weight SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: TURISMO, Model: SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013Pages: 796, PDF Size: 78.99 MB
Page 182 of 796
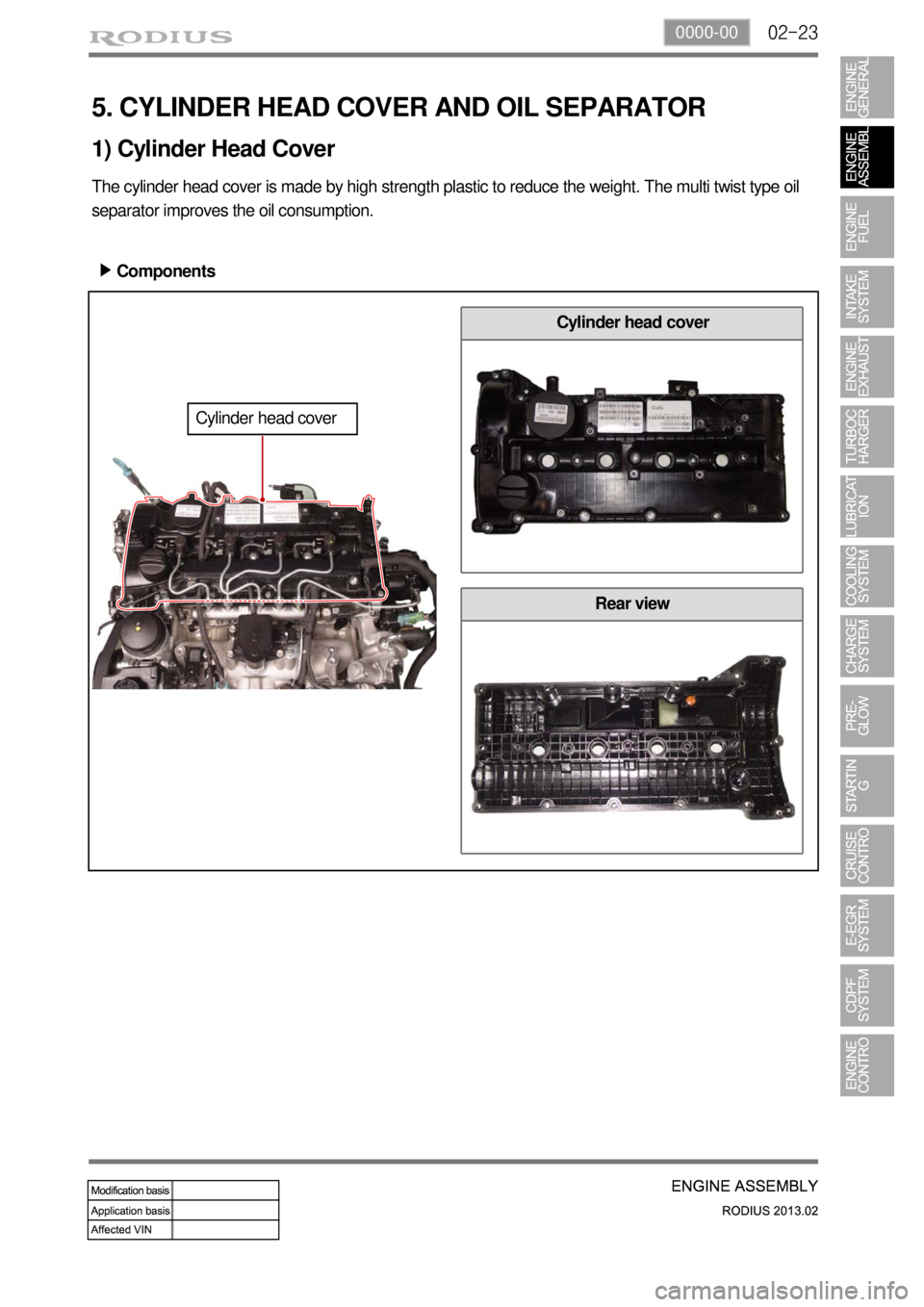
02-230000-00
Rear view
5. CYLINDER HEAD COVER AND OIL SEPARATOR
The cylinder head cover is made by high strength plastic to reduce the weight. The multi twist type oil
separator improves the oil consumption.
Components ▶
1) Cylinder Head Cover
Cylinder head cover
Cylinder head cover
Page 189 of 796

02-30
1) Chain Drive
(1) Overview
The drive chain is single chain drive system with simple design and variable performance, and it utilizes
the hydraulic tensioner to reduce the wave impact generated by the chain. This chain is light weight and
has high durability through single bush chain. Shoulder bolts are used for better NHV.
7. CHAIN AND GEAR DRIVE SYSTEM
D20DTR engine uses single stage chain drive system. Timing chain drives the exhaust side and gear
drive the intake side. Timing chain is single bush type. Upper chain drives HP pump connected to
intake Camshaft by driving exhaust cam shift sprocke, and lower chain drives oil pump to lubricate the
engine.
Page 234 of 796

