navigation system SUBARU LEGACY 2008 4.G Navigation Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2008, Model line: LEGACY, Model: SUBARU LEGACY 2008 4.GPages: 126, PDF Size: 2.42 MB
Page 18 of 126
17
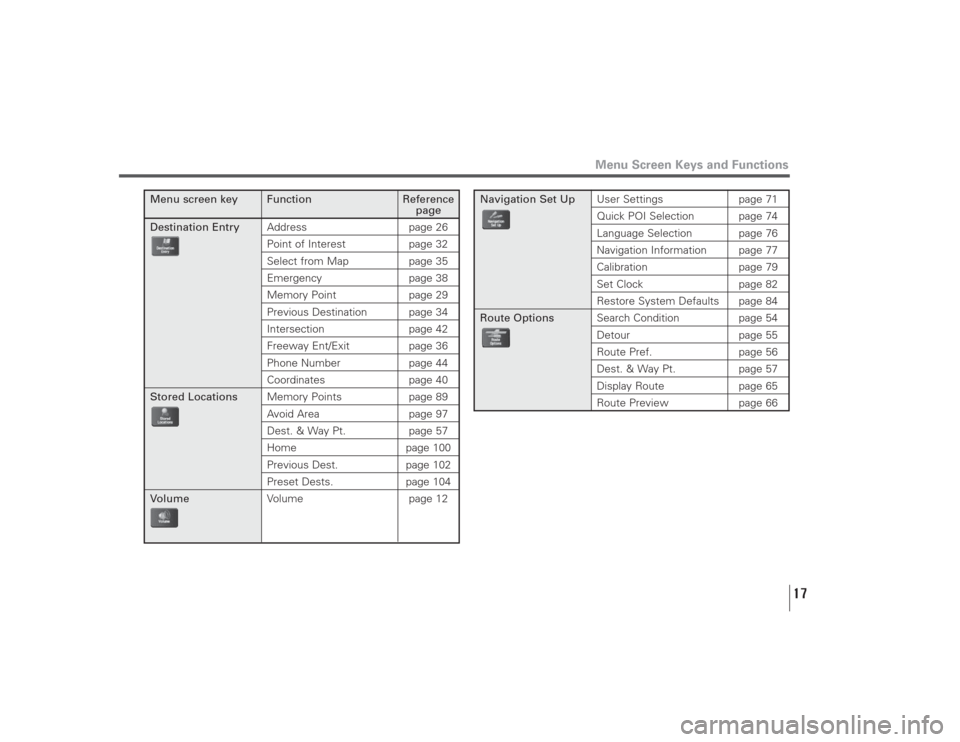
Menu Screen Keys and Functions
Menu screen key Function Reference
page
Destination EntryAddress page 26
Point of Interest page 32Select from Map page 35Emergency page 38Memory Point page 29Previous Destination page 34Intersection page 42Freeway Ent/Exit page 36Phone Number page 44Coordinates page 40
Stored LocationsMemory Points page 89
Avoid Area page 97Dest. & Way Pt. page 57Home page 100Previous Dest. page 102Preset Dests. page 104
VolumeVolume page 12
Navigation Set UpUser Settings page 71
Quick POI Selection page 74Language Selection page 76Navigation Information page 77Calibration page 79Set Clock page 82Restore System Defaults page 84
Route OptionsSearch Condition page 54
Detour page 55Route Pref. page 56Dest. & Way Pt. page 57Display Route page 65
Route Preview page 66
Page 70 of 126

69
Navigation SetupUsing the functions available from the Navigation Setup screen, you can change the map display conditions
and alter the route guidance conditions.
1
Press the button or select .
2
Select (navigation setup).The NAVIGATION SET UP screen will appear.
