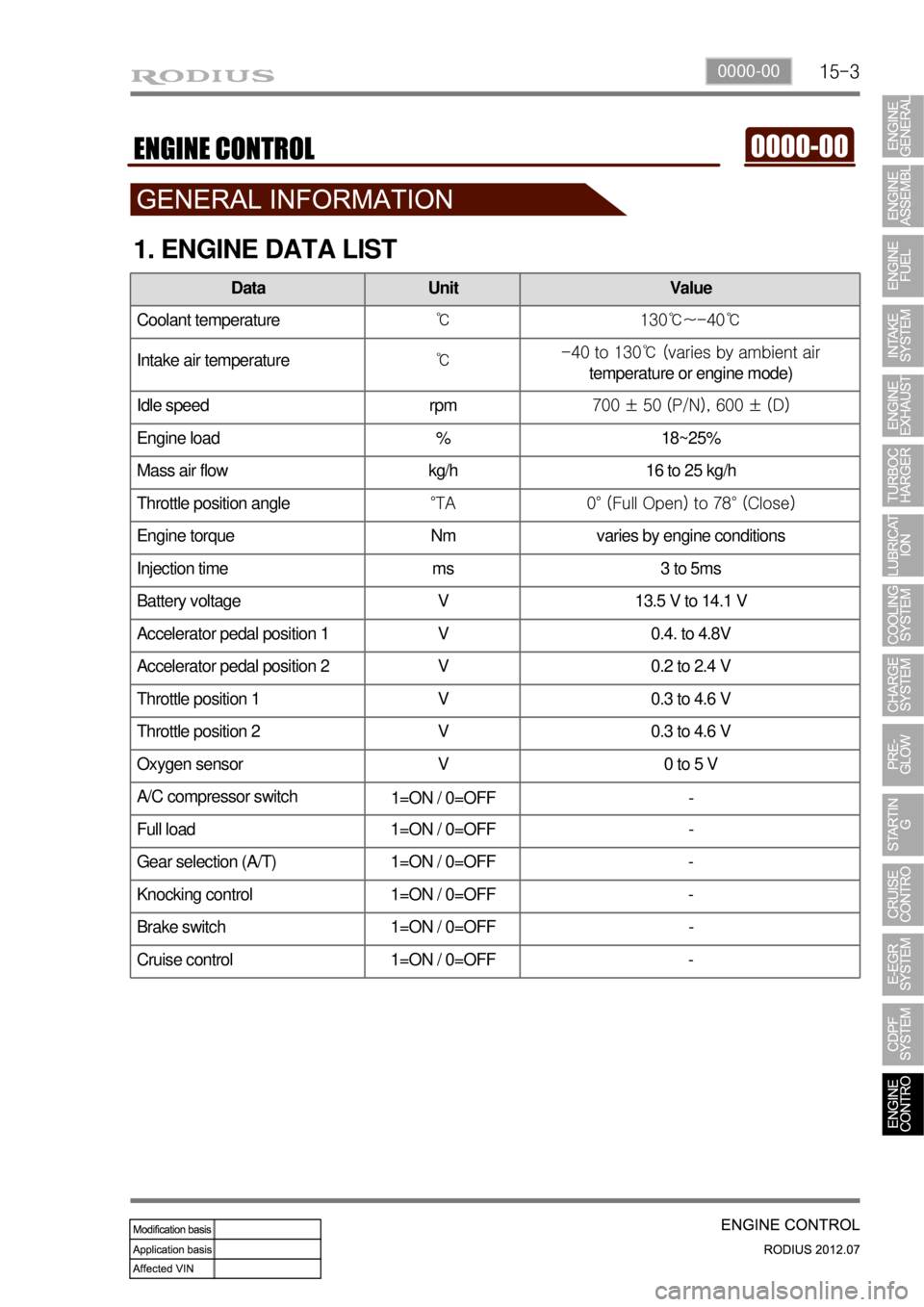
1. ENGINE DATA LIST
Data Unit Value
Coolant temperature℃ 130℃~-40℃
Intake air temperature℃ -40 to 130℃ (varies by ambient air
temperature or engine mode)
Idle speed rpm 700 ± 50 (P/N), 600 ± (D)
Engine load % 18~25%
Mass air flow kg/h 16 to 25 kg/h
Throttle position angle°TA 0° (Full Open) to 78° (Close)
Engine torque Nm varies by engine conditions
Injection time ms 3 to 5ms
Battery voltage V 13.5 V to 14.1 V
Accelerator pedal position 1 V 0.4. to 4.8V
Accelerator pedal position 2 V 0.2 to 2.4 V
Throttle position 1 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Throttle position 2 V 0.3 to 4.6 V
Oxygen sensor V 0 to 5 V
A/C compressor switch
1=ON / 0=OFF -
Full load 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Gear selection (A/T) 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Knocking control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Brake switch 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Cruise control 1=ON / 0=OFF -
Page 334 of 715

15-90000-00
Fuel rail pressure Water sensor
(2) Components for ECU Input
CAN
- ABS & ESP
- GCU
- Indicator/
Warning Lamp,
Meter Cluster
- TCUSwirl valve
position
sensor
Differential
pressure sensorE-EGR valve
position
sensorCamshaft position
sensorCoolant
temperature
sensor
EGT sensorHFM sensorOxygen sensorT-MAP sensor
Crankshaft
position
sensorAccelerator pedal
sensorThrottle
position
sensorKnock sensor
- Auto cruise switch
- Refrigerant pressure
sensor
- Blower switch signal
- Brake pedal signal
Page 336 of 715

15-110000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed and
crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and emission
gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure and
activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so controls
various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce
emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences. For example,
there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer and adopted CAN
communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in the
vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied instantly
so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and hold-