04-31719-00
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Shorten the service interval under severe conditions such as driving on a dusty road or off-road. *
Unit Description Specification
Air cleaner elementFilter type Dry, filter element
Initial resistance Max. 300 mmAq
Service interval EU: Change every 20,000 km
GEN: Change every 15,000 km
Air cleaner assemblyWeight 2.36kg
Operating temperature-30 ~ 100℃
IntercoolerRadiation over 13,000 Kcal
Pressure loss at turbocharger below 90 mmHg
Cooling type Air cooled type
Core size 450W*130H*70T
Core type C/FIN
Page 248 of 796

06-31914-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit Description Specification
TurbochargerMax. expansion coefficient 4.0
Max. turbine speed 226,000rpm
Max. temperature of turbine
housing790 ℃
Weight 6.5kg
E-VGT actuator Operation duty cycle 250Hz
E-VGT turbocharger ▶
Plate
Impeller
Turbine
Unison ring
Turbine housingCompressor
housing
E-VGT actuator
Page 272 of 796
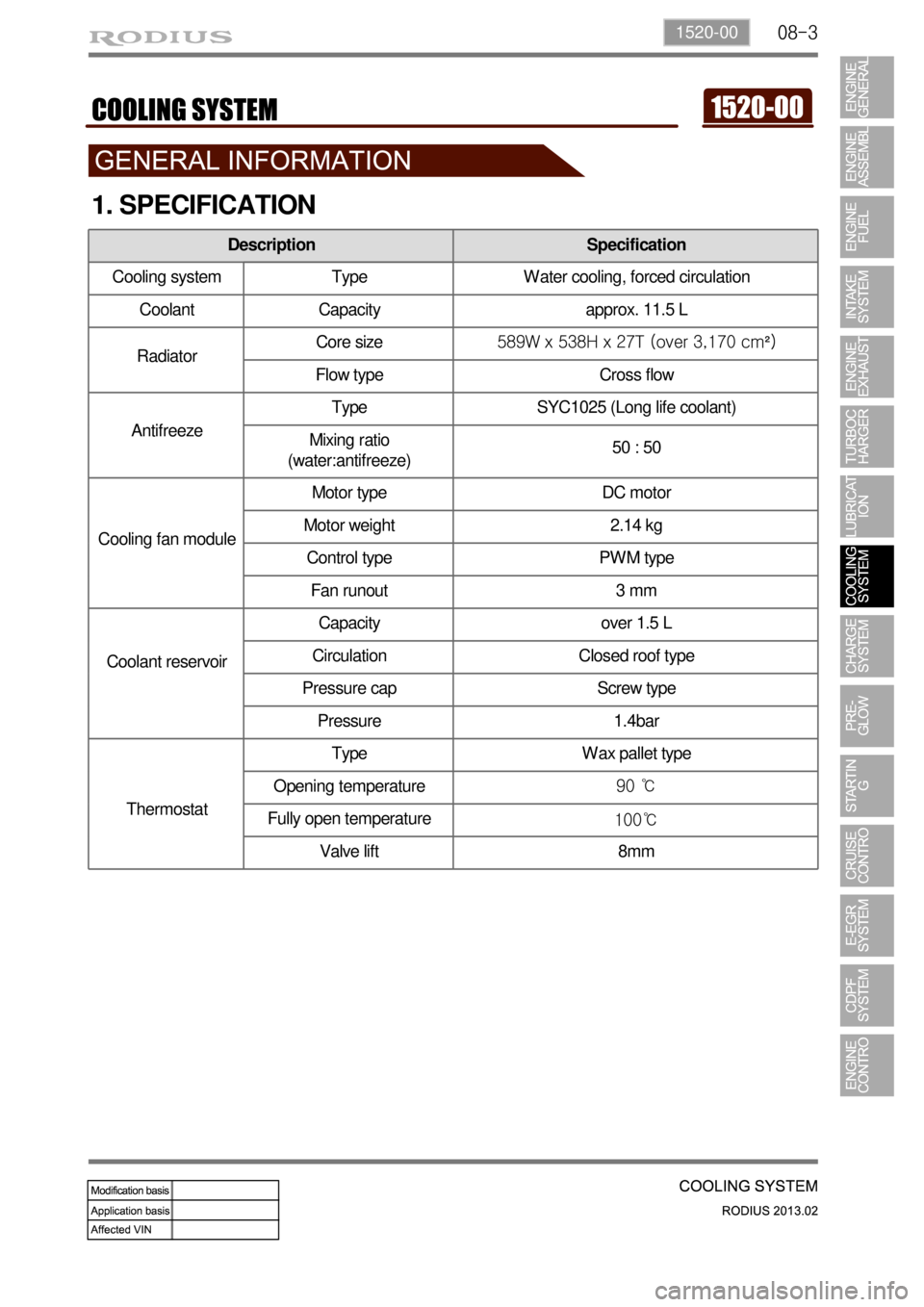
08-31520-00
1. SPECIFICATION
Description Specification
Cooling system Type Water cooling, forced circulation
Coolant Capacity approx. 11.5 L
RadiatorCore size589W x 538H x 27T (over 3,170 cm²)
Flow type Cross flow
AntifreezeType SYC1025 (Long life coolant)
Mixing ratio
(water:antifreeze)50 : 50
Cooling fan moduleMotor type DC motor
Motor weight 2.14 kg
Control type PWM type
Fan runout 3 mm
Coolant reservoirCapacity over 1.5 L
Circulation Closed roof type
Pressure cap Screw type
Pressure 1.4bar
ThermostatType Wax pallet type
Opening temperature90 ℃
Fully open temperature
100℃
Valve lift 8mm
Page 298 of 796