Setting Your Navigation System
Page 71 of 126
70
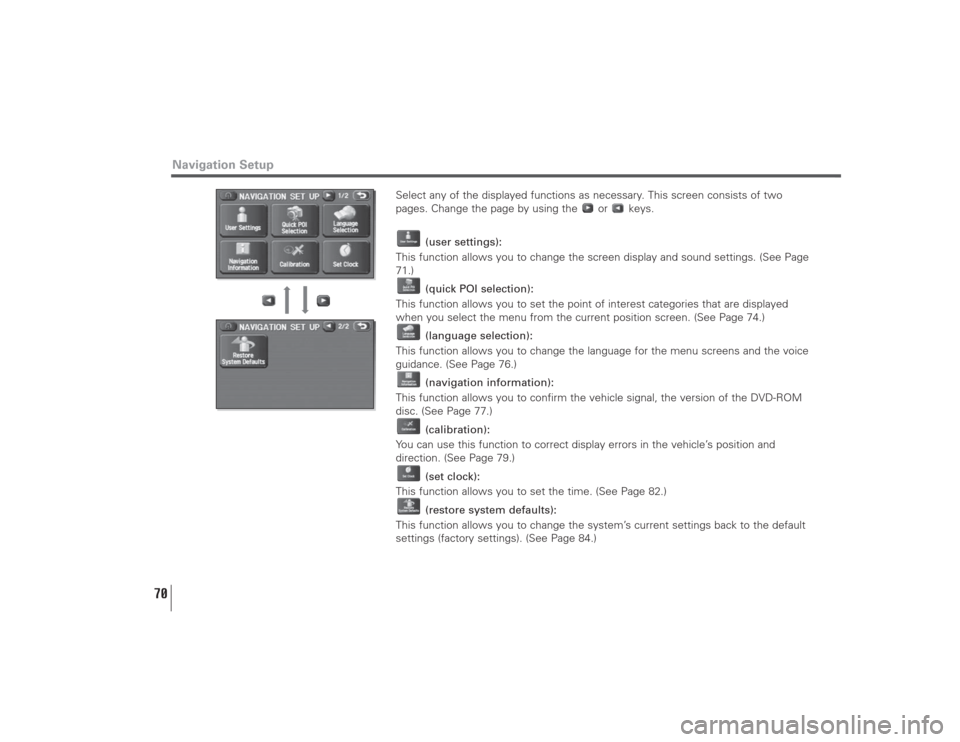
Select any of the displayed functions as necessary. This screen consists of two
pages. Change the page by using the or keys.
(user settings):
This function allows you to change the screen display and sound settings. (See Page
71.)
(quick POI selection):
This function allows you to set the point of interest categories that are displayed
when you select the menu from the current position screen. (See Page 74.)
(language selection):
This function allows you to change the language for the menu screens and the voice
guidance. (See Page 76.)
(navigation information):
This function allows you to confirm the vehicle signal, the version of the DVD-ROM
disc. (See Page 77.)
(calibration):
You can use this function to correct display errors in the vehicle’s position and
direction. (See Page 79.)
(set clock):
This function allows you to set the time. (See Page 82.)
(restore system defaults):
This function allows you to change the system’s current settings back to the default
settings (factory settings). (See Page 84.)
Navigation Setup
Page 85 of 126
84
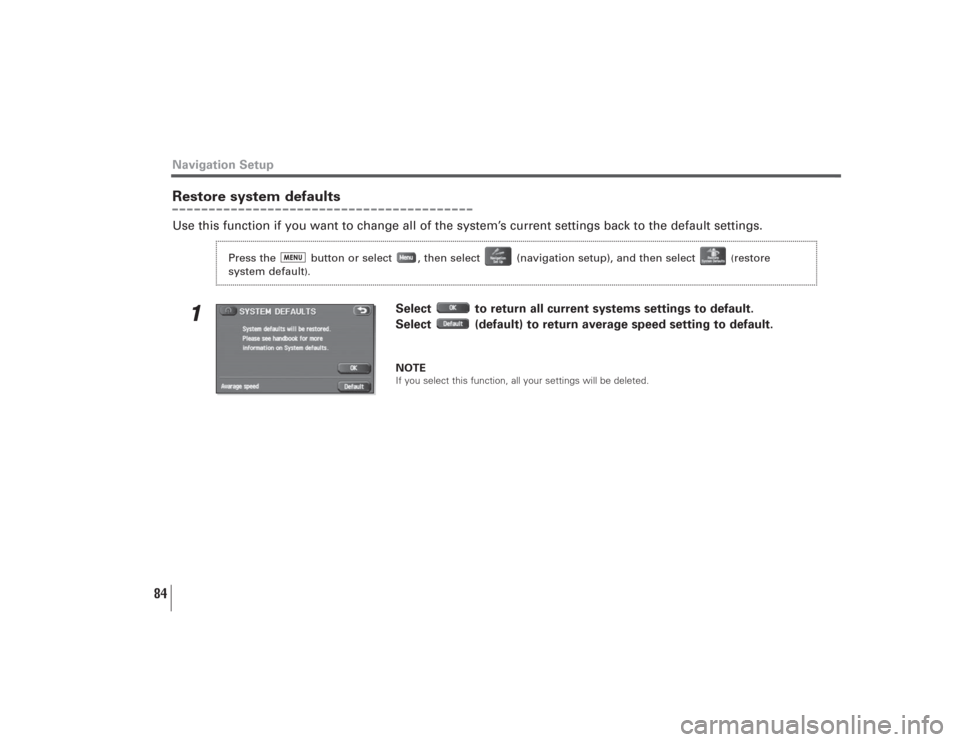
Restore system defaultsUse this function if you want to change all of the system’s current settings back to the default settings.