current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-
Page 522 of 715

01-33650-01
Diameter( Torque converter) 270mm
Lockup function Yes
Gear ratios 1st 3.595
2nd 2.186
3rd 1.405
4th 1.000
5th 0.831
Reverse:
S mode / W mode3.167/1.926
Driving type 2WD(4WD)
Fluid specification Shell ATF 134
Fluid capacityapprox. 8ℓ
Selected lever
indicationP.R.N.D Mechanical
D+/D- Electrical
Parking lock systemBrake switch(signal) → TGS lever
Reverse lock systemCAN → TGS lever
Selected lever
indicationP.R.N.D Lever position
1, 2, 3, 4, 5 CAN
Oil temperature
sensorResistance: R, D0.5 ~ 2.5kΩ
Resistance: P, N20kΩ
TCU EGS 52
Shift solenoid
valve(25℃)Resistance3.8 ± 0.2Ω
Operating distance 0.2mm
Operating current 1.5 ~ 2A
Item W5A580(2WD) / W5A400(4WD)
Input torque 450Nm
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Page 523 of 715

01-4
항목W5A330(300) W5A580(400)
M/P, S/P solenoid
valve(23℃)Resistance5.0 ± 0.2Ω
Operating distance 0.6mm
Operating current 0 ~ 1A
Lockup solenoid
valve(25℃)Resistance2.5 ± 0.2Ω
Operating distance 0.2mm
Operating current 1.5 ~ 2.0A
Operating range 3rd to 5th gears
Speed sensor Resistance HALL type
Operating voltae 6V
Start lockout switch Switch contact ON(D position)
Switch contact OFF(P, N position)
Mode switch W(Winter)
S(Standard)
One-way clutch F1, F2
Planetary gear set Plain planetary gear:
3(number of pinion)3, 4, 3 4, 4, 4
Disc clutch Disc: C2*, C2, C3* Single plate type*
Disc brake Disc: B1*, B2, B3 Single plate type*
Item W5A580(2WD)/W5A400(4WD)
Page 529 of 715
01-10
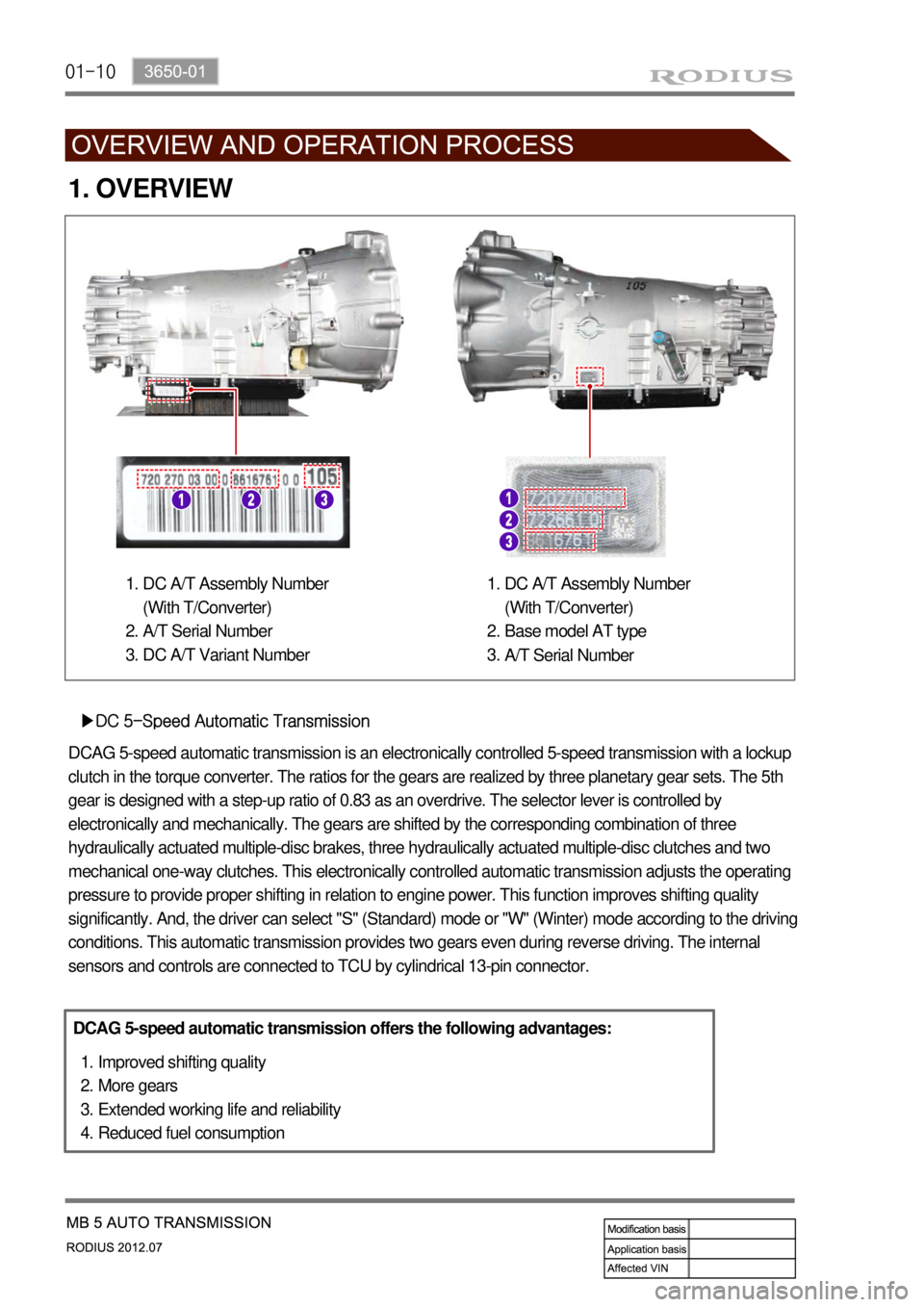
1. OVERVIEW
▶DC 5-Speed Automatic Transmission
DCAG 5-speed automatic transmission is an electronically controlled 5-speed transmission with a lockup
clutch in the torque converter. The ratios for the gears are realized by three planetary gear sets. The 5th
gear is designed with a step-up ratio of 0.83 as an overdrive. The selector lever is controlled by
electronically and mechanically. The gears are shifted by the corresponding combination of three
hydraulically actuated multiple-disc brakes, three hydraulically actuated multiple-disc clutches and two
mechanical one-way clutches. This electronically controlled automatic transmission adjusts the operating