11-31461-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Description Specification
Capacity 12V 2.3kW
Engagement Meshed type
Rotating direction Clockwise
Pinion gear manufacturing Cooled forging
Solenoid operating voltage Max. 8 V
Weight 2.5 kg
Bracket manufacturing Aluminum die casting
Page 602 of 796

05-33240-01
Weight 32.4 kg (including oil)
Oil capacity 1.4 L
Oil type ATF DEXRON II or III
Location Transfer case
Major element Housing Part-time
Bolt 11EA, M8 x 1.25
Input shaft A/T: outer spline
Description Specifications
Total length 343 mm
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Page 676 of 796

10-34891-01
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels
are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability or rotate resulting in an
accident. ABS helps to maintain directional stability and control of the vehicle. ABS is designed to
secure more safety and increase the control of steering wheel during emergency braking situation.
But, ABS does not guarantee perfect safety beyond its physical limit. ABS in this vehicle contains EBD
function. In normal driving conditions, the brake system operates without ABS function.
1) Basic Theory of ABS Function
To give you a better understanding of the tasks and functions of ABS, we will first look at the physics
principles.
▶Stopping distance
The stopping distance depends on the vehicle weight and initial speed when braking starts. This also
applies for vehicle with ABS, where ABS always tries to set an optimum brake force on each wheel. As
great forces are exerted between the tires and the carriageway when braking, even with ABS the
wheels may scream and rubber is left on the road. With an ABS skid mark one may be able to clearly
recognize the tire profile. The skid mark of an ABS vehicle does not however leave any hint of the
speed of the vehicle in the case of an accident, as it can only be clearly drawn at the start of braking.
▶Brake force on a wheel
The maximum possible brake force on a wheel depends on the wheel load and the adhesion
coefficient between tire and carriageway. With a low adhesion coefficient the brake force, which can be
obtained is very low. You are bound to know the result already from driving on winter roads. With a
high adhesion coefficient on a dry road, the brake force, which can be obtained, is considerably higher.
The brake force, which can be obtained, can be calculated from below formula:
Page 698 of 796

12-34170-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Description Specification
Tire 16 inch 225/65R16
17 inch 235/60R17
Tire inflation pressure 35 psi
Wheel 16 inch 6.5JX16
17 inch 7.0JX17
Balance weight Inner: Clip-on type
Outer: Tape type
Tightening torques of wheel bolt 127.4 to 156.8 Nm
Wheel offset 2WD 38 mm
4WD 50 mm
Page 700 of 796

12-54170-01
1. OVERVIEW
A radial tire uses a cord angle of 90 degrees. That is, the cord material runs in a radial or direct line
from one bead to the other across the tread. In addition, a radial tire has a belt overwrap under the
tread surface to provide greater structural stability. The belt overwrap of a radial tire distortion while the
radial structure enables high speed driving.
Tire supports the weight of the vehicle, reduces the impact from the road and at the same time,
transmits the power to propel, brake and steer on the road. It also functions to maintain a
vehicle’s movement. In order to complete such tasks, a tire must be structured to be a resilient
vessel of air.
There is wear limit mark on the tire, which protrudes as a strip shape located approximately 1.6 mm
from the groove bottom. This wear limit mark is not seen from the outside so there is additional
"▲" mark on the shoulder to let the driver find the wear mark easily. To measure the tire groove
depth, measure at any point other than the point which has a wear limit mark.
The tire is worn unevenly according to the driver's driving habit, improper servicing, low tire inflation
pressure, changed tire location, etc.
1) Structure of Tire
Tread
This thick layer of rubber provides the interface
between the tire and the road. Wear-resistant
rubber is used to protect the carcass and belt
against fractures and impacts and to deliver a
long driving life.
Shoulder
Located between the tread and sidewall, the
shoulder rubber is the thickest so that the
design must allow for the easy diffusion of heat
generated within the tire while driving.
Sidewall
The part between the shoulder and bead, the
flexible sidewall protects the carcass and
enhances the ride. A tire’s type, size,
structure, pattern, manufacturing company,
product name and various characters are
indicated here. Bead
The bead attaches the tire to the rim and wraps
the end of the cord fabric. Comprised of the bead
wire, core, flipper and other parts, the bead is
generally designed to be slightly tight around the
rim so that in the case of a sudden drop in
inflation pressure, the tire will not fall off the rim.
Carcass
As the most important framework of a tire, the
entire inner layer of cord fabric is called the
carcass. The carcass acts to support air
pressure, vertical load and absorb shocks.
Valve
Belt
Bead core