1
Select to return all current systems settings to default.
Select (default) to return average speed setting to default.NOTEIf you select this function, all your settings will be deleted.
Navigation Setup
Press the button or select , then select (navigation setup), and then select
(restore
system default
).
Page 121 of 126

120
■Accuracy of vehicle positionArea in which GPS signals cannot be received
Because the radiowave signals from the GPS satellites travel
primarily by line of sight, the navigation system might not be
able to receive the signals in the areas described below.
(If the GPS mark does not appear on the map screen, it
means that the GPS radiowave signals are not being
properly received.)
(1) Inside a tunnel
(2) Inside a building
(3) Under a three-dimensional road system such as for high-
speed roads
(4) On boulevards lined with trees
(5) Between buildings
(6) Under a cliff or in a cave
• If the GPS antenna or its surroundings are blocked by an
obstacle (including cargo), it might not be possible for the
system to receive the GPS radiowave signals.
• If multiple paths are created due to the reflection from
buildings, a large measurement error could occur, causing
the vehicle’s mark to deviate from its actual position.Deviation of the vehicle’s position mark
The vehicle’s position mark could deviate from its actual
position when the vehicle is being driven under the
conditions listed below or due to conditions of the GPS
satellites.If the vehicle travels on a road whose actual shape differs
from that in the map data, the vehicle’s mark could deviate
from the actual position. The correct position will eventually
appear on the screen through the correction function. If the
screen does not show the correct position for an excessively
long time, correct the current position or make an automatic
correction.
(1) The vehicle’s mark could appear on a parallel road.
(2) When the road splits into a narrow Y, the vehicle’s mark
could appear on the other fork of the Y.
(3) When the vehicle makes a right or left turn, the vehicle’s
mark could appear on one street ahead or behind.
(4) If the vehicle is transported by means other than the
vehicle’s own power, such as on a ferryboat, the
vehicle’s mark will remain in the position it was before
the transport until the system can calculate the position
through the GPS.
(5) When the vehicle is driven on a steep incline, the
vehicle’s mark could deviate from its actual position.
(6) If there are continuous gradual curves in the same
direction, the vehicle’s mark could deviate from its
actual position.
(7) If the vehicle is driven in a zigzag pattern, such as
through frequent lane changes, the vehicle’s mark could
deviate from its actual position.
(8) If the vehicle is placed on a turntable, such as in a
parking area, and turned with the ignition OFF, the
vehicle’s mark could deviate from its actual orientation.General Information
Page 122 of 126

121
The vehicle’s mark could also deviate even after the
vehicle has exited the parking area.
(9) The vehicle’s mark could deviate from its actual position
if the vehicle is driven using tire chains or snow tires on
a snow-covered road or on a mountainous road.
(10) The vehicle’s mark could deviate from its actual position
after the tires have been replaced.
■How the vehicle position is detectedDetecting the vehicle’s position through the GPS
GPS stands for “Global Positioning System”, which is a
system used for detecting an object’s position through the
use of satellites of the U.S. Department of Defense.
Radiowave signals from three or more satellites are received
by the navigation system, which utilizes the principle of
triangulation to detect the position at which the radiowave
signals are received.
When the navigation unit is receiving the GPS radiowave
signals, a “GPS” mark will appear on the map screen.Detecting the vehicle’s position through self-containednavigation
Self-contained navigation is a system that detects the
vehicle’s position by calculating the vehicle’s driven distance
and turning angle though the use of various types of sensors
that are mounted on the vehicle.Through the use of self-contained navigation, the vehicle’s
position can be detected even in an area where the GPS
radiowave signals cannot be received.
Making corrections to the detection of the vehicle’sposition through map matching
• In map matching, the position information resulting from
the detection of the vehicle’s position and the locus of the
travel of the vehicle up to the present are constantly
compared to the shape of the roads on the map in order to
correct the vehicle’s position mark to the most appropriate
road.
• If the vehicle is driven on a road whose actual shape
differs from its map data, the vehicle’s position mark on
the map could deviate from its actual position.
Occasionally, the correction of the vehicle’s position mark
to the actual road on the map can be observed, particularly
after the vehicle has turned at an intersection or has exited
from a parking area.
General Information