pressure to provide proper shifting in relation to engine power. This function improves shifting quality
significantly. And, the driver can select "S" (Standard) mode or "W" (Winter) mode according to the driving
conditions. This automatic transmission provides two gears even during reverse driving. The internal
sensors and controls are connected to TCU by cylindrical 13-pin connector.
DCAG 5-speed automatic transmission offers the following advantages:
Improved shifting quality
More gears
Extended working life and reliability
Reduced fuel consumption 1.
2.
3.
4.
DC A/T Assembly Number
(With T/Converter)
A/T Serial Number
DC A/T Variant Number 1.
2.
3.DC A/T Assembly Number
(With T/Converter)
Base model AT type
A/T Serial Number 1.
2.
3.
Page 594 of 715

08-34850-03
Brake oil Grade DOT 4
Service interval Replace every 2 years
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Description Specification
Front brake Type Ventilated disc
Rear brake Type Ventilated disc
Master cylinder Type Step feed bore tandem, double cylinder
Brake booster Type Tandem type(integrated level sensor)
Operating type Foot operated type
Page 621 of 715

09-134891-01
3) HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist System)
(1) Purpose
HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist) system helps in an emergency braking situation when the driver
applies the brake fast, but not with sufficient pressure, which leads to dangerously long braking
distance. ECU recognizes the attempt at full braking and transmits the signal calling for full brake
pressure from the hydraulic booster. An inexperienced, elderly or physically weak driver may
suffer from the accident by not fully pressing the brake pedal when hard braking is required
under emergency. The HBA System increases the braking force under urgent situations to
enhance the inputted braking force from the driver.
Based on the fact that some drivers depress the brake pedal too soft even under when hard
braking is necessary, the HECU system is a safety supplementary system that builds high braking
force during initial braking according to pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and the
pressure changes of the pressure sensor intervals.
When the system is designed to apply high braking force when brake pedal is depressed softly by
an elderly or physically weak driver, the vehicle will make abrupt stopping under normal braking
situation due to high braking pressure at each wheels.
Page 622 of 715
09-14
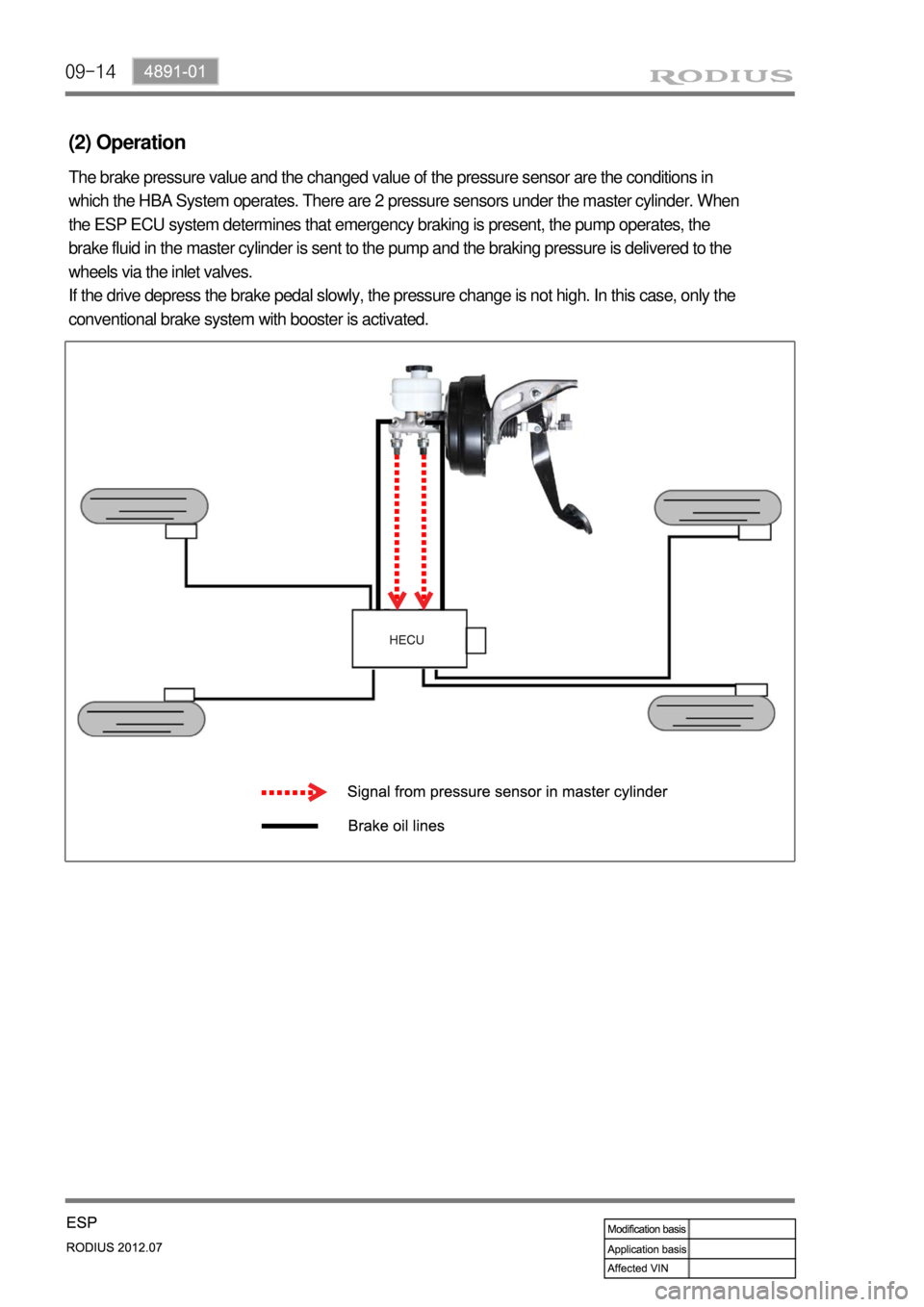
(2) Operation
The brake pressure value and the changed value of the pressure sensor are the conditions in
which the HBA System operates. There are 2 pressure sensors under the master cylinder. When
the ESP ECU system determines that emergency braking is present, the pump operates, the
brake fluid in the master cylinder is sent to the pump and the braking pressure is delivered to the
wheels via the inlet valves.
If the drive depress the brake pedal slowly, the pressure change is not high. In this case, only the
conventional brake system with booster is activated.